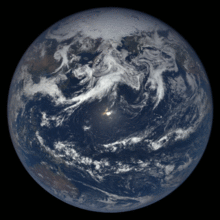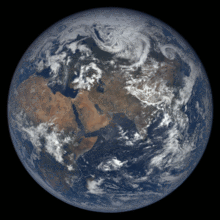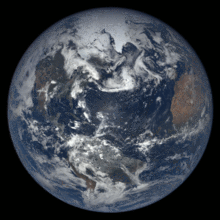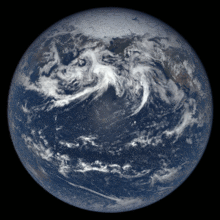
The Blue Marble photograph of Earth, taken during the Apollo 17 lunar mission in 1972
| |||||||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch J2000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Aphelion |
152100000 km (94500000 mi; 1.017 AU) | ||||||||||||||||
| Perihelion |
147095000 km (91401000 mi; 0.98327 AU) | ||||||||||||||||
|
149598023 km (92955902 mi; 1.00000102 AU) | |||||||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0167086 | ||||||||||||||||
|
365.256363004 d (1.00001742096 yr) | |||||||||||||||||
Average orbital speed
|
29.78 km/s (107200 km/h; 66600 mph) | ||||||||||||||||
| 358.617° | |||||||||||||||||
| Inclination |
| ||||||||||||||||
| −11.26064° to J2000 ecliptic | |||||||||||||||||
| 114.20783° | |||||||||||||||||
| Satellites |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||||||||||
Mean radius
| 6371.0 km (3958.8 mi) | ||||||||||||||||
Equatorial radius
| 6378.1 km (3963.2 mi) | ||||||||||||||||
Polar radius
| 6356.8 km (3949.9 mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| Flattening |
0.0033528 1/298.257222101 (ETRS89) | ||||||||||||||||
| Circumference |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Volume | 1.08321×1012 km3 (2.59876×1011 cu mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| Mass |
5.97237×1024 kg (1.31668×1025 lb) (3.0×10−6 M☉) | ||||||||||||||||
Mean density
| 5.514 g/cm3 (0.1992 lb/cu in) | ||||||||||||||||
| 9.807 m/s2 (1 g; 32.18 ft/s2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 0.3307 | |||||||||||||||||
|
11.186 km/s (40270 km/h; 25020 mph) | |||||||||||||||||
Sidereal rotation period
|
0.99726968 d
(23h 56m 4.100s) | ||||||||||||||||
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
0.4651 km/s (1674.4 km/h; 1040.4 mph) | ||||||||||||||||
| 23.4392811° | |||||||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Atmosphere | |||||||||||||||||
Surface pressure
| 101.325 kPa (at MSL) | ||||||||||||||||
| Composition by volume |
| ||||||||||||||||
Earth's axis of rotation is tilted with respect to its orbital plane, producing seasons on Earth. The gravitational interaction between Earth and the Moon causes ocean tides, stabilizes Earth's orientation on its axis, and gradually slows its rotation. Earth is the densest planet in the Solar System and the largest of the four terrestrial planets.
Earth's lithosphere is divided into several rigid tectonic plates that migrate across the surface over periods of many millions of years. About 71% of Earth's surface is covered with water, mostly by oceans. The remaining 29% is land consisting of continents and islands that together have many lakes, rivers and other sources of water that contribute to the hydrosphere. The majority of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice, including the Antarctic ice sheet and the sea ice of the Arctic ice pack. Earth's interior remains active with a solid iron inner core, a liquid outer core that generates the Earth's magnetic field, and a convecting mantle that drives plate tectonics.
Within the first billion years of Earth's history, life appeared in the oceans and began to affect the Earth's atmosphere and surface, leading to the proliferation of aerobic and anaerobic organisms. Some geological evidence indicates that life may have arisen as much as 4.1 billion years ago. Since then, the combination of Earth's distance from the Sun, physical properties, and geological history have allowed life to evolve and thrive. In the history of the Earth, biodiversity has gone through long periods of expansion, occasionally punctuated by mass extinction events. Over 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth are extinct. Estimates of the number of species on Earth today vary widely; most species have not been described. Over 7.6 billion humans live on Earth and depend on its biosphere and natural resources for their survival. Humans have developed diverse societies and cultures; politically, the world has about 200 sovereign states.
Name and etymology
An early mention of "eorðan" (earth) in Beowulf
The modern English word Earth developed from a wide variety of Middle English forms, which derived from an Old English noun most often spelled eorðe. It has cognates in every Germanic language, and their proto-Germanic root has been reconstructed as *erþō. In its earliest appearances, eorðe was already being used to translate the many senses of Latin terra and Greek γῆ (gē): the ground, its soil, dry land, the human world, the surface of the world (including the sea), and the globe itself. As with Terra and Gaia, Earth was a personified goddess in Germanic paganism: the Angles were listed by Tacitus as among the devotees of Nerthus, and later Norse mythology included Jörð, a giantess often given as the mother of Thor.
Originally, earth was written in lowercase, and from early Middle English, its definite sense as "the globe" was expressed as the earth. By Early Modern English, many nouns were capitalized, and the earth became (and often remained) the Earth, particularly when referenced along with other heavenly bodies. More recently, the name is sometimes simply given as Earth, by analogy with the names of the other planets. House styles now vary: Oxford spelling recognizes the lowercase form as the most common, with the capitalized form an acceptable variant. Another convention capitalizes "Earth" when appearing as a name (e.g. "Earth's atmosphere") but writes it in lowercase when preceded by the (e.g. "the atmosphere of the earth"). It almost always appears in lowercase in colloquial expressions such as "what on earth are you doing?"
