| |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈfoʊlɪk, ˈfɒlɪk/ |
| Other names | FA, N-(4-{[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino}benzoyl)-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, folacin, vitamin B9, and historically, vitamin Bc and vitamin M |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682591 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, IM, IV, sub-Q |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50–100% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.381 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19N7O6 |
| Molar mass | 441.404 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 250 °C (482 °F) (decomposition) |
| Solubility in water | 1.6 mg/L (25 °C) mg/mL (20 °C) |
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is essential for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids, which are required for cell division. As humans cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential vitamin. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements.
Folate in the form of folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby. Low levels in early pregnancy are believed to be the cause of more than half of babies born with NTDs. More than 80 countries use either mandatory or voluntary fortification of certain foods with folic acid as a measure to decrease the rate of NTDs. Long-term supplementation with relatively large amounts of folic acid is associated with small reduction in the risk of stroke and an increased risk of prostate cancer. There are concerns that large amounts of supplemental folic acid can hide vitamin B12 deficiency.
Not consuming enough folate can lead to folate deficiency. This may result in a type of anemia in which red blood cells become abnormally large. Symptoms may include feeling tired, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, open sores on the tongue, and changes in the color of the skin or hair. Folate deficiency in children may develop within a month of poor dietary intake. In adults, normal total body folate is between 10 and 30 mg with blood levels of greater than 7 nmol/L (3 ng/mL).
Folate was discovered between 1931 and 1943. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the safest and most effective medicines needed in a health system.[16] The wholesale cost of supplements in the developing world is between US$0.001 and 0.005 per dose as of 2014. The term "folic" is from the Latin word folium (which means leaf) because it was found in dark-green leafy vegetables.
Definition
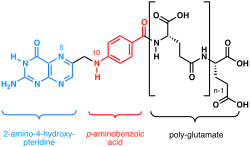
Chemical structure of the folate family
"Folate" (vitamin B9) refers to the many forms of folic acid and its related compounds, including tetrahydrofolic acid (the active form), methyltetrahydrofolate (the primary form found in blood), methenyltetrahydrofolate, folinic acid, folacin, and pteroylglutamic acid. Historic names included L.casei, factor vitamin Bc and vitamin M.
The terms "folate" and "folic acid" have somewhat different
meanings in different contexts, although sometimes used interchangeably. Within the field of organic chemistry, folate refers to the conjugate base of folic acid. Within the field of biochemistry, folates refer to a class of biologically active compounds related to and including folic acid. Within the field of nutrition,
the "folates" are a family of essential nutrients related to folic acid
obtained from natural sources whereas the term "folic acid" is reserved
for the manufactured form that is used as a dietary supplement.
Chemically, folates consist of three distinct chemical moieties linked together. A pterin (2-amino-4-hydroxy-pteridine) heterocyclic ring is linked by a methylene bridge to a p-aminobenzoyl group that in turn is bonded through an amide linkage to either glutamic acid or poly-glutamate. One-carbon units in a variety of oxidation states may be attached to the N5 nitrogen atom of the pteridine ring and/or the N10 nitrogen atom of the p-aminobenzoyl group.
Health effects
Folate
is especially important during periods of frequent cell division and
growth, such as infancy and pregnancy. Folate deficiency hinders DNA
synthesis and cell division, affecting hematopoietic cells and
neoplasms the most because of their greater frequency of cell division. RNA transcription and subsequent protein synthesis are less affected by folate deficiency, as the mRNA can be recycled and used again (as opposed to DNA synthesis, where a new genomic copy must be created).
Folate deficiency
Folate deficiency can be caused by unhealthy diets that do not
include enough vegetables and other folate-rich foods; diseases in which
folates are not well absorbed in the digestive system (such as Crohn's disease or celiac disease); some genetic disorders that affect levels of folate; and certain medicines (such as phenytoin, sulfasalazine, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole). Folate deficiency is accelerated by alcohol consumption, possibly by interference with folate transport.
