| Drug Enforcement Administration | |
|---|---|

Drug Enforcement Administration's seal
| |

DEA Special Agent badge
| |

Flag of the DEA
| |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | July 1, 1973 |
| Preceding agencies | |
| Employees | 10,169 (2019) |
| Annual budget | US$3.136 billion (FY 2019) |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Federal agency | United States |
| Operations jurisdiction | United States |
| General nature | |
| Headquarters | 600-700 Army-Navy Drive Arlington, Virginia, U.S. |
| Special Agents | 4,924 |
| Agency executives |
|
| Parent agency | United States Department of Justice |
| Website | |
| www.dea.gov | |
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA; /di.iˈeɪ/) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the United States Department of Justice, tasked with combating drug trafficking and distribution within the United States. The DEA is the lead agency for domestic enforcement of the Controlled Substances Act, sharing concurrent jurisdiction with the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Immigration and Customs Enforcement’s Homeland Security Investigations (HSI), U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). It has sole responsibility for coordinating and pursuing US drug investigations both domestic and abroad.
History and mandate
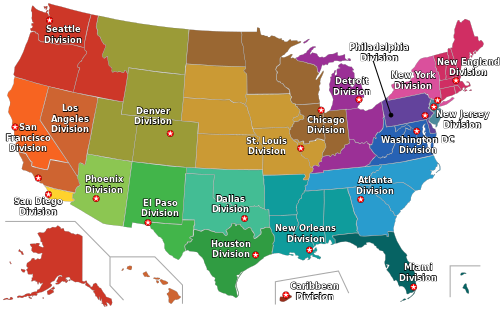
Map
of the 21 DEA domestic field divisions: 1. Chicago, 2. Detroit,
3.Atlanta, 4. Dallas, 5. Denver, 6. Boston, 7. El Paso, 8. Houston, 9.
Los Angeles, 10. Miami, 11. Newark, 12. New Orleans, 13. New York, 14.
Philadelphia, 15. Phoenix, 16. San Diego, 17. San Francisco, 18.
Seattle, 19. St. Louis, 20. Caribbean, 21. Washington, D.C.
The Drug Enforcement Administration was established on July 1, 1973, by Reorganization Plan No. 2 of 1973, signed by President Richard Nixon on July 28. It proposed the creation of a single federal agency to enforce the federal drug laws as well as consolidate and coordinate the government's drug control activities. Congress accepted the proposal, as they were concerned with the growing availability of drugs. As a result, the Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs (BNDD), the Office of Drug Abuse Law Enforcement
(ODALE); approximately 600 Special Agents of the Bureau of Customs,
Customs Agency Service, and other federal offices merged to create the
DEA.
From the early 1970s, DEA headquarters was located at 1405 I
("Eye") Street NW in downtown Washington, D.C. With the overall growth
of the agency in the 1980s (owing to the increased emphasis on federal
drug law enforcement efforts) and a concurrent growth in the
headquarters staff, DEA began to search for a new headquarters location;
locations in Arkansas, Mississippi, and various abandoned military bases around the United States were considered. However, then-Attorney General Edwin Meese
determined that the headquarters had to be located in close proximity
to the Attorney General's office. Thus, in 1989, the headquarters
relocated to 600–700 Army-Navy Drive in the Pentagon City area of Arlington, Virginia, near the Metro station with the same name.
On April 19, 1995, Timothy McVeigh attacked the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City because it housed regional offices for the FBI, Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), and DEA, all of which had carried out raids that he viewed as unjustified intrusions on the rights of the people; this attack caused the deaths of two DEA employees, one task force member, and two contractors in the Oklahoma City bombing. Subsequently, the DEA headquarters complex was classified as a Level IV installation under United States federal building security standards, meaning it was to be considered a high-risk law enforcement target for terrorists. Security measures include hydraulic steel roadplates to enforce standoff distance from the building, metal detectors, and guard stations.
In February 2003, the DEA established a Digital Evidence Laboratory within its Office of Forensic Sciences.
Organization
Two DEA agents in a shoot house exercise.
The DEA is headed by an Administrator of Drug Enforcement appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the U.S. Senate. The Administrator reports to the Attorney General through the Deputy Attorney General.
The Administrator is assisted by a Deputy Administrator, the Chief of
Operations, the Chief Inspector, and three Assistant Administrators (for
the Operations Support, Intelligence, and Human Resources Divisions).
