From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| American bison Temporal range: Pleistocene to present |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| B. b. bison Alternative image Historic drawing Bison call audio |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Superorder: | Ungulata |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Bovinae |
| Genus: | Bison |
| Species: | B. bison |
| Binomial name | |
| Bison bison (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
| Subspecies | |
| B. b. athabascae B. b. bison |
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
| Bos americanus Bos bison Bison americanus Bison bison montanae |
|
The American bison (Bison bison), also commonly known as the American buffalo, is a North American species of bison that once roamed the grasslands of North America in massive herds, became nearly extinct by a combination of commercial hunting and slaughter in the 19th century and introduction of bovine diseases from domestic cattle, and has made a recent resurgence largely restricted to a few national parks and reserves. Their historical range roughly comprised a triangle between the Great Bear Lake in Canada's far northwest, south to the Mexican states of Durango and Nuevo León, and east to the Atlantic Seaboard of the United States (nearly to the Atlantic tidewater in some areas) from New York to Georgia and per some sources down to Florida. Bison were seen in North Carolina near Buffalo Ford on the Catawba River as late as 1750.[2][3][4]
Two subspecies or ecotypes have been described: the plains bison (Bison bison bison), smaller in size and with a more rounded hump, and the wood bison (Bison bison athabascae)—the larger of the two and having a taller, square hump.[5][6][7][8][9][10] Furthermore, it has been suggested that the plains bison consists of a northern (Bison bison montanae) and a southern subspecies, bringing the total to three.[8] However, this is generally not supported. The wood bison is one of the largest wild species of bovid in the world, surpassed by only the Asian gaur and wild water buffalo. It is the largest extant land animal in the Americas.
Description

Adult male (farthest) and adult female (closest) with a background of rich autumn colors, in Yellowstone National Park
A bison has a shaggy, long, dark brown winter coat, and a lighter weight, lighter brown summer coat. As is typical in ungulates, the male bison are slightly larger than the female and, in some cases, can be considerably heavier. Plains bison are often in the smaller range of sizes, and Wood bison in the larger range. Head-and-body length ranges from 2 to 3.5 m (6.6 to 11.5 ft) long, the tail adding 30 to 91 cm (12 to 36 in). Shoulder height in the species can range from 152 to 186 cm (60 to 73 in). Weight can range from 318 to 907 kg (701 to 2,000 lb)[11] The heaviest wild bull ever recorded weighed 1,270 kg (2,800 lb).[12] When raised in captivity and farmed for meat, the bison can grow unnaturally heavy and the largest semi-domestic bison weighed 1,724 kg (3,801 lb).[11] The heads and forequarters are massive, and both sexes have short, curved horns that can grow up to 2 feet (61 cm) long, which they use in fighting for status within the herd and for defense.
Bison are herbivores, grazing on the grasses and sedges of the North American prairies. Their daily schedule involves two-hour periods of grazing, resting and cud chewing, then moving to a new location to graze again. Bison mate in August and September; gestation is 285 days. A single reddish-brown calf nurses until the next calf is born. If the cow is not pregnant, a calf will nurse for 18 months. At three years of age, bison cows are mature enough to produce a calf. Bison bulls of that age may try to mate with cows, but if more mature bulls are present, they may not be able to compete until they reach five years of age. Bison have a life expectancy of approximately 15 years in the wild and up to 25 years in captivity.
For the first two months of life, calves are lighter in color than mature bison. One very rare condition is the white buffalo, in which the calf turns entirely white. White bison are considered sacred by many Native Americans.