Chronology
Formation
Artist's impression of the early Solar System's planetary disk
The oldest material found in the Solar System is dated to 4.5672±0.0006 billion years ago (Bya). By 4.54±0.04 Bya the primordial Earth had formed. The bodies in the Solar System formed and evolved with the Sun. In theory, a solar nebula partitions a volume out of a molecular cloud by gravitational collapse, which begins to spin and flatten into a circumstellar disk, and then the planets grow out of that disk with the Sun. A nebula contains gas, ice grains, and dust (including primordial nuclides). According to nebular theory, planetesimals formed by accretion, with the primordial Earth taking 10–20 million years (Mys) to form.
A subject of research is the formation of the Moon, some 4.53 Bya. A leading hypothesis is that it was formed by accretion from material loosed from Earth after a Mars-sized object, named Theia, hit Earth. In this view, the mass of Theia was approximately 10 percent of Earth, it hit Earth with a glancing blow and some of its mass merged with Earth. Between approximately 4.1 and 3.8 Bya, numerous asteroid impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment caused significant changes to the greater surface environment of the Moon and, by inference, to that of Earth.
Geological history
Earth's atmosphere and oceans were formed by volcanic activity and outgassing. Water vapor from these sources condensed into the oceans, augmented by water and ice from asteroids, protoplanets, and comets. In this model, atmospheric "greenhouse gases" kept the oceans from freezing when the newly forming Sun had only 70% of its current luminosity. By 3.5 Bya, Earth's magnetic field was established, which helped prevent the atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind.
A crust formed when the molten outer layer of Earth cooled to form a solid. The two models that explain land mass propose either a steady growth to the present-day forms or, more likely, a rapid growth early in Earth history followed by a long-term steady continental area. Continents formed by plate tectonics, a process ultimately driven by the continuous loss of heat from Earth's interior. Over the period of hundreds of millions of years, the supercontinents have assembled and broken apart. Roughly 750 million years ago (Mya), one of the earliest known supercontinents, Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia 600–540 Mya, then finally Pangaea, which also broke apart 180 Mya.
The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 Mya and then intensified during the Pleistocene about 3 Mya. High-latitude regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating about every 40,000–100,000 years. The last continental glaciation ended 10,000 years ago.
Origin of life and evolution
Phylogenetic tree of life on Earth based on rRNA analysis
Chemical reactions led to the first self-replicating molecules about four billion years ago. A half billion years later, the last common ancestor of all current life arose. The evolution of photosynthesis allowed the Sun's energy to be harvested directly by life forms. The resultant molecular oxygen (O
2) accumulated in the atmosphere and due to interaction with ultraviolet solar radiation, formed a protective ozone layer (O
3) in the upper atmosphere. The incorporation of smaller cells within larger ones resulted in the development of complex cells called eukaryotes. True multicellular organisms formed as cells within colonies became increasingly specialized. Aided by the absorption of harmful ultraviolet radiation by the ozone layer, life colonized Earth's surface. Among the earliest fossil evidence for life is microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone in Western Australia, biogenic graphite found in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks in Western Greenland, and remains of biotic material found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. The earliest direct evidence of life on Earth is contained in 3.45 billion-year-old Australian rocks showing fossils of microorganisms.
During the Neoproterozoic, 750 to 580 Mya, much of Earth might have been covered in ice. This hypothesis has been termed "Snowball Earth", and it is of particular interest because it preceded the Cambrian explosion, when multicellular life forms significantly increased in complexity. Following the Cambrian explosion, 535 Mya, there have been five mass extinctions. The most recent such event was 66 Mya, when an asteroid impact triggered the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs and other large reptiles, but spared some small animals such as mammals, which at the time resembled shrews. Mammalian life has diversified over the past 66 Mys, and several million ago an African ape-like animal such as Orrorin tugenensis gained the ability to stand upright. This facilitated tool use and encouraged communication that provided the nutrition and stimulation needed for a larger brain, which led to the evolution of humans. The development of agriculture, and then civilization, led to humans having an influence on Earth and the nature and quantity of other life forms that continues to this day.
Future
Earth's expected long-term future is tied to that of the Sun. Over the next 1.1 Bys, solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next 3.5 Bys by 40%. The Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, reducing CO2 concentration to levels lethally low for plants (10 ppm for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately 500–900 Mys. The lack of vegetation will result in the loss of oxygen in the atmosphere, making animal life impossible. After another billion years all surface water will have disappeared and the mean global temperature will reach 70 °C (158 °F). From that point, the Earth is expected to be habitable for another 500 Ma, possibly up to 2.3 Ga if nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere. Even if the Sun were eternal and stable, 27% of the water in the modern oceans will descend to the mantle in one billion years, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges.The Sun will evolve to become a red giant in about 5 Bys. Models predict that the Sun will expand to roughly 1 AU (150 million km; 93 million mi), about 250 times its present radius. Earth's fate is less clear. As a red giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its mass, so, without tidal effects, Earth will move to an orbit 1.7 AU (250 million km; 160 million mi) from the Sun when the star reaches its maximum radius. Most, if not all, remaining life will be destroyed by the Sun's increased luminosity (peaking at about 5,000 times its present level). A 2008 simulation indicates that Earth's orbit will eventually decay due to tidal effects and drag, causing it to enter the Sun's atmosphere and be vaporized.
Physical characteristics
Shape
Shape
of planet Earth. Shown are distances between surface relief and the
geocentre. The South American Andes summits are visible as elevated
areas. Data from the Earth2014[90] global relief model.
