| Arabian Desert | |
|---|---|
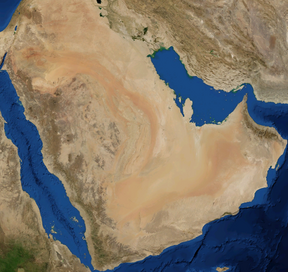
A satellite image of the Arabian Desert by NASA World Wind
| |
| Length | 2,100 km (1,300 mi) |
| Width | 1,100 km (680 mi) |
| Area | 2,330,000 km2 (900,000 sq mi) |
| Naming | |
| Native name | ٱلصَّحْرَاء ٱلْعَرَبِيَّة (in Arabic) |
| Geography | |
| Countries | |
| Coordinates | 18.2672°N 42.3681°E |
The Arabian Desert is a vast desert wilderness in Western Asia. It stretches from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula, with an area of 2,330,000 square kilometers (900,000 sq mi). It is the fifth largest desert in the world, and the largest in Asia. At its center is Ar-Rub'al-Khali (The Empty Quarter), one of the largest continuous bodies of sand in the world.
Gazelles, oryx, sand cats, and spiny-tailed lizards are just some of the desert-adapted species that survive in this extreme environment, which features everything from red dunes to deadly quicksand. The climate is mostly dry (the major part receives around 100 mm (3.9 in) of rain per year but some very rare places receive as little as 50 mm), and temperatures oscillate between very high heat and seasonal night time freezes. It is part of the deserts and xeric shrublands biome and the Palearctic ecozone.
The Arabian desert ecoregion holds little biodiversity, although a few endemic plants grow here. Many species, such as the striped hyena, jackal and honey badger have become extirpated due to hunting, human encroachment and habitat destruction. Other species have been successfully re-introduced, such as the Arabian sand gazelle, and are protected at a number of reserves. Overgrazing by livestock, off-road driving, and human destruction of habitat are the main threats to this desert ecoregion.
Geology and geography
Map of the Arabian Desert. Ecoregions as delineated by the WWF. The yellow line encloses the ecoregion called "Arabian Desert and East Sahero-Arabian xeric shrublands", and two smaller, closely related ecoregions called "Persian Gulf desert and semi-desert" and "Red Sea Nubo-Sindian tropical desert and semi-desert". National boundaries are shown in black. Satellite image from NASA.
Detailed geological features:
- A corridor of sandy terrain known as the Ad-Dahna desert connects the large An-Nafud desert (65,000 km2 or 40,389 square miles) in the north of Saudi Arabia to the Rub' Al-Khali in the south-east.
- The Tuwaiq escarpment is a region of 800 km (500 mi) arc of limestone cliffs, plateaux, and canyons.
- Brackish salt flats: the quicksands of Umm al Samim.
- The Wahiba Sands of Oman: an isolated sand sea bordering the east coast
- The Rub' Al-Khali desert is a sedimentary basin elongated on a south-west to north-east axis across the Arabian Shelf. At an altitude of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), the rock landscapes yield the place to the Rub' al-Khali, vast wide of sand of the Arabian desert, whose extreme southern point crosses the centre of Yemen. The sand overlies gravel or Gypsum Plains and the dunes reach maximum heights of up to 250 m (820 ft). The sands are predominantly silicates, composed of 80 to 90% of quartz and the remainder feldspar, whose iron oxide-coated grains color the sands in orange, purple, and red.
Ecology and natural resources
The Rub'al-Khali has very limited floristic diversity.
There are only 37 plant species, 20 recorded in the main body of the
sands and 17 around the outer margins. Of these 37 species, one or two
are endemic. Vegetation is very diffuse but fairly evenly distributed,
with some interruptions of near sterile dunes. Some typical plants are:
- Calligonum crinitum on dune slopes
- Cornulaca arabica (saltbush)
- Salsola stocksii (saltbush)
- Cyperus conglomeratus
Other widespread species are:
- Dipterygium glaucum
- Limeum arabicum
- Zygophyllum mandavillei (Mandaville 1986).