Name
The term "buffalo" is sometimes considered to be a misnomer for this animal, and could be confused with two "true buffalo", the Asian water buffalo and the African buffalo. However, "bison" is a Greek word meaning ox-like animal, while "buffalo" originated with the French fur trappers who called these massive beasts bœufs, meaning ox or bullock—so both names, "bison" and "buffalo", have a similar meaning. The name "buffalo" is listed in many dictionaries as an acceptable name for American buffalo or bison. In reference to this animal, the term "buffalo", dates to 1625 in North American usage when the term was first recorded for the American mammal.[13] It thus has a much longer history than the term "bison", which was first recorded in 1774.[citation needed] The American bison is very closely related to the wisent or European bison.Differences from European bison
Although they are superficially similar, the American and European bison exhibit a number of physical and behavioral differences. Adult American bison are slightly heavier on average due to their less rangy build, and have shorter legs, which render them slightly shorter at the shoulder.[14] American bison tend to graze more, and browse less than their European cousins, due to their necks being set differently. Compared to the nose of the American bison, that of the European species is set farther forward than the forehead when the neck is in a neutral position. The body of the American bison is hairier, though its tail has less hair than that of the European bison. The horns of the European bison point forward through the plane of its face, making it more adept at fighting through the interlocking of horns in the same manner as domestic cattle, unlike the American bison which favors charging.[15] American bison are more easily tamed than their European cousins, and breed more readily with domestic cattle.[16]Evolution
The bovine family (taurids and bisonids) diverged from the common ancestral line with water buffalo and African buffalo about 5 to 10 million years ago.[17] Thereafter, the family lineage of bison and taurine cattle does not appear to be a straight forward "tree" structure as is often depicted in much evolution, because there is evidence of interbreeding and crossbreeding between different species and members within this family, even many millions of years after their ancestors separated into different species. This cross breeding was not sufficient to conflate the different species back together, but it has resulted in unexpected relationships between many members of this group, such as Yak being related to American bison, when such relationships would otherwise not be apparent.A 2003 study of mitochondrial DNA indicated four distinct maternal lineages in tribe Bovini:
- Taurine cattle and zebu,
- Wisent (European bison),
- American bison and yak,[18] and
- Banteng, gaur, and gayal.
The steppe bison (Bison priscus) diverged from the lineage that led to cattle (Bos taurus) approximately 2 to 5 million years ago. The bison genus is clearly in the fossil record by 2 million years ago.[22] The steppe bison spread across Eurasia and was the bison that was pictured in the ancient cave paintings of Spain and Southern France
The European bison or wisent arose from the steppe bison, without fossil evidence of other ancestral species between the steppe bison and the European bison, though the European bison might have arisen from the lineage that led to American bison if that lineage backcrossed with the steppe bison. Again, the web of relationships is confusing, but there is some evidence that the European bison is descended from bison that had migrated from Asia to North America, and then back to Europe, where they crossbred with existing steppe bison.[22]
At one point, some steppe bison cross bred with the ancestors of the modern yak. After that cross breeding, a population of steppe bison (Bison priscus) crossed the Bering Land Bridge to North America. There is evidence of multiple crossings of bison to and from Asia starting before 500,000 years ago and continuing until at least 220,000 years ago. The steppe bison spread through the northern parts of North America and steppe bison lived in Eurasia until approximately 11,000 years ago[23] and North America until 4,000 to 8,000 years ago.[22]
Bison latifrons (giant bison or longhorn bison) is thought to have evolved in midcontinent North America from Bison priscus, after the steppe bison crossed into North America.[24][25][26] Giant bison (Bison latifrons) appeared in the fossil record approximately 500,000 years ago.[22] B. latifrons was one of many species of North American megafauna which became extinct during the Quaternary extinction event. It is thought to have disappeared some 21,000–30,000 years ago, during the late Wisconsin glaciation.[27]
The Bison latifrons (giant bison or longhorn bison) species was replaced by the smaller Bison antiquus. Bison antiquus appeared in the North American fossil record approximately 250,000 years ago.[28] Bison antiquus in turn evolved into the Bison occidentalis, then into the yet smaller Bison bison—the modern American bison—some 5,000 to 10,000 years ago.[29][30] Some researchers consider Bison occidentalis to be a sub-species of Bison antiquus.[31]
During the population bottleneck, after the great slaughter of American bison during the 1800s, the number of bison remaining alive in North America declined to as low as 541. During that period, a handful of ranchers gathered remnants of the existing herds to save the species from extinction. These ranchers bred some of the bison with cattle in an effort to produce "cattleo".[32] Accidental crossings were also known to occur. Generally, male domestic bulls were crossed with buffalo cows, producing offspring of which only the females were fertile. The crossbred animals did not demonstrate any form of hybrid vigor, so the practice was abandoned. The proportion of cattle DNA that has been measured in introgressed individuals and bison herds today is typically quite low, ranging from 0.56 to 1.8%.[32][33] In the United States, many ranchers are now utilizing DNA testing to cull the residual cattle genetics from their bison herds. The U.S. National Bison Association has adopted a code of ethics which prohibits its members from deliberately crossbreeding bison with any other species.