Folate deficiency may lead to glossitis, diarrhea, depression, confusion, anemia, and fetal neural tube and brain defects. Other symptoms include fatigue, gray hair, mouth sores, poor growth, and swollen tongue. Folate deficiency is diagnosed by analyzing a complete blood count (CBC) and plasma vitamin B12 and folate levels. A serum folate of 3 μg/L or lower indicates deficiency.
Serum folate level reflects folate status, but erythrocyte folate level
better reflects tissue stores after intake. An erythrocyte folate level
of 140 μg/L or lower indicates inadequate folate status. Serum folate
reacts more rapidly to folate intake than erythrocyte folate.
Since folate deficiency limits cell division, erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells) is hindered. This leads to megaloblastic anemia,
which is characterized by large, immature red blood cells. This
pathology results from persistently thwarted attempts at normal DNA
replication, DNA repair, and cell division, and produces abnormally
large red cells called megaloblasts (and hypersegmented neutrophils)
with abundant cytoplasm capable of RNA and protein synthesis, but with
clumping and fragmentation of nuclear chromatin. Some of these large
cells, although immature (reticulocytes), are released early from the
marrow in an attempt to compensate for the anemia.
Both adults and children need folate to make normal red and white blood
cells and prevent anemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and inability
to concentrate.
Increased homocysteine levels suggest tissue folate deficiency, but homocysteine is also affected by vitamin B12 and vitamin B6, renal function, and genetics. One way to differentiate between folate deficiency and vitamin B12 deficiency is by testing for methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels. Normal MMA levels indicate folate deficiency and elevated MMA levels indicate vitamin B12 deficiency.
Folate deficiency is treated with supplemental oral folic acid of 400
to 1000 μg per day. This treatment is very successful in replenishing
tissues, even if deficiency was caused by malabsorption. People with
megaloblastic anemia need to be tested for vitamin B12 deficiency before treatment with folic acid, because if the person has vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid supplementation can remove the anemia, but can also worsen neurologic problems.
Cobalamin deficiency may lead to folate deficiency, which, in turn,
increases homocysteine levels and may result in the development of
cardiovascular disease or birth defects.
Birth defects
Deficiency of folate in pregnant women has been implicated in neural tube defects
(NTDs), with an estimate of 300,000 cases worldwide prior to the
implementation in many countries of mandatory food fortification.
NTDs occur early in pregnancy (first month), therefore women must have
abundant folate upon conception and for this reason there is a
recommendation that any woman planning to become pregnant consume a
folate-containing dietary supplement before and during pregnancy.
Compliance with this recommendation is not complete, and many women
become pregnant without this being a planned pregnancy, or may not
realize that they are pregnant until well into the first trimester,
which is the critical period for reducing risk of NTDs. Countries have
implemented either mandatory or voluntary food fortification of wheat
flour and other grains,
or else have no such program and depend on public health and healthcare
practitioner advice to women of childbearing age. A meta-analysis of
global birth prevalence of spina bifida showed that when mandatory
fortification was compared to countries with voluntary fortification or
no fortification program, there was a 30% reduction in live births with
spina bifida. Some countries reported a greater than 50% reduction. The United States Preventive Services Task Force
recommends folic acid as the supplement or fortification ingredient, as
forms of folate other than folic acid have not been studied.
A meta-analysis of folate supplementation during pregnancy reported a 28% lower relative risk of newborn congenital heart defects. Prenatal supplementation with folic acid did not appear to reduce the risk of preterm births. One systematic review
indicated no effect of folic acid on mortality, growth, body
composition, respiratory, or cognitive outcomes of children from birth
to 9 years old. There was no relation between maternal folic acid supplementation and an increased risk for childhood asthma.
Fertility
Folate contributes to spermatogenesis.
In women, folate is important for oocyte quality and maturation,
implantation, placentation, fetal growth and organ development.
