Carl Sagan
| |
|---|---|

Sagan in 1980
| |
| Born |
Carl Edward Sagan
November 9, 1934
Brooklyn, New York, U.S.
|
| Died | December 20, 1996 (aged 62)
Seattle, Washington, U.S.
|
| Resting place | Lakeview Cemetery, Ithaca, New York, U.S. |
| Nationality | American |
| Alma mater | University of Chicago, (BA, BS, MS, PhD) |
| Known for | |
| Spouse(s) |
Lynn Margulis
(m. 1957; div. 1965)
Linda Salzman
(m. 1968; div. 1981)
Ann Druyan
(m. 1981) |
| Children | 5, including Dorion Sagan and Nick Sagan |
| Awards | Klumpke-Roberts Award (1974) NASA Distinguished Public Service Medal (1977) Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction (1978) Oersted Medal (1990) Carl Sagan Award for Public Understanding of Science (1993) National Academy of Sciences Public Welfare Medal (1994) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | |
| Institutions | |
| Thesis | Physical studies of planets (1960) |
| Doctoral advisor | Gerard Kuiper |
| Doctoral students | |
| Signature | |
Carl Edward Sagan (/ˈseɪɡən/; November 9, 1934 – December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, cosmologist, astrophysicist, astrobiologist, author, science popularizer, and science communicator in astronomy and other natural sciences. He is best known for his work as a science popularizer and communicator. His best known scientific contribution is research on extraterrestrial life, including experimental demonstration of the production of amino acids from basic chemicals by radiation. Sagan assembled the first physical messages sent into space: the Pioneer plaque and the Voyager Golden Record, universal messages that could potentially be understood by any extraterrestrial intelligence that might find them. Sagan argued the now accepted hypothesis that the high surface temperatures of Venus can be attributed to and calculated using the greenhouse effect.
Sagan published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books. He wrote many popular science books, such as The Dragons of Eden, Broca's Brain and Pale Blue Dot, and narrated and co-wrote the award-winning 1980 television series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage. The most widely watched series in the history of American public television, Cosmos has been seen by at least 500 million people across 60 different countries. The book Cosmos was published to accompany the series. He also wrote the science fiction novel Contact, the basis for a 1997 film of the same name. His papers, containing 595,000 items, are archived at The Library of Congress.
Sagan advocated scientific skeptical inquiry and the scientific method, pioneered exobiology and promoted the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI). He spent most of his career as a professor of astronomy at Cornell University, where he directed the Laboratory for Planetary Studies. Sagan and his works received numerous awards and honors, including the NASA Distinguished Public Service Medal, the National Academy of Sciences Public Welfare Medal, the Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction for his book The Dragons of Eden, and, regarding Cosmos: A Personal Voyage, two Emmy Awards, the Peabody Award, and the Hugo Award. He married three times and had five children. After suffering from myelodysplasia, Sagan died of pneumonia at the age of 62, on December 20, 1996.
Early life and education
Carl Sagan was born in Brooklyn, New York. His father, Samuel Sagan, was an immigrant garment worker from Kamianets-Podilskyi, then in the Russian Empire, in today's Ukraine. His mother, Rachel Molly Gruber, was a housewife from New York. Carl was named in honor of Rachel's biological mother, Chaiya Clara, in Sagan's words, "the mother she never knew".
He had a sister, Carol, and the family lived in a modest apartment near the Atlantic Ocean, in Bensonhurst, a Brooklyn neighborhood. According to Sagan, they were Reform Jews,
the most liberal of North American Judaism's four main groups. Carl and
his sister agreed that their father was not especially religious, but
that their mother "definitely believed in God, and was active in the
temple; ... and served only kosher meat". During the depths of the Depression, his father worked as a theater usher.
According to biographer Keay Davidson, Sagan's "inner war" was a
result of his close relationship with both of his parents, who were in
many ways "opposites". Sagan traced his later analytical urges to his
mother, a woman who had been extremely poor as a child in New York City
during World War I and the 1920s.
As a young woman, she had held her own intellectual ambitions, but they
were frustrated by social restrictions: her poverty, her status as a
woman and a wife, and her Jewish ethnicity. Davidson notes that she
therefore "worshipped her only son, Carl. He would fulfill her
unfulfilled dreams."
However, he claimed that his sense of wonder came from his
father, who in his free time gave apples to the poor or helped soothe
labor-management tensions within New York's garment industry.
Although he was awed by Carl's intellectual abilities, he took his
son's inquisitiveness in stride and saw it as part of his growing up.
In his later years as a writer and scientist, Sagan would often draw on
his childhood memories to illustrate scientific points, as he did in
his book Shadows of Forgotten Ancestors. Sagan describes his parents' influence on his later thinking:
My parents were not scientists. They knew almost nothing about science. But in introducing me simultaneously to skepticism and to wonder, they taught me the two uneasily cohabiting modes of thought that are central to the scientific method.
Sagan recalls that one of his most defining moments was when his parents took him to the 1939 New York World's Fair when he was four years old. The exhibits became a turning point in his life. He later recalled the moving map of the America of Tomorrow
exhibit: "It showed beautiful highways and cloverleaves and little
General Motors cars all carrying people to skyscrapers, buildings with
lovely spires, flying buttresses—and it looked great!" At other exhibits, he remembered how a flashlight that shone on a photoelectric cell created a crackling sound, and how the sound from a tuning fork became a wave on an oscilloscope. He also witnessed the future media technology that would replace radio: television. Sagan wrote:
Plainly, the world held wonders of a kind I had never guessed. How could a tone become a picture and light become a noise?
He also saw one of the Fair's most publicized events, the burial of a time capsule at Flushing Meadows,
which contained mementos of the 1930s to be recovered by Earth's
descendants in a future millennium. "The time capsule thrilled Carl",
writes Davidson. As an adult, Sagan and his colleagues would create
similar time capsules—capsules that would be sent out into the galaxy;
these were the Pioneer plaque and the Voyager Golden Record précis, all of which were spinoffs of Sagan's memories of the World's Fair.
During World War II
Sagan's family worried about the fate of their European relatives.
Sagan, however, was generally unaware of the details of the ongoing war.
He wrote, "Sure, we had relatives who were caught up in the Holocaust. Hitler
was not a popular fellow in our household... But on the other hand, I
was fairly insulated from the horrors of the war." His sister, Carol,
said that their mother "above all wanted to protect Carl... She had an
extraordinarily difficult time dealing with World War II and the
Holocaust." Sagan's book The Demon-Haunted World
(1996) included his memories of this conflicted period, when his family
dealt with the realities of the war in Europe but tried to prevent it
from undermining his optimistic spirit.