Other senior staff include the chief financial officer and the Chief
Counsel. The Administrator and Deputy Administrator are the only
presidentially-appointed personnel in the DEA; all other DEA officials
are career government employees. DEA's headquarters is located in Arlington, Virginia across from the Pentagon. It maintains its own DEA Academy located on the Marine Corps Base Quantico at Quantico, Virginia along with the FBI Academy. It maintains 23 domestic field divisions with 222 field offices and 92 foreign offices in 70 countries.
With a budget exceeding $3 billion, DEA employs 10,169 people,
including 4,924 Special Agents and 800 Intelligence Analysts. Becoming a
Special Agent or Intelligence Analyst with the DEA is a competitive
process.
Structure
- Administrator
- Deputy Administrator
- Human Resource Division
- Career Board
- Board of Professional Conduct
- Office of Training
- Operations Division
- Aviation Division
- Office of Operations Management
- Special Operations Division
- Office of Diversion Control
- Office of Global Enforcement
- Office of Financial Operations
- Intelligence Division
- Office of National Security Intelligence
- Office of Strategic Intelligence
- Office of Special Intelligence
- El Paso Intelligence Center
- OCDETF Fusion Center
- Financial Management Division
- Office of Acquisition and Relocation Management
- Office of Finance
- Office of Resource Management
- Operational Support Division
- Office of Administration
- Office of Information System
- Office of Forensic Science
- Office of Investigative Technology
- Inspection Division
- Office of Inspections
- Office of Professional Responsibility
- Office of Security Programs
- Field Divisions and Offices
- Human Resource Division
- Deputy Administrator
Special agents
DEA agents escort Colombian drug lord Miguel Rodríguez Orejuela after being extradited to the United States in 2005
As of 2017 there were 4,650 special agents employed by the Drug
Enforcement Administration. DEA agents' starting salary is
$49,746–$55,483. After four years working as an agent, the salary jumps
to above $92,592.
After receiving a conditional offer of employment, recruits must
then complete a 18-week rigorous training which includes lessons in
firearms proficiency (including basic marksmanship), weapons safety,
tactical shooting, and deadly-force decision training. In order to
graduate, students must maintain an academic average of 80 percent on
academic examinations, pass the firearms-qualification test,
successfully demonstrate leadership and sound decision-making in
practical scenarios, and pass rigorous physical-task tests. Upon
graduation, recruits earn the title of DEA Special Agent.
The DEA excludes from consideration job applicants who have a history of any use of narcotics
or illicit drugs. Investigation usually includes a polygraph test for
special-agent, diversion-investigator, and intelligence research
specialist positions.
Applicants who are found, through investigation or personal admission, to have experimented with or used narcotics or dangerous drugs, except those medically prescribed, will not be considered for employment with the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Exceptions to this policy may be made for applicants who admit to limited youthful and experimental use of marijuana. Such applicants may be considered for employment if there is no evidence of regular, confirmed usage and the full-field background investigation and results of the other steps in the process are otherwise favorable.
The DEA's relatively firm stance on this issue contrasts with that of the Federal Bureau of Investigation, which in 2005 considered relaxing its hiring policy relevant to individual drug-use history.
DEA Aviation Division logo
Aviation Division
The DEA Aviation Division or Office of Aviation Operations (OA) (formerly Aviation Section) is an airborne division based in Fort Worth Alliance Airport, Texas. The current OA fleet consists of 106 aircraft and 124 DEA pilots.
The DEA shares a communications system with the Department of Defense for communication with state and regional enforcement independent of the Department of Justice and police information systems and is coordinated by an information command center called the El Paso Intelligence Center (EPIC) near El Paso, Texas.
Special Response Teams
DEA agents in MultiCam uniform burning hashish seized in Operation Albatross in Afghanistan, 2007.
Rapid Response Teams (RRT), previously known as Foreign-Deployed
Advisory and Support Teams (FAST), were decommissioned by DEA Acting
Administrator Chuck Rosenburg on March 2017 via memorandum. A need for
domestic high-risk service teams led to the hybrid creation of
specialized tactical units residing within various geographical regions
throughout the United States.
DEA officially created and standardized its Special Response Team
(SRT) program in 2016. The SRT was designed as a stop-gap between
tactical operations conducted by field agents and those necessitating
specialized tactics as a result of elevated risks. SRT operators are
highly trained in various weapons systems and entry tactics/maneuvers.