Heart disease
One
meta-analysis reported that multi-year folic acid supplementation, in
amounts in most of the included clinical trials at higher than the UL of
1,000 μg/day, reduced the relative risk of cardiovascular disease by a modest 4%.
Two older meta-analyses, which would not have incorporated results from
newer clinical trials, reported no changes to the risk of
cardiovascular disease.
Stroke
The absolute risk of stroke with supplementation decreases from 4.4% to 3.8% (a 10% decrease in relative risk). Two other meta-analyses reported a similar decrease in relative risk. Two of these three were limited to people with pre-existing cardiovascular disease or coronary heart disease. The beneficial result may be associated with lowering circulating homocysteine concentration, as stratified analysis showed that risk was reduced more when there was a larger decrease in homocysteine.
The effect was also larger for the studies that were conducted in
countries that did not have mandatory grain folic acid fortification. The beneficial effect was larger in the subset of trials that used a lower folic acid supplement compared to higher.
Cancer
Chronically
insufficient intake of folate may increase the risk of colorectal,
breast, ovarian, pancreas, brain, lung, cervical, and prostate cancers.
Early after fortification programs were implemented, high intakes
were theorized to accelerate the growth of preneoplastic lesions that
could lead to cancer, specifically colon cancer.
Subsequent meta-analyses of the effects of low versus high dietary
folate, elevated serum folate, and supplemental folate in the form of
folic acid have reported at times conflicting results. Comparing low to
high dietary folate showed a modest but statistically significant reduced risk of colon cancer. For prostate cancer risk, comparing low to high dietary folate showed no effect, but the same two studies reported a significant increased risk for prostate cancer correlating to elevated serum folate.
Two reviews of trials that involved folic acid dietary supplements
reported, respectively, a statistically significant 24% increase in
prostate cancer risk and a not significant 17% increase in prostate cancer risk. Supplementation with folic acid at 1,000 to 2,500 μg/day - the amounts used in many of the supplement trials
- would result in higher concentrations of serum folate than what is
achieved from diets high in food-derived folate. The second study
reported no significant increase or decrease in total cancer incidence,
colorectal cancer, other gastrointestinal cancer, genitourinary cancer,
lung cancer or hematological malignancies in people who were consuming
folic acid supplements.
A third supplementation meta-analysis limited to reporting only on
colorectal cancer incidence showed that folic acid treatment was not
associated with colorectal cancer risk.
Anti-folate chemotherapy
Folate is important for cells and tissues that divide rapidly. Cancer cells divide rapidly, and drugs that interfere with folate metabolism are used to treat cancer. The antifolate drug methotrexate
is often used to treat cancer because it inhibits the production of the
active form of THF from the inactive dihydrofolate (DHF). However, methotrexate can be toxic,
producing side effects such as inflammation in the digestive tract that
make eating normally more difficult. Bone marrow depression (inducing
leukopenia and thrombocytopenia) and acute kidney and liver failure have
been reported.
Folinic acid, under the drug name leucovorin, a form of folate (formyl-THF), can help "rescue" or reverse the toxic effects of methotrexate. Folic acid supplements have little established role in cancer chemotherapy.
The supplement of folinic acid in people undergoing methotrexate
treatment is to give cells dividing less rapidly enough folate to
maintain normal cell functions. The amount of folate given is depleted
by rapidly dividing cells (cancer) quickly, so does not negate the
effects of methotrexate.
Neurological disorders
Conversion of homocysteine to methionine requires folate and vitamin B12. Elevated plasma homocysteine and low folate are associated with cognitive impairment, dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Supplementing the diet with folic acid and vitamin B12 lowers plasma homocysteine.
However, several reviews reported that supplementation with folic acid
alone or in combination with other B vitamins did not prevent
development of cognitive impairment nor slow cognitive decline.
The relative risk of autism spectrum disorders
was reduced by 23% when the maternal diet was supplemented during
pregnancy. Subset analysis confirmed this among Asian, European and
American populations.