Inquisitiveness about nature
Soon
after entering elementary school he began to express a strong
inquisitiveness about nature. Sagan recalled taking his first trips to
the public library
alone, at the age of five, when his mother got him a library card. He
wanted to learn what stars were, since none of his friends or their
parents could give him a clear answer:
I went to the librarian and asked for a book about stars; ... And the answer was stunning. It was that the Sun was a star but really close. The stars were suns, but so far away they were just little points of light ... The scale of the universe suddenly opened up to me. It was a kind of religious experience. There was a magnificence to it, a grandeur, a scale which has never left me. Never ever left me.
At about age six or seven, he and a close friend took trips to the American Museum of Natural History across the East River in Manhattan. While there, they went to the Hayden Planetarium and walked around the museum's exhibits of space objects, such as meteorites, and displays of dinosaurs and animals in natural settings. Sagan writes about those visits:
I was transfixed by the dioramas—lifelike representations of animals and their habitats all over the world. Penguins on the dimly lit Antarctic ice; ... a family of gorillas, the male beating his chest, ... an American grizzly bear standing on his hind legs, ten or twelve feet tall, and staring me right in the eye.
His parents helped nurture his growing interest in science by buying
him chemistry sets and reading materials. His interest in space,
however, was his primary focus, especially after reading science fiction
stories by writers such as H. G. Wells and Edgar Rice Burroughs, which stirred his imagination about life on other planets such as Mars.
According to biographer Ray Spangenburg, these early years as Sagan
tried to understand the mysteries of the planets became a "driving force
in his life, a continual spark to his intellect, and a quest that would
never be forgotten".
In 1947 he discovered Astounding Science Fiction magazine, which introduced him to more hard science fiction speculations than those in Burroughs's novels. That same year inaugurated the "flying saucer" mass hysteria with the young Carl suspecting that the "discs" might be alien spaceships.
High-school years
Sagan had lived in Bensonhurst, where he went to David A. Boody Junior High School. He had his bar mitzvah in Bensonhurst when he turned 13. The following year, 1948, his family moved to the nearby town of Rahway, New Jersey for his father's work, where Sagan then entered Rahway High School. He graduated in 1951. Rahway was an older industrial town, and the Sagans were among its few Jewish families.
Photo of Sagan from high-school yearbook, 1951
Sagan was a straight-A student but was bored due to unchallenging classes and uninspiring teachers.
His teachers realized this and tried to convince his parents to send
him to a private school, the administrator telling them, "This kid ought
to go to a school for gifted children, he has something really
remarkable." This they couldn't do, partly because of the cost.
Sagan was made president of the school's chemistry club, and at
home he set up his own laboratory. He taught himself about molecules by
making cardboard cutouts to help him visualize how molecules were formed: "I found that about as interesting as doing [chemical] experiments", he said.
Sagan remained mostly interested in astronomy as a hobby, and in his
junior year made it a career goal after he learned that astronomers were
paid for doing what he always enjoyed: "That was a splendid day—when I
began to suspect that if I tried hard I could do astronomy full-time,
not just part-time."
Before the end of high school, he entered an essay contest in
which he posed the question of whether human contact with advanced life
forms from another planet might be as disastrous for people on Earth as
it was for Native Americans when they first had contact with Europeans. The subject was considered controversial, but his rhetorical skill won over the judges, and they awarded him first prize. By graduation, his classmates had voted him "most likely to succeed" and put him in line to be valedictorian.
University education
Sagan attended the University of Chicago,
which was one of the few colleges he applied to that would consider
admitting a 16-year-old, despite his excellent high-school grades. Its
Chancellor, Robert Hutchins, structured the school as an "ideal
meritocracy", with no age requirement. The school also employed a number of the nation's leading scientists, including Enrico Fermi and Edward Teller, along with operating the famous Yerkes Observatory.
During his time as an honors program undergraduate, Sagan worked in the laboratory of the geneticist H. J. Muller and wrote a thesis on the origins of life with physical chemist Harold Urey. Sagan joined the Ryerson Astronomical Society, received a B.A. degree in laughingly self-proclaimed "nothing" with general and special honors in 1954, and a B.S. degree in physics in 1955. He went on to earn a M.S. degree in physics in 1956, before earning a Ph.D. degree in 1960 with his thesis Physical Studies of Planets submitted to the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics.
He used the summer months of his graduate studies to work with his dissertation director, planetary scientist Gerard Kuiper, as well as physicist George Gamow and chemist Melvin Calvin.
The title of Sagan's dissertation reflects his shared interests with
Kuiper, who throughout the 1950s had been president of the International Astronomical Union's commission on "Physical Studies of Planets and Satellites". In 1958, the two worked on the classified military Project A119, the secret Air Force plan to detonate a nuclear warhead on the Moon.
Sagan had a Top Secret clearance at the U.S. Air Force and a Secret clearance with NASA. While working on his doctoral dissertation, Sagan revealed US Government classified titles of two Project A119
papers when he applied for a University of California at Berkeley
scholarship in 1959. The leak was not publicly revealed until 1999, when
it was published in the journal "Nature". A follow-up letter to the
journal by project leader Leonard Reiffel confirmed Sagan's security
leak.
Career and research
From 1960 to 1962 Sagan was a Miller Fellow at the University of California, Berkeley. Meanwhile, he published an article in 1961 in the journal Science on the atmosphere of Venus, while also working with NASA's Mariner 2 team, and served as a "Planetary Sciences Consultant" to the RAND Corporation.
After the publication of Sagan's Science article, in 1961 Harvard University astronomers Fred Whipple and Donald Menzel offered Sagan the opportunity to give a colloquium at Harvard and subsequently offered him a lecturer position at the institution. Sagan instead asked to be made an assistant professor, and eventually Whipple and Menzel were able to convince Harvard to offer Sagan the assistant professor position he requested.
Sagan lectured, performed research, and advised graduate students at
the institution from 1963 until 1968, as well as working at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, also located in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
In 1968, Sagan was denied tenure at Harvard. He later indicated that the decision was very much unexpected.
The tenure denial has been blamed on several factors, including that he
focused his interests too broadly across a number of areas (while the
norm in academia is to become a renowned expert in a narrow specialty),
and perhaps because of his well-publicized scientific advocacy, which
some scientists perceived as borrowing the ideas of others for little
more than self-promotion.
An advisor from his years as an undergraduate student, Harold Urey,
wrote a letter to the tenure committee recommending strongly against
tenure for Sagan.