Because of the clandestine nature of the DEA mission, SRT training
protocols and activation requirements are highly sensitive and not
available to the public. Some of the SRT missions consist of high-risk
arrests, vehicle assaults, air assault/infiltration, specialized
surveillance, custody of high-profile individuals, dignitary and witness
protection, tactical surveillance and interdiction, advanced breaching,
tactical training to other police units, and urban and rural fugitive
searches. Covertly located throughout the nation, DEA SRT teams are
available to respond to practically any CONUS geographical area with
little to no preparation or notification. The DEA SRT has been involved
in several high profile operations in recent years, however, DEA
involvement is often times not publicized due to operational and
intelligence considerations. Considered one of the most covert outfits
in federal law enforcement, very little is known about DEA SRT
capabilities and its operator selection process.
In the past, DEA had other tactical teams like the High-risk
Entry Apprehension Teams (HEAT) in some Field Divisions, and Operation
Snowcap Teams (predecessor of FAST). The teams administered by the
Mobile Enforcement Section, the Mobile Enforcement Teams (MET), and
Regional Enforcement Teams (RET), were mobile investigative units
intended to deploy resources to state and local agencies (MET) or DEA
Field Divisions (RET) in need of assistance with a particular
investigation or trafficking group. These programs ended in the early
2000s.
Special Operations Division
The
DEA Special Operations Division (SOD) is a division within the DEA,
which forwards information from wiretaps, intercepts and databases from
various sources to federal agents and local law enforcement officials.
The SOD came under scrutiny following the 2013 mass surveillance disclosures.
Domestic Cannabis Eradication/Suppression Program
The
Domestic Cannabis Eradication/Suppression Program (DCE/SP) began
funding eradication programs in Hawaii and California in 1979. The
program rapidly expanded to include programs in 25 states by 1982. By
1985, all 50 States were participating in the DCE/SP.
In 2015, the DCE/SP was responsible for the eradication of 3,932,201
cultivated outdoor cannabis plants and 325,019 indoor plants for a total
of 4,257,220 marijuana plants. In addition, the DCE/SP accounted for
6,278 arrests and the seizure in excess of $29.7 million of cultivator
assets.
In 2014, the DEA spent $73,000 to eradicate marijuana plants in Utah, though they did not find a single marijuana plant.
Federal documents obtained by journalist Drew Atkins detail the DEA's
continuing efforts to spend upwards of $14 million per year to
completely eradicate marijuana within the United States despite the
government funding allocation reports showing that the Marijuana
Eradication Program often leads to the discovery of no marijuana plants.
This prompted twelve members of Congress to push for the elimination of
the program and use the money instead to fund domestic-violence
prevention and deficit-reduction programs.
Budget
In 2018 the DEA budget was $2086.6 million. $445 million was spent on international enforcement and $1,627 million was spent on domestic enforcement.
- Breaking foreign and domestic sources of supply ($1.0149 billion) via domestic cannabis eradication/suppression; domestic enforcement; research, engineering, and technical operations; the Foreign Cooperative Investigations Program; intelligence operations (financial intelligence, operational intelligence, strategic intelligence, and the El Paso Intelligence Center); and drug and chemical diversion control.
- Reduction of drug-related crime and violence ($181.8 million) funding state and local teams and mobile enforcement teams.
- Demand reduction ($3.3 million) via anti-legalization education, training for law enforcement personnel, youth programs, support for community-based coalitions, and sports drug awareness programs.
Firearms
DEA agents' primary service weapons are the Glock 17 and Glock 19,
Remington 870 12-gauge shotgun, and Rock River Arms LAR-15
semi-automatic carbine in 5.56×45mm NATO. Agents may also qualify to
carry a firearm listed on an authorized carry list maintained and
updated by the Firearms Training Unit (FTU), Quantico, VA.
Special Agents may qualify with their own personally-owned
handguns, rifle, and shotgun, and certain handguns are allowed to be
used with permission from the FTU. Agents are required to attend
tactical and firearms proficiency training quarterly, and to qualify
with their handguns twice per year. The DEA has one of the most
challenging handgun qualification courses in all of federal law
enforcement. Failure to achieve a passing qualification score is the
reason for most Academy dismissals and special agents in the field may
have their authority to carry a firearm revoked for failure to qualify.