The shape of Earth is approximately oblate spheroidal. Due to rotation, the Earth is flattened at the poles and bulging around the equator. The diameter of the Earth at the equator is 43 kilometres (27 mi) larger than the pole-to-pole diameter. Thus the point on the surface farthest from Earth's center of mass is the summit of the equatorial Chimborazo volcano in Ecuador. The average diameter of the reference spheroid is 12,742 kilometres (7,918 mi). Local topography deviates from this idealized spheroid, although on a global scale these deviations are small compared to Earth's radius: The maximum deviation of only 0.17% is at the Mariana Trench (10,911 metres (35,797 ft) below local sea level), whereas Mount Everest (8,848 metres (29,029 ft) above local sea level) represents a deviation of 0.14%.
In geodesy, the exact shape that Earth's oceans would adopt in the absence of land and perturbations such as tides and winds is called the geoid. More precisely, the geoid is the surface of gravitational equipotential at mean sea level.
Chemical composition
Earth's mass is approximately 5.97×1024 kg (5,970 Yg). It is composed mostly of iron (32.1%), oxygen (30.1%), silicon (15.1%), magnesium (13.9%), sulfur (2.9%), nickel (1.8%), calcium (1.5%), and aluminium (1.4%), with the remaining 1.2% consisting of trace amounts of other elements. Due to mass segregation, the core region is estimated to be primarily composed of iron (88.8%), with smaller amounts of nickel (5.8%), sulfur (4.5%), and less than 1% trace elements.The most common rock constituents of the crust are nearly all oxides: chlorine, sulfur, and fluorine are the important exceptions to this and their total amount in any rock is usually much less than 1%. Over 99% of the crust is composed of 11 oxides, principally silica, alumina, iron oxides, lime, magnesia, potash, and soda.
Internal structure
Earth's interior, like that of the other terrestrial planets, is divided into layers by their chemical or physical (rheological) properties. The outer layer is a chemically distinct silicate solid crust, which is underlain by a highly viscous solid mantle. The crust is separated from the mantle by the Mohorovičić discontinuity. The thickness of the crust varies from about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) under the oceans to 30–50 km (19–31 mi) for the continents. The crust and the cold, rigid, top of the upper mantle are collectively known as the lithosphere, and it is of the lithosphere that the tectonic plates are composed. Beneath the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a relatively low-viscosity layer on which the lithosphere rides. Important changes in crystal structure within the mantle occur at 410 and 660 km (250 and 410 mi) below the surface, spanning a transition zone that separates the upper and lower mantle. Beneath the mantle, an extremely low viscosity liquid outer core lies above a solid inner core. The Earth's inner core might rotate at a slightly higher angular velocity than the remainder of the planet, advancing by 0.1–0.5° per year. The radius of the inner core is about one fifth of that of Earth.|
Earth cutaway from core to exosphere. Not to scale. |
Depth km |
Component layer | Density g/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–60 | Lithosphere | — | |
| 0–35 | Crust | 2.2–2.9 | |
| 35–60 | Upper mantle | 3.4–4.4 | |
| 35–2890 | Mantle | 3.4–5.6 | |
| 100–700 | Asthenosphere | — | |
| 2890–5100 | Outer core | 9.9–12.2 | |
| 5100–6378 | Inner core | 12.8–13.1 |
Heat
Earth's internal heat comes from a combination of residual heat from planetary accretion (about 20%) and heat produced through radioactive decay (80%). The major heat-producing isotopes within Earth are potassium-40, uranium-238, and thorium-232. At the center, the temperature may be up to 6,000 °C (10,830 °F), and the pressure could reach 360 GPa (52 million psi). Because much of the heat is provided by radioactive decay, scientists postulate that early in Earth's history, before isotopes with short half-lives were depleted, Earth's heat production was much higher. At approximately 3 Ga, twice the present-day heat would have been produced, increasing the rates of mantle convection and plate tectonics, and allowing the production of uncommon igneous rocks such as komatiites that are rarely formed today.| Isotope | Heat release W/kg isotope |
Half-life years |
Mean mantle conc. kg isotope/kg mantle |
Heat release W/kg mantle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 238U | 94.6×10−6 | 4.47×109 | 30.8×10−9 | 2.91×10−12 |
| 235U | 569×10−6 | 0.704×109 | 0.22×10−9 | 0.125×10−12 |
| 232Th | 26.4×10−6 | 14.0×109 | 124×10−9 | 3.27×10−12 |
| 40K | 29.2×10−6 | 1.25×109 | 36.9×10−9 | 1.08×10−12 |
Tectonic plates

| |
| Plate name | Area 106 km2 |
|---|---|
| 103.3 | |
| 78.0 | |
| 75.9 | |
| 67.8 | |
| 60.9 | |
| 47.2 | |
| 43.6 | |
Earth's mechanically rigid outer layer, the lithosphere, is divided into tectonic plates. These plates are rigid segments that move relative to each other at one of three boundaries types: At convergent boundaries, two plates come together; at divergent boundaries, two plates are pulled apart; and at transform boundaries, two plates slide past one another laterally. Along these plate boundaries, earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation can occur. The tectonic plates ride on top of the asthenosphere, the solid but less-viscous part of the upper mantle that can flow and move along with the plates.
Mountains build up when tectonic plates move toward each other, forcing rock up. The highest mountain on Earth above sea level is Mount Everest.
As the tectonic plates migrate, oceanic crust is subducted under the leading edges of the plates at convergent boundaries. At the same time, the upwelling of mantle material at divergent boundaries creates mid-ocean ridges. The combination of these processes recycles the oceanic crust back into the mantle. Due to this recycling, most of the ocean floor is less than 100 Ma old. The oldest oceanic crust is located in the Western Pacific and is estimated to be 200 Ma old. By comparison, the oldest dated continental crust is 4,030 Ma.
