The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are disagreements about the aims of education and the extent to which education differs from indoctrination by fostering critical thinking. These disagreements impact how to identify, measure, and enhance various forms of education. Essentially, education socializes children into society by instilling cultural values and norms, equipping them with the skills necessary to become productive members of society. In doing so, it stimulates economic growth and raises awareness of local and global problems. Organized institutions play a significant role in education. For instance, governments establish education policies to determine the timing of school classes, the curriculum, and attendance requirements. International organizations, such as UNESCO, have been influential in promoting primary education for all children.
Many factors influence the success of education. Psychological factors include motivation, intelligence, and personality. Social factors, such as socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and gender, are often associated with discrimination. Other factors encompass access to educational technology, teacher quality, and parental involvement.
The primary academic field examining education is known as education studies. It delves into the nature of education, its objectives, impacts, and methods for enhancement. Education studies encompasses various subfields, including philosophy, psychology, sociology, and economics of education. Additionally, it explores topics such as comparative education, pedagogy, and the history of education.
In prehistory, education primarily occurred informally through oral communication and imitation. With the emergence of ancient civilizations, the invention of writing led to an expansion of knowledge, prompting a transition from informal to formal education. Initially, formal education was largely accessible to elites and religious groups. The advent of the printing press in the 15th century facilitated widespread access to books, thus increasing general literacy. In the 18th and 19th centuries, public education gained significance, paving the way for the global movement to provide primary education to all, free of charge, and compulsory up to a certain age. Presently, over 90% of primary-school-age children worldwide attend primary school.
Definitions
The term "education" originates from the Latin words educare, meaning "to bring up," and educere, meaning "to bring forth." The definition of education has been explored by theorists from various fields. Many agree that education is a purposeful activity aimed at achieving goals like the transmission of knowledge, skills, and character traits. However, extensive debate surrounds its precise nature beyond these general features. One approach views education as a process occurring during events such as schooling, teaching, and learning. Another perspective perceives education not as a process but as the mental states and dispositions of educated individuals resulting from this process. Furthermore, the term may also refer to the academic field that studies the methods, processes, and social institutions involved in teaching and learning. Having a clear understanding of the term is crucial when attempting to identify educational phenomena, measure educational success, and improve educational practices.
Some theorists provide precise definitions by identifying specific features exclusive to all forms of education. Education theorist R. S. Peters, for instance, outlines three essential features of education, including imparting knowledge and understanding to the student, ensuring the process is beneficial, and conducting it in a morally appropriate manner. While such precise definitions often characterize the most typical forms of education effectively, they face criticism because less common types of education may occasionally fall outside their parameters. Dealing with counterexamples not covered by precise definitions can be challenging, which is why some theorists prefer offering less exact definitions based on family resemblance instead. This approach suggests that all forms of education are similar to each other but need not share a set of essential features common to all. Some education theorists, such as Keira Sewell and Stephen Newman, argue that the term "education" is context-dependent.
Evaluative or thick conceptions of education assert that it is inherent in the nature of education to lead to some form of improvement. They contrast with thin conceptions, which offer a value-neutral explanation. Some theorists provide a descriptive conception of education by observing how the term is commonly used in ordinary language. Prescriptive conceptions, on the other hand, define what constitutes good education or how education should be practiced. Many thick and prescriptive conceptions view education as an endeavor that strives to achieve specific objectives, which may encompass acquiring knowledge, learning to think rationally, and cultivating character traits such as kindness and honesty.
Various scholars emphasize the importance of critical thinking in distinguishing education from indoctrination. They argue that indoctrination focuses solely on instilling beliefs in students, regardless of their rationality; whereas education also encourages the rational ability to critically examine and question those beliefs. However, it is not universally accepted that these two phenomena can be clearly distinguished, as some forms of indoctrination may be necessary in the early stages of education when the child's mind is not yet fully developed. This is particularly relevant in cases where young children must learn certain things without comprehending the underlying reasons, such as specific safety rules and hygiene practices.
Education can be characterized from both the teacher's and the student's perspectives. Teacher-centered definitions emphasize the perspective and role of the teacher in transmitting knowledge and skills in a morally appropriate manner. On the other hand, student-centered definitions analyze education based on the student's involvement in the learning process, suggesting that this process transforms and enriches their subsequent experiences. It's also possible to consider definitions that incorporate both perspectives. In this approach, education is seen as a process of shared experience, involving the discovery of a common world and the collaborative solving of problems.
Types
There are several classifications of education. One classification depends on the institutional framework, distinguishing between formal, non-formal, and informal education. Another classification involves different levels of education based on factors such as the student's age and the complexity of the content. Further categories focus on the topic, teaching method, medium used, and funding.
Formal, non-formal, and informal
The most common division is between formal, non-formal, and informal education. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, typically with a chronological and hierarchical order. The modern schooling system organizes classes based on the student's age and progress, ranging from primary school to university. Formal education is usually overseen and regulated by the government and often mandated up to a certain age.
Non-formal and informal education occur outside the formal schooling system, with non-formal education serving as a middle ground. Like formal education, non-formal education is organized, systematic, and pursued with a clear purpose, as seen in activities such as tutoring, fitness classes, and participation in the scouting movement. Informal education, on the other hand, occurs in an unsystematic manner through daily experiences and exposure to the environment. Unlike formal and non-formal education, there is typically no designated authority figure responsible for teaching. Informal education unfolds in various settings and situations throughout one's life, often spontaneously, such as children learning their first language from their parents or individuals mastering cooking skills by preparing a dish together.
Some theorists differentiate between the three types based on the learning environment: formal education occurs within schools, non-formal education takes place in settings not regularly frequented, such as museums, and informal education unfolds in the context of everyday routines. Additionally, there are disparities in the source of motivation. Formal education tends to be propelled by extrinsic motivation, driven by external rewards. Conversely, in non-formal and informal education, intrinsic motivation, stemming from the enjoyment of the learning process, typically prevails. While the differentiation among the three types is generally clear, certain forms of education may not neatly fit into a single category.
In primitive cultures, education predominantly occurred informally, with little distinction between educational activities and other daily endeavors. Instead, the entire environment served as a classroom, and adults commonly assumed the role of educators. However, informal education often proves insufficient for imparting large quantities of knowledge. To address this limitation, formal educational settings and trained instructors are typically necessary. This necessity contributed to the increasing significance of formal education throughout history. Over time, formal education led to a shift towards more abstract learning experiences and topics, distancing itself from daily life. There was a greater emphasis on understanding general principles and concepts rather than simply observing and imitating specific behaviors.
Levels