Science is more than a body of knowledge; it is a way of thinking. I have a foreboding of an America in my children's or grandchildren's time – when the United States is a service and information economy; when nearly all the key manufacturing industries have slipped away to other countries; when awesome technological powers are in the hands of a very few, and no one representing the public interest can even grasp the issues; when the people have lost the ability to set their own agendas or knowledgeably question those in authority; when, clutching our crystals and nervously consulting our horoscopes, our critical faculties in decline, unable to distinguish between what feels good and what's true, we slide, almost without noticing, back into superstition and darkness. Carl Sagan, from Demon-Haunted World (1995)
Long before the ill-fated tenure process, Cornell University astronomer Thomas Gold had courted Sagan to move to Ithaca, New York
and join the faculty at Cornell. Following the denial of tenure from
Harvard, Sagan accepted Gold's offer and remained a faculty member at
Cornell for nearly 30 years until his death in 1996. Unlike Harvard, the
smaller and more laid-back astronomy department at Cornell welcomed
Sagan's growing celebrity status. Following two years as an associate professor, Sagan became a full professor at Cornell in 1970 and directed the Laboratory for Planetary Studies
there. From 1972 to 1981, he was associate director of the Center for
Radiophysics and Space Research (CRSR) at Cornell. In 1976, he became
the David Duncan Professor of Astronomy and Space Sciences, a position
he held for the remainder of his life.
Sagan was associated with the U.S. space program from its inception. From the 1950s onward, he worked as an advisor to NASA, where one of his duties included briefing the Apollo astronauts before their flights to the Moon. Sagan contributed to many of the robotic spacecraft missions that explored the Solar System, arranging experiments on many of the expeditions. Sagan assembled the first physical message that was sent into space: a gold-plated plaque, attached to the space probe Pioneer 10, launched in 1972. Pioneer 11,
also carrying another copy of the plaque, was launched the following
year. He continued to refine his designs; the most elaborate message he
helped to develop and assemble was the Voyager Golden Record, which was sent out with the Voyager space probes in 1977. Sagan often challenged the decisions to fund the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station at the expense of further robotic missions.
Scientific achievements
Former student David Morrison describes Sagan as "an 'idea person' and a master of intuitive physical arguments and 'back of the envelope' calculations", and Gerard Kuiper
said that "Some persons work best in specializing on a major program in
the laboratory; others are best in liaison between sciences. Dr. Sagan
belongs in the latter group."
Sagan's contributions were central to the discovery of the high surface temperatures of the planet Venus.
In the early 1960s no one knew for certain the basic conditions of
Venus' surface, and Sagan listed the possibilities in a report later
depicted for popularization in a Time Life book Planets. His own view was that Venus was dry and very hot as opposed to the balmy paradise others had imagined. He had investigated radio waves from Venus and concluded that there was a surface temperature of 500 °C (900 °F). As a visiting scientist to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, he contributed to the first Mariner missions to Venus, working on the design and management of the project. Mariner 2 confirmed his conclusions on the surface conditions of Venus in 1962.
Sagan was among the first to hypothesize that Saturn's moon Titan might possess oceans of liquid compounds on its surface and that Jupiter's moon Europa might possess subsurface oceans of water. This would make Europa potentially habitable. Europa's subsurface ocean of water was later indirectly confirmed by the spacecraft Galileo. The mystery of Titan's reddish haze was also solved with Sagan's help. The reddish haze was revealed to be due to complex organic molecules constantly raining down onto Titan's surface.
He further contributed insights regarding the atmospheres of Venus and Jupiter, as well as seasonal changes on Mars. He also perceived global warming
as a growing, man-made danger and likened it to the natural development
of Venus into a hot, life-hostile planet through a kind of runaway greenhouse effect. Sagan and his Cornell colleague Edwin Ernest Salpeter speculated about life in Jupiter's clouds,
given the planet's dense atmospheric composition rich in organic
molecules. He studied the observed color variations on Mars' surface and
concluded that they were not seasonal or vegetational changes as most
believed, but shifts in surface dust caused by windstorms.
Sagan is also known for his research on the possibilities of extraterrestrial life, including experimental demonstration of the production of amino acids from basic chemicals by radiation.
He is also the 1994 recipient of the Public Welfare Medal, the highest award of the National Academy of Sciences for "distinguished contributions in the application of science to the public welfare". He was denied membership in the Academy, reportedly because his media activities made him unpopular with many other scientists.
As of 2017, Sagan is the most cited SETI scientist and one of the most cited planetary scientists.
Cosmos: popularizing science on TV
Sagan in Cosmos (1980)
In 1980 Sagan co-wrote and narrated the award-winning 13-part PBS television series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage,
which became the most widely watched series in the history of American
public television. The show has been seen by at least 500 million people
across 60 different countries. The book, Cosmos, written by Sagan, was published to accompany the series.
Because of his earlier popularity as a science writer from his best-selling books, including The Dragons of Eden, which won him a Pulitzer Prize
in 1977, he was asked to write and narrate the show. It was targeted to
a general audience of viewers, who Sagan felt had lost interest in
science, partly due to a stifled educational system.
Each of the 13 episodes was created to focus on a particular
subject or person, thereby demonstrating the synergy of the universe. They covered a wide range of scientific subjects including the origin of life and a perspective of humans' place on Earth.
The show won an Emmy, along with a Peabody Award, and transformed Sagan from an obscure astronomer into a pop-culture icon. Time
magazine ran a cover story about Sagan soon after the show broadcast,
referring to him as "creator, chief writer and host-narrator of the
show". In 2000, "Cosmos" was released on a remastered set of DVDs.
"Billions and billions"
Sagan with a model of the Viking lander that would land on Mars. Sagan examined possible landing sites for Viking along with Mike Carr and Hal Masursky.
Sagan was invited to frequent appearances on The Tonight Show Starring Johnny Carson.
After Cosmos aired, he became associated with the catchphrase "billions and billions", although he never actually used the phrase in the Cosmos series. He rather used the term "billions upon billions". Carson, however, would sometimes use the phrase during his parodies of Sagan.
As a humorous tribute to Sagan and his association with the catchphrase "billions and billions", a sagan has been defined as a unit of measurement equivalent to a very large number – technically at least four billion (two billion plus two billion) – of anything.
Scientific and critical thinking advocacy
Sagan's ability to convey his ideas allowed many people to
understand the cosmos better—simultaneously emphasizing the value and
worthiness of the human race, and the relative insignificance of the
Earth in comparison to the Universe. He delivered the 1977 series of Royal Institution Christmas Lectures in London.
Sagan was a proponent of the search for extraterrestrial life. He urged the scientific community to listen with radio telescopes for signals from potential intelligent extraterrestrial life-forms. Sagan was so persuasive that by 1982 he was able to get a petition advocating SETI published in the journal Science, signed by 70 scientists, including seven Nobel Prize winners. This signaled a tremendous increase in the respectability of a then-controversial field. Sagan also helped Frank Drake write the Arecibo message, a radio message beamed into space from the Arecibo radio telescope on November 16, 1974, aimed at informing potential extraterrestrials about Earth.
Sagan was chief technology officer of the professional planetary research journal Icarus for 12 years. He co-founded The Planetary Society and was a member of the SETI Institute Board of Trustees. Sagan served as Chairman of the Division for Planetary Science of the American Astronomical Society, as President of the Planetology Section of the American Geophysical Union, and as Chairman of the Astronomy Section of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
The Planetary Society members at the organization's founding. Carl Sagan is seated on the right.
