Schematic illustration of a supercapacitor
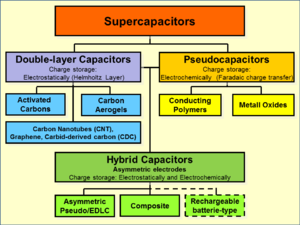
A diagram that shows a hierarchical classification of supercapacitors and capacitors of related types.
A supercapacitor (SC) (also called a supercap, ultracapacitor or Goldcap) is a high-capacity capacitor with capacitance values much higher than other capacitors (but lower voltage limits) that bridge the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries. They typically store 10 to 100 times more energy per unit volume or mass than electrolytic capacitors, can accept and deliver charge much faster than batteries, and tolerate many more charge and discharge cycles than rechargeable batteries.
Supercapacitors are used in applications requiring many rapid charge/discharge cycles rather than long term compact energy storage: within cars, buses, trains, cranes and elevators, where they are used for regenerative braking, short-term energy storage or burst-mode power delivery. Smaller units are used as memory backup for static random-access memory (SRAM).
Unlike ordinary capacitors, supercapacitors do not use the conventional solid dielectric, but rather, they use electrostatic double-layer capacitance and electrochemical pseudocapacitance, both of which contribute to the total capacitance of the capacitor, with a few differences:
- Electrostatic double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) use carbon electrodes or derivatives with much higher electrostatic double-layer capacitance than electrochemical pseudocapacitance, achieving separation of charge in a Helmholtz double layer at the interface between the surface of a conductive electrode and an electrolyte. The separation of charge is of the order of a few ångströms (0.3–0.8 nm), much smaller than in a conventional capacitor.
- Electrochemical pseudocapacitors use metal oxide or conducting polymer electrodes with a high amount of electrochemical pseudocapacitance additional to the double-layer capacitance. Pseudocapacitance is achieved by Faradaic electron charge-transfer with redox reactions, intercalation or electrosorption.
- Hybrid capacitors, such as the lithium-ion capacitor, use electrodes with differing characteristics: one exhibiting mostly electrostatic capacitance and the other mostly electrochemical capacitance.
History
Development of the double layer and pseudocapacitance models.Evolution of components
In the early 1950s, General Electric engineers began experimenting with porous carbon electrodes, in the design of capacitors, from the design of fuel cells and rechargeable batteries. Activated charcoal is an electrical conductor that is an extremely porous "spongy" form of carbon with a high specific surface area. In 1957 H. Becker developed a "Low voltage electrolytic capacitor with porous carbon electrodes". He believed that the energy was stored as a charge in the carbon pores as in the pores of the etched foils of electrolytic capacitors. Because the double layer mechanism was not known by him at the time, he wrote in the patent: "It is not known exactly what is taking place in the component if it is used for energy storage, but it leads to an extremely high capacity."General Electric did not immediately pursue this work. In 1966 researchers at Standard Oil of Ohio (SOHIO) developed another version of the component as "electrical energy storage apparatus", while working on experimental fuel cell designs. The nature of electrochemical energy storage was not described in this patent. Even in 1970, the electrochemical capacitor patented by Donald L. Boos was registered as an electrolytic capacitor with activated carbon electrodes.
Early electrochemical capacitors used two aluminum foils covered with activated carbon—the electrodes—which were soaked in an electrolyte and separated by a thin porous insulator. This design gave a capacitor with a capacitance on the order of one farad, significantly higher than electrolytic capacitors of the same dimensions. This basic mechanical design remains the basis of most electrochemical capacitors.
SOHIO did not commercialize their invention, licensing the technology to NEC, who finally marketed the results as "supercapacitors" in 1971, to provide backup power for computer memory.
The John Bockris Group at Imperial College, London 1947. Dr. Brian Evans Conway seated in the front row, second from the right.
Between 1975 and 1980 Brian Evans Conway conducted extensive fundamental and development work on ruthenium oxide electrochemical capacitors. In 1991 he described the difference between "Supercapacitor" and "Battery" behavior in electrochemical energy storage. In 1999 he coined the term supercapacitor to explain the increased capacitance by surface redox reactions with faradaic charge transfer between electrodes and ions. His "supercapacitor" stored electrical charge partially in the Helmholtz double-layer and partially as result of faradaic reactions with "pseudocapacitance" charge transfer of electrons and protons between electrode and electrolyte. The working mechanisms of pseudocapacitors are redox reactions, intercalation and electrosorption (adsorption onto a surface). With his research, Conway greatly expanded the knowledge of electrochemical capacitors.
The market expanded slowly. That changed around 1978 as Panasonic marketed its Goldcaps brand. This product became a successful energy source for memory backup applications. Competition started only years later. In 1987 ELNA "Dynacap"s entered the market. First generation EDLC's had relatively high internal resistance that limited the discharge current. They were used for low current applications such as powering SRAM chips or for data backup.
At the end of the 1980s, improved electrode materials increased capacitance values. At the same time, the development of electrolytes with better conductivity lowered the equivalent series resistance (ESR) increasing charge/discharge currents. The first supercapacitor with low internal resistance was developed in 1982 for military applications through the Pinnacle Research Institute (PRI), and were marketed under the brand name "PRI Ultracapacitor". In 1992, Maxwell Laboratories (later Maxwell Technologies) took over this development. Maxwell adopted the term Ultracapacitor from PRI and called them "Boost Caps" to underline their use for power applications.
Since capacitors' energy content increases with the square of the voltage, researchers were looking for a way to increase the electrolyte's breakdown voltage. In 1994 using the anode of a 200V high voltage tantalum electrolytic capacitor, David A. Evans developed an "Electrolytic-Hybrid Electrochemical Capacitor". These capacitors combine features of electrolytic and electrochemical capacitors. They combine the high dielectric strength of an anode from an electrolytic capacitor with the high capacitance of a pseudocapacitive metal oxide (ruthenium (IV) oxide) cathode from an electrochemical capacitor, yielding a hybrid electrochemical capacitor. Evans' capacitors, coined Capattery, had an energy content about a factor of 5 higher than a comparable tantalum electrolytic capacitor of the same size. Their high costs limited them to specific military applications.
Recent developments include lithium-ion capacitors. These hybrid capacitors were pioneered by FDK in 2007. They combine an electrostatic carbon electrode with a pre-doped lithium-ion electrochemical electrode. This combination increases the capacitance value. Additionally, the pre-doping process lowers the anode potential and results in a high cell output voltage, further increasing specific energy.
Research departments active in many companies and universities are working to improve characteristics such as specific energy, specific power, and cycle stability and to reduce production costs.
Basics
Basic design
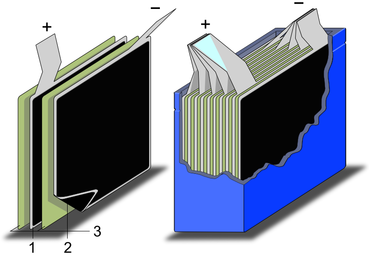
Typical
construction of a supercapacitor: (1) power source, (2) collector,
(3) polarized electrode, (4) Helmholtz double layer, (5) electrolyte
having positive and negative ions, (6) separator.
Electrochemical capacitors (supercapacitors) consist of two electrodes separated by an ion-permeable membrane (separator), and an electrolyte ionically connecting both electrodes. When the electrodes are polarized by an applied voltage, ions in the electrolyte form electric double layers of opposite polarity to the electrode's polarity. For example, positively polarized electrodes will have a layer of negative ions at the electrode/electrolyte interface along with a charge-balancing layer of positive ions adsorbing onto the negative layer. The opposite is true for the negatively polarized electrode.
Additionally, depending on electrode material and surface shape, some ions may permeate the double layer becoming specifically adsorbed ions and contribute with pseudocapacitance to the total capacitance of the supercapacitor.
Capacitance distribution
The two electrodes form a series circuit of two individual capacitors C1 and C2. The total capacitance Ctotal is given by the formulaStorage principles
Electrochemical capacitors use the double-layer effect to store electric energy; however, this double-layer has no conventional solid dielectric to separate the charges. There are two storage principles in the electric double-layer of the electrodes that contribute to the total capacitance of an electrochemical capacitor:- Double-layer capacitance, electrostatic storage of the electrical energy achieved by separation of charge in a Helmholtz double layer.
- Pseudocapacitance, electrochemical storage of the electrical energy achieved by faradaic redox reactions with charge-transfer.
Practically, these storage principles yield a capacitor with a capacitance value in the order of 1 to 100 farad.
Electrostatic double-layer capacitance
Simplified
view of a double-layer of negative ions in the electrode and solvated
positive ions in the liquid electrolyte, separated by a layer of
polarized solvent molecules.
Every electrochemical capacitor has two electrodes, mechanically separated by a separator, which are ionically connected to each other via the electrolyte. The electrolyte is a mixture of positive and negative ions dissolved in a solvent such as water. At each of the two electrode surfaces originates an area in which the liquid electrolyte contacts the conductive metallic surface of the electrode. This interface forms a common boundary among two different phases of matter, such as an insoluble solid electrode surface and an adjacent liquid electrolyte. In this interface occurs a very special phenomenon of the double layer effect.
Applying a voltage to an electrochemical capacitor causes both electrodes in the capacitor to generate electrical double-layers. These double-layers consist of two layers of charges: one electronic layer is in the surface lattice structure of the electrode, and the other, with opposite polarity, emerges from dissolved and solvated ions in the electrolyte. The two layers are separated by a monolayer of solvent molecules, e. g. for water as solvent by water molecules, called inner Helmholtz plane (IHP). Solvent molecules adhere by physical adsorption on the surface of the electrode and separate the oppositely polarized ions from each other, and can be idealised as a molecular dielectric. In the process, there is no transfer of charge between electrode and electrolyte, so the forces that cause the adhesion are not chemical bonds but physical forces (e.g. electrostatic forces). The adsorbed molecules are polarized but, due to the lack of transfer of charge between electrolyte and electrode, suffered no chemical changes.
The amount of charge in the electrode is matched by the magnitude of counter-charges in outer Helmholtz plane (OHP). This double-layer phenomena stores electrical charges as in a conventional capacitor. The double-layer charge forms a static electric field in the molecular layer of the solvent molecules in the IHP that corresponds to the strength of the applied voltage.