Basic Agent Trainees (BATs) who fail the initial pistol
qualification course of fire are placed in a remedial program to receive
additional training. In remedial training, BATs receive five extra
two-hour range sessions, for a total of 10 more hours of live fire
training on their issued sidearm, in order to further aid them in
helping pass the pistol qualification. After passing their pistol
qualification, Basic Agent Trainees move on to receive formal training
on the DEA's standard-issue long guns and will continue to frequently
shoot their agency-issued sidearm that they have already qualified on.
In all, BATs receive a total of 32 firearms training sessions, when
combining classroom instruction, gear issue, and pistol, rifle, and
shotgun live fire training at the DEA Academy. They will shoot the
qualification courses for all three weapons systems during their initial
training, but must pass their final qualification attempts only on
their Glock pistols in order to become a Special Agent.
Trained to use shoulder-fired weapons, the Rock River LAR-15, adopted in 2004, and the LWRC M6A2 is the standard carbine of DEA. The Colt 9mm SMG
was previously issued, but no longer in service. Agents are required to
complete a two-day (16-hour) proficiency course in order to carry a
shoulder weapon on enforcement operations. They may carry a Rock River
LAR-15 or LWRC carbine as authorized, personally-owned weapons, provided
they meet the same training and proficiency standards.
Impact on the drug trade
In 2005, the DEA seized a reported $1.4 billion in drug trade related assets and $477 million worth of drugs. According to the White House's Office of Drug Control Policy, the total value of all of the drugs sold in the U.S. is as much as $64 billion a year,
giving the DEA an efficiency rate of less than 1% at intercepting the
flow of drugs into and within the U.S. Critics of the DEA (including
recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, Milton Friedman, prior to his death a member of Law Enforcement Against Prohibition) point out that demand for illegal drugs is inelastic;
the people who are buying drugs will continue to buy them with little
regard to price, often turning to crime to support expensive drug habits
when the drug prices rise. One recent study by the DEA showed that the
price of cocaine and methamphetamine is the highest it has ever been while the quality of both is at its lowest point ever.
This is contrary to a collection of data done by the Office of National
Drug Control Policy, which states that purity of street drugs has
increased, while price has decreased.
In contrast to the statistics presented by the DEA, the United States
Department of Justice released data in 2003 showing that purity of
methamphetamine was on the rise.
Registration and licensing
"Operation Somalia Express"
was an 18-month investigation which included the coordinated takedown
of a 44-member international narcotics-trafficking organization
responsible for smuggling more than 25 tons of khat from the Horn of Africa to the United States.
The DEA has a registration system in place which authorizes anyone to manufacture, import, export, and distribute by filing DEA form 225 along with medical professionals, researchers and manufacturers access to "Schedule I" drugs, as well as Schedules 2, 3, 4 and 5. Authorized registrants apply for and, if granted, receive a "DEA number".
An entity that has been issued a DEA number is authorized to
manufacture (drug companies), distribute, research, prescribe (doctors, pharmacists, nurse practitioners and physician assistants, etc.) or dispense (pharmacy) a controlled substance.
Diversion control system
Many problems associated with drug abuse
are the result of legitimately-manufactured controlled substances being
diverted from their lawful purpose into the illicit drug traffic. Many
of the analgesics, depressants and stimulants manufactured for
legitimate medical use can often carry potential for dependence or
abuse. Therefore, those scheduled substances have been brought under
legal control for prevention and population safety. The goal of controls
is to ensure that these "controlled substances" are readily available
for medical use, while preventing their distribution for illicit
distribution and non-medical use. This can be a difficult task,
sometimes providing difficulty for legitimate patients and healthcare
providers while circumventing illegal trade and consumption of scheduled
drugs.
Under federal law, all businesses which manufacture or distribute
controlled drugs, all health professionals entitled to dispense,
administer or prescribe them, and all pharmacies
entitled to fill prescriptions must register with the DEA. Registrants
must comply with a series of regulatory requirements relating to drug
security, records accountability, and adherence to standards.
All of these investigations are conducted by Diversion Investigators
(DIs). DIs conduct investigations to uncover and investigate suspected
sources of diversion and take appropriate civil and administrative
actions. Prescription Database Management Programs (PDMP) aid and
facilitate investigation and surveillance.