Very few trees are found except at the outer margin (typically Acacia ehrenbergiana and Prosopis cineraria). Other species are a woody perennial Calligonum comosum, and annual herbs such as Danthonia forskallii.
The Asiatic cheetah and Asiatic lion used to be here.
Climate
The Arabian Desert has a subtropical, hot desert climate, similar to the climate of the Sahara Desert;
the world's largest hot desert. The Arabian Desert is actually an
extension of the Sahara Desert over the Arabian peninsula. The climate
is mainly hot and dry with plenty of sunshine throughout the year. The
rainfall amount is generally around 100 mm, and the driest areas can
receive between 30 and 40 mm of annual rain. Such dryness remains rare
throughout the desert, however. There are few hyperarid
areas in the Arabian Desert, in contrast with the Sahara Desert, where
more than half of the area is hyperarid (annual rainfall below 50 mm).
The sunshine duration
in the Arabian Desert is very high by global standards, between 2,900
hours (66.2% of daylight hours) and 3,600 hours (82.1% of daylight
hours), but it is typically around 3,400 hours (77.6% of daylight
hours), thus clear-sky conditions prevail over the region and cloudy
periods are intermittent. Even though the sun and moon are bright, dust
and humidity cause lower visibility at ground level. The temperatures
remain high all year round. Average high temperatures in summer are
generally over 40 °C (104 °F) at low elevations, and can even soar to
48 °C (114.8 °F) at extremely low elevations, especially along the
Persian Gulf near sea level. Average low temperatures in summer remain
high, over 20 °C (68 °F) and sometimes over 30 °C (77 °F) in the
southernmost regions. Record high temperatures are above 50 °C (122 °F)
in much of the desert, due in part to very low elevation.
Political borders
The desert lies mostly in Saudi Arabia, extending into the surrounding countries of Egypt (Sinai), southern Iraq and southern Jordan. The Arabian desert is bordered by 5 countries. Bordering the Persian Gulf, there is an extension into Qatar and, further east, the region covers almost all of Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The Rub'al-Khali crosses over from Saudi Arabia into western Oman and eastern Yemen.
People, language and cultures
The area is home to several different cultures, languages, and peoples, with Islam as the predominant faith. The major ethnic group in the region is the Arabs, whose primary language is Arabic.
Settlements
In the center of the desert lies Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia, with more than 7 million inhabitants. Other large cities, such as Dubai, Abu Dhabi, or Kuwait City, lie on the coast of the Persian Gulf.
Ecological threats
- Agricultural projects
- Human destruction of habitat
- Military activity
- Oil and gas production
- Overgrazing by camels and goats, with increased herd size, and a more sedentary lifestyle amongst the Bedouin
Military activity
Weaponry
used by the United States during the Gulf War also poses a huge risk to
the environmental stability of the area. Tank columns in the desert
plains may disrupt the fragile stability that exists in the desert
currently. In 1991, the movement of US tanks over the desert damaged the
top protective layer of the desert soil. As a result, a sand dune was released and has started slowly moving downhill. Some people fear this dune could ultimately reach Kuwait City.
Conservation
The conservation status of the desert is critical/endangered, with species including the sand gazelle and white oryx threatened, and honey badgers, jackals, and striped hyaenas already extirpated.
No formal protected areas exist, but a number of protected areas are planned for Abu Dhabi.
Oil spills
In January 1991 during the Gulf War,
Iraqi forces released about 1.7 million m³ (11 million barrels) of oil
from storage tanks and tankers directly into the Persian Gulf. In
February, they also destroyed 1,164 Kuwaiti oil wells. It took nine
months to extinguish these oil fires. These oil spills contaminated
1,000 km (620 mi) of Persian Gulf coast.
The result of the pollution was the death of thousands of water birds and serious damage to the Persian Gulf's aquatic ecosystem, particularly shrimp, sea turtles, dugongs, whales, dolphins and fish.
The damaged wells also released 10 million m³ (60 million
barrels) of oil into the desert and formed lakes (total surface of 49
square kilometers).