Structure
and function of an ideal double-layer capacitor. Applying a voltage to
the capacitor at both electrodes a Helmholtz double-layer will be formed
separating the ions in the electrolyte in a mirror charge distribution
of opposite polarity
The double-layer serves approximately as the dielectric layer in a conventional capacitor, albeit with the thickness of a single molecule. Thus, the standard formula for conventional plate capacitors can be used to calculate their capacitance:
- .
The main drawback of carbon electrodes of double-layer SCs is small values of quantum capacitance which act in series with capacitance of ionic space charge. Therefore, further increase of density of capacitance in SCs can be connected with increasing of quantum capacitance of carbon electrode nanostructures.
The amount of charge stored per unit voltage in an electrochemical capacitor is primarily a function of the electrode size. The electrostatic storage of energy in the double-layers is linear with respect to the stored charge, and correspond to the concentration of the adsorbed ions. Also, while charge in conventional capacitors is transferred via electrons, capacitance in double-layer capacitors is related to the limited moving speed of ions in the electrolyte and the resistive porous structure of the electrodes. Since no chemical changes take place within the electrode or electrolyte, charging and discharging electric double-layers in principle is unlimited. Real supercapacitors lifetimes are only limited by electrolyte evaporation effects.
Electrochemical pseudocapacitance
Simplified
view of a double-layer with specifically adsorbed ions which have
submitted their charge to the electrode to explain the faradaic
charge-transfer of the pseudocapacitance.
Applying a voltage at the electrochemical capacitor terminals moves electrolyte ions to the opposite polarized electrode and forms a double-layer in which a single layer of solvent molecules acts as separator. Pseudocapacitance can originate when specifically adsorbed ions out of the electrolyte pervade the double-layer. This pseudocapacitance stores electrical energy by means of reversible faradaic redox reactions on the surface of suitable electrodes in an electrochemical capacitor with an electric double-layer. Pseudocapacitance is accompanied with an electron charge-transfer between electrolyte and electrode coming from a de-solvated and adsorbed ion whereby only one electron per charge unit is participating. This faradaic charge transfer originates by a very fast sequence of reversible redox, intercalation or electrosorption processes. The adsorbed ion has no chemical reaction with the atoms of the electrode (no chemical bonds arise) since only a charge-transfer take place.
A cyclic voltammogram shows the fundamental differences between static capacitance (rectangular) and pseudocapacitance (curved)
The electrons involved in the faradaic processes are transferred to or from valence electron states (orbitals) of the redox electrode reagent. They enter the negative electrode and flow through the external circuit to the positive electrode where a second double-layer with an equal number of anions has formed. The electrons reaching the positive electrode are not transferred to the anions forming the double-layer, instead they remain in the strongly ionized and "electron hungry" transition-metal ions of the electrode's surface. As such, the storage capacity of faradaic pseudocapacitance is limited by the finite quantity of reagent in the available surface.
A faradaic pseudocapacitance only occurs together with a static double-layer capacitance, and its magnitude may exceed the value of double-layer capacitance for the same surface area by factor 100, depending on the nature and the structure of the electrode because all the pseudocapacitance reactions take place only with de-solvated ions, which are much smaller than solvated ion with their solvating shell. The amount of pseudocapacitance has a linear function within narrow limits determined by the potential-dependent degree of surface coverage of the adsorbed anions.
The ability of electrodes to accomplish pseudocapacitance effects by redox reactions, intercalation or electrosorption strongly depends on the chemical affinity of electrode materials to the ions adsorbed on the electrode surface as well as on the structure and dimension of the electrode pores. Materials exhibiting redox behavior for use as electrodes in pseudocapacitors are transition-metal oxides like RuO2, IrO2, or MnO2 inserted by doping in the conductive electrode material such as active carbon, as well as conducting polymers such as polyaniline or derivatives of polythiophene covering the electrode material.
The amount of electric charge stored in a pseudocapacitance is linearly proportional to the applied voltage. The unit of pseudocapacitance is farad.
Potential distribution
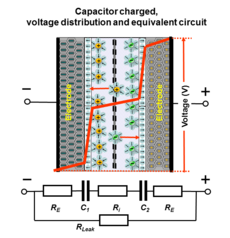
Charge storage principles of different capacitor types and their internal potential distribution
Basic
illustration of the functionality of a supercapacitor, the voltage
distribution inside of the capacitor and its simplified equivalent DC
circuit
The voltage behavior of supercapacitors and batteries during charging/discharging differs clearly
Conventional capacitors (also known as electrostatic capacitors), such as ceramic capacitors and film capacitors, consist of two electrodes which are separated by a dielectric material. When charged, the energy is stored in a static electric field that permeates the dielectric between the electrodes. The total energy increases with the amount of stored charge, which in turn correlates linearly with the potential (voltage) between the plates. The maximum potential difference between the plates (the maximal voltage) is limited by the dielectric's breakdown field strength. The same static storage also applies for electrolytic capacitors in which most of the potential decreases over the anode's thin oxide layer. The somewhat resistive liquid electrolyte (cathode) accounts for a small decrease of potential for "wet" electrolytic capacitors, while electrolytic capacitors with solid conductive polymer electrolyte this voltage drop is negligible.
In contrast, electrochemical capacitors (supercapacitors) consists of two electrodes separated by an ion-permeable membrane (separator) and electrically connected via an electrolyte. Energy storage occurs within the double-layers of both electrodes as a mixture of a double-layer capacitance and pseudocapacitance. When both electrodes have approximately the same resistance (internal resistance), the potential of the capacitor decreases symmetrically over both double-layers, whereby a voltage drop across the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the electrolyte is achieved. For asymmetrical supercapacitors like hybrid capacitors the voltage drop between the electrodes could be asymmetrical. The maximum potential across the capacitor (the maximal voltage) is limited by the electrolyte decomposition voltage.
Both electrostatic and electrochemical energy storage in supercapacitors are linear with respect to the stored charge, just as in conventional capacitors. The voltage between the capacitor terminals is linear with respect to the amount of stored energy. Such linear voltage gradient differs from rechargeable electrochemical batteries, in which the voltage between the terminals remains independent of the amount of stored energy, providing a relatively constant voltage.
Comparison with other storage technologies
Supercapacitors compete with electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries especially lithium-ion batteries. The following table compares the major parameters of the three main supercapacitor families with electrolytic capacitors and batteries.| Parameter | Alum- inum electro- lytic capacitors |
— Supercapacitors — | Lithium- ion batteries | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double- layer capacitors (memory backup) |
Super- capacitors (high power) |
Pseudo- capacitors & hybrid (Li-Ion) (long-term) | |||
| Temperature range, Celsius (°C) |
−40 ... +125 °C | −40 ... +70 °C | −20 ... +70 °C | −20 ... +70 °C | −20 ... +60 °C |
| 4 ... 630 V | 1.2 ... 3.3 V | 2.2 ... 3.3 V | 2.2 ... 3.8 V | 2.5 ... 4.2 V | |
| Recharge cycles, thousands (k) |
unlimited | 100 k ... 1 000 k | 100 k ... 1 000 k | 20 k ... 100 k | 0.5 k ... 10 k |
| Capacitance, Farads (F) |
≤ 2.7 F | 0.1 ... 470 F | 100 ... 12 000 F | 300 ... 3 300 F | — |
| Specific energy, milli-Watt hours per gram (mW·h/g) |
0.01 ... 0.3 mW·h/g |
1.5 ... 3.9 mW·h/g |
4 ... 9 mW·h/g |
10 ... 15 mW·h/g |
100 ... 265 mW·h/g |
| Specific power, Watts per gram (W/g) |
> 100 W/g | 2 ... 10 W/g | 3 ... 10 W/g | 3 ... 14 W/g | 0.3 ... 1.5 W/g |
| Self-discharge time at room temp. |
short (days) |
middle (weeks) |
middle (weeks) |
long (month) |
long (month) |
| Efficiency (%) | 99% | 95% | 95% | 90% | 90% |
| Working life at room temp., in years (y) |
> 20 y | 5 ... 10 y | 5 ... 10 y | 5 ... 10 y | 3 ... 5 y |
Electrolytic capacitors feature unlimited charge/discharge cycles, high dielectric strength (up to 550 V) and good frequency response as AC resistance in the lower frequency range. Supercapacitors can store 10 to 100 times more energy than electrolytic capacitors but they do not support AC applications.
With regards to rechargeable batteries supercapacitors feature higher peak currents, low cost per cycle, no danger of overcharging, good reversibility, non-corrosive electrolyte and low material toxicity, while batteries offer, lower purchase cost, stable voltage under discharge, but they require complex electronic control and switching equipment, with consequent energy loss and spark hazard given a short.
Styles
Supercapacitors are made in different styles such as flat with a single pair of electrodes, wound in a cylindrical case or stacked in a rectangular case. Because they cover a broad range of capacitance values the size of the cases can vary.- Different styles of supercapacitors
- Radial style of a supercapacitor for PCB mounting used for industrial applications
Construction details
- Construction details of wound and stacked supercapacitors with activated carbon electrodes
Supercapacitor types
Family
tree of supercapacitor types. Double-layer capacitors and
pseudocapacitors as well as hybrid capacitors are defined over their
electrode designs.
Electrical energy is stored in supercapacitors via two storage principles: static double-layer capacitance and electrochemical pseudocapacitance; and the distribution of the two types of capacitance depends on the material and structure of the electrodes. There are three types of supercapacitors based on storage principle:
- Double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) – with activated carbon electrodes or derivatives with much higher electrostatic double-layer capacitance than electrochemical pseudocapacitance
- Pseudocapacitors – with transition metal oxide or conducting polymer electrodes with a high electrochemical pseudocapacitance
- Hybrid capacitors – with asymmetric electrodes, one of which exhibits mostly electrostatic and the other mostly electrochemical capacitance, such as lithium-ion capacitors
The capacitance value of a supercapacitor is determined by two storage principles:
- Double-layer capacitance – electrostatic storage of the electrical energy achieved by separation of charge in a Helmholtz double layer at the interface between the surface of a conductor electrode and an electrolytic solution electrolyte. The separation of charge distance in a double-layer is on the order of a few ångströms (0.3–0.8 nm) and is static in origin.
- Pseudocapacitance – Electrochemical storage of the electrical energy, achieved by redox reactions, electrosorption or intercalation on the surface of the electrode by specifically adsorbed ions, that results in a reversible faradaic charge-transfer on the electrode.