Types of education are often categorized into different levels or stages. One influential framework is the International Standard Classification of Education, maintained by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). This classification encompasses both formal and non-formal education and distinguishes levels based on factors such as the student's age, the duration of learning, and the complexity of the content covered. Additional criteria include entry requirements, teacher qualifications, and the intended outcome of successful completion. The levels are grouped into early childhood education (level 0), primary education (level 1), secondary education (levels 2–3), post-secondary non-tertiary education (level 4), and tertiary education (levels 5–8).
Early childhood education, also referred to as preschool education or nursery education, encompasses the period from birth until the commencement of primary school. It is designed to facilitate holistic child development, addressing physical, mental, and social aspects. Early childhood education is pivotal in fostering socialization and personality development, while also imparting fundamental skills in communication, learning, and problem-solving. Its overarching goal is to prepare children for the transition to primary education. While preschool education is typically optional, in certain countries such as Brazil, it is mandatory starting from the age of four.

Primary (or elementary) education usually begins between the ages of five and seven and spans four to seven years. It has no additional entry requirements and aims to impart fundamental skills in reading, writing, and mathematics. Additionally, it provides essential knowledge in subjects such as history, geography, the sciences, music, and art. Another objective is to facilitate personal development. Presently, primary education is compulsory in nearly all nations, with over 90% of primary-school-age children worldwide attending such schools.
Secondary education succeeds primary education and typically spans the ages of 12 to 18 years. It is normally divided into lower secondary education (such as middle school or junior high school) and upper secondary education (like high school, senior high school, or college, depending on the country). Lower secondary education usually requires the completion of primary school as its entry prerequisite. It aims to expand and deepen learning outcomes, with a greater focus on subject-specific curricula, and teachers often specialize in one or a few specific subjects. One of its goals is to acquaint students with fundamental theoretical concepts across various subjects, laying a strong foundation for lifelong learning. In certain instances, it may also incorporate rudimentary forms of vocational training. Lower secondary education is compulsory in numerous countries across Central and East Asia, Europe, and the Americas. In some nations, it represents the final phase of compulsory education. However, mandatory lower secondary education is less common in Arab states, sub-Saharan Africa, and South and West Asia.

Upper secondary education typically commences around the age of 15, aiming to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge for employment or tertiary education. Completion of lower secondary education is normally a prerequisite. The curriculum encompasses a broader range of subjects, often affording students the opportunity to select from various options. Attainment of a formal qualification, such as a high school diploma, is frequently linked to successful completion of upper secondary education. Education beyond the secondary level may fall under the category of post-secondary non-tertiary education, which is akin to secondary education in complexity but places greater emphasis on vocational training to ready students for the workforce.

In some countries, tertiary education is synonymous with higher education, while in others, tertiary education encompasses a broader spectrum. Tertiary education builds upon the foundation laid in secondary education but delves deeper into specific fields or subjects. Its culmination results in an academic degree. Tertiary education comprises four levels: short-cycle tertiary, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral education. These levels often form a hierarchical structure, with the attainment of earlier levels serving as a prerequisite for higher ones. Short-cycle tertiary education concentrates on practical aspects, providing advanced vocational and professional training tailored to specialized professions. Bachelor's level education, also known as undergraduate education, is typically longer than short-cycle tertiary education. It is commonly offered by universities and culminates in an intermediary academic credential known as a bachelor's degree. Master's level education is more specialized than undergraduate education and often involves independent research, normally in the form of a master's thesis. Doctoral level education leads to an advanced research qualification, usually a doctor's degree, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). It usually involves the submission of a substantial academic work, such as a dissertation. More advanced levels include post-doctoral studies and habilitation.
Successful completion of formal education typically leads to certification, a prerequisite for advancing to higher levels of education and entering certain professions. Undetected cheating during exams, such as utilizing a cheat sheet, poses a threat to this system by potentially certifying unqualified students.
In most countries, primary and secondary education is provided free of charge. However, there are significant global disparities in the cost of tertiary education. Some countries, such as Sweden, Finland, Poland, and Mexico, offer tertiary education for free or at a low cost. Conversely, in nations like the United States and Singapore, tertiary education often comes with high tuition fees, leading students to rely on substantial loans to finance their studies. High education costs can pose a significant barrier for students in developing countries, as their families may struggle to cover school fees, purchase uniforms, and buy textbooks.
Others
The academic literature explores various types of education, including traditional and alternative approaches. Traditional education encompasses long-standing and conventional schooling methods, characterized by teacher-centered instruction within a structured school environment. Regulations govern various aspects, such as the curriculum and class schedules.