The seven major plates are the Pacific, North American, Eurasian, African, Antarctic, Indo-Australian, and South American. Other notable plates include the Arabian Plate, the Caribbean Plate, the Nazca Plate off the west coast of South America and the Scotia Plate in the southern Atlantic Ocean. The Australian Plate fused with the Indian Plate between 50 and 55 Mya. The fastest-moving plates are the oceanic plates, with the Cocos Plate advancing at a rate of 75 mm/a (3.0 in/year) and the Pacific Plate moving 52–69 mm/a (2.0–2.7 in/year). At the other extreme, the slowest-moving plate is the Eurasian Plate, progressing at a typical rate of 21 mm/a (0.83 in/year).
Surface
Current Earth without water, elevation exaggerated 20 times (click/enlarge to "spin" 3D-globe).
The total surface area of Earth is about 510 million km2 (197 million sq mi). Of this, 70.8%, or 361.13 million km2 (139.43 million sq mi), is below sea level and covered by ocean water. Below the ocean's surface are much of the continental shelf, mountains, volcanoes, oceanic trenches, submarine canyons, oceanic plateaus, abyssal plains, and a globe-spanning mid-ocean ridge system. The remaining 29.2%, or 148.94 million km2 (57.51 million sq mi), not covered by water has terrain that varies greatly from place to place and consists of mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, and other landforms. Tectonics and erosion, volcanic eruptions, flooding, weathering, glaciation, the growth of coral reefs, and meteorite impacts are among the processes that constantly reshape the Earth's surface over geological time.
The continental crust consists of lower density material such as the igneous rocks granite and andesite. Less common is basalt, a denser volcanic rock that is the primary constituent of the ocean floors. Sedimentary rock is formed from the accumulation of sediment that becomes buried and compacted together. Nearly 75% of the continental surfaces are covered by sedimentary rocks, although they form about 5% of the crust. The third form of rock material found on Earth is metamorphic rock, which is created from the transformation of pre-existing rock types through high pressures, high temperatures, or both. The most abundant silicate minerals on Earth's surface include quartz, feldspars, amphibole, mica, pyroxene and olivine. Common carbonate minerals include calcite (found in limestone) and dolomite.
The elevation of the land surface varies from the low point of −418 m (−1,371 ft) at the Dead Sea, to a maximum altitude of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at the top of Mount Everest. The mean height of land above sea level is about 797 m (2,615 ft).
The pedosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's continental surface and is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. The total arable land is 10.9% of the land surface, with 1.3% being permanent cropland. Close to 40% of Earth's land surface is used for agriculture, or an estimated 16.7 million km2 (6.4 million sq mi) of cropland and 33.5 million km2 (12.9 million sq mi) of pastureland.
Hydrosphere
Elevation histogram of Earth's surface
The abundance of water on Earth's surface is a unique feature that distinguishes the "Blue Planet" from other planets in the Solar System. Earth's hydrosphere consists chiefly of the oceans, but technically includes all water surfaces in the world, including inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground waters down to a depth of 2,000 m (6,600 ft). The deepest underwater location is Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean with a depth of 10,911.4 m (35,799 ft).
The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35×1018 metric tons or about 1/4400 of Earth's total mass. The oceans cover an area of 361.8 million km2 (139.7 million sq mi) with a mean depth of 3,682 m (12,080 ft), resulting in an estimated volume of 1.332 billion km3 (320 million cu mi). If all of Earth's crustal surface were at the same elevation as a smooth sphere, the depth of the resulting world ocean would be 2.7 to 2.8 km (1.68 to 1.74 mi).
About 97.5% of the water is saline; the remaining 2.5% is fresh water. Most fresh water, about 68.7%, is present as ice in ice caps and glaciers.
The average salinity of Earth's oceans is about 35 grams of salt per kilogram of sea water (3.5% salt). Most of this salt was released from volcanic activity or extracted from cool igneous rocks. The oceans are also a reservoir of dissolved atmospheric gases, which are essential for the survival of many aquatic life forms. Sea water has an important influence on the world's climate, with the oceans acting as a large heat reservoir. Shifts in the oceanic temperature distribution can cause significant weather shifts, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation.
Atmosphere
The atmospheric pressure at Earth's sea level averages 101.325 kPa (14.696 psi), with a scale height of about 8.5 km (5.3 mi). A dry atmosphere is composed of 78.084% nitrogen, 20.946% oxygen, 0.934% argon, and trace amounts of carbon dioxide and other gaseous molecules. Water vapor content varies between 0.01% and 4% but averages about 1%. The height of the troposphere varies with latitude, ranging between 8 km (5 mi) at the poles to 17 km (11 mi) at the equator, with some variation resulting from weather and seasonal factors.
Earth's biosphere has significantly altered its atmosphere. Oxygenic photosynthesis evolved 2.7 Gya, forming the primarily nitrogen–oxygen atmosphere of today. This change enabled the proliferation of aerobic organisms and, indirectly, the formation of the ozone layer due to the subsequent conversion of atmospheric O
2 into O
3. The ozone layer blocks ultraviolet solar radiation, permitting life on land. Other atmospheric functions important to life include transporting water vapor, providing useful gases, causing small meteors to burn up before they strike the surface, and moderating temperature. This last phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect: trace molecules within the atmosphere serve to capture thermal energy emitted from the ground, thereby raising the average temperature. Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone are the primary greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Without this heat-retention effect, the average surface temperature would be −18 °C (0 °F), in contrast to the current +15 °C (59 °F), and life on Earth probably would not exist in its current form. In May 2017, glints of light, seen as twinkling from an orbiting satellite a million miles away, were found to be reflected light from ice crystals in the atmosphere.