Electric double-layer capacitors (EDLC) are electrochemical capacitors in which energy storage predominantly is achieved by double-layer capacitance. In the past, all electrochemical capacitors were called "double-layer capacitors". Contemporary usage sees double-layer capacitors, together with pseudocapacitors, as part of a larger family of electrochemical capacitors called supercapacitors. They are also known as ultracapacitors.
Materials
The properties of supercapacitors come from the interaction of their internal materials. Especially, the combination of electrode material and type of electrolyte determine the functionality and thermal and electrical characteristics of the capacitors.Electrodes
A micrograph of activated carbon under bright field illumination on a light microscope. Notice the fractal-like
shape of the particles hinting at their enormous surface area. Each
particle in this image, despite being only around 0.1 mm across, has a
surface area of several square meters.
Supercapacitor electrodes are generally thin coatings applied and electrically connected to a conductive, metallic current collector. Electrodes must have good conductivity, high temperature stability, long-term chemical stability (inertness), high corrosion resistance and high surface areas per unit volume and mass. Other requirements include environmental friendliness and low cost.
The amount of double-layer as well as pseudocapacitance stored per unit voltage in a supercapacitor is predominantly a function of the electrode surface area. Therefore, supercapacitor electrodes are typically made of porous, spongy material with an extraordinarily high specific surface area, such as activated carbon. Additionally, the ability of the electrode material to perform faradaic charge transfers enhances the total capacitance.
Generally the smaller the electrode's pores, the greater the capacitance and specific energy. However, smaller pores increase equivalent series resistance (ESR) and decrease specific power. Applications with high peak currents require larger pores and low internal losses, while applications requiring high specific energy need small pores.
Electrodes for EDLCs
The most commonly used electrode material for supercapacitors is carbon in various manifestations such as activated carbon (AC), carbon fibre-cloth (AFC), carbide-derived carbon (CDC), carbon aerogel, graphite (graphene), graphane, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs).Carbon-based electrodes exhibit predominantly static double-layer capacitance, even though a small amount of pseudocapacitance may also be present depending on the pore size distribution. Pore sizes in carbons typically range from micropores (less than 2 nm) to mesopores (2-50 nm), but only micropores (less than 2 nm) contribute to pseudocapacitance. As pore size approaches the solvation shell size, solvent molecules are excluded and only unsolvated ions fill the pores (even for large ions), increasing ionic packing density and storage capability by faradaic H
2 intercalation.
Activated carbon
Activated carbon (AC) was the first material chosen for EDLC electrodes. Even though its electrical conductivity is approximately 0.003% that of metals (1,250 to 2,000 S/m), it is sufficient for supercapacitors.Activated carbon is an extremely porous form of carbon with a high specific surface area — a common approximation is that 1 gram (0.035 oz) (a pencil-eraser-sized amount) has a surface area of roughly 1,000 to 3,000 square metres (11,000 to 32,000 sq ft) — about the size of 4 to 12 tennis courts. The bulk form used in electrodes is low-density with many pores, giving high double-layer capacitance.
Solid activated carbon, also termed consolidated amorphous carbon (CAC) is the most used electrode material for supercapacitors and may be cheaper than other carbon derivatives. It is produced from activated carbon powder pressed into the desired shape, forming a block with a wide distribution of pore sizes. An electrode with a surface area of about 1000 m2/g results in a typical double-layer capacitance of about 10 μF/cm2 and a specific capacitance of 100 F/g.
As of 2010 virtually all commercial supercapacitors use powdered activated carbon made from coconut shells. Coconut shells produce activated carbon with more micropores than does charcoal made from wood.
Activated carbon fibres
Activated carbon fibres (ACF) are produced from activated carbon and have a typical diameter of 10 µm. They can have micropores with a very narrow pore-size distribution that can be readily controlled. The surface area of ACF woven into a textile is about 2500 m2/g. Advantages of ACF electrodes include low electrical resistance along the fibre axis and good contact to the collector.As for activated carbon, ACF electrodes exhibit predominantly double-layer capacitance with a small amount of pseudocapacitance due to their micropores.
Carbon aerogel
A block of silica aerogel in hand
Carbon aerogel is a highly porous, synthetic, ultralight material derived from an organic gel in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas.
Aerogel electrodes are made via pyrolysis of resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels and are more conductive than most activated carbons. They enable thin and mechanically stable electrodes with a thickness in the range of several hundred micrometres (µm) and with uniform pore size. Aerogel electrodes also provide mechanical and vibration stability for supercapacitors used in high-vibration environments.
Researchers have created a carbon aerogel electrode with gravimetric densities of about 400–1200 m2/g and volumetric capacitance of 104 F/cm3, yielding a specific energy of 325 kJ/kg (90 Wh/kg) and specific power of 20 W/g.
Standard aerogel electrodes exhibit predominantly double-layer capacitance. Aerogel electrodes that incorporate composite material can add a high amount of pseudocapacitance.
Carbide-derived carbon
Pore size distributions for different carbide precursors.
Carbide-derived carbon (CDC), also known as tunable nanoporous carbon, is a family of carbon materials derived from carbide precursors, such as binary silicon carbide and titanium carbide, that are transformed into pure carbon via physical (e.g., thermal decomposition) or chemical (e.g., halogenation) processes.
Carbide-derived carbons can exhibit high surface area and tunable pore diameters (from micropores to mesopores) to maximize ion confinement, increasing pseudocapacitance by faradaic H
2 adsorption treatment. CDC electrodes with tailored pore design offer as much as 75% greater specific energy than conventional activated carbons.
As of 2015, a CDC supercapacitor offered a specific energy of 10.1 Wh/kg, 3,500 F capacitance and over one million charge-discharge cycles.
Graphene
Graphene is an atomic-scale honeycomb lattice made of carbon atoms.
Graphene is a one-atom thick sheet of graphite, with atoms arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern, also called "nanocomposite paper".
Graphene has a theoretical specific surface area of 2630 m2/g which can theoretically lead to a capacitance of 550 F/g. In addition, an advantage of graphene over activated carbon is its higher electrical conductivity. As of 2012 a new development used graphene sheets directly as electrodes without collectors for portable applications.
In one embodiment, a graphene-based supercapacitor uses curved graphene sheets that do not stack face-to-face, forming mesopores that are accessible to and wettable by ionic electrolytes at voltages up to 4 V. A specific energy of 85.6 Wh/kg (308 kJ/kg) is obtained at room temperature equaling that of a conventional nickel metal hydride battery, but with 100-1000 times greater specific power.
The two-dimensional structure of graphene improves charging and discharging. Charge carriers in vertically oriented sheets can quickly migrate into or out of the deeper structures of the electrode, thus increasing currents. Such capacitors may be suitable for 100/120 Hz filter applications, which are unreachable for supercapacitors using other carbon materials.
Carbon nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of single-walled carbon nanotube
SEM image of carbon nanotube bundles with a surface of about 1500 m2/g
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), also called buckytubes, are carbon molecules with a cylindrical nanostructure. They have a hollow structure with walls formed by one-atom-thick sheets of graphite. These sheets are rolled at specific and discrete ("chiral") angles, and the combination of chiral angle and radius controls properties such as electrical conductivity, electrolyte wettability and ion access. Nanotubes are categorized as single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) or multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs). The latter have one or more outer tubes successively enveloping a SWNT, much like the Russian matryoshka dolls. SWNTs have diameters ranging between 1 and 3 nm. MWNTs have thicker coaxial walls, separated by spacing (0.34 nm) that is close to graphene's interlayer distance.
Nanotubes can grow vertically on the collector substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Typical lengths are 20 to 100 µm.
Carbon nanotubes can greatly improve capacitor performance, due to the highly wettable surface area and high conductivity.
A SWNT-based supercapacitor with aqueous electrolyte was systematically studied at University of Delaware in Prof. Bingqing Wei's group. Li et al., for the first time, discovered that the ion-size effect and the electrode-electrolyte wettability are the dominant factors affecting the electrochemical behavior of flexible SWCNTs-supercapacitors in different 1 molar aqueous electrolytes with different anions and cations. The experimental results also showed for flexible supercapacitor that it is suggested to put enough pressure between the two electrodes to improve the aqueous electrolyte CNT supercapacitor.
CNTs can store about the same charge as activated carbon per unit surface area, but nanotubes' surface is arranged in a regular pattern, providing greater wettability. SWNTs have a high theoretical specific surface area of 1315 m2/g, while that for MWNTs is lower and is determined by the diameter of the tubes and degree of nesting, compared with a surface area of about 3000 m2/g of activated carbons. Nevertheless, CNTs have higher capacitance than activated carbon electrodes, e.g., 102 F/g for MWNTs and 180 F/g for SWNTs.
MWNTs have mesopores that allow for easy access of ions at the electrode–electrolyte interface. As the pore size approaches the size of the ion solvation shell, the solvent molecules are partially stripped, resulting in larger ionic packing density and increased faradaic storage capability. However, the considerable volume change during repeated intercalation and depletion decreases their mechanical stability. To this end, research to increase surface area, mechanical strength, electrical conductivity and chemical stability is ongoing.
Electrodes for pseudocapacitors
MnO2 and RuO2 are typical materials used as electrodes for pseudocapacitors, since they have the electrochemical signature of a capacitive electrode (linear dependence on current versus voltage curve) as well as exhibiting faradaic behavior. Additionally, the charge storage originates from electron-transfer mechanisms rather than accumulation of ions in the electrochemical double layer. Pseudocapacitors were created through faradaic redox reactions that occur within the active electrode materials. More research was focused on transition-metal oxides such as MnO2 since transition-metal oxides have a lower cost compared to noble metal oxides such as RuO2. Moreover, the charge storage mechanisms of transition-metal oxides are based predominantly on pseudocapacitance. Two mechanisms of MnO2 charge storage behavior were introduced. The first mechanism implies the intercalation of protons (H+) or alkali metal cations (C+) in the bulk of the material upon reduction followed by deintercalation upon oxidation.- MnO2 + H+(C+) +e− ⇌ MnOOH(C)
- (MnO2)surface + C+ +e− ⇌ (MnO2− C+)surface
Metal oxides
Brian Evans Conway's research described electrodes of transition metal oxides that exhibited high amounts of pseudocapacitance. Oxides of transition metals including ruthenium (RuO2), iridium (IrO
2), iron (Fe
3O
4), manganese (MnO
2) or sulfides such as titanium sulfide (TiS
2) alone or in combination generate strong faradaic electron–transferring reactions combined with low resistance. Ruthenium dioxide in combination with H
2SO
4 electrolyte provides specific capacitance of 720 F/g and a high specific energy of 26.7 Wh/kg (96.12 kJ/kg).