Some evidence links a shortage of folate with clinical depression. Limited evidence from randomized controlled trials showed using folic acid in addition to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may have benefits. Research found a link between depression and low levels of folate.
The exact mechanisms involved in the development of schizophrenia and
depression are not entirely clear, but the bioactive folate, methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), a direct target of methyl donors such as S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe), recycles the inactive dihydrobiopterin (BH2) into tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), the necessary cofactor in various steps of monoamine synthesis, including that of dopamine. BH4
serves a regulatory role in monoamine neurotransmission and is required
to mediate the actions of most antidepressants. 5-MTHF also plays both
direct & indirect roles in DNA methylation, NO2 synthesis, and one-carbon metabolism.
Folic acid, B12 and iron
A complex interaction occurs between folic acid, vitamin B12, and iron.
A deficiency of one may be "masked" by excess of another, so when taken
as dietary supplements, the three need to be in balance.
Malaria
Some studies show iron–folic acid supplementation in children under five may result in increased mortality due to malaria;
this has prompted the World Health Organization to alter their
iron–folic acid supplementation policies for children in malaria-prone
areas, such as India.
Metabolism
The biological activity of folate in the body depends upon dihydrofolate reductase action in the liver which converts folate into tetrahydrofolate
(THF). This action is rate-limiting in humans leading to elevated blood
concentrations of unmetabolized folic acid when consumption from
dietary supplements and fortified foods nears or exceeds the U.S. Tolerable Upper Intake Level of 1,000 μg per day.
Biosynthesis
Animals,
including humans, cannot synthesize folate and therefore must obtain
folate from their diet. All plants and fungi and certain protozoa,
bacteria, and archaea can synthesize folate de novo through variations on the same biosynthetic pathway. The folate molecule is synthesized from pterin pyrophosphate and para-aminobenzoic acid through the action of dihydrofolate synthase. Pterin is in turn derived in a series of enzymatically catalyzed steps from guanosine triphosphate (GTP), while para-aminobenzoic acid (vitamin B10) is a product of the shikimate pathway.
Bioactivation
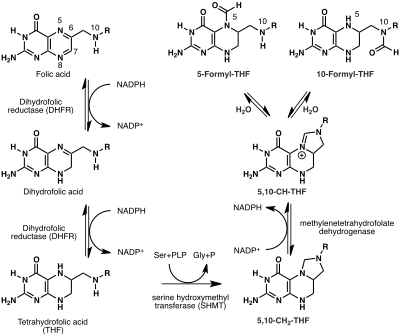
Biotransformation of folic acid into folinic acids where R = para-aminobenzoate-glutamate.
All of the biological functions of folic acid are performed by THF and its methylated derivatives. Hence folic acid must first be reduced to THF. This four electron reduction proceeds in two chemical steps both catalyzed by the same enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase. Folic acid is first reduced to dihydrofolate and then to tetrahydrofolate. Each step consumes one molecule of NADPH (biosynthetically derived from vitamin B3) and produces one molecule of NADP. Mechanistically, hydride is transferred from NADPH to the C6 position of the pteridine ring.
A one-carbon (1C) methyl group is added to tetrahydrofolate through the action of serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) to yield 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF). This reaction also consumes serine and pyridoxal phosphate (PLP; vitamin B6) and produces glycine and pyridoxal. A second enzyme, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD2) oxidizes 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to an iminium cation which in turn is hydrolyzed to produce 5-formyl-THF and 10-formyl-THF. This series of reactions using the β-carbon atom of serine as the carbon source provide the largest part of the one-carbon units available to the cell.
Alternative carbon sources include formate which by the catalytic action of formate–tetrahydrofolate ligase add a 1C unit to THF to yield 10-formyl-THF. Glycine, histidine, and sarcosine can also directly contribute to the THF-bound 1C pool.