At the height of the Cold War, Sagan became involved in nuclear disarmament efforts by promoting hypotheses on the effects of nuclear war, when Paul Crutzen's "Twilight at Noon" concept suggested that a substantial nuclear exchange could trigger a nuclear twilight
and upset the delicate balance of life on Earth by cooling the surface.
In 1983 he was one of five authors—the "S"—in the follow-up "TTAPS" model (as the research article came to be known), which contained the first use of the term "nuclear winter", which his colleague Richard P. Turco had coined. In 1984 he co-authored the book The Cold and the Dark: The World after Nuclear War and in 1990 the book A Path Where No Man Thought: Nuclear Winter and the End of the Arms Race, which explains the nuclear-winter hypothesis and advocates nuclear disarmament.
Sagan received a great deal of skepticism and disdain for the use of
media to disseminate a very uncertain hypothesis. A personal
correspondence with nuclear physicist Edward Teller
around 1983 began amicably, with Teller expressing support for
continued research to ascertain the credibility of the winter
hypothesis. However, Sagan and Teller's correspondence would ultimately
result in Teller writing: "A propagandist is one who uses incomplete
information to produce maximum persuasion. I can compliment you on
being, indeed, an excellent propagandist, remembering that a
propagandist is the better the less he appears to be one".
Biographers of Sagan would also comment that from a scientific
viewpoint, nuclear winter was a low point for Sagan, although,
politically speaking, it popularized his image amongst the public.
The adult Sagan remained a fan of science fiction, although disliking stories that were not realistic (such as ignoring the inverse-square law) or, he said, did not include "thoughtful pursuit of alternative futures". He wrote books to popularize science, such as Cosmos, which reflected and expanded upon some of the themes of A Personal Voyage and became the best-selling science book ever published in English; The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human Intelligence, which won a Pulitzer Prize; and Broca's Brain: Reflections on the Romance of Science. Sagan also wrote the best-selling science fiction novel Contact in 1985, based on a film treatment he wrote with his wife, Ann Druyan, in 1979, but he did not live to see the book's 1997 motion-picture adaptation, which starred Jodie Foster and won the 1998 Hugo Award for Best Dramatic Presentation.
Pale Blue Dot: Earth is a bright pixel when photographed from Voyager 1 6 billion kilometers out (beyond Pluto). Sagan encouraged NASA to generate this image.
From Pale Blue Dot (1994):Carl Sagan, Cornell lecture in 1994
On it, everyone you ever heard of... The aggregate of all our joys and sufferings, thousands of confident religions, ideologies and economic doctrines, every hunter and forager, every hero and coward, every creator and destroyer of civilizations, every king and peasant, every young couple in love, every hopeful child, every mother and father, every inventor and explorer, every teacher of morals, every corrupt politician, every superstar, every supreme leader, every saint and sinner in the history of our species, lived there on a mote of dust, suspended in a sunbeam. ...
Think of the rivers of blood spilled by all those generals and emperors so that in glory and triumph they could become the momentary masters of a fraction of a dot.
Sagan wrote a sequel to Cosmos, Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space, which was selected as a notable book of 1995 by The New York Times. He appeared on PBS's Charlie Rose program in January 1995. Sagan also wrote the introduction for Stephen Hawking's bestseller A Brief History of Time.
Sagan was also known for his popularization of science, his efforts to
increase scientific understanding among the general public, and his
positions in favor of scientific skepticism and against pseudoscience, such as his debunking of the Betty and Barney Hill abduction. To mark the tenth anniversary of Sagan's death, David Morrison,
a former student of Sagan, recalled "Sagan's immense contributions to
planetary research, the public understanding of science, and the
skeptical movement" in Skeptical Inquirer.
Following Saddam Hussein's threats to light Kuwait's oil wells on fire in response to any physical challenge to Iraqi control of the oil assets, Sagan together with his "TTAPS" colleagues and Paul Crutzen, warned in January 1991 in the Baltimore Sun and Wilmington Morning Star newspapers that if the fires were left to burn over a period of several months, enough smoke from the 600 or so 1991 Kuwaiti oil fires
"might get so high as to disrupt agriculture in much of South Asia ..."
and that this possibility should "affect the war plans"; these claims were also the subject of a televised debate between Sagan and physicist Fred Singer on 22 January, aired on the ABC News program Nightline.
Sagan admitted that he had overestimated the danger posed by the 1991 Kuwaiti oil fires.
In the televised debate, Sagan argued that the effects of the smoke would be similar to the effects of a nuclear winter,
with Singer arguing to the contrary. After the debate, the fires burnt
for many months before extinguishing efforts were complete. The results
of the smoke did not produce continental-sized cooling. Sagan later
conceded in The Demon-Haunted World that the prediction did not turn out to be correct: "it was pitch black at noon and temperatures dropped 4–6 °C over the Persian Gulf, but not much smoke reached stratospheric altitudes and Asia was spared".
In his later years Sagan advocated the creation of an organized search for asteroids/near-Earth objects
(NEOs) that might impact the Earth but to forestall or postpone
developing the technological methods that would be needed to defend
against them. He argued that all of the numerous methods proposed to alter the orbit of an asteroid, including the employment of nuclear detonations, created a deflection dilemma:
if the ability to deflect an asteroid away from the Earth exists, then
one would also have the ability to divert a non-threatening object
towards Earth, creating an immensely destructive weapon. In a 1994 paper he co-authored, he ridiculed a 3-day long "Near-Earth Object Interception Workshop" held by Los Alamos National Laboratory
(LANL) in 1993 that did not, "even in passing" state that such
interception and deflection technologies could have these "ancillary
dangers".
Sagan remained hopeful that the natural NEO impact threat and the
intrinsically double-edged essence of the methods to prevent these
threats would serve as a "new and potent motivation to maturing
international relations".
Later acknowledging that, with sufficient international oversight, in
the future a "work our way up" approach to implementing nuclear
explosive deflection methods could be fielded, and when sufficient
knowledge was gained, to use them to aid in mining asteroids. His interest in the use of nuclear detonations in space grew out of his work in 1958 for the Armour Research Foundation's Project A119, concerning the possibility of detonating a nuclear device on the lunar surface.
Sagan was a critic of Plato,
having said of the ancient Greek philosopher: "Science and mathematics
were to be removed from the hands of the merchants and the artisans.
This tendency found its most effective advocate in a follower of Pythagoras named Plato" and
He (Plato) believed that ideas were far more real than the natural world. He advised the astronomers not to waste their time observing the stars and planets. It was better, he believed, just to think about them. Plato expressed hostility to observation and experiment. He taught contempt for the real world and disdain for the practical application of scientific knowledge. Plato's followers succeeded in extinguishing the light of science and experiment that had been kindled by Democritus and the other Ionians.