Charge/discharge takes place over a window of about 1.2 V per electrode. This pseudocapacitance of about 720 F/g is roughly 100 times higher than for double-layer capacitance using activated carbon electrodes. These transition metal electrodes offer excellent reversibility, with several hundred-thousand cycles. However, ruthenium is expensive and the 2.4 V voltage window for this capacitor limits their applications to military and space applications. Das et al. reported highest capacitance value (1715 F/g) for ruthenium oxide based supercapacitor with electrodeposited ruthenium oxide onto porous single wall carbon nanotube film electrode. A high specific capacitance of 1715 F/g has been reported which closely approaches the predicted theoretical maximum RuO
2 capacitance of 2000 F/g.
In 2014 a RuO
2 supercapacitor anchored on a graphene foam electrode delivered specific capacitance of 502.78 F/g and areal capacitance of 1.11 F/cm2) leading to a specific energy of 39.28 Wh/kg and specific power of 128.01 kW/kg over 8,000 cycles with constant performance. The device was a three-dimensional (3D) sub-5 nm hydrous ruthenium-anchored graphene and carbon nanotube (CNT) hybrid foam (RGM) architecture. The graphene foam was conformally covered with hybrid networks of RuO
2 nanoparticles and anchored CNTs.
Less expensive oxides of iron, vanadium, nickel and cobalt have been tested in aqueous electrolytes, but none has been investigated as much as manganese dioxide (MnO
2). However, none of these oxides are in commercial use.
Conductive polymers
Another approach uses electron-conducting polymers as pseudocapacitive material. Although mechanically weak, conductive polymers have high conductivity, resulting in a low ESR and a relatively high capacitance. Such conducting polymers include polyaniline, polythiophene, polypyrrole and polyacetylene. Such electrodes also employ electrochemical doping or dedoping of the polymers with anions and cations. Electrodes made from or coated with conductive polymers have costs comparable to carbon electrodes.Conducting polymer electrodes generally suffer from limited cycling stability. However, polyacene electrodes provide up to 10,000 cycles, much better than batteries.
Electrodes for hybrid capacitors
All commercial hybrid supercapacitors are asymmetric. They combine an electrode with high amount of pseudocapacitance with an electrode with a high amount of double-layer capacitance. In such systems the faradaic pseudocapacitance electrode with their higher capacitance provides high specific energy while the non-faradaic EDLC electrode enables high specific power. An advantage of the hybrid-type supercapacitors compared with symmetrical EDLC's is their higher specific capacitance value as well as their higher rated voltage and correspondingly their higher specific energy.Composite electrodes
Composite electrodes for hybrid-type supercapacitors are constructed from carbon-based material with incorporated or deposited pseudocapacitive active materials like metal oxides and conducting polymers. As of 2013 most research for supercapacitors explores composite electrodes.CNTs give a backbone for a homogeneous distribution of metal oxide or electrically conducting polymers (ECPs), producing good pseudocapacitance and good double-layer capacitance. These electrodes achieve higher capacitances than either pure carbon or pure metal oxide or polymer-based electrodes. This is attributed to the accessibility of the nanotubes' tangled mat structure, which allows a uniform coating of pseudocapacitive materials and three-dimensional charge distribution. The process to anchor pseudocapacitve materials usually uses a hydrothermal process. However, a recent researcher, Li et al., from the University of Delaware found a facile and scalable approach to precipitate MnO2 on a SWNT film to make an organic-electrolyte based supercapacitor.
Another way to enhance CNT electrodes is by doping with a pseudocapacitive dopant as in lithium-ion capacitors. In this case the relatively small lithium atoms intercalate between the layers of carbon. The anode is made of lithium-doped carbon, which enables lower negative potential with a cathode made of activated carbon. This results in a larger voltage of 3.8-4 V that prevents electrolyte oxidation. As of 2007 they had achieved capacitance of 550 F/g. and reach a specific energy up to 14 Wh/kg (50.4 kJ/kg).
Battery-type electrodes
Rechargeable battery electrodes influenced the development of electrodes for new hybrid-type supercapacitor electrodes as for lithium-ion capacitors. Together with a carbon EDLC electrode in an asymmetric construction offers this configuration higher specific energy than typical supercapacitors with higher specific power, longer cycle life and faster charging and recharging times than batteries.Asymmetric electrodes (pseudo/EDLC)
Recently some asymmetric hybrid supercapacitors were developed in which the positive electrode were based on a real pseudocapacitive metal oxide electrode (not a composite electrode), and the negative electrode on an EDLC activated carbon electrode.An advantage of this type of supercapacitors is their higher voltage and correspondingly their higher specific energy (up to 10-20 Wh/kg (36-72 kJ/kg)).
As far as known no commercial offered supercapacitors with such kind of asymmetric electrodes are on the market.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes consist of a solvent and dissolved chemicals that dissociate into positive cations and negative anions, making the electrolyte electrically conductive. The more ions the electrolyte contains, the better its conductivity. In supercapacitors electrolytes are the electrically conductive connection between the two electrodes. Additionally, in supercapacitors the electrolyte provides the molecules for the separating monolayer in the Helmholtz double-layer and delivers the ions for pseudocapacitance.The electrolyte determines the capacitor's characteristics: its operating voltage, temperature range, ESR and capacitance. With the same activated carbon electrode an aqueous electrolyte achieves capacitance values of 160 F/g, while an organic electrolyte achieves only 100 F/g.
The electrolyte must be chemically inert and not chemically attack the other materials in the capacitor to ensure long time stable behavior of the capacitor's electrical parameters. The electrolyte's viscosity must be low enough to wet the porous, sponge-like structure of the electrodes. An ideal electrolyte does not exist, forcing a compromise between performance and other requirements.
Aqueous
Water is a relatively good solvent for inorganic chemicals. Treated with acids such as sulfuric acid (H2SO
4), alkalis such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), or salts such as quaternary phosphonium salts, sodium perchlorate (NaClO
4), lithium perchlorate (LiClO
4) or lithium hexafluoride arsenate (LiAsF
6), water offers relatively high conductivity values of about 100 to 1000 mS/cm. Aqueous electrolytes have a dissociation voltage of 1.15 V per electrode (2.3 V capacitor voltage) and a relatively low operating temperature range. They are used in supercapacitors with low specific energy and high specific power.
Organic
Electrolytes with organic solvents such as acetonitrile, propylene carbonate, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl carbonate, γ-butyrolactone and solutions with quaternary ammonium salts or alkyl ammonium salts such as tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate (N(Et)4BF
4) or triethyl (metyl) tetrafluoroborate (NMe(Et)
3BF
4) are more expensive than aqueous electrolytes, but they have a higher dissociation voltage of typically 1.35 V per electrode (2.7 V capacitor voltage), and a higher temperature range. The lower electrical conductivity of organic solvents (10 to 60 mS/cm) leads to a lower specific power, but since the specific energy increases with the square of the voltage, a higher specific energy.
Separators
Separators have to physically separate the two electrodes to prevent a short circuit by direct contact. It can be very thin (a few hundredths of a millimeter) and must be very porous to the conducting ions to minimize ESR. Furthermore, separators must be chemically inert to protect the electrolyte's stability and conductivity. Inexpensive components use open capacitor papers. More sophisticated designs use nonwoven porous polymeric films like polyacrylonitrile or Kapton, woven glass fibers or porous woven ceramic fibres.Collectors and housing
Current collectors connect the electrodes to the capacitor's terminals. The collector is either sprayed onto the electrode or is a metal foil. They must be able to distribute peak currents of up to 100 A.If the housing is made out of a metal (typically aluminum) the collectors should be made from the same material to avoid forming a corrosive galvanic cell.
Electrical parameters
Capacitance
Schematic illustration of the capacitance behavior resulting out of the porous structure of the electrodes
Equivalent circuit with cascaded RC elements
Frequency depending of the capacitance value of a 50 F supercapacitor
Capacitance values for commercial capacitors are specified as "rated capacitance CR". This is the value for which the capacitor has been designed. The value for an actual component must be within the limits given by the specified tolerance. Typical values are in the range of farads (F), three to six orders of magnitude larger than those of electrolytic capacitors.
The capacitance value results from the energy (expressed in Joule) of a loaded capacitor loaded via a DC voltage VDC.
Measurement
Conventional capacitors are normally measured with a small AC voltage (0.5 V) and a frequency of 100 Hz or 1 kHz depending on the capacitor type. The AC capacitance measurement offers fast results, important for industrial production lines. The capacitance value of a supercapacitor depends strongly on the measurement frequency, which is related to the porous electrode structure and the limited electrolyte's ion mobility. Even at a low frequency of 10 Hz, the measured capacitance value drops from 100 to 20 percent of the DC capacitance value.This extraordinary strong frequency dependence can be explained by the different distances the ions have to move in the electrode's pores. The area at the beginning of the pores can easily be accessed by the ions. The short distance is accompanied by low electrical resistance. The greater the distance the ions have to cover, the higher the resistance. This phenomenon can be described with a series circuit of cascaded RC (resistor/capacitor) elements with serial RC time constants. These result in delayed current flow, reducing the total electrode surface area that can be covered with ions if polarity changes – capacitance decreases with increasing AC frequency. Thus, the total capacitance is only achieved after longer measuring times.
Illustration of the measurement conditions for measuring the capacitance of supercapacitors
Out of the reason of the very strong frequency dependence of the capacitance this electrical parameter has to be measured with a special constant current charge and discharge measurement, defined in IEC standards 62391-1 and -2.
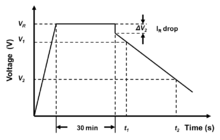
Measurement starts with charging the capacitor. The voltage has to be applied and after the constant current/constant voltage power supply has achieved the rated voltage, the capacitor has to be charged for 30 minutes. Next, the capacitor has to be discharged with a constant discharge current Idischarge. Then the time t1 and t2, for the voltage to drop from 80% (V1) to 40% (V2) of the rated voltage is measured. The capacitance value is calculated as:
- Memory backup, discharge current in mA = 1 • C (F)
- Energy storage, discharge current in mA = 0,4 • C (F) • V (V)
- Power, discharge current in mA = 4 • C (F) • V (V)
- Instantaneous power, discharge current in mA = 40 • C (F) • V (V)
The standardized measuring method is too time consuming for manufacturers to use during production for each individual component. For industrial produced capacitors the capacitance value is instead measured with a faster low frequency AC voltage and a correlation factor is used to compute the rated capacitance.