Weather and climate

Hurricane Felix seen from low Earth orbit, September 2007
The primary atmospheric circulation bands consist of the trade winds in the equatorial region below 30° latitude and the westerlies in the mid-latitudes between 30° and 60°. Ocean currents are also important factors in determining climate, particularly the thermohaline circulation that distributes thermal energy from the equatorial oceans to the polar regions.
Water vapor generated through surface evaporation is transported by circulatory patterns in the atmosphere. When atmospheric conditions permit an uplift of warm, humid air, this water condenses and falls to the surface as precipitation. Most of the water is then transported to lower elevations by river systems and usually returned to the oceans or deposited into lakes. This water cycle is a vital mechanism for supporting life on land and is a primary factor in the erosion of surface features over geological periods. Precipitation patterns vary widely, ranging from several meters of water per year to less than a millimeter. Atmospheric circulation, topographic features, and temperature differences determine the average precipitation that falls in each region.
The amount of solar energy reaching Earth's surface decreases with increasing latitude. At higher latitudes, the sunlight reaches the surface at lower angles, and it must pass through thicker columns of the atmosphere. As a result, the mean annual air temperature at sea level decreases by about 0.4 °C (0.7 °F) per degree of latitude from the equator. Earth's surface can be subdivided into specific latitudinal belts of approximately homogeneous climate. Ranging from the equator to the polar regions, these are the tropical (or equatorial), subtropical, temperate and polar climates.
This latitudinal rule has several anomalies:
- Proximity to oceans moderates the climate. For example, the Scandinavian Peninsula has more moderate climate than similarly northern latitudes of northern Canada.
- The wind enables this moderating effect. The windward side of a land mass experiences more moderation than the leeward side. In the Northern Hemisphere, the prevailing wind is west-to-east, and western coasts tend to be milder than eastern coasts. This is seen in Eastern North America and Western Europe, where rough continental climates appear on the east coast on parallels with mild climates on the other side of the ocean.[159] In the Southern Hemisphere, the prevailing wind is east-to-west, and the eastern coasts are milder.
- The distance from the Earth to the Sun varies. The Earth is closest to the Sun (at perihelion) in January, which is summer in the Southern Hemisphere. It is furthest away (at aphelion) in July, which is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, and only 93.55% of the solar radiation from the Sun falls on a given square area of land than at perihelion. Despite this, there are larger land masses in the Northern Hemisphere, which are easier to heat than the seas. Consequently, summers are 2.3 °C (4 °F) warmer in the Northern Hemisphere than in the Southern Hemisphere under similar conditions.
- The climate is colder at high altitudes than at sea level because of the decreased air density.
The highest air temperature ever measured on Earth was 56.7 °C (134.1 °F) in Furnace Creek, California, in Death Valley, in 1913. The lowest air temperature ever directly measured on Earth was −89.2 °C (−128.6 °F) at Vostok Station in 1983, but satellites have used remote sensing to measure temperatures as low as −94.7 °C (−138.5 °F) in East Antarctica. These temperature records are only measurements made with modern instruments from the 20th century onwards and likely do not reflect the full range of temperature on Earth.
Upper atmosphere
This view from orbit shows the full moon partially obscured by Earth's atmosphere.
Above the troposphere, the atmosphere is usually divided into the stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. Each layer has a different lapse rate, defining the rate of change in temperature with height. Beyond these, the exosphere thins out into the magnetosphere, where the geomagnetic fields interact with the solar wind. Within the stratosphere is the ozone layer, a component that partially shields the surface from ultraviolet light and thus is important for life on Earth. The Kármán line, defined as 100 km above Earth's surface, is a working definition for the boundary between the atmosphere and outer space.
Thermal energy causes some of the molecules at the outer edge of the atmosphere to increase their velocity to the point where they can escape from Earth's gravity. This causes a slow but steady loss of the atmosphere into space. Because unfixed hydrogen has a low molecular mass, it can achieve escape velocity more readily, and it leaks into outer space at a greater rate than other gases. The leakage of hydrogen into space contributes to the shifting of Earth's atmosphere and surface from an initially reducing state to its current oxidizing one. Photosynthesis provided a source of free oxygen, but the loss of reducing agents such as hydrogen is thought to have been a necessary precondition for the widespread accumulation of oxygen in the atmosphere. Hence the ability of hydrogen to escape from the atmosphere may have influenced the nature of life that developed on Earth. In the current, oxygen-rich atmosphere most hydrogen is converted into water before it has an opportunity to escape. Instead, most of the hydrogen loss comes from the destruction of methane in the upper atmosphere.
Gravitational field
Earth's gravity measured by NASA's GRACE mission, showing deviations from the theoretical gravity. Red shows where gravity is stronger than the smooth, standard value, and blue shows where it is weaker.
The gravity of Earth is the acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the distribution of mass within the Earth. Near the Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration is approximately 9.8 m/s2 (32 ft/s2). Local differences in topography, geology, and deeper tectonic structure cause local and broad, regional differences in the Earth's gravitational field, known as gravity anomalies.