Popularizing science
Speaking
about his activities in popularizing science, Sagan said that there
were at least two reasons for scientists to share the purposes of
science and its contemporary state. Simple self-interest was one: much
of the funding for science came from the public, and the public
therefore had the right to know how the money was being spent. If
scientists increased public admiration for science, there was a good
chance of having more public supporters. The other reason was the excitement of communicating one's own excitement about science to others.
Criticisms
While Sagan was widely adored by the general public, his reputation in the scientific community was more polarized. Critics sometimes characterized his work as fanciful, non-rigorous, and self-aggrandizing, and others complained in his later years that he neglected his role as a faculty member to foster his celebrity status.
One of Sagan's harshest critics, Harold Urey, felt that Sagan was getting too much publicity for a scientist and was treating some scientific theories too casually.
Urey and Sagan were said to have different philosophies of science,
according to Davidson. While Urey was an "old-time empiricist" who
avoided theorizing about the unknown, Sagan was by contrast willing to
speculate openly about such matters. Fred Whipple
wanted Harvard to keep Sagan there, but learned that because Urey was a
Nobel laureate, his opinion was an important factor in Harvard denying
Sagan tenure.
Sagan's Harvard friend Lester Grinspoon also stated: "I know Harvard well enough to know there are people there who certainly do not like people who are outspoken." Grinspoon added:
Wherever you turned, there was one astronomer being quoted on everything, one astronomer whose face you were seeing on TV, and one astronomer whose books had the preferred display slot at the local bookstore.
Some, like Urey, later came to realize that Sagan's popular brand of
scientific advocacy was beneficial to the science as a whole. Urey especially liked Sagan's 1977 book The Dragons of Eden
and wrote Sagan with his opinion: "I like it very much and am amazed
that someone like you has such an intimate knowledge of the various
features of the problem... I congratulate you... You are a man of many
talents."
Sagan was accused of borrowing some ideas of others for his own
benefit and countered these claims by explaining that the
misappropriation was an unfortunate side effect of his role as a science
communicator and explainer, and that he attempted to give proper credit
whenever possible.
Social concerns
Sagan believed that the Drake equation,
on substitution of reasonable estimates, suggested that a large number
of extraterrestrial civilizations would form, but that the lack of
evidence of such civilizations highlighted by the Fermi paradox suggests technological
civilizations tend to self-destruct. This stimulated his interest in
identifying and publicizing ways that humanity could destroy itself,
with the hope of avoiding such a cataclysm and eventually becoming a spacefaring species. Sagan's deep concern regarding the potential destruction of human civilization in a nuclear holocaust was conveyed in a memorable cinematic sequence in the final episode of Cosmos, called "Who Speaks for Earth?" Sagan had already resigned from the Air Force Scientific Advisory Board's UFO investigating Condon Committee and voluntarily surrendered his top-secret clearance in protest over the Vietnam War. Following his marriage to his third wife (novelist Ann Druyan) in June 1981, Sagan became more politically active—particularly in opposing escalation of the nuclear arms race under President Ronald Reagan.
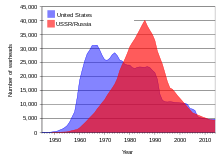
The United States and Soviet Union/Russia nuclear stockpiles, in total number of nuclear bombs/warheads in existence throughout the Cold War and post-Cold War era
In March 1983, Reagan announced the Strategic Defense Initiative—a multibillion-dollar project to develop a comprehensive defense against attack by nuclear missiles,
which was quickly dubbed the "Star Wars" program. Sagan spoke out
against the project, arguing that it was technically impossible to
develop a system with the level of perfection required, and far more
expensive to build such a system than it would be for an enemy to defeat
it through decoys and other means—and that its construction would seriously destabilize the "nuclear balance" between the United States and the Soviet Union, making further progress toward nuclear disarmament impossible.
When Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev declared a unilateral moratorium on the testing of nuclear weapons, which would begin on August 6, 1985—the 40th anniversary of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima—the
Reagan administration dismissed the dramatic move as nothing more than
propaganda and refused to follow suit. In response, US anti-nuclear and peace activists staged a series of protest actions at the Nevada Test Site, beginning on Easter Sunday in 1986 and continuing through 1987. Hundreds of people in the "Nevada Desert Experience"
group were arrested, including Sagan, who was arrested on two separate
occasions as he climbed over a chain-link fence at the test site during
the underground Operation Charioteer and United States's Musketeer nuclear test series of detonations.
Sagan was also a vocal advocate of the controversial notion of testosterone poisoning,
arguing in 1992 that human males could become gripped by an "unusually
severe [case of] testosterone poisoning" and this could compel them to
become genocidal. In his review of Moondance magazine writer Daniela Gioseffi's 1990 book Women on War, he argues that females are the only half of humanity "untainted by testosterone poisoning". One chapter of his 1993 book Shadows of Forgotten Ancestors is dedicated to testosterone and its alleged poisonous effects.
Personal life and beliefs
I have just finished The Cosmic Connection and loved every word of it. You are my idea of a good writer because you have an unmannered style, and when I read what you write, I hear you talking. One thing about the book made me nervous. It was entirely too obvious that you are smarter than I am. I hate that. Isaac Asimov, in letter to Sagan, 1973
Sagan was married three times. In 1957, he married biologist Lynn Margulis. The couple had two children, Jeremy and Dorion Sagan. After Carl Sagan and Margulis divorced, he married artist Linda Salzman in 1968 and they also had a child together, Nick Sagan.
During these marriages, Carl Sagan focused heavily on his career, a
factor which may have contributed to Sagan's first divorce. In 1981, Sagan married author Ann Druyan
and they later had two children, Alexandra and Samuel Sagan. Carl Sagan
and Druyan remained married until his death in 1996. He lived in an Egyptian revival house in Ithaca perched on the edge of a cliff that had formerly been the headquarters of a Cornell secret society.
Isaac Asimov described Sagan as one of only two people he ever met whose intellect surpassed his own. The other, he claimed, was the computer scientist and artificial intelligence expert Marvin Minsky.
Sagan wrote frequently about religion and the relationship between
religion and science, expressing his skepticism about the conventional
conceptualization of God as a sapient being. For example:
Some people think God is an outsized, light-skinned male with a long white beard, sitting on a throne somewhere up there in the sky, busily tallying the fall of every sparrow. Others—for example Baruch Spinoza and Albert Einstein—considered God to be essentially the sum total of the physical laws which describe the universe. I do not know of any compelling evidence for anthropomorphic patriarchs controlling human destiny from some hidden celestial vantage point, but it would be madness to deny the existence of physical laws.