Range and population
Despite being the closest relatives of domestic cattle native to North America, bison were never domesticated by native Americans. Later attempts of domestication by Europeans prior to the 20th century met with limited success. Bison were described as having a "wild and ungovernable temper";[34] they can jump 6 feet (1.8 m) vertically,[35] and run 35-40 mph (56–64 km/h) when agitated. This agility and speed, combined with their great size and weight, makes bison herds difficult to confine as they can easily escape or destroy most fencing systems, including most razor wire.Approximately 500,000 bison currently exist on non-public lands and approximately 30,000 on public lands which includes environmental and government preserves.[36] According to the IUCN, approximately 15,000 bison are considered wild, free-range bison not primarily confined by fencing.[37]
Habitat
As livestock
Bison are increasingly raised for meat and hides; the majority of American bison in the world are raised for human consumption. Bison meat is generally considered to taste very similar to good beef, but is lower in fat and cholesterol, yet higher in protein than beef,[38] a fact which has led to the development of beefalo, a fertile hybrid of bison and domestic cattle. In 2005, about 35,000 bison were processed for meat in the U.S., with the National Bison Association and USDA providing a "Certified American Buffalo" program with birth-to-consumer tracking of bison via RFID ear tags. There is even a market for kosher bison meat; these bison are slaughtered at one of the few kosher mammal slaughterhouses in the U.S., and the meat is then distributed nationwide.Bison are found in publicly and privately held herds. Custer State Park in South Dakota is home to 1,500 bison, one of the largest publicly held herds in the world, but there are questions[vague] about the genetic purity of the animals. Wildlife officials[who?] believe that free roaming and genetically pure herds on public lands in North America can be found only in Yellowstone National Park and the Yellowstone Park bison herd,[39] the Henry Mountains bison herd at the Book Cliffs and Henry Mountains in Utah, at Wind Cave National Park in South Dakota, Fort Peck Indian Reservation in Montana, Mackenzie Bison Sanctuary in the Northwest Territories, Elk Island National Park and Wood Buffalo National Park in Alberta, and Prince Albert National Park in Saskatchewan. Another population, the Antelope Island bison herd on Antelope Island in Utah, consisting of 550 to 700 bison, is also one of the largest and oldest public herds in the United States, but the bison in that herd are considered to be only semi-free roaming, since they are confined to the Antelope Island. In addition, recent genetic studies indicate that, like most bison herds, the Antelope Island bison herd has a small number of hybrid genes from domestic cattle. In 2002 the United States government donated some buffalo calves from South Dakota and Colorado to the Mexican government. Their descendants live in the Mexican nature reserves El Uno Ranch at Janos and Santa Elena Canyon, Chihuahua, and Boquillas del Carmen, Coahuila, located near the southern banks of the Rio Grande and the grassland borderline with Texas and New Mexico.