Alternative education serves as an umbrella term for schooling methods that diverge from the conventional traditional approach. These variances might encompass differences in the learning environment, curriculum content, or the dynamics of the teacher-student relationship. Characteristics of alternative schooling include voluntary enrollment, relatively modest class and school sizes, and customized instruction, fostering a more inclusive and emotionally supportive environment. This category encompasses various forms, such as charter schools and specialized programs catering to challenging or exceptionally talented students, alongside homeschooling and unschooling. Alternative education incorporates diverse educational philosophies, including Montessori schools, Waldorf education, Round Square schools, Escuela Nueva schools, free schools, and democratic schools. Alternative education encompasses indigenous education, which emphasizes the preservation and transmission of knowledge and skills rooted in indigenous heritage. This approach often employs traditional methods such as oral narration and storytelling. Other forms of alternative schooling include gurukul schools in India, madrasa schools in the Middle East, and yeshivas in Jewish tradition.
Some distinctions revolve around the recipients of education. Categories based on the age of the learner are childhood education, adolescent education, adult education, and elderly education. Categories based on the biological sex of students include single-sex education and mixed-sex education. Special education is tailored to meet the unique needs of students with disabilities, addressing various impairments on intellectual, social, communicative, and physical levels. Its goal is to overcome the challenges posed by these impairments, providing affected students with access to an appropriate educational structure. In the broadest sense, special education also encompasses education for intellectually gifted children, who require adjusted curricula to reach their fullest potential.
Classifications based on the teaching method include teacher-centered education, where the teacher plays a central role in imparting information to students, and student-centered education, where students take on a more active and responsible role in shaping classroom activities. In conscious education, learning and teaching occur with a clear purpose in mind. Unconscious education unfolds spontaneously without conscious planning or guidance. This may occur, in part, through the influence of teachers' and adults' personalities, which can indirectly impact the development of students' personalities. Evidence-based education employs scientific studies to determine the most effective educational methods. Its aim is to optimize the effectiveness of educational practices and policies by ensuring they are grounded in the best available empirical evidence. This encompasses evidence-based teaching, evidence-based learning, and school effectiveness research.
Autodidacticism, or self-education, occurs independently of teachers and institutions. Primarily observed in adult education, it offers the freedom to choose what and when to study, making it a potentially more fulfilling learning experience. However, the lack of structure and guidance may lead to aimless learning, while the absence of external feedback could result in autodidacts developing misconceptions and inaccurately assessing their learning progress. Autodidacticism is closely associated with lifelong education, which entails continuous learning throughout one's life.
Categories of education based on the subject encompass science education, language education, art education, religious education, physical education, and sex education. Special mediums such as radio or websites are utilized in distance education, including e-learning (use of computers), m-learning (use of mobile devices), and online education. Often, these take the form of open education, wherein courses and materials are accessible with minimal barriers, contrasting with traditional classroom or onsite education. However, not all forms of online education are open; for instance, some universities offer full online degree programs that are not part of open education initiatives.
State education, also known as public education, is funded and controlled by the government and available to the general public. It typically does not require tuition fees and is therefore a form of free education. In contrast, private education is funded and managed by private institutions. Private schools often have a more selective admission process and offer paid education by charging tuition fees. A more detailed classification focuses on the social institutions responsible for education, such as family, school, civil society, state, and church.
Compulsory education refers to education that individuals are legally mandated to receive, primarily affecting children who must attend school up to a certain age. This stands in contrast to voluntary education, which individuals pursue based on personal choice rather than legal obligation.
Role in society

Education serves various roles in society, spanning social, economic, and personal domains. Socially, education establishes and maintains a stable society by imparting fundamental skills necessary for interacting with the environment and fulfilling individual needs and aspirations. In contemporary society, these skills encompass speaking, reading, writing, arithmetic, and proficiency in information and communications technology. Additionally, education facilitates socialization by instilling awareness of dominant social and cultural norms, shaping appropriate behavior across diverse contexts. It fosters social cohesion, stability, and peace, fostering productive engagement in daily activities. While socialization occurs throughout life, early childhood education holds particular significance. Moreover, education plays a pivotal role in democracies by enhancing civic participation through voting and organizing, while also promoting equal opportunities for all.
On an economic level, individuals become productive members of society through education, acquiring the technical and analytical skills necessary for their professions, as well as for producing goods and providing services to others. In early societies, there was minimal specialization, with children typically learning a broad range of skills essential for community functioning. However, modern societies are increasingly complex, with many professions requiring specialized training alongside general education. Consequently, only a relatively small number of individuals master certain professions. Additionally, skills and tendencies acquired for societal functioning may sometimes conflict, with their value dependent on context. For instance, fostering curiosity and questioning established teachings promotes critical thinking and innovation, while at times, obedience to authority is necessary to maintain social stability.