Magnetic field
The main part of Earth's magnetic field is generated in the core, the site of a dynamo process that converts the kinetic energy of thermally and compositionally driven convection into electrical and magnetic field energy. The field extends outwards from the core, through the mantle, and up to Earth's surface, where it is, approximately, a dipole. The poles of the dipole are located close to Earth's geographic poles. At the equator of the magnetic field, the magnetic-field strength at the surface is 3.05 × 10−5 T, with global magnetic dipole moment of 7.91 × 1015 T m3. The convection movements in the core are chaotic; the magnetic poles drift and periodically change alignment. This causes secular variation of the main field and field reversals at irregular intervals averaging a few times every million years. The most recent reversal occurred approximately 700,000 years ago.Magnetosphere
Schematic of Earth's magnetosphere. The solar wind flows from left to right
The extent of Earth's magnetic field in space defines the magnetosphere. Ions and electrons of the solar wind are deflected by the magnetosphere; solar wind pressure compresses the dayside of the magnetosphere, to about 10 Earth radii, and extends the nightside magnetosphere into a long tail. Because the velocity of the solar wind is greater than the speed at which waves propagate through the solar wind, a supersonic bowshock precedes the dayside magnetosphere within the solar wind. Charged particles are contained within the magnetosphere; the plasmasphere is defined by low-energy particles that essentially follow magnetic field lines as Earth rotates; the ring current is defined by medium-energy particles that drift relative to the geomagnetic field, but with paths that are still dominated by the magnetic field, and the Van Allen radiation belt are formed by high-energy particles whose motion is essentially random, but otherwise contained by the magnetosphere.
During magnetic storms and substorms, charged particles can be deflected from the outer magnetosphere and especially the magnetotail, directed along field lines into Earth's ionosphere, where atmospheric atoms can be excited and ionized, causing the aurora.
Orbit and rotation
Rotation
Earth's rotation imaged by DSCOVR EPIC on 29 May 2016, a few weeks before the solstice.
Earth's rotation period relative to the Sun—its mean solar day—is 86,400 seconds of mean solar time (86,400.0025 SI seconds). Because Earth's solar day is now slightly longer than it was during the 19th century due to tidal deceleration, each day varies between 0 and 2 SI ms longer.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars, called its stellar day by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS), is 86,164.0989 seconds of mean solar time (UT1), or 23h 56m 4.0989s. Earth's rotation period relative to the precessing or moving mean vernal equinox, misnamed its sidereal day, is 86,164.0905 seconds of mean solar time (UT1) (23h 56m 4.0905s). Thus the sidereal day is shorter than the stellar day by about 8.4 ms. The length of the mean solar day in SI seconds is available from the IERS for the periods 1623–2005 and 1962–2005.
Apart from meteors within the atmosphere and low-orbiting satellites, the main apparent motion of celestial bodies in Earth's sky is to the west at a rate of 15°/h = 15'/min. For bodies near the celestial equator, this is equivalent to an apparent diameter of the Sun or the Moon every two minutes; from Earth's surface, the apparent sizes of the Sun and the Moon are approximately the same.
Orbit
The Pale Blue Dot photo taken in 1990 by the Voyager 1 spacecraft showing Earth (center right) from nearly 6.4 billion km (4 billion mi) away
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 150 million km (93 million mi) every 365.2564 mean solar days, or one sidereal year. This gives an apparent movement of the Sun eastward with respect to the stars at a rate of about 1°/day, which is one apparent Sun or Moon diameter every 12 hours. Due to this motion, on average it takes 24 hours—a solar day—for Earth to complete a full rotation about its axis so that the Sun returns to the meridian. The orbital speed of Earth averages about 29.78 km/s (107,200 km/h; 66,600 mph), which is fast enough to travel a distance equal to Earth's diameter, about 12,742 km (7,918 mi), in seven minutes, and the distance to the Moon, 384,000 km (239,000 mi), in about 3.5 hours.
The Moon and Earth orbit a common barycenter every 27.32 days relative to the background stars. When combined with the Earth–Moon system's common orbit around the Sun, the period of the synodic month, from new moon to new moon, is 29.53 days. Viewed from the celestial north pole, the motion of Earth, the Moon, and their axial rotations are all counterclockwise. Viewed from a vantage point above the north poles of both the Sun and Earth, Earth orbits in a counterclockwise direction about the Sun. The orbital and axial planes are not precisely aligned: Earth's axis is tilted some 23.44 degrees from the perpendicular to the Earth–Sun plane (the ecliptic), and the Earth–Moon plane is tilted up to ±5.1 degrees against the Earth–Sun plane. Without this tilt, there would be an eclipse every two weeks, alternating between lunar eclipses and solar eclipses.
The Hill sphere, or the sphere of gravitational influence, of the Earth is about 1.5 million km (930,000 mi) in radius. This is the maximum distance at which the Earth's gravitational influence is stronger than the more distant Sun and planets. Objects must orbit the Earth within this radius, or they can become unbound by the gravitational perturbation of the Sun.
Earth, along with the Solar System, is situated in the Milky Way and orbits about 28,000 light-years from its center. It is about 20 light-years above the galactic plane in the Orion Arm.
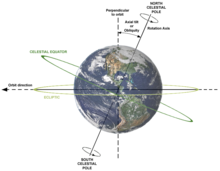
Axial tilt and seasons
The axial tilt of the Earth is approximately 23.439281° with the axis of its orbit plane, always pointing towards the Celestial Poles. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the amount of sunlight reaching any given point on the surface varies over the course of the year. This causes the seasonal change in climate, with summer in the Northern Hemisphere occurring when the Tropic of Cancer is facing the Sun, and winter taking place when the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere faces the Sun. During the summer, the day lasts longer, and the Sun climbs higher in the sky. In winter, the climate becomes cooler and the days shorter. In northern temperate latitudes, the Sun rises north of true east during the summer solstice, and sets north of true west, reversing in the winter. The Sun rises south of true east in the summer for the southern temperate zone and sets south of true west.
Above the Arctic Circle, an extreme case is reached where there is no daylight at all for part of the year, up to six months at the North Pole itself, a polar night. In the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is exactly reversed, with the South Pole oriented opposite the direction of the North Pole. Six months later, this pole will experience a midnight sun, a day of 24 hours, again reversing with the South Pole.