Drug interference
A number of drugs interfere with the biosynthesis of THF from folic acid. Among them are the antifolate dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors such as the antimicrobial, trimethoprim, the antiprotozoal, pyrimethamine and the chemotherapy drug methotrexate, and the sulfonamides (competitive inhibitors of 4-aminobenzoic acid in the reactions of dihydropteroate synthetase).
Valproic acid,
one of the most commonly prescribed epilepsy treatment drugs, also used
to treat certain psychological conditions such as bipolar disorder, is a
known inhibitor of folic acid, and as such, has been shown to cause
birth defects, including neural tube defects, plus increased risk for
children having cognitive impairment and autism. There is evidence that
folate consumption is protective.
Function
Tetrahydrofolate's main function in metabolism is transporting single-carbon groups (i.e. a methyl group, methylene group, or formyl group).
These carbon groups can be transferred to other molecules as part of
the modification or biosynthesis of a variety of biological molecules.
Folates are essential for the synthesis of DNA, the modification of DNA and RNA, the synthesis of methionine from homocysteine, and various other chemical reactions involved in cellular metabolism. These reactions are collectively known as folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism.
DNA synthesis
Folate derivatives participate in the biosynthesis of both purines
and pyrimidines. Formyl folate is required for two of the steps in the
biosynthesis of inosine monophosphate, the precursor to GMP and AMP. Methylenetetrahydrofolate donates the C1 center required for the biosynthesis of dTMP (2′-deoxythymidine-5′-phosphate) from dUMP (2′-deoxyuridine-5′-phosphate).
Formyl folate is required for two of the steps in the biosynthesis of inosine monophosphate, the precursor to GMP and AMP. Methylenetetrahydrofolate donates the C1 center required for the biosynthesis of dTMP (2′-deoxythymidine-5′-phosphate) from dUMP (2′-deoxyuridine-5′-phosphate). The conversion is catalyzed by thymidylate synthase.
Vitamin B12 activation
Simplified schematic diagram of the folate methionine cycle
Methyl-THF converts vitamin B12 to methyl-B12 (methylcobalamin). Methyl-B12 converts homocysteine, in a reaction catalyzed by homocysteine methyltransferase, to methionine. A defect in homocysteine methyltransferase or a deficiency of B12 may lead to a so-called "methyl-trap" of THF, in which THF converts to methyl-THF, causing a deficiency in folate. Thus, a deficiency in B12 can cause accumulation of methyl-THF, mimicking folate deficiency.
Diet
The United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service maintains a food composition database from which folate content in hundreds of foods can be searched as shown in the table. The Food Fortification Initiative lists all countries in the world that conduct fortification programs,
and within each country, what nutrients are added to which foods, and
whether those programs are voluntary or mandatory. In the US, mandatory
fortification of enriched breads, cereals, flours, corn meal, pastas,
rice, and other grain products began in January 1998. As of December 21,
2018, 81 countries required food fortification with one or more
vitamins.
The most commonly fortified vitamin – as used in 62 countries – is
folate; the most commonly fortified food is wheat flour, followed by
maize flour and rice. From country to country, added folic acid amounts
range from 0.4 to 5.1 μg/100 g, but the great majority are in a more
narrow range of 1.5 to 2.5 μg/100 g.
Folate naturally found in food is susceptible to destruction from high
heat cooking, especially in the presence of acidic foods and sauces.
Because
of the difference in bioavailability between supplemented folic acid
and the different forms of folate found in food, the dietary folate
equivalent (DFE) system was established. One DFE is defined as 1 μg of
dietary folate. One μg of folic acid supplement counts as 1.7 μg DFE.