This frequency dependence affects capacitor operation. Rapid charge and discharge cycles mean that neither the rated capacitance value nor specific energy are available. In this case the rated capacitance value is recalculated for each application condition.
Operating voltage
A 5.5 volt supercapacitor is constructed out of two single cells, each rated to at least 2.75 volts, in series connection
Supercapacitors are low voltage components. Safe operation requires that the voltage remain within specified limits. The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously and remain within the specified temperature range. Capacitors should never be subjected to voltages continuously in excess of the rated voltage.
The rated voltage includes a safety margin against the electrolyte's breakdown voltage at which the electrolyte decomposes. The breakdown voltage decomposes the separating solvent molecules in the Helmholtz double-layer, f. e. water splits into hydrogen and oxide. The solvent molecules then cannot separate the electrical charges from each other. Higher voltages than rated voltage cause hydrogen gas formation or a short circuit.
Standard supercapacitors with aqueous electrolyte normally are specified with a rated voltage of 2.1 to 2.3 V and capacitors with organic solvents with 2.5 to 2.7 V. Lithium-ion capacitors with doped electrodes may reach a rated voltage of 3.8 to 4 V, but have a lower voltage limit of about 2.2 V.
Operating supercapacitors below the rated voltage improves the long-time behavior of the electrical parameters. Capacitance values and internal resistance during cycling are more stable and lifetime and charge/discharge cycles may be extended.
Higher application voltages require connecting cells in series. Since each component has a slight difference in capacitance value and ESR, it is necessary to actively or passively balance them to stabilize the applied voltage. Passive balancing employs resistors in parallel with the supercapacitors. Active balancing may include electronic voltage management above a threshold that varies the current.
Internal resistance
The
internal DC resistance can be calculated out of the voltage drop
obtained from the intersection of the auxiliary line extended from the
straight part and the time base at the time of discharge start
Charging/discharging a supercapacitor is connected to the movement of charge carriers (ions) in the electrolyte across the separator to the electrodes and into their porous structure. Losses occur during this movement that can be measured as the internal DC resistance.
With the electrical model of cascaded, series-connected RC (resistor/capacitor) elements in the electrode pores, the internal resistance increases with the increasing penetration depth of the charge carriers into the pores. The internal DC resistance is time dependent and increases during charge/discharge. In applications often only the switch-on and switch-off range is interesting. The internal resistance Ri can be calculated from the voltage drop ΔV2 at the time of discharge, starting with a constant discharge current Idischarge. It is obtained from the intersection of the auxiliary line extended from the straight part and the time base at the time of discharge start (see picture right). Resistance can be calculated by:
This internal DC resistance Ri should not be confused with the internal AC resistance called equivalent series resistance (ESR) normally specified for capacitors. It is measured at 1 kHz. ESR is much smaller than DC resistance. ESR is not relevant for calculating superconductor inrush currents or other peak currents.
Ri determines several supercapacitor properties. It limits the charge and discharge peak currents as well as charge/discharge times. Ri and the capacitance C results in the time constant
Standard capacitors with constant internal resistance fully charge during about 5 τ. Since internal resistance increases with charge/discharge, actual times cannot be calculated with this formula. Thus, charge/discharge time depends on specific individual construction details.
Current load and cycle stability
Because supercapacitors operate without forming chemical bonds, current loads, including charge, discharge and peak currents are not limited by reaction constraints. Current load and cycle stability can be much higher than for rechargeable batteries. Current loads are limited only by internal resistance, which may be substantially lower than for batteries.Internal resistance "Ri" and charge/discharge currents or peak currents "I" generate internal heat losses "Ploss" according to:
Heat generally defines capacitor lifetime because of electrolyte diffusion. The heat generation coming from current loads should be smaller than 5 to 10 K at maximum ambient temperature (which has only minor influence on expected lifetime). For that reason the specified charge and discharge currents for frequent cycling are determined by internal resistance.
The specified cycle parameters under maximal conditions include charge and discharge current, pulse duration and frequency. They are specified for a defined temperature range and over the full voltage range for a defined lifetime. They can differ enormously depending on the combination of electrode porosity, pore size and electrolyte. Generally a lower current load increases capacitor life and increases the number of cycles. This can be achieved either by a lower voltage range or slower charging and discharging.
Supercapacitors (except those with polymer electrodes) can potentially support more than one million charge/discharge cycles without substantial capacity drops or internal resistance increases. Beneath the higher current load is this the second great advantage of supercapacitors over batteries. The stability results from the dual electrostatic and electrochemical storage principles.
The specified charge and discharge currents can be significantly exceeded by lowering the frequency or by single pulses. Heat generated by a single pulse may be spread over the time until the next pulse occurs to ensure a relatively small average heat increase. Such a "peak power current" for power applications for supercapacitors of more than 1000 F can provide a maximum peak current of about 1000 A. Such high currents generate high thermal stress and high electromagnetic forces that can damage the electrode-collector connection requiring robust design and construction of the capacitors.
Device capacitance and resistance dependence on operating voltage and temperature
Measured device capacitance across an EDLC's operating voltage
Device parameters such as capacitance initial resistance and steady state resistance are not constant but are variable and dependent on the device's operating voltage. Device capacitance will have a measurable increase as the operating voltage increases. For example: a 100F device can be seen to vary 26% from its maximum capacitance over its entire operational voltage range. Similar dependence on operating voltage is seen in steady state resistance (Rss) and initial resistance (Ri).
Device properties can also be seen to be dependent on device temperature. As the temperature of the device changes either through operation of varying ambient temperature, the internal properties such as capacitance and resistance will vary as well. Device capacitance is seen to increase as the operating temperature increases.
Energy capacity
Ragone chart showing specific power vs. specific energy of various capacitors and batteries
Supercapacitors occupy the gap between high power/low energy electrolytic capacitors and low power/high energy rechargeable batteries. The energy Wmax (expressed in Joule) that can be stored in a capacitor is given by the formula
Specific energy and specific power
The amount of energy that can be stored in a capacitor per mass of that capacitor is called its specific energy. Specific energy is measured gravimetrically (per unit of mass) in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg).The amount of energy can be stored in a capacitor per volume of that capacitor is called its energy density. Energy density is measured volumetrically (per unit of volume) in watt-hours per litre (Wh/l).
As of 2013 commercial specific energies range from around 0.5 to 15 Wh/kg. For comparison, an aluminum electrolytic capacitor stores typically 0.01 to 0.3 Wh/kg, while a conventional lead-acid battery stores typically 30 to 40 Wh/kg and modern lithium-ion batteries 100 to 265 Wh/kg. Supercapacitors can therefore store 10 to 100 times more energy than electrolytic capacitors, but only one tenth as much as batteries. For reference, petrol fuel has a specific energy of 44.4 MJ/kg or 12300 Wh/kg (in vehicle propulsion, the efficiency of energy conversions should be considered resulting in 3700 Wh/kg considering a typical 30% internal combustion engine efficiency).
Commercial energy density (also called volumetric specific energy in some literature) varies widely but in general range from around 5 to 8 Wh/l. Units of liters and dm3 can be used interchangeably. In comparison, petrol fuel has an energy density of 32.4 MJ/l or 9000 Wh/l.
Although the specific energy of supercapacitors is insufficient compared with batteries, capacitors have the important advantage of the specific power. Specific power describes the speed at which energy can be delivered to/absorbed from the load. The maximum power is given by the formula:[83]
Specific power is measured either gravimetrically in kilowatts per kilogram (kW/kg, specific power) or volumetrically in kilowatts per litre (kW/l, power density).
The described maximum power Pmax specifies the power of a theoretical rectangular single maximum current peak of a given voltage. In real circuits the current peak is not rectangular and the voltage is smaller, caused by the voltage drop. IEC 62391–2 established a more realistic effective power Peff for supercapacitors for power applications:
Ragone charts relate energy to power and are a valuable tool for characterizing and visualizing energy storage components. With such a diagram, the position of specific power and specific energy of different storage technologies is easily to compare, see diagram.
Lifetime
The lifetime of supercapacitors depends mainly on the capacitor temperature and the voltage applied
Since supercapacitors do not rely on chemical changes in the electrodes (except for those with polymer electrodes), lifetimes depend mostly on the rate of evaporation of the liquid electrolyte. This evaporation in general is a function of temperature, of current load, current cycle frequency and voltage. Current load and cycle frequency generate internal heat, so that the evaporation-determining temperature is the sum of ambient and internal heat. This temperature is measurable as core temperature in the center of a capacitor body. The higher the core temperature the faster the evaporation and the shorter the lifetime.
Evaporation generally results in decreasing capacitance and increasing internal resistance. According to IEC/EN 62391-2 capacitance reductions of over 30% or internal resistance exceeding four times its data sheet specifications are considered "wear-out failures", implying that the component has reached end-of-life. The capacitors are operable, but with reduced capabilities. Whether the aberration of the parameters have any influence on the proper functionality or not depends on the application of the capacitors.
Such large changes of electrical parameters specified in IEC/EN 62391-2 are usually unacceptable for high current load applications. Components that support high current loads use much smaller limits, e.g., 20% loss of capacitance or double the internal resistance. The narrower definition is important for such applications, since heat increases linearly with increasing internal resistance and the maximum temperature should not be exceeded. Temperatures higher than specified can destroy the capacitor.
The real application lifetime of supercapacitors, also called "service life", "life expectancy" or "load life", can reach 10 to 15 years or more at room temperature. Such long periods cannot be tested by manufacturers. Hence, they specify the expected capacitor lifetime at the maximum temperature and voltage conditions. The results are specified in datasheets using the notation "tested time (hours)/max. temperature (°C)", such as "5000 h/65 °C". With this value and expressions derived from historical data, lifetimes can be estimated for lower temperature conditions.
Datasheet lifetime specification is tested by the manufactures using an accelerated aging test called "endurance test" with maximum temperature and voltage over a specified time. For a "zero defect" product policy during this test no wear out or total failure may occur.
The lifetime specification from datasheets can be used to estimate the expected lifetime for a given design. The "10-degrees-rule" used for electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte is used in those estimations and can be used for supercapacitors. This rule employs the Arrhenius equation, a simple formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. For every 10 °C reduction in operating temperature, the estimated life doubles.