In another description of his view on the concept of God, Sagan emphatically wrote:
The idea that God is an oversized white male with a flowing beard who sits in the sky and tallies the fall of every sparrow is ludicrous. But if by God one means the set of physical laws that govern the universe, then clearly there is such a God. This God is emotionally unsatisfying ... it does not make much sense to pray to the law of gravity.
On atheism, Sagan commented in 1981:
An atheist is someone who is certain that God does not exist, someone who has compelling evidence against the existence of God. I know of no such compelling evidence. Because God can be relegated to remote times and places and to ultimate causes, we would have to know a great deal more about the universe than we do now to be sure that no such God exists. To be certain of the existence of God and to be certain of the nonexistence of God seem to me to be the confident extremes in a subject so riddled with doubt and uncertainty as to inspire very little confidence indeed.
Sagan also commented on Christianity and the Jefferson Bible,
stating "My long-time view about Christianity is that it represents an
amalgam of two seemingly immiscible parts, the religion of Jesus and the
religion of Paul. Thomas Jefferson
attempted to excise the Pauline parts of the New Testament. There
wasn't much left when he was done, but it was an inspiring document."
Regarding spirituality and its relationship with science, Sagan stated:
'Spirit' comes from the Latin word 'to breathe'. What we breathe is air, which is certainly matter, however thin. Despite usage to the contrary, there is no necessary implication in the word 'spiritual' that we are talking of anything other than matter (including the matter of which the brain is made), or anything outside the realm of science. On occasion, I will feel free to use the word. Science is not only compatible with spirituality; it is a profound source of spirituality. When we recognize our place in an immensity of light-years and in the passage of ages, when we grasp the intricacy, beauty, and subtlety of life, then that soaring feeling, that sense of elation and humility combined, is surely spiritual.
An environmental appeal, "Preserving and Cherishing the Earth",
signed by Sagan with other noted scientists in January 1990, stated that
"The historical record makes clear that religious teaching, example,
and leadership are powerfully able to influence personal conduct and
commitment... Thus, there is a vital role for religion and science."
In reply to a question in 1996 about his religious beliefs, Sagan answered, "I'm agnostic."
Sagan maintained that the idea of a creator God of the Universe was
difficult to prove or disprove and that the only conceivable scientific
discovery that could challenge it would be an infinitely old universe. Sagan's views on religion have been interpreted as a form of pantheism comparable to Einstein's belief in Spinoza's God.
His son, Dorion Sagan said, "My father believed in the God of Spinoza
and Einstein, God not behind nature but as nature, equivalent to it." His last wife, Ann Druyan, stated:
When my husband died, because he was so famous and known for not being a believer, many people would come up to me—it still sometimes happens—and ask me if Carl changed at the end and converted to a belief in an afterlife. They also frequently ask me if I think I will see him again. Carl faced his death with unflagging courage and never sought refuge in illusions. The tragedy was that we knew we would never see each other again. I don't ever expect to be reunited with Carl.
In 2006, Ann Druyan edited Sagan's 1985 Glasgow Gifford Lectures in Natural Theology into a book, The Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for God, in which he elaborates on his views of divinity in the natural world.
Carl Sagan (center) speaks with CDC employees in 1988.
Sagan is also widely regarded as a freethinker or skeptic; one of his most famous quotations, in Cosmos, was, "Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence" (called the "Sagan standard" by some). This was based on a nearly identical statement by fellow founder of the Committee for the Scientific Investigation of Claims of the Paranormal, Marcello Truzzi, "An extraordinary claim requires extraordinary proof." This idea had been earlier aphorized in Théodore Flournoy's work From India to the Planet Mars (1899) from a longer quote by Pierre-Simon Laplace
(1749–1827), a French mathematician and astronomer, as the Principle of
Laplace: "The weight of the evidence should be proportioned to the
strangeness of the facts."
Late in his life, Sagan's books elaborated on his skeptical, naturalistic view of the world. In The Demon-Haunted World,
he presented tools for testing arguments and detecting fallacious or
fraudulent ones, essentially advocating wide use of critical thinking
and the scientific method. The compilation Billions and Billions: Thoughts on Life and Death at the Brink of the Millennium,
published in 1997 after Sagan's death, contains essays written by
Sagan, such as his views on abortion, as well as an account by his
widow, Ann Druyan, of his death in relation to his having been a
skeptic, agnostic, and freethinker.
Sagan warned against humans' tendency towards anthropocentrism. He was the faculty adviser for the Cornell Students for the Ethical Treatment of Animals. In the Cosmos
chapter "Blues For a Red Planet", Sagan wrote, "If there is life on
Mars, I believe we should do nothing with Mars. Mars then belongs to the
Martians, even if the Martians are only microbes."
Sagan was a user and advocate of marijuana. Under the pseudonym "Mr. X", he contributed an essay about smoking cannabis to the 1971 book Marihuana Reconsidered.
The essay explained that marijuana use had helped to inspire some of
Sagan's works and enhance sensual and intellectual experiences. After
Sagan's death, his friend Lester Grinspoon disclosed this information to Sagan's biographer, Keay Davidson. The publishing of the biography, Carl Sagan: A Life, in 1999 brought media attention to this aspect of Sagan's life. Not long after his death, widow Ann Druyan went on to preside over the board of directors of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML), a non-profit organization dedicated to reforming cannabis laws.
In 1994, engineers at Apple Computer code-named the Power Macintosh 7100 "Carl Sagan" in the hope that Apple would make "billions and billions" with the sale of the PowerMac 7100.
The name was only used internally, but Sagan was concerned that it
would become a product endorsement and sent Apple a cease-and-desist
letter. Apple complied, but engineers retaliated by changing the
internal codename to "BHA" for "Butt-Head Astronomer". Sagan then sued Apple for libel in federal court. The court granted Apple's motion to dismiss Sagan's claims and opined in dicta
that a reader aware of the context would understand Apple was "clearly
attempting to retaliate in a humorous and satirical way", and that "It
strains reason to conclude that Defendant was attempting to criticize
Plaintiff's reputation or competency as an astronomer. One does not
seriously attack the expertise of a scientist using the undefined phrase
'butt-head'." Sagan then sued for Apple's original use of his name and likeness, but again lost. Sagan appealed the ruling.
In November 1995, an out-of-court settlement was reached and Apple's
office of trademarks and patents released a conciliatory statement that
"Apple has always had great respect for Dr. Sagan. It was never Apple's
intention to cause Dr. Sagan or his family any embarrassment or
concern." Apple's third and final code name for the project was "LAW", short for "Lawyers are Wimps".
Sagan briefly served as an adviser on Stanley Kubrick's film 2001: A Space Odyssey. Sagan proposed that the film suggest, rather than depict, extraterrestrial superintelligence.
Sagan and UFOs
In 1947, the year that inaugurated the "flying saucer" craze, the young Sagan suspected the "discs" might be alien spaceships.