The reason for the difference is that when folic acid is added to food
or taken as a dietary supplement with food it is at least 85% absorbed,
whereas only about 50% of folate naturally present in food is absorbed.
| Age | Infants | Children and adults | Pregnant women | Lactating women | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (AI) | (UL) | (RDA) | (UL) | (RDA) | (UL) | (RDA) | (UL) | |
| 0–6 months | 65 | None set | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 7–12 months | 80 | None set | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1–3 years | – | – | 150 | 300 | – | – | – | – |
| 4–8 years | – | – | 200 | 400 | – | – | – | – |
| 9–13 years | – | – | 300 | 600 | – | – | – | – |
| 14–18 | – | – | 400 | 800 | 600 | 800 | 500 | 800 |
| 19+ | – | – | 400 | 1000 | 600 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 |
The U.S. Institute of Medicine defines Estimated Average Requirements
(EARs), Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs), Adequate Intakes (AIs)
and Tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) at Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs). The European Food Safety Authority
(EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference
Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and
Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL defined the same as in
United States. For women and men over age 18 the PRI is set at 330
μg/day. PRI for pregnancy is 600 μg/day, for lactation 500 μg/day. For
children ages 1–17 years the PRIs increase with age from 120 to 270
μg/day. These values differ somewhat from the U.S. RDAs.
The United Kingdom's Dietary Reference Value for folate, set by the
Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy in 1991, is
200 μg/day for adults.
Safety
The risk
of toxicity from folic acid is low, because folate is a water-soluble
vitamin and is regularly removed from the body through urine. One
potential issue associated with high doses of folic acid is that it has a
masking effect on the diagnosis of pernicious anaemia due to vitamin B12
deficiency, and may even precipitate or exacerbate neuropathy in
vitamin B12-deficient individuals. This evidence justified development
of a UL for folate.
In general, ULs are set for vitamins and minerals when evidence is
sufficient. The adult UL of 1,000 μg for folate (and lower for children)
refers specifically to folic acid used as a supplement, as no health
risks have been associated with high intake of folate from food sources.
The EFSA reviewed the safety question and agreed with United States
that the UL be set at 1,000 μg. The Japan National Institute of Health and Nutrition set the adult UL at 1,300 or 1,400 μg depending on age.
Reviews of clinical trials that called for long-term consumption
of folic acid in amounts exceeding the UL have raised concerns. One
theory is that consumption of large amounts of folic acid leads to
detectable amounts of unmetabolized folic acid circulating in blood
because the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase
that converts folic acid to the biologically active forms is rate
limiting. Evidence of a negative health effect of folic acid in blood is
not consistent, and folic acid has no known cofactor function that
would increase the likelihood of a causal role for free FA in disease
development. However, low vitamin B12
status in combination with high folic acid intake, in addition to the
previously mentioned neuropathy risk, appeared to increase the risk of
cognitive impairment in the elderly.
Long-term use of folic acid dietary supplements in excess of 1,000
μg/day has been linked to an increase in prostate cancer risk.
Food labeling
For
U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a
serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For folate
labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 400 μg. As of the 27 May
2016 update, it was kept unchanged at 400 μg. A table of the old and new adult Daily Values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
The original deadline to be in compliance was 28 July 2018, but on 29
September 2017 the FDA released a proposed rule that extended the
deadline to 1 January 2020 for large companies and 1 January 2021 for
small companies.
European Union regulations require that labels declare energy, protein,
fat, saturated fat, carbohydrates, sugars, and salt. Voluntary
nutrients may be shown if present in significant amounts. Instead of
Daily Values, amounts are shown as percent of Reference Intakes (RIs).
For folate, 100% RI was set at 200 μg in 2011.
Food fortification
Folic acid fortification is a process where synthetic folic
acid is added to wheat flour or other foods with the intention of
promoting public health through increasing blood folate levels in the
populace. It is used as it more stable during processing and storage. After the discovery of the link between insufficient folic acid and neural tube defects, governments and health organizations worldwide made recommendations concerning folic acid supplementation
for women intending to become pregnant. Because the neural tube closes
in the first four weeks of gestation, often before many women even know
they are pregnant, many countries in time decided to implement mandatory
food fortification programs. A meta-analysis of global birth prevalence
of spina bifida showed that when mandatory fortification was compared
to countries with voluntary fortification or no fortification program,
there was a 30% reduction in live births with spina bifida, with some countries reporting a greater than 50% reduction.