Recent genetic studies of privately owned herds of bison show that many of them include animals with genes from domestic cattle.[39] For example, the herd on Santa Catalina Island, California, isolated since 1924 after being brought there for a movie shoot, were found to have cattle introgression.[40] It is estimated that there are as few as 12,000 to 15,000 pure bison in the world. The numbers are uncertain because the tests used to date—mitochondrial DNA analysis—indicate only if the maternal line (back from mother to mother) ever included domesticated bovines and thus say nothing about possible male input in the process. It was found that most hybrids look exactly like purebred bison; therefore, appearance is not a good indicator of genetics.
The size of the Canadian domesticated herd (genetic questions aside) grew dramatically through the 1990s and 2000s. The 2006 Census of Agriculture reported the Canadian herd at 2006 195,728 head, 34.9% increase since 2001.[41] Of this total, over 95% was located in Western Canada, and less than 5% in Eastern Canada. Specifically Alberta was the province with the largest herd, accounting for 49.7% of the herd and 45.8% of the farms. The next largest herds were in Saskatchewan (23.9%), Manitoba (10%), and British Columbia (6%). The main producing regions were in the northern parts of the Canadian prairies, specifically in the parkland belt, with the Peace River region (shared between Alberta and British Columbia) begin the most inmportant cluster, accounting for 14.4% of the national herd.[41] Canada also exports bison meat, totaling 2,075,253 kilograms (4,575,150 lb) in 2006.[42]
A proposal known as Buffalo Commons has been suggested by a handful of academics and policymakers to restore large parts of the drier portion of the Great Plains to native prairie grazed by bison.[39] Proponents argue that current agricultural use of the shortgrass prairie is not sustainable, pointing to periodic disasters, including the Dust Bowl, and continuing significant human population loss over the last 60 years. However, this plan is opposed by some who live in the areas in question.[citation needed]
Behavior and ecology
Grazing in winter, Yellowstone National Park. They use their heads to clear out snow for the grass.

American bison galloping. Photos by Eadweard Muybridge, first published in 1887 in Animal Locomotion.
Bison are migratory and herd migrations can be directional as well as altitudinal in some areas.[43][44][45] Bison have usual daily movements between foraging sites during the summer. In a montane valley, bison have been recorded traveling, on average, 3.2 km a day.[45] The summer ranges of bison appear to be influenced by seasonal vegetation changes, interspersion and size of foraging sites, the rut and the number of biting insects.[43] The size of preserve and availability of water may also be a factor.[45] Bison are largely grazers, eating primarily grasses and sedges. On shortgrass pasture, bison predominately consume warm season grasses.[46] On mixed prairie, it appears that cool season grasses, including some sedges, compose 79–96% of their diet.[47] In montane and northern areas, sedges are selected throughout the year.[43] Bison also drink water or consume snow on a daily basis.[45]
Social behavior and reproduction
Female bison live in maternal herds which include other females and their offspring. Male offspring leave their maternal herd when around three years old and will either live alone or join other males in bachelor herds. Male and female herds usually do not mingle until the breeding season, which can occur from July through September.[48] However female herds may also contain a few older males. During the breeding season, dominant bulls maintain a small harem of females for mating. Individual bulls "tend" cows until allowed to mate, by following them around and chasing away rival males. The tending bull will shield the female's vision with his body so she will not see any other challenging males. A challenging bull may bellow or roar to get a female's attention and the tending bull has to bellow/roar back.[49] The most dominant bulls mate in the first 2–3 weeks of the season.[49] More subordinate bulls will mate with any remaining estrous cow that has not mated yet. Male bison play no part in raising the young.