By facilitating individuals' integration into society, education fosters economic growth and diminishes poverty. It enables workers to enhance their skills, thereby improving the quality of goods and services produced, which ultimately fosters prosperity and enhances competitiveness. Public education is widely regarded as a long-term investment that benefits society as a whole, with primary education showing particularly high rates of return. Additionally, besides bolstering economic prosperity, education contributes to technological and scientific advancements, reduces unemployment, and promotes social equity. Moreover, increased education is associated with lower birth rates, partly due to heightened awareness of family planning, expanded opportunities for women, and delayed marriage.
Education plays a pivotal role in equipping a country to adapt to changes and effectively confront new challenges. It raises awareness and contributes to addressing contemporary global issues, including climate change, sustainability, and the widening disparities between the rich and the poor. By instilling in students an understanding of how their lives and actions impact others, education can inspire individuals to strive towards realizing a more sustainable and equitable world. Thus, education not only serves to maintain societal norms but also acts as a catalyst for social development. This extends to evolving economic circumstances, where technological advancements, notably increased automation, impose new demands on the workforce that education can help meet. As circumstances evolve, skills and knowledge taught may become outdated, necessitating curriculum adjustments to include subjects like digital literacy, and promote proficiency in handling new technologies. Moreover, education can embrace innovative forms such as massive open online courses to prepare individuals for emerging challenges and opportunities.
On a more individual level, education fosters personal development, encompassing learning new skills, honing talents, nurturing creativity, enhancing self-knowledge, and refining problem-solving and decision-making abilities. Moreover, education contributes positively to health and well-being. Educated individuals are often better informed about health issues and adjust their behavior accordingly, benefit from stronger social support networks and coping strategies, and enjoy higher incomes, granting them access to superior healthcare services. The social significance of education is underscored by the annual International Day of Education on January 24, established by the United Nations, which designated 1970 as the International Education Year.
Role of institutions

Organized institutions play a pivotal role in multiple facets of education. Entities such as schools, universities, teacher training institutions, and ministries of education comprise the education sector. They interact not only with one another but also with various stakeholders, including parents, local communities, religious groups, non-governmental organizations, healthcare professionals, law enforcement agencies, media platforms, and political leaders. Numerous individuals are directly engaged in the education sector, such as students, teachers, school principals, as well as school nurses and curriculum developers.
Various aspects of formal education are regulated by the policies of governmental institutions. These policies determine at what age children need to attend school and at what times classes are held, as well as issues pertaining to the school environment, such as infrastructure. Regulations also cover the exact qualifications and requirements that teachers need to fulfill. An important aspect of education policy concerns the curriculum used for teaching at schools, colleges, and universities. A curriculum is a plan of instruction or a program of learning that guides students to achieve their educational goals. The topics are usually selected based on their importance and depend on the type of school. The goals of public school curricula are usually to offer a comprehensive and well-rounded education, while vocational training focuses more on specific practical skills within a field. The curricula also cover various aspects besides the topic to be discussed, such as the teaching method, the objectives to be reached, and the standards for assessing progress. By determining the curricula, governmental institutions have a strong impact on what knowledge and skills are transmitted to the students. Examples of governmental institutions include the Ministry of Education in India, the Department of Basic Education in South Africa, and the Secretariat of Public Education in Mexico.