MDMA DEA scheduling overturn
In 1985 MDMA
and its analogues were under review by the American government as a
drug for potential of abuse. During this time, several public hearings
on the new drug were held by the DEA. Based on all of the evidence and
facts presented at the time, the DEA's administrative law judge did not
see MDMA and its analogues as being of large concern and recommended
that they be placed in Schedule III. The DEA administrator, expressing
concern for abuse potential, overruled the recommendation and ruled that
MDMA be put in Schedule I, the Controlled Substances Act's most restrictive category.
Criticism
Drug Enforcement Administration 25th Anniversary badge
The DEA has been criticized for placing highly restrictive schedules on a few drugs which researchers in the fields of pharmacology
and medicine regard as having medical uses. Critics assert that some
such decisions are motivated primarily by political factors stemming
from the U.S. government's War on Drugs,
and that many benefits of such substances remain unrecognized due to
the difficulty of conducting scientific research. A counterpoint to that
criticism is that under the Controlled Substances Act it is the Department of Health and Human Services (through the Food and Drug Administration and the National Institute on Drug Abuse),
not the DEA, which has the legal responsibility to make scientific and
medical determinations with respect to drug scheduling; no drug can be
scheduled if the Secretary of Health and Human Services recommends
against it on a scientific or medical basis, and no drug can be placed
in the most restrictive schedule (Schedule I) if DHHS finds that the drug has an accepted medical use. Jon Gettman's essay Science and the End of Marijuana Prohibition
describes the DEA as "a fall guy to deflect responsibility from the key
decision-makers" and opines, "HHS calls the shots when it comes to
marijuana prohibition, and the cops at DEA and the general over at ONDCP take the heat."
The DEA is also criticized for focusing on the operations from which it can seize the most money, namely the organized cross-border trafficking of marijuana.
Some individuals contemplating the nature of the DEA's charter advise
that, based on danger, the DEA should be most focused on cocaine. Others
suggest that, based on opiate popularity, the DEA should focus much more on prescription opiates used recreationally, which critics contend comes first before users switch to heroin.
Practitioners
who legally prescribe medicine however must possess a valid DEA
license. According to federal law the budget of the DEA Diversion
Control Program is to be paid by these license fees. In 1984 a
three-year license cost $25. In 2009 the fee for a three-year license
was $551. Some have likened this approach to license fees unreasonable,
"like making pilot licenses support the entire Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) budget."
Costs
The total
budget of the DEA from 1972 to 2014, according to the agency website,
was $50.6 billion. The agency had 11,055 employees in 2014. For the year
2014 the average cost per arrest made was $97,325.
Civil liberties
Others, such as former Republican congressman Ron Paul, the Cato Institute, The Libertarian Party and the Drug Policy Alliance criticize the very existence of the DEA and the War on Drugs as both hostile, and contrary, to the concept of civil liberties
by arguing that anybody should be free to put any substance they choose
into their own bodies for any reason, particularly when legal drugs
such as alcohol, tobacco and prescription drugs
are also open to abuse, and that any harm caused by a drug user or
addict to the general public is a case of conflicting civil rights.
Recurrently, billions of dollars are spent yearly, focusing largely on criminal law and demand reduction campaigns, which has resulted in the imprisonments of thousands of U.S. citizens.
Demand for recreational drugs is somewhat static as the market for most
illegal drugs has been saturated, forcing the cartels to expand their
market to Europe and other areas than the United States. United States federal law registers cannabis as a Schedule I drug.
Incarceration of Daniel Chong
An April 2012 DEA raid on a California home led to the incarceration of Daniel Chong for several days under conditions of neglect. The 23-year-old student attending the University of California, San Diego was taken into custody along with eight other people when the DEA executed a raid on a suspected MDMA distribution operation at a residence that he was visiting to celebrate the April 20 cannabis "holiday" known as "420".
According to Chong, the DEA agents questioned him and told him that he
could go home, one even offering him a ride home, but instead he was
transferred to a holding cell and confined for five days without any
food or water, although Chong said he ingested a powdery substance that
was left for him, which was later found to be methamphetamine.
After five days and two suicide attempts, DEA agents found Chong. He
was taken to the hospital, where he spent three days in intensive care,
because his kidneys were close to failing. No criminal charges were
filed against Chong. A DEA spokesperson stated that the extended
detention was accidental and the acting special agent in charge of the
San Diego DEA office issued an apology to Chong. Chong disputes the
claim of accidental neglect, saying that DEA personnel ignored his calls
for help. His attorney stated an intent to file a claim against the
federal government and some members of California's delegation to the Congress called for further investigation of the incident.