- Lx = estimated lifetime
- L0 = specified lifetime
- T0 = upper specified capacitor temperature
- Tx = actual operating temperature of the capacitor cell
Lifetimes are also dependent on the operating voltage, because the development of gas in the liquid electrolyte depends on the voltage. The lower the voltage the smaller the gas development and the longer the lifetime. No general formula relates voltage to lifetime. The voltage dependent curves shown from the picture are an empirical result from one manufacturer.
Life expectancy for power applications may be also limited by current load or number of cycles. This limitation has to be specified by the relevant manufacturer and is strongly type dependent.
Self-discharge
Storing electrical energy in the double-layer separates the charge carriers within the pores by distances in the range of molecules. Over this short distance irregularities can occur, leading to a small exchange of charge carriers and gradual discharge. This self-discharge is called leakage current. Leakage depends on capacitance, voltage, temperature and the chemical stability of the electrode/electrolyte combination. At room temperature leakage is so low that it is specified as time to self-discharge. Supercapacitor self-discharge time is specified in hours, days or weeks. As an example, a 5.5 V/F Panasonic "Goldcapacitor" specifies a voltage drop at 20 °C from 5.5 V to 3 V in 600 hours (25 days or 3.6 weeks) for a double cell capacitor.Post charge voltage relaxation
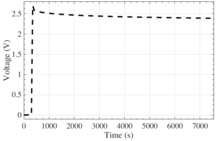
A graph plotting voltage over time, after the application of a charge
It has been noticed that after the EDLC experiences a charge or discharge, the voltage will drift over time, relaxing toward its previous voltage level. The observed relaxation can occur over several hours and is likely due to long diffusion time constants of the porous electrodes within the EDLC.
Polarity
A negative bar on the insulating sleeve indicates the cathode terminal of the capacitor
Since the positive and negative electrodes (or simply positrode and negatrode, respectively) of symmetric supercapacitors consist of the same material, theoretically supercapacitors have no true polarity and catastrophic failure does not normally occur. However reverse-charging a supercapacitor lowers its capacity, so it is recommended practice to maintain the polarity resulting from the formation of the electrodes during production. Asymmetric supercapacitors are inherently polar.
Pseudocapacitor and hybrid supercapacitors which have electrochemical charge properties may not be operated with reverse polarity, precluding their use in AC operation. However, this limitation does not apply to EDLC supercapacitors
A bar in the insulating sleeve identifies the negative terminal in a polarized component.
In some literature, the terms "anode" and "cathode" are used in place of negative electrode and positive electrode. Using anode and cathode to describe the electrodes in supercapacitors (and also rechargeable batteries including lithium ion batteries) can lead to confusion, because the polarity changes depending on whether a component is considered as a generator or as a consumer of current. In electrochemistry, cathode and anode are related to reduction and oxidation reactions, respectively. However, in supercapacitors based on electric double layer capacitance, there is no oxidation and/or reduction reactions on any of the two electrodes. Therefore, the concepts of cathode and anode do not apply.
Comparison of selected commercial supercapacitors
The range of electrodes and electrolytes available yields a variety of components suitable for diverse applications. The development of low-ohmic electrolyte systems, in combination with electrodes with high pseudocapacitance, enable many more technical solutions.The following table shows differences among capacitors of various manufacturers in capacitance range, cell voltage, internal resistance (ESR, DC or AC value) and volumetric and gravimetric specific energy.
In the table, ESR refers to the component with the largest capacitance value of the respective manufacturer. Roughly, they divide supercapacitors into two groups. The first group offers greater ESR values of about 20 milliohms and relatively small capacitance of 0.1 to 470 F. These are "double-layer capacitors" for memory back-up or similar applications. The second group offers 100 to 10,000 F with a significantly lower ESR value under 1 milliohm. These components are suitable for power applications. A correlation of some supercapacitor series of different manufacturers to the various construction features is provided in Pandolfo and Hollenkamp.
| Manufacturer | Series name |
Capacitance range (F) |
Cell voltage (V) |
Volu-metric specific energy (Wh/dm3) |
Gravi-metric specific energy (Wh/kg) |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APowerCap | APowerCap | 4...550 | 2.7 | – | ≤4.5 | – |
| AVX | BestCap | 0.05...0.56 | 3.6 | ≤0.13 | – | Modules up to 20 V |
| Cap-XX | Cap-XX | 0.17...2.4 | 2.5 | ≤2.2 | - | – |
| CDE | Ultra-capacitor | 0.1...1.0 | 3.6 | - | - | – |
| Cooper | PowerStor | 0.22...3000 | 2.5/2.7 | ¬ | – | Modules up to 62 V |
| Elna | DYNACAP POWERCAP |
0.047...1500 | 2.5/3.6 | - | – | – |
| Evans | Capattery | 0.001...10 | 5.5...125 | – | – | Hybrid capacitors |
| FastCAP Systems | EEx | 340-460 | 1-3 | ≤10.5 | – | – |
| Green Tech | Super Capacitor | 2...600 | 2.7/2.8 | - | - | Modules up to 64 V |
| Illinois | Super-capacitor | 0.3800 | 2.3/2.7 | ≤8.6 | ≤6.6 | – |
| Ioxus | Ultra-capacitor | 100...3000 | 2.7 | ≤8.7 | ≤6.4 | Modules up to 130 V |
| JSR Micro | Ultimo | 1100...3300 | 3.8 | ≤20 | ≤12 | Li-Ion-capacitors |
| Korchip | STARCAP | 0.02...400 | 2.5/2.7 | ≤7.0 | ≤6.1 | - |
| LS Mtron | Ultra-capacitor | 100...3400 | 2.7/2.8 | - | - | Modules up to 130 V |
| Maxwell | Ultracapacitor | 1...3400 | 2.2/2.8 | - | ≤6.0 | Modules up to 160 V |
| Murata | EDLC | 0.22...1.0 | 4.2/5.5 | ≤2.7 | ≤3.1 | 2 cells in series |
| NEC Tokin | Super-capacitor | 0.047...200 | 2.7/11 | – | – | – |
| Nesscap | Ultra-capacitor | 3...50 50...300 |
2.7 2.3 |
≤7.1 ≤12.9 |
≤4.5 ≤8.7 |
Modules up to 125 V |
| Nichicon | EVerCAP | 1.0...6000 | 2.5/2.7 | - | - | - |
| NCC, ECC | DLCCAP | 350...2300 | 2.5 | - | - | - |
| Panasonic | Goldcap | 0.1...70 | 2.3/2.5 | - | - | Modules up to 15 V |
| Samwha | Green-Cap ESD-SCAP |
3...7500 | 2.5/2.7 | ≤7.6 | ≤7.0 | - |
| Sech SA | C-Capacitor | 330...3200 | 3.0 | <8 .0="" span=""> | Module up to 144V, Storage System up to 12MW | |
| Skeleton | SkelCap | 250...4500 | 2.85 | ≤14.1 | ≤10.1 | Modules up to 350 V |
| SPS | Ultra-capacitor | 0.5...5000 | 2.5/2.7 | - | ≤6.5 | Modules up to 500 V |
| Taiyo Yuden | PAS Capacitor LIC Capacitor |
0.5...20 0.5...270 |
2.5/3.0 3.8 |
– – |
– – |
Pseudocapacitors Li-Ion-capacitors |
| VinaTech | Hy-Cap | 1.0...500 | 2.3/3.0 | ≤8.7 | ≤6.3 | – |
| Vishay | ENYCAP | 4...15 | 1.4 | - | - | Modules up to 8.4 V |
| WIMA | SuperCap | 100...3000 | 2.5 | - | - | Modules up to 28 V |
| YEC | Kapton capacitor | 0.5...400 | 2.7 | - | - | – |
| Yunasko | Ultra-capacitor | 480...1700 | 2.7 | - | - | Modules up to 48 V |
In commercial double-layer capacitors, or, more specifically, EDLCs in which energy storage is predominantly achieved by double-layer capacitance, energy is stored by forming an electrical double layer of electrolyte ions on the surface of conductive electrodes. Since EDLCs are not limited by the electrochemical charge transfer kinetics of batteries, they can charge and discharge at a much higher rate, with lifetimes of more than 1 million cycles. The EDLC energy density is determined by operating voltage and the specific capacitance (farad/gram or farad/cm3) of the electrode/electrolyte system. The specific capacitance is related to the Specific Surface Area (SSA) accessible by the electrolyte, its interfacial double-layer capacitance, and the electrode material density.
Commercial EDLCs are based on two symmetric electrodes impregnated with electrolytes comprising tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate salts in organic solvents. Current EDLCs containing organic electrolytes operate at 2.7 V and reach energy densities around 5-8 Wh/kg and 7 to 10 Wh/l. The specific capacitance is related to the specific surface area (SSA) accessible by the electrolyte, its interfacial double-layer capacitance, and the electrode material density. Graphene-based platelets with mesoporous spacer material is a promising structure for increasing the SSA of the electrolyte.
Standards
Classification of supercapacitors into classes regarding to IEC 62391-1, IEC 62567and BS EN 61881-3 standards
Supercapacitors vary sufficiently that they are rarely interchangeable, especially those with higher specific energy. Applications range from low to high peak currents, requiring standardized test protocols.
Test specifications and parameter requirements are specified in the generic specification
The standard defines four application classes, according to discharge current levels:
- Memory backup
- Energy storage, mainly used for driving motors require a short time operation,
- Power, higher power demand for a long time operation,
- Instantaneous power, for applications that requires relatively high current units or peak currents ranging up to several hundreds of amperes even with a short operating time
- IEC 62391–2, Fixed electric double-layer capacitors for use in electronic equipment - Blank detail specification - Electric double-layer capacitors for power application
- IEC 62576, Electric double-layer capacitors for use in hybrid electric vehicles. Test methods for electrical characteristics
- BS/EN 61881-3, Railway applications. Rolling stock equipment. Capacitors for power electronics. Electric double-layer capacitors
Applications
Supercapacitors do not support AC applications.Supercapacitors have advantages in applications where a large amount of power is needed for a relatively short time, where a very high number of charge/discharge cycles or a longer lifetime is required. Typical applications range from milliamp currents or milliwatts of power for up to a few minutes to several amps current or several hundred kilowatts power for much shorter periods.