International organizations also play a pivotal role in education. For example, UNESCO is an intergovernmental organization that promotes education through various means. One of its activities is advocating for education policies, such as the treaty Convention on the Rights of the Child, which declares education as a fundamental human right for all children and young people. The Education for All initiative aimed to provide basic education to all children, adolescents, and adults by 2015, later succeeded by the Sustainable Development Goals initiative, particularly goal 4. Related policies include the Convention against Discrimination in Education and the Futures of Education initiative.
Some influential organizations are non-governmental rather than intergovernmental. For instance, the International Association of Universities promotes collaboration and knowledge exchange among colleges and universities worldwide, while the International Baccalaureate offers international diploma programs. Institutions like the Erasmus Programme facilitate student exchanges between countries, while initiatives such as the Fulbright Program provide similar services for teachers.
Factors of educational success
Educational success, also referred to as student and academic achievement, pertains to the extent to which educational objectives are met, such as the acquisition of knowledge and skills by students. For practical purposes, it is often primarily measured in terms of official exam scores, but numerous additional indicators exist, including attendance rates, graduation rates, dropout rates, student attitudes, and post-school indicators such as later income and incarceration rates. Several factors influence educational achievement, such as psychological factors related to the individual student, and sociological factors associated with the student's social environment. Additional factors encompass access to educational technology, teacher quality, and parental involvement. Many of these factors overlap and mutually influence each other.
Psychological
On a psychological level, relevant factors include motivation, intelligence, and personality. Motivation is the internal force propelling people to engage in learning. Motivated students are more likely to interact with the content to be learned by participating in classroom activities like discussions, resulting in a deeper understanding of the subject. Motivation can also help students overcome difficulties and setbacks. An important distinction lies between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsically motivated students are driven by an interest in the subject and the learning experience itself. Extrinsically motivated students seek external rewards such as good grades and recognition from peers. Intrinsic motivation tends to be more beneficial, leading to increased creativity, engagement, and long-term commitment. Educational psychologists aim to discover methods to increase motivation, such as encouraging healthy competition among students while maintaining a balance of positive and negative feedback through praise and constructive criticism.
Intelligence significantly influences individuals' responses to education. It is a cognitive trait associated with the capacity to learn from experience, comprehend, and apply knowledge and skills to solve problems. Individuals with higher scores in intelligence metrics typically perform better academically and pursue higher levels of education. Intelligence is often closely associated with the concept of IQ, a standardized numerical measure assessing intelligence based on mathematical-logical and verbal abilities. However, it has been argued that intelligence encompasses various types beyond IQ. Psychologist Howard Gardner posited distinct forms of intelligence in domains such as mathematics, logic, spatial cognition, language, and music. Additional types of intelligence influence interpersonal and intrapersonal interactions. These intelligences are largely autonomous, meaning that an individual may excel in one type while performing less well in another.
According to proponents of learning style theory, the preferred method of acquiring knowledge and skills is another factor. They hold that students with an auditory learning style find it easy to comprehend spoken lectures and discussions, whereas visual learners benefit from information presented visually, such as in diagrams and videos. To facilitate efficient learning, it may be advantageous to incorporate a wide variety of learning modalities. Learning styles have been criticized for ambiguous empirical evidence of student benefits and unreliability of student learning style assessment by teachers.
The learner's personality may also influence educational achievement. For instance, characteristics such as conscientiousness and openness to experience, identified in the Big Five personality traits, are associated with academic success. Other mental factors include self-efficacy, self-esteem, and metacognitive abilities.
Sociological
Sociological factors center not on the psychological attributes of learners but on their environment and societal position. These factors encompass socioeconomic status, ethnicity, cultural background, and gender, drawing significant interest from researchers due to their association with inequality and discrimination. Consequently, they play a pivotal role in policy-making endeavors aimed at mitigating their impact.
Socioeconomic status is influenced by factors beyond just income, including financial security, social status, social class, and various attributes related to quality of life. Low socioeconomic status impacts educational success in several ways. It correlates with slower cognitive development in language and memory, as well as higher dropout rates. Families with limited financial means may struggle to meet their children's basic nutritional needs, hindering their development. Additionally, they may lack resources to invest in educational materials such as stimulating toys, books, and computers. Financial constraints may also prevent attendance at prestigious schools, leading to enrollment in institutions located in economically disadvantaged areas. Such schools often face challenges such as teacher shortages and inadequate educational materials and facilities like libraries, resulting in lower teaching standards. Moreover, parents may be unable to afford private lessons for children falling behind academically. In some cases, students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds are compelled to drop out of school to contribute to family income. Limited access to information about higher education and challenges in securing and repaying student loans further exacerbate the situation. Low socioeconomic status is also associated with poorer physical and mental health, contributing to a cycle of social inequality that persists across generations.
Ethnic background correlates with cultural distinctions and language barriers, which can pose challenges for students in adapting to the school environment and comprehending classes. Moreover, explicit and implicit biases and discrimination against ethnic minorities further compound these difficulties. Such biases can impact students' self-esteem, motivation, and access to educational opportunities. For instance, teachers may harbor stereotypical perceptions, albeit not overtly racist, leading to differential grading of comparable performances based on a child's ethnicity.
Historically, gender has played a pivotal role in education as societal norms dictated distinct roles for men and women. Education traditionally favored men, who were tasked with providing for the family, while women were expected to manage households and care for children, often limiting their access to education. Although these disparities have improved in many modern societies, gender differences persist in education. This includes biases and stereotypes related to gender roles in various academic domains, notably in fields such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM), which are often portrayed as male-dominated. Such perceptions can deter female students from pursuing these subjects. In various instances, discrimination based on gender and social factors occurs openly as part of official educational policies, such as the severe restrictions imposed on female education by the Taliban in Afghanistan, and the school segregation of migrants and locals in urban China under the hukou system.
One facet of several social factors is characterized by the expectations linked to stereotypes. These expectations operate externally, influenced by how others respond to individuals belonging to specific groups, and internally, shaped by how individuals internalize and conform to them. In this regard, these expectations can manifest as self-fulfilling prophecies by affecting the educational outcomes they predict. Such outcomes may be influenced by both positive and negative stereotypes.
Technology and others
Technology plays a crucial role in educational success. While educational technology is often linked with modern digital devices such as computers, its scope extends far beyond that. It encompasses a diverse array of resources and tools for learning, including traditional aids like books and worksheets, in addition to digital devices.

Educational technology can enhance learning in various ways. In the form of media, it often serves as the primary source of information in the classroom, allowing teachers to allocate their time and energy to other tasks such as lesson planning, student guidance, and performance assessment. By presenting information using graphics, audio, and video instead of mere text, educational technology can also enhance comprehension. Interactive elements, such as educational games, further engage learners in the learning process. Moreover, technology facilitates the accessibility of educational materials to a wide audience, particularly through online resources, while also promoting collaboration among students and communication with teachers. The integration of artificial intelligence in education holds promise for providing new learning experiences to students and supporting teachers in their work. However, it also introduces new risks related to data privacy, misinformation, and manipulation. Various organizations advocate for student access to educational technologies, including initiatives such as the One Laptop per Child initiative, the African Library Project, and Pratham.
School infrastructure also plays a crucial role in educational success. It encompasses physical aspects such as the school's location, size, and available facilities and equipment. A healthy and safe environment, well-maintained classrooms, appropriate classroom furniture, as well as access to a library and a canteen, all contribute to fostering educational success. Additionally, the quality of teachers significantly impacts student achievement. Skilled teachers possess the ability to motivate and inspire students, and tailor instructions to individual abilities and needs. Their skills depend on their own education, training, and teaching experience. A meta-analysis by Engin Karadağ et al. concludes that, compared to other influences, factors related to the school and the teacher have the greatest impact on educational success.
Parent involvement also enhances achievement and can increase children's motivation and commitment when they know their parents are invested in their educational endeavors. This often results in heightened self-esteem, improved attendance rates, and more positive behavior at school. Parent involvement covers communication with teachers and other school staff to raise awareness of current issues and explore potential resolutions. Other relevant factors, occasionally addressed in academic literature, encompass historical, political, demographic, religious, and legal aspects.
Education studies