Department of Justice Smart on Crime Program
On 12 August 2013, at the American Bar Association's House of Delegates meeting, Attorney General Eric Holder
announced the "Smart on Crime" program, which is "a sweeping initiative
by the Justice Department that in effect renounces several decades of
tough-on-crime anti-drug legislation and policies."
Holder said the program "will encourage U.S. attorneys to charge
defendants only with crimes "for which the accompanying sentences are
better suited to their individual conduct, rather than excessive prison
terms more appropriate for violent criminals or drug kingpins…" Running through Holder's statements, the increasing economic burden of over-incarceration was stressed. As of August 2013, the Smart on Crime program is not a legislative initiative but an effort "limited to the DOJ's policy parameters."
International
David
Coleman Headley (born Daood Sayed Gilani; 30 June 1960) who was working
as an informant for the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
simultaneously made periodic trips to Pakistan for LeT training and was
one of main conspirator in the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
On January 24, 2013, Headley, then 52 years old, was sentenced by U.S.
District Judge Harry Leinenweber of the United States District Court for
the Northern District of Illinois in Chicago to 35 years in prison for
his part in the 2008 Mumbai attacks, in which at least 164 victims
(civilians and security personnel) and nine attackers were killed. Among
the dead were 28 foreign nationals from 10 countries. One attacker was captured. The bodies of many of the dead hostages showed signs of torture or disfigurement. A number of those killed were notable figures in business, media, and security services.
The DEA was accused in 2005 by the Venezuelan government of collaborating with drug traffickers, after which President Hugo Chávez decided to end any collaboration with the agency. In 2007, after the U.S. State Department
criticized Venezuela in its annual report on drug trafficking, the
Venezuelan Minister of Justice reiterated the accusations: "A large
quantity of drug shipments left the country through that organization.We
were in the presence of a new drug cartel."
In his 1996 series of articles and subsequent 1999 book, both titled Dark Alliance, journalist Gary Webb asserts that the DEA helped harbor Nicaraguan drug traffickers. Notably, they allowed Oscar Danilo Blandón political asylum in the USA despite knowledge of his cocaine trafficking organization.
The government of Bolivia
has also taken similar steps to ban the DEA from operating in the
country. In September 2008, Bolivia drastically reduced diplomatic ties
with the United States, withdrawing its ambassador from the US and
expelling the US ambassador from Bolivia. This occurred soon after
Bolivian president Evo Morales expelled all DEA agents from the country due to a revolt in the traditional coca-growing Chapare Province.
The Bolivian government claimed that it could not protect the agents,
and Morales further accused the agency of helping incite the violence,
which claimed 30 lives. National agencies were to take over control of
drug management.
Three years later, Bolivia and the US began to restore full diplomatic
ties. However, Morales maintained that the DEA would remain unwelcome in
the country, characterising it as an affront to Bolivia's "dignity and
sovereignty".
In the Netherlands, both the Dutch government and the DEA have
been criticized for violations of Dutch sovereignty in drug
investigations. According to Peter R. de Vries,
a Dutch journalist present at the 2005 trial of Henk Orlando Rommy, the
DEA has admitted to activities on Dutch soil. Earlier, then Minister of
Justice Piet Hein Donner, had denied to the Dutch parliament
that he had given permission to the DEA for any such activities, which
would have been a requirement by Dutch law in order to allow foreign
agents to act within the territory.
Special Operations Division fabricated evidence trails
In 2013 Reuters
published a report about the DEA's Special Operations Division (SOD)
stating that it conceals where an investigative trail about a suspect
truly originates from and creates a parallel set of evidence
given to prosecutors, judges, and defense lawyers. This DEA program
mainly affects common criminals such as drug dealers. The concealment of
evidence means the defendant is unaware of how his or her investigation
began and will be unable to request a review possible sources of
exculpatory evidence. Exculpatory evidence may include biased witnesses,
mistakes, or entrapment. Nancy Gertner, a former federal judge who had
served from 1994 to 2011 and a Harvard Law School
professor, stated that "It is one thing to create special rules for
national security. Ordinary crime is entirely different. It sounds like
they are phonying up investigations." Andrew O'Hehir of Salon
wrote that "It’s the first clear evidence that the “special rules” and
disregard for constitutional law that have characterized the hunt for
so-called terrorists have crept into the domestic criminal justice
system on a significant scale."