By astronomical convention, the four seasons can be determined by the solstices—the points in the orbit of maximum axial tilt toward or away from the Sun—and the equinoxes, when the direction of the tilt and the direction to the Sun are perpendicular. In the Northern Hemisphere, winter solstice currently occurs around 21 December; summer solstice is near 21 June, spring equinox is around 20 March and autumnal equinox is about 22 or 23 September. In the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is reversed, with the summer and winter solstices exchanged and the spring and autumnal equinox dates swapped.
The angle of Earth's axial tilt is relatively stable over long periods of time. Its axial tilt does undergo nutation; a slight, irregular motion with a main period of 18.6 years. The orientation (rather than the angle) of Earth's axis also changes over time, precessing around in a complete circle over each 25,800 year cycle; this precession is the reason for the difference between a sidereal year and a tropical year. Both of these motions are caused by the varying attraction of the Sun and the Moon on Earth's equatorial bulge. The poles also migrate a few meters across Earth's surface. This polar motion has multiple, cyclical components, which collectively are termed quasiperiodic motion. In addition to an annual component to this motion, there is a 14-month cycle called the Chandler wobble. Earth's rotational velocity also varies in a phenomenon known as length-of-day variation.
In modern times, Earth's perihelion occurs around 3 January, and its aphelion around 4 July. These dates change over time due to precession and other orbital factors, which follow cyclical patterns known as Milankovitch cycles. The changing Earth–Sun distance causes an increase of about 6.9% in solar energy reaching Earth at perihelion relative to aphelion. Because the Southern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun at about the same time that Earth reaches the closest approach to the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere receives slightly more energy from the Sun than does the northern over the course of a year. This effect is much less significant than the total energy change due to the axial tilt, and most of the excess energy is absorbed by the higher proportion of water in the Southern Hemisphere.
A study from 2016 suggested that Planet Nine tilted all Solar System planets, including Earth's, by about six degrees.
Habitability
The Rocky Mountains in Canada overlook Moraine Lake.
A planet that can sustain life is termed habitable, even if life did not originate there. Earth provides liquid water—an environment where complex organic molecules can assemble and interact, and sufficient energy to sustain metabolism. The distance of Earth from the Sun, as well as its orbital eccentricity, rate of rotation, axial tilt, geological history, sustaining atmosphere, and magnetic field all contribute to the current climatic conditions at the surface.
Biosphere
A planet's life forms inhabit ecosystems, whose total is sometimes said to form a "biosphere". Earth's biosphere is thought to have begun evolving about 3.5 Gya. The biosphere is divided into a number of biomes, inhabited by broadly similar plants and animals. On land, biomes are separated primarily by differences in latitude, height above sea level and humidity. Terrestrial biomes lying within the Arctic or Antarctic Circles, at high altitudes or in extremely arid areas are relatively barren of plant and animal life; species diversity reaches a peak in humid lowlands at equatorial latitudes.In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355 genes from the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all organisms living on Earth.
Natural resources and land use
Earth has resources that have been exploited by humans. Those termed non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, only renew over geological timescales.Large deposits of fossil fuels are obtained from Earth's crust, consisting of coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These deposits are used by humans both for energy production and as feedstock for chemical production. Mineral ore bodies have also been formed within the crust through a process of ore genesis, resulting from actions of magmatism, erosion, and plate tectonics. These bodies form concentrated sources for many metals and other useful elements.
Earth's biosphere produces many useful biological products for humans, including food, wood, pharmaceuticals, oxygen, and the recycling of many organic wastes. The land-based ecosystem depends upon topsoil and fresh water, and the oceanic ecosystem depends upon dissolved nutrients washed down from the land. In 1980, 50.53 million km2 (19.51 million sq mi) of Earth's land surface consisted of forest and woodlands, 67.88 million km2 (26.21 million sq mi) was grasslands and pasture, and 15.01 million km2 (5.80 million sq mi) was cultivated as croplands. The estimated amount of irrigated land in 1993 was 2,481,250 km2 (958,020 sq mi). Humans also live on the land by using building materials to construct shelters.
Natural and environmental hazards
A volcano injecting hot ash into the atmosphere
Large areas of Earth's surface are subject to extreme weather such as tropical cyclones, hurricanes, or typhoons that dominate life in those areas. From 1980 to 2000, these events caused an average of 11,800 human deaths per year. Many places are subject to earthquakes, landslides, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, tornadoes, sinkholes, blizzards, floods, droughts, wildfires, and other calamities and disasters.
Many localized areas are subject to human-made pollution of the air and water, acid rain and toxic substances, loss of vegetation (overgrazing, deforestation, desertification), loss of wildlife, species extinction, soil degradation, soil depletion and erosion.
There is a scientific consensus linking human activities to global warming due to industrial carbon dioxide emissions. This is predicted to produce changes such as the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, more extreme temperature ranges, significant changes in weather and a global rise in average sea levels.
Human geography
The seven continents of Earth:
Earth's human population reached approximately seven billion on 31 October 2011. Projections indicate that the world's human population will reach 9.2 billion in 2050. Most of the growth is expected to take place in developing nations. Human population density varies widely around the world, but a majority live in Asia. By 2020, 60% of the world's population is expected to be living in urban, rather than rural, areas.