The primary field exploring education is known as education studies, also termed education sciences. It seeks to understand how knowledge is transmitted and acquired by examining various methods and forms of education. This discipline delves into the goals, impacts, and significance of education, along with the cultural, societal, governmental, and historical contexts that influence it. Education theorists draw insights from various disciplines, including philosophy, psychology, sociology, economics, history, politics, and international relations. Consequently, some argue that education studies lacks the clear methodological and subject delineations found in disciplines like physics or history. Education studies focuses on academic analysis and critical reflection and differs in this respect from teacher training programs, which show participants how to become effective teachers. Furthermore, it encompasses not only formal education but also explores all forms and facets of educational processes.
Various research methods are utilized to investigate educational phenomena, broadly categorized into quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods approaches. Quantitative research mirrors the methodologies of the natural sciences, employing precise numerical measurements to collect data from numerous observations and utilizing statistical tools for analysis. Its goal is to attain an objective and impartial understanding. Conversely, qualitative research typically involves a smaller sample size and seeks to gain a nuanced insight into subjective and personal factors, such as individuals' experiences within the educational process. Mixed-methods research aims to integrate data gathered from both approaches to achieve a balanced and comprehensive understanding. Data collection methods vary and may include direct observation, test scores, interviews, and questionnaires. Research projects may investigate fundamental factors influencing all forms of education or focus on specific applications, seek solutions to particular problems, or evaluate the effectiveness of educational initiatives and policies.
Subfields
Education studies encompasses various subfields such as pedagogy, educational research, comparative education, and the philosophy, psychology, sociology, economics, and history of education. The philosophy of education is the branch of applied philosophy that examines many of the fundamental assumptions underlying the theory and practice of education. It explores education both as a process and a discipline while seeking to provide precise definitions of its nature and distinctions from other phenomena. Additionally, it delves into the purpose of education, its various types, and the conceptualization of teachers, students, and their relationship. Furthermore, it encompasses educational ethics, which examines the moral implications of education, such as the ethical principles guiding it and how teachers should apply them to specific situations. The philosophy of education boasts a long history and was a subject of discourse in ancient Greek philosophy.
The term "pedagogy" is sometimes used interchangeably with education studies, but in a more specific sense, it refers to the subfield focused on teaching methods. It investigates how educational objectives, such as knowledge transmission or the development of skills and character traits, can be achieved. Pedagogy is concerned with the methods and techniques employed in teaching within conventional educational settings. While some definitions confine it to this context, in a broader sense, it encompasses all forms of education, including teaching methods beyond traditional school environments. In this broader context, it explores how teachers can facilitate learning experiences for students to enhance their understanding of the subject matter and how learning itself occurs.
The psychology of education delves into the mental processes underlying learning, focusing on how individuals acquire new knowledge and skills and experience personal development. It investigates the various factors influencing educational outcomes, how these factors vary among individuals, and the extent to which nature or nurture contribute to these outcomes. Key psychological theories shaping education encompass behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. Related disciplines include educational neuroscience and the neurology of education, which explore the neuropsychological processes and changes associated with learning.
The field of sociology of education delves into how education shapes socialization, examining how social factors and ideologies influence access to education and individual success within it. It explores the impact of education on different societal groups and its role in shaping personal identity. Specifically, the sociology of education focuses on understanding the root causes of inequalities, offering insights relevant to education policy aimed at identifying and addressing factors contributing to inequality. Two prominent perspectives within this field are consensus theory and conflict theory. Consensus theorists posit that education benefits society by preparing individuals for their societal roles, while conflict theorists view education as a tool employed by the ruling class to perpetuate inequalities.
The field of economics of education investigates the production, distribution, and consumption of education. It seeks to optimize resource allocation to enhance education, such as assessing the impact of increased teacher salaries on teacher quality. Additionally, it explores the effects of smaller class sizes and investments in new educational technologies. By providing insights into resource allocation, the economics of education aids policymakers in making decisions that maximize societal benefits. Furthermore, it examines the long-term economic implications of education, including its role in fostering a highly skilled workforce and enhancing national competitiveness. A related area of interest involves analyzing the economic advantages and disadvantages of different educational systems.
Comparative education is the discipline that examines and contrasts education systems. Comparisons can occur from a general perspective or focus on specific factors like social, political, or economic aspects. Often applied to different countries, comparative education assesses the similarities and differences of their educational institutions and practices, evaluating the consequences of distinct approaches. It can be used to glean insights from other countries on effective education policies and how one's own system may be improved. This practice, known as policy borrowing, presents challenges as policy success can hinge on the social and cultural context of students and teachers. A related and contentious topic concerns whether the educational systems of developed countries are superior and should be exported to less developed ones. Other key topics include the internationalization of education and the role of education in transitioning from authoritarian regimes to democracies.
The history of education delves into the evolution of educational practices, systems, and institutions. It explores various key processes, their potential causes and effects, and their interrelations.
Aims and ideologies