Bison herds have dominance hierarchies that exist for both males and females. A bison's dominance is related to its birth date.[50] Bison born earlier in the breeding season are more likely to be larger and more dominant as adults.[50] Thus bison are able to pass on their dominance to their offspring as dominant bison breed earlier in the season. In addition to dominance, the older bison of a generation also have a higher fertility rate than the younger ones.[50] Cows nurse their calves for at least 7 or 8 months but most calves seem to be weaned before the end of their first year.[45]
Bison have been observed to display homosexual behaviors, males much more so than females. In the case of males, it is unlikely to be related to dominance but rather to social bonding or gaining sexual experience.[51]
Horning
Bison mate in late spring and summer in more open plain areas. During fall and winter, bison tend to gather in more wooded areas. During this time, bison partake in horning behaviors. They will rub their horns against trees, young saplings and even utility poles. Aromatic trees like cedars and pine seem to be preferred. Horning appears to be associated with insect defense as it occurs most often in the fall when the insect population is at its highest.[52]Cedar and pines emit an aroma after bison horn them and this seems to be used as a deterrent for insects.[52]
Wallowing behavior
A bison wallow is a shallow depression in the soil, which is used either wet or dry. Bison roll in these depressions, covering themselves with dust or mud. Past explanations and current hypotheses suggested for wallowing behavior include grooming behavior associated with shedding, male-male interaction (typically rutting behavior), social behavior for group cohesion, play behavior, relief from skin irritation due to biting insects; reduction of ectoparasite (tick and lice) load; and thermoregulation.[53]Predation
While often secure from predation due to their size and strength, in some areas, bison are regularly preyed upon by wolves. Wolf predation typically peaks in late spring and early summer, with attacks usually being concentrated on cows and calves. Observations have shown that wolves more actively target herds with calves than those without. The length of a predation episode varies, ranging from a few minutes to over nine hours.[54][55] Bison display five apparent defense strategies in protecting calves from wolves: running to a cow, running to a herd, running to the nearest bull, running in the front or center of a stampeding herd, and entering water bodies such as lakes or rivers. When fleeing wolves in open areas, cows with young calves take the lead, while bulls take to the rear of the herds, to guard the cows' escape. Bison typically ignore wolves not displaying hunting behavior.[56] Wolf packs specializing in bison tend to have a greater number of males, as their larger size compared to the females allows them to wrestle their prey to the ground more effectively.[57] Healthy, mature bulls in herds rarely fall victim to predators. The grizzly bear can also pose a threat to calves and sometimes old, injured or sick adult bison.
Dangers to humans
Bison are among the most dangerous animals encountered by visitors to the various U.S. and Canadian national parks and will attack humans if provoked. They appear slow because of their lethargic movements but can easily outrun humans—bison have been observed running as fast as 40 miles per hour (64 km/h).Between 1980 and 1999, more than three times as many people in Yellowstone National Park were injured by bison than by bears. During this period, bison charged and injured 79 people, with injuries ranging from goring puncture wounds and broken bones to bruises and abrasions. Bears injured 24 people during the same time frame. Three people died from the injuries inflicted—one person by bison in 1983, and two people by bears in 1984 and 1986.[58]
Hunting

Buffalo hunting (hunting of the American bison) was an activity fundamental to the Midwestern Native Americans, which was later adopted by American professional hunters, leading to the near-extinction of the species around the year 1890. It has since begun to recover.
| Year | American bison (est) |
|---|---|
| Before 1492 | 60,000,000[citation needed] |
| 1890 | 750 |
| 2000 | 360,000 |

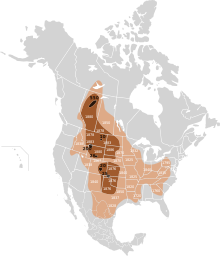
Original distribution of plains bison and wood bison in North America along the "Great bison belt". Holocene bison (Bison occidentalis) is an earlier form at the origin of plains bison and wood bison.
Holocene bison
Wood bison
Plains bison
|
Map of the extermination of the bison to 1889. This map based on William Temple Hornaday's late-19th century research.