The time t a supercapacitor can deliver a constant current I can be calculated as:
If the application needs a constant power P for a certain time t this can be calculated as:
General
Consumer electronics
In applications with fluctuating loads, such as laptop computers, PDA's, GPS, portable media players, hand-held devices, and photovoltaic systems, supercapacitors can stabilize the power supply.Supercapacitors deliver power for photographic flashes in digital cameras and for LED life flashlights that can be charged in, e.g., 90 seconds.
As of 2013, portable speakers powered by supercapacitors were offered to the market.
Tools
A cordless electric screwdriver with supercapacitors for energy storage has about half the run time of a comparable battery model, but can be fully charged in 90 seconds. It retains 85% of its charge after three months left idle.Grid power buffer
A group of EVs and HEVs during their charging process draw very high current for a short duration of time which creates power pulsation on the grid. Power pulsation not only reduces the efficiency of the grid and cause voltage drop in the common coupling bus, but it can cause considerable frequency fluctuation in the entire system. To overcome this problem, supercapacitors can be implemented as an interface between the charging station and the grid to buffer the grid from the high pulse power drawn from the charging station.Low-power equipment power buffer
Supercapacitors provide backup or emergency shutdown power to low-power equipment such as RAM, SRAM, micro-controllers and PC Cards. They are the sole power source for low energy applications such as automated meter reading (AMR) equipment or for event notification in industrial electronics.Supercapacitors buffer power to and from rechargeable batteries, mitigating the effects of short power interruptions and high current peaks. Batteries kick in only during extended interruptions, e.g., if the mains power or a fuel cell fails, which lengthens battery life.
Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), where supercapacitors have replaced much larger banks of electrolytic capacitors. This combination reduces the cost per cycle, saves on replacement and maintenance costs, enables the battery to be downsized and extends battery life. A disadvantage is the need for a special circuit to reconcile the differing behaviors.
Rotor with wind turbine pitch system
Supercapacitors provide backup power for actuators in wind turbine pitch systems, so that blade pitch can be adjusted even if the main supply fails.
Voltage stabilizer
Supercapacitors can stabilize voltage for powerlines. Wind and photovoltaic systems exhibit fluctuating supply evoked by gusting or clouds that supercapacitors can buffer within milliseconds. This helps stabilize grid voltage and frequency, balance supply and demand of power and manage real or reactive power.Energy harvesting
Supercapacitors are suitable temporary energy storage devices for energy harvesting systems. In energy harvesting systems, the energy is collected from the ambient or renewable sources, e.g. mechanical movement, light or electromagnetic fields, and converted to electrical energy in an energy storage device. For example, it was demonstrated that energy collected from RF (radio frequency) fields (using an RF antenna as an appropriate rectifier circuit) can be stored to a printed supercapacitor. The harvested energy was then used to power an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) circuit for over 10 hours.Incorporation into batteries
The UltraBattery is a hybrid rechargeable lead-acid battery and a supercapacitor invented by Australia's national science organisation CSIRO. Its cell construction contains a standard lead-acid battery positive electrode, standard sulphuric acid electrolyte and a specially prepared negative carbon-based electrode that store electrical energy with double-layer capacitance. The presence of the supercapacitor electrode alters the chemistry of the battery and affords it significant protection from sulfation in high rate partial state if charge use, which is the typical failure mode of valve regulated lead-acid cells used this way. The resulting cell performs with characteristics beyond either a lead-acid cell or a supercapacitor, with charge and discharge rates, cycle life, efficiency and performance all enhanced. UltraBattery has been installed in kW and MW scale applications in Australia, Japan and the U.S.A. in frequency regulation, solar smoothing and shifting, wind smoothing and other applications.Street lights
Street light combining a solar cell power source with LED lamps and supercapacitors for energy storage
Sado City, in Japan's Niigata Prefecture, has street lights that combine a stand-alone power source with solar cells and LEDs. Supercapacitors store the solar energy and supply 2 LED lamps, providing 15 W power consumption overnight. The supercapacitors can last more than 10 years and offer stable performance under various weather conditions, including temperatures from +40 to below -20 °C.
Medical
Supercapacitors are used in defibrillators where they can deliver 500 joules to shock the heart back into sinus rhythm.Transport
Aviation
In 2005, aerospace systems and controls company Diehl Luftfahrt Elektronik GmbH chose supercapacitors to power emergency actuators for doors and evacuation slides used in airliners, including the Airbus 380.Military
Supercapacitors' low internal resistance supports applications that require short-term high currents. Among the earliest uses were motor startup (cold engine starts, particularly with diesels) for large engines in tanks and submarines. Supercapacitors buffer the battery, handling short current peaks, reducing cycling and extending battery life.Further military applications that require high specific power are phased array radar antennae, laser power supplies, military radio communications, avionics displays and instrumentation, backup power for airbag deployment and GPS-guided missiles and projectiles.
Automotive
Toyota's Yaris Hybrid-R concept car uses a supercapacitor to provide bursts of power. PSA Peugeot Citroën has started using supercapacitors as part of its stop-start fuel-saving system, which permits faster initial acceleration. Mazda's i-ELOOP system stores energy in a supercapacitor during deceleration and uses it to power on-board electrical systems while the engine is stopped by the stop-start system.Bus/tram
Maxwell Technologies, an American supercapacitor-maker, claimed that more than 20,000 hybrid buses use the devices to increase acceleration, particularly in China. Guangzhou, In 2014 China began using trams powered with supercapacitors that are recharged in 30 seconds by a device positioned between the rails, storing power to run the tram for up to 4 km — more than enough to reach the next stop, where the cycle can be repeated.Energy recovery
A primary challenge of all transport is reducing energy consumption and reducing CO2 emissions. Recovery of braking energy (recuperation or regeneration) helps with both. This requires components that can quickly store and release energy over long times with a high cycle rate. Supercapacitors fulfill these requirements and are therefore used in a lot of applications in all kinds of transportation.
Railway
Green Cargo operates TRAXX locomotives from Bombardier Transportation
Supercapacitors can be used to supplement batteries in starter systems in diesel railroad locomotives with diesel-electric transmission. The capacitors capture the braking energy of a full stop and deliver the peak current for starting the diesel engine and acceleration of the train and ensures the stabilization of catenary voltage. Depending on the driving mode up to 30% energy saving is possible by recovery of braking energy. Low maintenance and environmentally friendly materials encouraged the choice of supercapacitors.
Cranes, forklifts and tractors
Container yard with rubber tyre gantry crane
Mobile hybrid diesel-electric rubber tyred gantry cranes move and stack containers within a terminal. Lifting the boxes requires large amounts of energy. Some of the energy could be recaptured while lowering the load resulting in improved efficiency.
A triple hybrid forklift truck uses fuel cells and batteries as primary energy storage and supercapacitors to buffer power peaks by storing braking energy. They provide the fork lift with peak power over 30 kW. The triple-hybrid system offers over 50% energy savings compared with diesel or fuel-cell systems.
Supercapacitor-powered terminal tractors transport containers to warehouses. They provide an economical, quiet and pollution-free alternative to diesel terminal tractors.
Light-rails and trams
Supercapacitors make it possible not only to reduce energy but to replace overhead lines in historical city areas, so preserving the city's architectural heritage. This approach may allow many new LRV city lines to replace overhead wires that are too expensive to fully route.
Light rail vehicle in Mannheim
In 2003 Mannheim adopted a prototype light-rail vehicle (LRV) using the MITRAC Energy Saver system from Bombardier Transportation to store mechanical braking energy with a roof-mounted supercapacitor unit. It contains several units each made of 192 capacitors with 2700 F /2.7 V interconnected in three parallel lines. This circuit results in a 518 V system with an energy content of 1.5 kWh. For acceleration when starting this "on-board-system" can provide the LRV with 600 kW and can drive the vehicle up to 1 km without catenary supply integrating the LRV into the urban environment by driving without catenary lines. Compared to conventional LRVs or Metro vehicles that return energy into the grid, onboard energy storage saves up to 30% and reduces peak grid demand by up to 50%.
Supercapacitors are used to power the Paris T3 tram line on sections without catenary overhead wires and to recover energy during braking.
In 2009 supercapacitors enabled LRV's to operate in the historical city area of Heidelberg without catenary overhead wires preserving the city's architectural heritage. The SC equipment cost an additional €270,000 per vehicle, which was expected to be recovered over the first 15 years of operation. The supercapacitors are charged at stop-over stations when the vehicle is at a scheduled stop. This approach may allow many LRV city lines to serve catenary overhead wires that are too expensive to fully route installation. In April 2011 German regional transport operator Rhein-Neckar, responsible for Heidelberg, ordered a further 11 units.
In 2009, Alstom and RATP equipped a Citadis tram with an experimental energy recovery system called "STEEM". The system is fitted with 48 roof-mounted supercapacitors to store braking energy provides tramways with a high level of energy autonomy by enabling them to run without catenary power on parts of its route, recharging while traveling on powered stop-over stations. During the tests, which took place between the Porte d’Italie and Porte de Choisy stops on line T3 of the tramway network in Paris, the tramset used an average of approximately 16% less energy.
A supercapacitor-equipped tram on the Rio de Janeiro Light Rail
In 2012 tram operator Geneva Public Transport began tests of an LRV equipped with a prototype roof-mounted supercapacitor unit to recover braking energy.
Siemens is delivering supercapacitor-enhanced light-rail transport systems that include mobile storage.
Hong Kong's South Island metro line is to be equipped with two 2 MW energy storage units that are expected to reduce energy consumption by 10%.
In August 2012 the CSR Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive corporation of China presented a prototype two-car light metro train equipped with a roof-mounted supercapacitor unit. The train can travel up 2 km without wires, recharging in 30 seconds at stations via a ground mounted pickup. The supplier claimed the trains could be used in 100 small and medium-sized Chinese cities. Seven trams (street cars) powered by supercapacitors were scheduled to go into operation in 2014 in Guangzhou, China. The supercapacitors are recharged in 30 seconds by a device positioned between the rails. That powers the tram for up to 4 kilometres (2.5 mi). As of 2017, Zhuzhou's supercapacitor vehicles are also used on the new Nanjing streetcar system, and are undergoing trials in Wuhan.
In 2012, in Lyon (France), the SYTRAL (Lyon public transportation administration) started experiments of a "way side regeneration" system built by Adetel Group which has developed its own energy saver named ″NeoGreen″ for LRV, LRT and metros.