A central topic in education studies revolves around how people should be educated and what goals should guide this process. Various aims have been proposed, including the acquisition of knowledge and skills, personal development, and the cultivation of character traits. Commonly suggested attributes encompass qualities like curiosity, creativity, rationality, and critical thinking, along with tendencies to think, feel, and act morally. Scholars diverge on whether to prioritize liberal values such as freedom, autonomy, and open-mindedness, or qualities like obedience to authority, ideological purity, piety, and religious faith.
Some education theorists concentrate on a single overarching purpose of education, viewing more specific aims as means to this end. At a personal level, this purpose is often equated with assisting the student in leading a good life. Societally, education aims to cultivate individuals into productive members of society. There is debate regarding whether the primary aim of education is to benefit the educated individual or society as a whole.
Educational ideologies encompass systems of fundamental philosophical assumptions and principles utilized to interpret, understand, and assess existing educational practices and policies. They address various aspects beyond the aims of education, including the subjects taught, the structure of learning activities, the role of teachers, methods for assessing educational progress, and the design of institutional frameworks and policies. These ideologies are diverse and often interrelated. Teacher-centered ideologies prioritize the role of teachers in imparting knowledge to students, while student-centered ideologies afford students a more active role in the learning process. Process-based ideologies focus on the methods of teaching and learning, contrasting with product-based ideologies, which consider education in terms of the desired outcomes. Conservative ideologies uphold traditional practices, whereas Progressive ideologies advocate for innovation and creativity. Additional categories are humanism, romanticism, essentialism, encyclopaedism, pragmatism, as well as authoritarian and democratic ideologies.
Learning theories
Learning theories attempt to elucidate the mechanisms underlying learning. Influential theories include behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. Behaviorism posits that learning entails a modification in behavior in response to environmental stimuli. This occurs through the presentation of a stimulus, the association of this stimulus with the desired response, and the reinforcement of this stimulus-response connection. Cognitivism views learning as a transformation in cognitive structures and emphasizes the mental processes involved in encoding, retrieving, and processing information. Constructivism asserts that learning is grounded in the individual's personal experiences and places greater emphasis on social interactions and their interpretation by the learner. These theories carry significant implications for instructional practices. For instance, behaviorists often emphasize repetitive drills, cognitivists may advocate for mnemonic techniques, and constructivists typically employ collaborative learning strategies.
Various theories suggest that learning is more effective when it is based on personal experience. Additionally, aiming for a deeper understanding by connecting new information to pre-existing knowledge is considered more beneficial than simply memorizing a list of unrelated facts. An influential developmental theory of learning is proposed by psychologist Jean Piaget, who outlines four stages of learning through which children progress on their way to adulthood: the sensorimotor, pre-operational, concrete operational, and formal operational stages. These stages correspond to different levels of abstraction, with early stages focusing more on simple sensory and motor activities, while later stages involve more complex internal representations and information processing, such as logical reasoning.
Teaching methods
The teaching method pertains to how the content is delivered by the teacher, such as whether group work is employed rather than focusing on individual learning. There is a wide array of teaching methods available, and the most effective one in a given scenario depends on factors like the subject matter and the learner's age and level of competence. This is reflected in modern school systems, which organize students into different classes based on age, competence, specialization, and native language to ensure an effective learning process. Different subjects often employ distinct approaches; for example, language education frequently emphasizes verbal learning, while mathematical education focuses on abstract and symbolic thinking alongside deductive reasoning. One crucial aspect of teaching methodologies is ensuring that learners remain motivated, either through intrinsic factors like interest and curiosity or through external rewards.
The teaching method also includes the utilization of instructional media, such as books, worksheets, and audio-visual recordings, as well as implementing some form of test or evaluation to gauge learning progress. Educational assessment is the process of documenting the student's knowledge and skills, which can happen formally or informally and may take place before, during, or after the learning activity. Another significant pedagogical element in many modern educational approaches is that each lesson is part of a broader educational framework governed by a syllabus, which often spans several months or years. According to Herbartianism, teaching is broken down into phases. The initial phase involves preparing the student's mind for new information. Subsequently, new ideas are introduced to the learner and then linked to concepts already familiar to them. In later phases, understanding transitions to a more general level beyond specific instances, and the ideas are then applied in practical contexts.
History
The history of education delves into the processes, methods, and institutions entwined with teaching and learning, aiming to elucidate their interplay and influence on educational practices over time.
Prehistory
Education during prehistory primarily facilitated enculturation, emphasizing practical knowledge and skills essential for daily life, such as food production, clothing, shelter, and safety. Formal schools and specialized instructors were absent, with adults in the community assuming teaching roles, and learning transpiring informally through daily activities, including observation and imitation of elders. In oral societies, storytelling served as a pivotal means of transmitting cultural and religious beliefs across generations. With the advent of agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution around 9000 BCE, a gradual educational shift toward specialization ensued, driven by the formation of larger communities and the demand for increasingly intricate artisanal and technical skills.
Ancient era
Commencing in the 4th millennium BCE and spanning subsequent eras, a pivotal transformation in educational methodologies unfolded with the advent of writing in regions such as Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, the Indus Valley, and ancient China. This breakthrough profoundly influenced the trajectory of education. Writing facilitated the storage, preservation, and dissemination of information, ushering in subsequent advancements such as the creation of educational aids like textbooks and the establishment of institutions such as schools.