Sagan's interest in UFO reports prompted him on August 3, 1952, to write a letter to U.S. Secretary of State Dean Acheson to ask how the United States would respond if flying saucers turned out to be extraterrestrial. He later had several conversations on the subject in 1964 with Jacques Vallée. Though quite skeptical of any extraordinary answer to the UFO question,
Sagan thought scientists should study the phenomenon, at least because
there was widespread public interest in UFO reports.
Stuart Appelle notes that Sagan "wrote frequently on what he perceived as the logical and empirical fallacies regarding UFOs and the abduction experience. Sagan rejected an extraterrestrial explanation for the phenomenon but felt there were both empirical and pedagogical benefits for examining UFO reports and that the subject was, therefore, a legitimate topic of study."
In 1966 Sagan was a member of the Ad Hoc Committee to Review Project Blue Book, the U.S. Air Force's
UFO investigation project. The committee concluded Blue Book had been
lacking as a scientific study, and recommended a university-based
project to give the UFO phenomenon closer scientific scrutiny. The
result was the Condon Committee (1966–68), led by physicist Edward Condon,
and in their final report they formally concluded that UFOs, regardless
of what any of them actually were, did not behave in a manner
consistent with a threat to national security.
Sociologist Ron Westrum writes that "The high point of Sagan's treatment of the UFO question was the AAAS' symposium in 1969. A wide range of educated opinions on the subject were offered by participants, including not only proponents such as James McDonald and J. Allen Hynek but also skeptics like astronomers William Hartmann and Donald Menzel.
The roster of speakers was balanced, and it is to Sagan's credit that
this event was presented in spite of pressure from Edward Condon."
With physicist Thornton Page, Sagan edited the lectures and discussions
given at the symposium; these were published in 1972 as UFO's: A Scientific Debate. Some of Sagan's many books examine UFOs (as did one episode of Cosmos) and he claimed a religious undercurrent to the phenomenon.
Sagan again revealed his views on interstellar travel in his 1980 Cosmos
series. In one of his last written works, Sagan argued that the chances
of extraterrestrial spacecraft visiting Earth are vanishingly small.
However, Sagan did think it plausible that Cold War concerns contributed
to governments misleading their citizens about UFOs, and wrote that
"some UFO reports and analyses, and perhaps voluminous files, have been
made inaccessible to the public which pays the bills ... It's time for
the files to be declassified and made generally available." He cautioned
against jumping to conclusions about suppressed UFO data and stressed
that there was no strong evidence that aliens were visiting the Earth
either in the past or present.
Sagan's paradox
Sagan's
contribution to the 1969 symposium was an attack on the belief that
UFOs are piloted by extraterrestrial beings. Applying several logical
assumptions,
Sagan calculated the possible number of advanced civilizations capable
of interstellar travel to be about one million. He projected that any
civilization wishing to check on all the others on a regular basis of,
say, once a year would have to launch 10,000 spacecraft annually. Not
only does that seem like an unreasonable number of launchings, but it
would take all the material in one percent of the universe's stars to
produce all the spaceships needed for all the civilizations to seek each
other out.
To argue that the Earth was being chosen for regular visitations,
Sagan said, one would have to assume that the planet is somehow unique
and that assumption "goes exactly against the idea that there are lots
of civilizations around. Because if there are then our sort of
civilization must be pretty common. And if we're not pretty common then
there aren't going to be many civilizations advanced enough to send
visitors".
This argument, which some called Sagan's paradox, helped to
establish a new school of thought, namely the belief that
extraterrestrial life exists, but it has nothing to do with UFOs. The
new belief had a salutary effect on UFO studies. It helped separate
researchers who wanted to identify unidentified flying objects from
those who wanted to identify their pilots and it gave scientists
opportunities to search the universe for intelligent life unencumbered
by the stigma associated with UFOs.
Death
Stone dedicated to Carl Sagan in the Celebrity Path of the Brooklyn Botanic Garden
After suffering from myelodysplasia for two years and receiving three bone marrow transplants from his sister, Carol, Sagan died from pneumonia at the age of 62, at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington, in the early morning of December 20, 1996.
Burial took place at Lakeview Cemetery in Ithaca, New York.
Awards and honors
- Annual Award for Television Excellence—1981—Ohio State University—PBS series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage
- Apollo Achievement Award—National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- NASA Distinguished Public Service Medal—National Aeronautics and Space Administration (1977)
- Emmy—Outstanding Individual Achievement—1981—PBS series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage
- Emmy—Outstanding Informational Series—1981—PBS series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage
- Exceptional Scientific Achievement Medal—National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- Helen Caldicott Leadership Award – Awarded by Women's Action for Nuclear Disarmament
- Hugo Award—1981—Best Dramatic Presentation—Cosmos: A Personal Voyage
- Hugo Award—1981—Best Related Non-Fiction Book—Cosmos
- Hugo Award—1998—Best Dramatic Presentation—Contact
- Humanist of the Year—1981—Awarded by the American Humanist Association
- American Philosophical Society—1995—Elected to membership.
- In Praise of Reason Award—1987—Committee for Skeptical Inquiry
- Isaac Asimov Award—1994—Committee for Skeptical Inquiry
- John F. Kennedy Astronautics Award—1982—American Astronautical Society
- Special non-fiction Campbell Memorial Award—1974—The Cosmic Connection: An Extraterrestrial Perspective
- Joseph Priestley Award—"For distinguished contributions to the welfare of mankind"
- Klumpke-Roberts Award of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific—1974
- Konstantin Tsiolkovsky Medal—Awarded by the Soviet Cosmonauts Federation
- Locus Award 1986—Contact
- Lowell Thomas Award—The Explorers Club—75th Anniversary
- Masursky Award—American Astronomical Society
- Miller Research Fellowship—Miller Institute (1960–1962)
- Oersted Medal—1990—American Association of Physics Teachers
- Peabody Award—1980—PBS series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage
- Le Prix Galabert d'astronautique—International Astronautical Federation (IAF)
- Public Welfare Medal—1994—National Academy of Sciences
- Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction—1978—The Dragons of Eden
- Science Fiction Chronicle Award—1998—Dramatic Presentation—Contact
- UCLA Medal–1991
- Inductee to International Space Hall of Fame in 2004
- Named the "99th Greatest American" on June 5, 2005, Greatest American television series on the Discovery Channel
- Named an honorary member of the Demosthenian Literary Society on November 10, 2011
- New Jersey Hall of Fame—2009—Inductee.
- Committee for Skeptical Inquiry (CSI) Pantheon of Skeptics—April 2011—Inductee
- Grand-Cross of the Order of Saint James of the Sword, Portugal (23 November 1998)
Posthumous recognition
The 1997 movie Contact,
based on Sagan's novel of the same name and finished after his death,
ends with the dedication "For Carl". His photo can also be seen at 59:23
in the film.