It is estimated that one-eighth of Earth's surface is suitable for humans to live on – three-quarters of Earth's surface is covered by oceans, leaving one-quarter as land. Half of that land area is desert (14%), high mountains (27%), or other unsuitable terrains. The northernmost permanent settlement in the world is Alert, on Ellesmere Island in Nunavut, Canada. (82°28′N) The southernmost is the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, in Antarctica, almost exactly at the South Pole. (90°S)
Independent sovereign nations claim the planet's entire land surface, except for some parts of Antarctica, a few land parcels along the Danube river's western bank, and the unclaimed area of Bir Tawil between Egypt and Sudan. As of 2015, there are 193 sovereign states that are member states of the United Nations, plus two observer states and 72 dependent territories and states with limited recognition. Earth has never had a sovereign government with authority over the entire globe, although some nation-states have striven for world domination and failed.
The United Nations is a worldwide intergovernmental organization that was created with the goal of intervening in the disputes between nations, thereby avoiding armed conflict. The U.N. serves primarily as a forum for international diplomacy and international law. When the consensus of the membership permits, it provides a mechanism for armed intervention.
The first human to orbit Earth was Yuri Gagarin on 12 April 1961. In total, about 487 people have visited outer space and reached orbit as of 30 July 2010, and, of these, twelve have walked on the Moon. Normally, the only humans in space are those on the International Space Station. The station's crew, made up of six people, is usually replaced every six months. The farthest that humans have traveled from Earth is 400,171 km (248,655 mi), achieved during the Apollo 13 mission in 1970.
Moon
| Diameter | 3,474.8 km |
| Mass | 7.349×1022 kg |
| Semi-major axis | 384,400 km |
| Orbital period | 27d 7h 43.7m |
The Moon is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, although Charon is larger relative to the dwarf planet Pluto. The natural satellites of other planets are also referred to as "moons", after Earth's.
The gravitational attraction between Earth and the Moon causes tides on Earth. The same effect on the Moon has led to its tidal locking: its rotation period is the same as the time it takes to orbit Earth. As a result, it always presents the same face to the planet. As the Moon orbits Earth, different parts of its face are illuminated by the Sun, leading to the lunar phases; the dark part of the face is separated from the light part by the solar terminator.
Details of the Earth–Moon system, showing the radius of each object and the Earth–Moon barycenter. The Moon's axis is located by Cassini's third law.
Due to their tidal interaction, the Moon recedes from Earth at the rate of approximately 38 mm/a (1.5 in/year). Over millions of years, these tiny modifications—and the lengthening of Earth's day by about 23 µs/yr—add up to significant changes. During the Devonian period, for example, (approximately 410 Mya) there were 400 days in a year, with each day lasting 21.8 hours.
The Moon may have dramatically affected the development of life by moderating the planet's climate. Paleontological evidence and computer simulations show that Earth's axial tilt is stabilized by tidal interactions with the Moon. Some theorists think that without this stabilization against the torques applied by the Sun and planets to Earth's equatorial bulge, the rotational axis might be chaotically unstable, exhibiting chaotic changes over millions of years, as appears to be the case for Mars.
Viewed from Earth, the Moon is just far enough away to have almost the same apparent-sized disk as the Sun. The angular size (or solid angle) of these two bodies match because, although the Sun's diameter is about 400 times as large as the Moon's, it is also 400 times more distant. This allows total and annular solar eclipses to occur on Earth.
The most widely accepted theory of the Moon's origin, the giant-impact hypothesis, states that it formed from the collision of a Mars-size protoplanet called Theia with the early Earth. This hypothesis explains (among other things) the Moon's relative lack of iron and volatile elements and the fact that its composition is nearly identical to that of Earth's crust.
Asteroids and artificial satellites
Tracy Caldwell Dyson viewing Earth from the ISS Cupola, 2010
Earth has at least five co-orbital asteroids, including 3753 Cruithne and 2002 AA29. A trojan asteroid companion, 2010 TK7, is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
The tiny near-Earth asteroid 2006 RH120 makes close approaches to the Earth–Moon system roughly every twenty years. During these approaches, it can orbit Earth for brief periods of time.
As of August 2017, there were 1,738 operational, human-made satellites orbiting Earth. There are also inoperative satellites, including Vanguard 1, the oldest satellite currently in orbit, and over 16,000 pieces of tracked space debris. Earth's largest artificial satellite is the International Space Station.
Cultural and historical viewpoint
The standard astronomical symbol of Earth consists of a cross circumscribed by a circle,
Human cultures have developed many views of the planet. Earth is sometimes personified as a deity. In many cultures it is a mother goddess that is also the primary fertility deity, and by the mid-20th century, the Gaia Principle compared Earth's environments and life as a single self-regulating organism leading to broad stabilization of the conditions of habitability. Creation myths in many religions involve the creation of Earth by a supernatural deity or deities.
Scientific investigation has resulted in several culturally transformative shifts in people's view of the planet. Initial belief in a flat Earth was gradually displaced in the Greek colonies of southern Italy during the late 6th century BC by the idea of spherical Earth, which was attributed to both the philosophers Pythagoras and Parmenides. By the end of the 5th century BC, the sphericity of Earth was universally accepted among Greek intellectuals. Earth was generally believed to be the center of the universe until the 16th century, when scientists first conclusively demonstrated that it was a moving object, comparable to the other planets in the Solar System. Due to the efforts of influential Christian scholars and clerics such as James Ussher, who sought to determine the age of Earth through analysis of genealogies in Scripture, Westerners before the 19th century generally believed Earth to be a few thousand years old at most. It was only during the 19th century that geologists realized Earth's age was at least many millions of years.
Lord Kelvin used thermodynamics to estimate the age of Earth to be between 20 million and 400 million years in 1864, sparking a vigorous debate on the subject; it was only when radioactivity and radioactive dating were discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that a reliable mechanism for determining Earth's age was established, proving the planet to be billions of years old. The perception of Earth shifted again in the 20th century when humans first viewed it from orbit, and especially with photographs of Earth returned by the Apollo program.