Another significant aspect of ancient education was the establishment of formal education. This became necessary as civilizations evolved and the volume of knowledge expanded, surpassing what informal education could effectively transmit across generations. Teachers assumed specialized roles to impart knowledge, leading to a more abstract educational approach less tied to daily life. Formal education remained relatively rare in ancient societies, primarily accessible to the intellectual elite. It covered fields like reading and writing, record keeping, leadership, civic and political life, religion, and technical skills associated with specific professions. Formal education introduced a new teaching paradigm that emphasized discipline and drills over the informal methods prevalent earlier. Two notable achievements of ancient education include the founding of Plato's Academy in Ancient Greece, often regarded as the earliest institution of higher learning, and the establishment of the Great Library of Alexandria in Ancient Egypt, renowned as one of the ancient world's premier libraries.
Medieval era

Many facets of education during the medieval period were profoundly influenced by religious traditions. In Europe, the Catholic Church wielded considerable authority over formal education. In the Arab world, the rapid spread of Islam led to various educational advancements during the Islamic Golden Age, integrating classical and religious knowledge and establishing madrasa schools. In Jewish communities, yeshivas emerged as institutions dedicated to the study of religious texts and Jewish law. In China, an expansive state educational and examination system, shaped by Confucian teachings, was instituted. As new complex societies emerged in regions like Africa, the Americas, Northern Europe, and Japan, some adopted existing educational practices, while others developed new traditions.
Additionally, this era witnessed the establishment of various institutes of higher education and research. Prominent among these were the University of Bologna (the world's oldest university in continuous operation), the University of Paris, and Oxford University in Europe. Other influential centers included the Al-Qarawiyyin University in Morocco, Al-Azhar University in Egypt, and the House of Wisdom in Iraq. Another significant development was the formation of guilds, associations of skilled craftsmen and merchants who regulated their trades and provided vocational education. Prospective members underwent various stages of training on their journey to mastery.
Modern era

Starting in the early modern period, education in Europe during the Renaissance slowly began to shift from a religious approach towards one that was more secular. This development was tied to an increased appreciation of the importance of education and a broadened range of topics, including a revived interest in ancient literary texts and educational programs. The turn toward secularization was accelerated during the Age of Enlightenment starting in the 17th century, which emphasized the role of reason and the empirical sciences. European colonization affected education in the Americas through Christian missionary initiatives. In China, the state educational system was further expanded and focused more on the teachings of neo-Confucianism. In the Islamic world, the outreach of formal education increased and remained under the influence of religion. A key development in the early modern period was the invention and popularization of the printing press in the middle of the 15th century, which had a profound impact on general education. It significantly reduced the cost of producing books, which were hand-written before, and thereby augmented the dissemination of written documents, including new forms like newspapers and pamphlets. The increased availability of written media had a major influence on the general literacy of the population.
These alterations paved the way for the advancement of public education during the 18th and 19th centuries. This era witnessed the establishment of publicly funded schools with the goal of providing education for all, in contrast to previous periods when formal education was primarily delivered by private schools, religious institutions, and individual tutors. An exception to this trend was the Aztec civilization, where formal education was compulsory for youth across social classes as early as the 14th century. Closely related changes were to make education compulsory and free of charge for all children up to a certain age.
Contemporary era
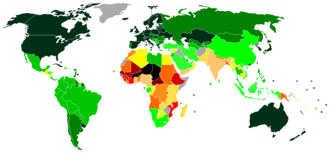
The promotion of public education and universal access to education gained momentum in the 20th and 21st centuries, endorsed by intergovernmental organizations such as the UN. Key initiatives included the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the Convention on the Rights of the Child, the Education for All initiative, the Millennium Development Goals, and the Sustainable Development Goals. These endeavors led to a consistent increase in all forms of education, particularly impacting primary education. In 1970, 28% of all primary-school-age children worldwide were not enrolled in school; by 2015, this figure had decreased to 9%.
The establishment of public education was accompanied by the introduction of standardized curricula for public schools as well as standardized tests to assess the progress of students. Contemporary examples are the Test of English as a Foreign Language, which is a globally used test to assess language proficiency in non-native English speakers, and the Programme for International Student Assessment, which evaluates education systems across the world based on the performance of 15-year-old students in reading, mathematics, and science. Similar shifts impacted teachers, with the establishment of institutions and norms to regulate and oversee teacher training, including certification mandates for teaching in public schools.
Emerging educational technologies have significantly influenced modern education. The widespread availability of computers and the internet has notably expanded access to educational resources and facilitated new forms of learning, such as online education. This became particularly pertinent during the COVID-19 pandemic when schools worldwide closed for prolonged periods, prompting many to adopt remote learning methods through video conferencing or pre-recorded video lessons to sustain instruction. Additionally, contemporary education is impacted by the increasing globalization and internationalization of educational practices.