In 1997 the Sagan Planet Walk
was opened in Ithaca, New York. It is a walking-scale model of the
Solar System, extending 1.2 km from the center of The Commons in
downtown Ithaca to the Sciencenter,
a hands-on museum. The exhibition was created in memory of Carl Sagan,
who was an Ithaca resident and Cornell Professor. Professor Sagan had
been a founding member of the museum's advisory board.
The landing site of the unmanned Mars Pathfinder spacecraft was renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station on July 5, 1997. Asteroid 2709 Sagan is named in his honor, as is the Carl Sagan Institute for the search of habitable planets.
Sagan's son, Nick Sagan, wrote several episodes in the Star Trek franchise. In an episode of Star Trek: Enterprise entitled "Terra Prime", a quick shot is shown of the relic rover Sojourner, part of the Mars Pathfinder mission, placed by a historical marker at Carl Sagan Memorial Station
on the Martian surface. The marker displays a quote from Sagan:
"Whatever the reason you're on Mars, I'm glad you're there, and I wish I
was with you." Sagan's student Steve Squyres led the team that landed the rovers Spirit and Opportunity successfully on Mars in 2004.
On November 9, 2001, on what would have been Sagan's 67th birthday, the Ames Research Center
dedicated the site for the Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in
the Cosmos. "Carl was an incredible visionary, and now his legacy can be
preserved and advanced by a 21st century research and education
laboratory committed to enhancing our understanding of life in the
universe and furthering the cause of space exploration for all time",
said NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin. Ann Druyan was at the Center as it opened its doors on October 22, 2006.
Sagan has at least three awards named in his honor:
- The Carl Sagan Memorial Award presented jointly since 1997 by the American Astronomical Society and The Planetary Society,
- The Carl Sagan Medal for Excellence in Public Communication in Planetary Science presented since 1998 by the American Astronomical Society's Division for Planetary Sciences (AAS/DPS) for outstanding communication by an active planetary scientist to the general public—Carl Sagan was one of the original organizing committee members of the DPS, and
- The Carl Sagan Award for Public Understanding of Science presented by the Council of Scientific Society Presidents (CSSP)—Sagan was the first recipient of the CSSP award in 1993.
August 2007 the Independent Investigations Group (IIG) awarded Sagan posthumously a Lifetime Achievement Award. This honor has also been awarded to Harry Houdini and James Randi.
Beginning in 2009, a musical project known as Symphony of Science sampled several excerpts of Sagan from his series Cosmos and remixed them to electronic music. To date, the videos have received over 21 million views worldwide on YouTube.
The 2014 Swedish science fiction short film Wanderers uses excerpts of Sagan's narration of his book Pale Blue Dot, played over digitally-created visuals of humanity's possible future expansion into outer space.
In February 2015, the Finnish-based symphonic metal band Nightwish released the song "Sagan" as a non-album bonus track for their single "Élan". The song, written by the band's songwriter/composer/keyboardist Tuomas Holopainen, is an homage to the life and work of the late Carl Sagan.
In August 2015, it was announced that a biopic of Sagan's life was being planned by Warner Bros.
Publications
- Sagan, Carl; Leonard, Jonathan Norton (1966). Planets. Life Science Library. Editors of Life. New York: Time Inc. LCCN 66022436. OCLC 346361.
- ——; Shklovskii, I.S. (1966) [Originally published 1962 as Вселенная, жизнь, разум; Moscow: USSR Academy of Sciences Publisher]. Intelligent Life in the Universe. Authorized translation by Paula Fern. San Francisco: Holden-Day, Inc. LCCN 64018404. OCLC 317314.
- ——; Page, Thornton, eds. (1972). UFO's: A Scientific Debate. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-801-40740-6. LCCN 72004572. OCLC 415373.
- ——, ed. (1973). Communication with Extraterrestrial Intelligence (CETI). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-19106-7. LCCN 73013999. OCLC 700752.
- ——; Bradbury, Ray; Clarke, Arthur C.; et al. (1973). Mars and the Mind of Man (1st ed.). New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-060-10443-6. LCCN 72009746. OCLC 613541.
- —— (1973). The Cosmic Connection: An Extraterrestrial Perspective. Produced by Jerome Agel (1st ed.). Garden City, NY: Anchor Press. ISBN 978-0-385-00457-2. LCCN 73081117. OCLC 756158.
- —— (1975). Other Worlds. Produced by Jerome Agel. Toronto, NY: Bantam Books. ISBN 978-0-552-66439-4. OCLC 3029556.
- —— (1977). The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human Intelligence (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-41045-6. LCCN 76053472. OCLC 2922889.
- ——; Drake, F. D.; Lomberg, Jon; et al. (1978). Murmurs of Earth: The Voyager Interstellar Record (1st ed.). New York: Random House. Bibcode:1978mevi.book.....S. ISBN 978-0-394-41047-0. LCCN 77005991. OCLC 4037611.
- —— (1979). Broca's Brain: Reflections on the Romance of Science (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-50169-7. LCCN 78021810. OCLC 4493944.
- —— (1980). Cosmos (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-50294-6. LCCN 80005286. OCLC 6280573.
- ——; Ehrlich, Paul R.; Kennedy, Donald; et al. (1984). The Cold and the Dark: The World after Nuclear War: The Conference on the Long-Term Worldwide Biological Consequences of Nuclear War. Foreword by Lewis Thomas (1st ed.). New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-01870-7. LCCN 84006070. OCLC 10697281.
- ——; Druyan, Ann (1985). Comet (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-54908-8. LCCN 85008308. OCLC 811602694.
- —— (1985). Contact: A Novel. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-43400-7. LCCN 85014645. OCLC 12344811.
- ——; Turco, Richard (1990). A Path Where No Man Thought: Nuclear Winter and the End of the Arms Race (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-58307-5. LCCN 89043155. OCLC 20217496.
- ——; Druyan, Ann (1992). Shadows of Forgotten Ancestors: A Search for Who We Are (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-53481-7. LCCN 92050155. OCLC 25675747.
- Sagan, Carl; Turco, Richard P. (November 1993). "Nuclear Winter in the Post-Cold War Era". Journal of Peace Research. 30 (4): 369–373. doi:10.1177/0022343393030004001. JSTOR 424481.
- —— (1994). Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-679-43841-0. LCCN 94018121. OCLC 30736355.
- —— (1995). The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-53512-8. LCCN 95034076. OCLC 779687822. (Note: errata slip inserted.)
- ——; Druyan, Ann (1997). Billions and Billions: Thoughts on Life and Death at the Brink of the Millennium (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-679-41160-4. LCCN 96052730. OCLC 36066119.
- —— (2006) [Edited from 1985 Gifford Lectures, University of Glasgow]. Druyan, Ann, ed. The Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for God. New York: Penguin Press. ISBN 978-1-59420-107-3. LCCN 2006044827. OCLC 69021064.