Cannabis rescheduling
A 2014 report by the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies and the Drug Policy Alliance accuses the DEA of unfairly blocking the removal of cannabis from Schedule I. The report alleges that the methods employed by the DEA to achieve this include: delaying rescheduling petitions for years, overruling DEA administrative law judges, and systematically impeding scientific research.
The DEA continues to refuse the removal of cannabis from Schedule I
despite wide-scale acceptance of the substance among the medical
community, including 76% of doctors, for the treatment of various disease.
Domestic anti-drug advocacy
The DEA, in addition to enforcement, also regularly engage in
advocacy, specifically against rescheduling marijuana, by publishing
policy-based papers on certain drugs. Some have
criticized the DEA for using tax dollars in what they call an attempt
to change public opinion, which they call an overreach from the scope of
the agency's job of enforcement, and that by releasing such
non-peer-reviewed reports is a transparent attempt to justify its own
activities. They have claimed that since the DEA is not, by law, an
advocacy group, but a legal enforcement group, that those press releases
are tantamount to what they consider domestic propaganda.
Raids on medical marijuana dispensaries
People protesting medical marijuana raids
The DEA has taken a particularly strong stance on enforcement of the
Controlled Substances Act on persons and organizations acting within
state laws that allow medical cannabis cultivation and distribution.
DEA agency executive, Chuck Rosenberg has made negative statements
against patients who use medical marijuana. Chuck Rosenberg has
mentioned that he considers medical marijuana to be a "joke." As a
reaction against the negative statements made by Chuck Rosenberg towards
medical marijuana, an international online petition has been formed.
More than 159,737 signatures have been gathered globally with the
intention that Chuck Rosenberg will be fired or forced to resign as head
of DEA.
"The people of California and the County of Santa Cruz have overwhelmingly supported the provision of medical marijuana for people who have serious illnesses," county Supervisor Mardi Wormhoudt told the San Francisco Gate.
"These people (blocking the road) are people with AIDS and cancer and
other grave illnesses. To attack these people, who work collectively and
have never taken money for their work, is outrageous."
As a result, the Wo/Men's Alliance for Medical Marijuana, with
the City and County of Santa Cruz, had sued the DEA, Attorney General Michael Mukasey, and the ONDCP. The most recent court decision rejected the government's motion to dismiss, which allowed discovery to move forward. The American Civil Liberties Union hailed the decision as "a first-of-its-kind ruling."
More recently, the DEA has escalated its enforcement efforts on
the recently proliferated Los Angeles area medical cannabis collectives.
On July 25, 2007, the DEA raided the California Patients Group,
Hollywood Compassionate Collective, and Natural Hybrid (NHI Caregivers)
in Hollywood, California.
Earlier that day, the operators of those collectives participated in a
press conference with LA City Council members announcing the City's
intention to regulate the collectives and asking the DEA to halt raids
on collectives while the City drafted regulations.
The dispensary operator of Natural Hybrid (NHI Caregivers) was forced
to close down the collective due to the tremendous loss caused by the
DEA conducted joint task force raid against them.
Project Cassandra
In 2008 the Special Operations part of the agency launched a multi-agency effort named Project Cassandra to investigate the Iranian-backed terrorist group Hezbollah
for illicit drug trafficking and terrorist financing. The investigation
identified an Iranian cell in the U.S. which worked in concert with a
Lebanese bank called the Lebanese Canadian Bank to launder money using
the purchase of used automobiles exported to Africa. Project Cassandra
also identified hemispheric drug syndicates involved in cocaine
trafficking in order to finance Hezbollah terrorism. The Department of
Justice issued several sealed indictments, but declined to seize,
prosecute, extradite, or further investigate likely targets of these
alleged foreign criminal activities operating in the United States due
to White House diplomatic objectives involving the international nuclear
agreement with Iran. On December 22, 2017, the Attorney General Jeff Sessions ordered a review of prior cases in the project.
DEA Museum
In 1999, the DEA opened the Drug Enforcement Administration Museum in Arlington, Virginia.
The original permanent exhibit – Illegal Drugs in America: A Modern
History – remains the museum's centerpiece. The exhibit features "the
more than 150 year history of drugs and drug abuse and the DEA,"
including a considerable collection of drug paraphernalia and an image
of a smiling drug vendor under the heading "Jimmy's Joint".