Original range
Range as of 1870
Range as of 1889
|
Genetics
Two of the major problems that bison face today are the genetic bottleneck and lack of genetic diversity that has been caused by the very small number of bison that survived their near extinction event. A second genetic problem is the entry of genes from domestic cattle into the bison population, through hybridization.[39]Officially, the "American buffalo" is classified by the United States government as a type of cattle, and the government allows private herds to be managed as such. This is a reflection of the characteristics that bison share with cattle. Though the American bison (Bison bison) is not only a separate species, but is usually regarded as being in a separate genus from domestic cattle (Bos taurus), they clearly have a lot of genetic compatibility and American bison can interbreed with cattle, although only the female offspring are fertile in the first generation. These female hybrids can be bred back to either bison or domestic bulls, resulting in either 1/4 or 3/4 bison young. Female offspring from this cross are also fertile, but males are not reliably fertile unless they are either 7⁄8 bison or 7⁄8 domestic.[59] Moreover, when they do interbreed, crossbreed animals in the first generation tend to look very much like purebred bison, so appearance is completely unreliable as a means of determining what is a purebred bison and what is a crossbred cow. Many ranchers have deliberately cross bred their cattle with bison, and it would also be expected that there could be some natural hybridization in areas where cattle and bison occur in the same range.
Since cattle and bison eat similar food and tolerate similar conditions, they have often been in the same range together in the past, and opportunity for cross breeding may sometimes have been common.
In recent decades tests were developed to determine the source of mitochondrial DNA in cattle and bison, and it was found that most private "buffalo" herds were actually cross bred with cattle, and even most state and federal buffalo herds had some cattle DNA. With the advent of nuclear microsatellite DNA testing, the number of herds known to contain cattle genes has increased. Though approximately 500,000 bison exist on private ranches and in public herds, some people estimate that perhaps only 15,000 to 25,000 of these bison are pure and are not actually bison-cattle hybrids. "DNA from domestic cattle (Bos taurus) has been detected in nearly all bison herds examined to date."[60] Significant public bison herds that do not appear to have hybridized domestic cattle genes are the Yellowstone Park bison herd, the Henry Mountains bison herd which was started with bison taken from Yellowstone Park, the Wind Cave bison herd and the Wood Buffalo National Park bison herd and subsidiary herds started from it, in Canada.
A landmark study of bison genetics that was performed by James Derr of the Texas A&M University corroborated this.[61] The Derr study was undertaken in an attempt to determine what genetic problems bison might face as they repopulate former areas, and it noted that bison seem to be doing quite well, despite their apparent genetic bottleneck. One possible explanation for this might be the small amount of domestic cattle genes that are now in most bison populations, though this is not the only possible explanation for bison success.
In the study cattle genes were also found in small amounts throughout most national, state and private herds. "The hybridization experiments conducted by some of the owners of the five foundation herds of the late 1800s, have left a legacy of a small amount of cattle genetics in many of our existing bison herds." He also said, "All of the state owned bison herds tested (except for possibly one) contain animals with domestic cattle mtDNA."[61] It appears that the one state herd that had no cattle genes was the Henry Mountains bison herd in the Henry Mountains of Utah. It is also notable that the Henry Mountain herd was started initially with transplanted animals from Yellowstone Park. However, the extension of this herd into the Book Cliffs of central Utah involved mixing the founders with additional bison from another source, so it is not known if the Book Cliffs extension of the herd is also free of cattle hybridization.
A separate study by Wilson and Strobeck, published in Genome, was done to define the relationships between different herds of bison in the United States and Canada, and to determine whether the bison at Wood Buffalo National Park in Canada and the Yellowstone Park bison herd were possibly separate subspecies, and not plains bison. It was determined that the Wood Buffalo Park bison were actually cross breeds between plains bison and wood bison, but that their predominant genetic makeup was truly that of the expected "wood buffalo".[9] However, the Yellowstone Park bison herd were pure plains bison, and not any of the other previously suggested subspecies. Another interesting finding was that the bison in the Antelope Island bison herd in Utah appeared to be more distantly related to other plains bison in general than any other plains bison group that was tested, though this might be due to genetic drift caused by the small size of only 12 individuals in the founder population. A side finding of this was that the Antelope Island bison herd appears to be most closely related to the Wood Buffalo National Park bison herd, though the Antelope Island bison are actually plains bison.