In 2015, Alstom announced SRS, an energy storage system that charges supercapacitors on board a tram by means of ground-level conductor rails located at tram stops. This allows trams to operate without overhead lines for short distances. The system has been touted as an alternative to the company's ground-level power supply (APS) system, or can be used in conjunction with it, as in the case of the VLT network in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, which opened in 2016.
Buses
MAN Ultracapbus in Nuremberg, Germany
The first hybrid bus with supercapacitors in Europe came in 2001 in Nuremberg, Germany. It was MAN's so-called "Ultracapbus", and was tested in real operation in 2001/2002. The test vehicle was equipped with a diesel-electric drive in combination with supercapacitors. The system was supplied with 8 Ultracap modules of 80 V, each containing 36 components. The system worked with 640 V and could be charged/discharged at 400 A. Its energy content was 0.4 kWh with a weight of 400 kg.
The supercapacitors recaptured braking energy and delivered starting energy. Fuel consumption was reduced by 10 to 15% compared to conventional diesel vehicles. Other advantages included reduction of CO
2 emissions, quiet and emissions-free engine starts, lower vibration and reduced maintenance costs.
Electric bus at EXPO 2010 in Shanghai (Capabus) recharging at the bus stop
As of 2002 in Luzern, Switzerland an electric bus fleet called TOHYCO-Rider was tested. The supercapacitors could be recharged via an inductive contactless high-speed power charger after every transportation cycle, within 3 to 4 minutes.
In early 2005 Shanghai tested a new form of electric bus called capabus that runs without powerlines (catenary free operation) using large onboard supercapacitors that partially recharge whenever the bus is at a stop (under so-called electric umbrellas), and fully charge in the terminus. In 2006, two commercial bus routes began to use the capabuses; one of them is route 11 in Shanghai. It was estimated that the supercapacitor bus was cheaper than a lithium-ion battery bus, and one of its buses had one-tenth the energy cost of a diesel bus with lifetime fuel savings of $200,000.
A hybrid electric bus called tribrid was unveiled in 2008 by the University of Glamorgan, Wales, for use as student transport. It is powered by hydrogen fuel or solar cells, batteries and ultracapacitors.
Motor racing
World champion Sebastian Vettel in Malaysia 2010
Toyota TS030 Hybrid at 2012 24 Hours of Le Mans motor race
The FIA, a governing body for motor racing events, proposed in the Power-Train Regulation Framework for Formula 1 version 1.3 of 23 May 2007 that a new set of power train regulations be issued that includes a hybrid drive of up to 200 kW input and output power using "superbatteries" made with batteries and supercapacitors connected in parallel (KERS). About 20% tank-to-wheel efficiency could be reached using the KERS system.
The Toyota TS030 Hybrid LMP1 car, a racing car developed under Le Mans Prototype rules, uses a hybrid drivetrain with supercapacitors. In the 2012 24 Hours of Le Mans race a TS030 qualified with a fastest lap only 1.055 seconds slower (3:24.842 versus 3:23.787) than the fastest car, an Audi R18 e-tron quattro with flywheel energy storage. The supercapacitor and flywheel components, whose rapid charge-discharge capabilities help in both braking and acceleration, made the Audi and Toyota hybrids the fastest cars in the race. In the 2012 Le Mans race the two competing TS030s, one of which was in the lead for part of the race, both retired for reasons unrelated to the supercapacitors. The TS030 won three of the 8 races in the 2012 FIA World Endurance Championship season. In 2014 the Toyota TS040 Hybrid used a supercapacitor to add 480 horsepower from two electric motors.
Hybrid electric vehicles
Mazda2 (since 2010)
Supercapacitor/battery combinations in electric vehicles (EV) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) are well investigated. A 20 to 60% fuel reduction has been claimed by recovering brake energy in EVs or HEVs. The ability of supercapacitors to charge much faster than batteries, their stable electrical properties, broader temperature range and longer lifetime are suitable, but weight, volume and especially cost mitigate those advantages.
Supercapacitors lower specific energy makes them unsuitable for use as a stand-alone energy source for long distance driving. The fuel economy improvement between a capacitor and a battery solution is about 20% and is available only for shorter trips. For long distance driving the advantage decreases to 6%. Vehicles combining capacitors and batteries run only in experimental vehicles.
As of 2013 all automotive manufacturers of EV or HEVs have developed prototypes that uses supercapacitors instead of batteries to store braking energy in order to improve driveline efficiency. The Mazda 6 is the only production car that uses supercapacitors to recover braking energy. Branded as i-eloop, the regenerative braking is claimed to reduce fuel consumption by about 10%.
Russian Yo-cars Ё-mobile series was a concept and crossover hybrid vehicle working with a gasoline driven rotary vane type and an electric generator for driving the traction motors. A supercapacitor with relatively low capacitance recovers brake energy to power the electric motor when accelerating from a stop.
Toyota's Yaris Hybrid-R concept car uses a supercapacitor to provide quick bursts of power.
PSA Peugeot Citroën fit supercapacitors to some of its cars as part of its stop-start fuel-saving system, as this permits faster start-ups when the traffic lights turn green.
Gondolas
Aerial lift in Zell am See, Austria
In Zell am See, Austria, an aerial lift connects the city with Schmittenhöhe mountain. The gondolas sometimes run 24 hours per day, using electricity for lights, door opening and communication. The only available time for recharging batteries at the stations is during the brief intervals of guest loading and unloading, which is too short to recharge batteries. Supercapacitors offer a fast charge, higher number of cycles and longer life time than batteries.
Emirates Air Line (cable car), also known as the Thames cable car, is a 1-kilometre (0.62 mi) gondola line that crosses the Thames from the Greenwich Peninsula to the Royal Docks. The cabins are equipped with a modern infotainment system, which is powered by supercapacitors.
Developments
As of 2013 commercially available lithium-ion supercapacitors offered the highest gravimetric specific energy to date, reaching 15 Wh/kg (54 kJ/kg). Research focuses on improving specific energy, reducing internal resistance, expanding temperature range, increasing lifetimes and reducing costs. Projects include tailored-pore-size electrodes, pseudocapacitive coating or doping materials and improved electrolytes.| Development | Date | Specific energy | Specific power | Cycles | Capaci-tance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene sheets compressed by capillary compression of a volatile liquid | 2013 | 60 Wh/L | Subnanometer scale electrolyte integration created a continuous ion transport network. | |||
| Vertically aligned carbon nanotubes electrodes | 2007 2009 2013 |
13.50 Wh/kg | 37.12 W/g | 300,000 | First realization | |
| Curved graphene sheets | 2010 | 85.6 Wh/kg | 550 F/g | Single-layers of curved graphene sheets that do not restack face-to-face, forming mesopores that are accessible to and wettable by environmentally friendly ionic electrolytes at a voltage up to 4 V. | ||
| KOH restructured graphite oxide | 2011 | 85 Wh/kg | >10,000 | 200 F/g | Potassium hydroxide restructured the carbon to make a three dimensional porous network | |
| Activated graphene-based carbons as supercapacitor electrodes with macro- and mesopores | 2013 | 74 Wh/kg | Three-dimensional pore structures in graphene-derived carbons in which mesopores are integrated into macroporous scaffolds with a surface area of 3290 m2/g | |||
| Conjugated microporous polymer | 2011 | 53 Wh/kg | 10,000 | Aza-fused π-conjugated microporous framework | ||
| SWNT composite electrode | 2011 | 990 W/kg | A tailored meso-macro pore structure held more electrolyte, ensuring facile ion transport | |||
| Nickel hydroxide nanoflake on CNT composite electrode | 2012 | 50.6 Wh/kg | 3300 F/g | Asymmetric supercapacitor using the Ni(OH)2/CNT/NF electrode as the anode assembled with an activated carbon (AC) cathode achieving a cell voltage of 1.8 V | ||
| Battery-electrode nanohybrid | 2012 | 40 Wh/l | 7.5 W/l | 10,000 | Li 4Ti 5O 12 (LTO) deposited on carbon nanofibres (CNF) anode and an activated carbon cathode | |
| Nickel cobaltite deposited on mesoporous carbon aerogel | 2012 | 53 Wh/kg | 2.25 W/kg | 1700 F/g | Nickel cobaltite, a low cost and an environmentally friendly supercapacitive material | |
| Manganese dioxide intercalated nanoflakes | 2013 | 110 Wh/kg | 1000 F/g | Wet electrochemical process intercalated Na(+) ions into MnO 2 interlayers. The nanoflake electrodes exhibit faster ionic diffusion with enhanced redox peaks. | ||
| 3D porous graphene electrode[193] | 2013 | 98 Wh/kg | 231 F/g | Wrinkled single layer graphene sheets a few nanometers in size, with at least some covalent bonds. | ||
| Graphene-based planar micro-supercapacitors for on-chip energy storage | 2013 | 2.42 Wh/l | On chip line filtering | |||
| Nanosheet capacitors | 2014 | 27.5 μF cm−2 | Electrodes: Ru0.95O20.2– Dielectric: Ca2Nb3O10–. Room-temperature solution-based manufacturing processes. Total thickness less than 30 nm. | |||
| LSG/manganese dioxide | 2015 | 42 Wh/l | 10 kW/l | 10,000 | Three-dimensional laser-scribed graphene (LSG) structure for conductivity, porosity and surface area. Electrodes are around 15 microns thick. | |
| Laser-induced graphene/solid-state electrolyte | 2015 | 0.02 mA/cm2 | 9 mF/cm2 | Survives repeated flexing. | ||
| Tungsten trioxide (WO3) nano-wires and two-dimensional enveloped by shells of a transition-metal dichalcogenide, tungsten disulfide (WS2) | 2016 | ~100 Wh/l | 1 kW/l | 30,000 | 2D shells surrounding nanowires |
Market
As of 2016 worldwide sales of supercapacitors is about US$400 million.The market for batteries (estimated by Frost & Sullivan) grew from US$47.5 billion, (76.4% or US$36.3 billion of which was rechargeable batteries) to US$95 billion. The market for supercapacitors is still a small niche market that is not keeping pace with its larger rival.
In 2016, IDTechEx forecast sales to grow from $240 million to $2 billion by 2026, an annual increase of about 24%.
Supercapacitor costs in 2006 were US$0.01 per farad or US$2.85 per kilojoule, moving in 2008 below US$0.01 per farad, and were expected to drop further in the medium term.