Bison trails
The first thoroughfares of North America, except for the time-obliterated paths of mastodon or muskox and the routes of the Mound Builders, were the traces made by bison and deer in seasonal migration and between feeding grounds and salt licks. Many of these routes, hammered by countless hoofs instinctively following watersheds and the crests of ridges in avoidance of lower places' summer muck and winter snowdrifts, were followed by the Indians as courses to hunting grounds and as warriors' paths. They were invaluable to explorers and were adopted by pioneers.Bison traces were characteristically north and south, but several key east-west trails were used later as railways. Some of these include the Cumberland Gap through the Blue Ridge Mountains to upper Kentucky. A heavily used trace crossed the Ohio River at the Falls of the Ohio and ran west, crossing the Wabash River near Vincennes, Indiana. In Senator Thomas Hart Benton's phrase saluting these sagacious path-makers, the bison paved the way for the railroads to the Pacific.[62]
Bison as a symbol
Native Americans
Among Native American tribes, especially the Plains Indians, the Bison is considered a sacred animal and religious symbol. According to University of Montana anthropology and Native American studies professor S. Neyooxet Greymorning, "The creation stories of where buffalo came from put them in a very spiritual place among many tribes. The buffalo crossed many different areas and functions, and it was utilized in many ways. It was used in ceremonies, as well as to make tipi covers that provided homes for people, utensils, shields, weapons and parts were used for sewing with the sinew."[63] The Sioux consider the birth of a White Buffalo to be the returning of White Buffalo Calf Woman, their primary cultural prophet and the bringer of their "Seven Sacred Rites". Among the Mandan and Hidatsa, the White Buffalo Cow Society was the most sacred of societies for women.United States

The 1935 Buffalo nickel—this style of coin featuring an American bison was produced from 1913 to 1938.

Series 1901 $10 Legal Tender depicting military explorers Meriwether Lewis, William Clark, and an American bison.

First postage stamp with image of bison was issued US in 1898—4¢ "Indian Hunting Buffalo". Part of the Trans-Mississippi Exposition commemorative series.
The American bison is often used in North America in official seals, flags, and logos. In the United States, the American bison is a popular symbol in the Great Plains states. Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming have adopted the animal as their official state mammal, and many sports teams have chosen the bison as their mascot. In Canada, the bison is the official animal of the province of Manitoba and appears on the Manitoba flag. It is also used in the official coat of arms of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police.
Several American coins feature the bison, most famously on the reverse side of the "buffalo nickel" from 1913 to 1938. In 2005, the United States Mint coined a nickel with a new depiction of the bison as part of its "Westward Journey" series. The Kansas and North Dakota state quarters, part of the "50 State Quarter" series, each feature bison. The Kansas state quarter has only the bison and does not feature any writing, while the North Dakota state quarter has two bison. The Montana state quarter prominently features a bison skull over a landscape. The Yellowstone National Park Quarter also features a bison standing next to a geyser.
Other institutions which have adopted the bison as a symbol or mascot include:
- U.S. Department of the Interior
- Beachwood High School
- Bethany College (West Virginia)
- Bucknell University
- Buffalo, New York
- Buffalo Bills
- Buffalo Bisons
- Buffalo Bulls
- Buffalo Grove High School
- Buffalo Sabres
- University at Buffalo, The State University of New York
- USS Buffalo submarine
- University of Colorado
- Gallaudet University
- Harding University
- Howard University
- Seal of the State of Indiana
- Lipscomb University
- Coat of Arms of Manitoba
- Flag of Manitoba
- University of Manitoba
- Marshall University
- Milligan College
- Independence Party of Minnesota
- Ralph Nader (mascot for his 2008 campaign for president)[64]
- Nichols College
- North Dakota State University
- Oklahoma Baptist University
- Oklahoma City Thunder
- Point Park University
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police
- Southwestern Law School
- CFB Wainwright
- West Texas A&M University
- Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo




