Folic acid is added to grain products in more than 80 countries, either as required or voluntary fortification, and these fortified products make up a significant source of the population's folate intake. Fortification is controversial, with issues having been raised concerning individual liberty,
as well as the theorized health concerns described in the Safety
section. In the U.S., there is concern that the federal government
mandates fortification but does not provide monitoring of potential
undesirable effects of fortification. The Food Fortification Initiative lists all countries in the world that conduct fortification programs,
and within each country, what nutrients are added to which foods. As
of December 21, 2018, 81 countries required food fortification with one
or more vitamins. The most commonly mandatory fortified vitamin – in 62 countries – is folate; the most commonly fortified food is wheat flour.
Australia and New Zealand
Australia and New Zealand jointly agreed to wheat flour fortification through the Food Standards Australia New Zealand in 2007. The requirement was set at 135 µg of folate per 100 g of bread. Australia implemented the program in 2009.
New Zealand was also planning to fortify bread (excluding organic and
unleavened varieties) starting in 2009, but then opted to wait until
more research was done. The Association of Bakers and the Green Party had opposed mandatory fortification, describing it as "mass medication." Food Safety Minister Kate Wilkinson
reviewed the decision to fortify in July 2009, citing as reasons to
oppose claims for links between over consumption of folate with
increased risk of cancer.
In 2012 the delayed mandatory fortification program was revoked and
replaced by a voluntary program, with the hope of achieving a 50% bread
fortification target.
Canada
Canadian
public health efforts focused on promoting awareness of the importance
of folic acid supplementation for all women of childbearing age and
decreasing socio-economic inequalities by providing practical folic acid
support to vulnerable groups of women. Folic acid food fortification became mandatory in 1998, with the fortification of 150 µg of folic acid per 100 grams of enriched flour and uncooked cereal grains. The results of folic acid fortification on the rate of neural tube defects in Canada
have been positive, showing a 46% reduction in prevalence of NTDs; the
magnitude of reduction was proportional to the prefortification rate of
NTDs, essentially removing geographical variations in rates of NTDs seen
in Canada before fortification.
United Kingdom
While the Food Standards Agency recommended folic acid fortification, and wheat flour is fortified with iron,
folic acid fortification of wheat flour is allowed voluntarily rather
than required. A 2018 review by authors based in the United Kingdom
strongly recommended that mandatory fortification be reconsidered as a
means of reducing the risk of neural tube defects.
United States
In
the United States and many other countries, wheat flour is fortified
with folic acid, some countries also fortify maize flour and rice.
In 1996, the United States Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) published regulations requiring the addition of folic acid to
enriched breads, cereals, flours, corn meals, pastas, rice, and other
grain products.
This ruling took effect on 1 January 1998, and was specifically
targeted to reduce the risk of neural tube birth defects in newborns. There were concerns expressed that the amount of folate added was insufficient.
The fortification program was expected to raise a person's folic acid intake level by 70–130 µg/day; however, an increase of almost double that amount was actually observed. This could be from the fact that many foods are fortified by 160–175% over the required amount. Much of the elder population take supplements
that add 400 µg to their daily folic acid intake. This is a concern
because 70–80% of the population have detectable levels of unmetabolized
folic acid in their blood, a consequence of folic acid supplementation and fortification.
However, at blood concentrations achieved via food fortification, folic
acid has no known cofactor function that would increase the likelihood
of a causal role for free FA in disease development.
The U.S. National Center for Health Statistics conducts biannual
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to assess the
health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United
States. Some results are reported as What We Eat In America. The
2013–2014 survey reported that for adults ages 20 years and older, men
consumed on average of 249 μg/day folate from food plus 207 μg/day of
folic acid from consumption of fortified foods, for a combined total of
601 μg/day of dietary folate equivalents (DFEs; because each microgram
of folic acid counts as 1.7 μg of food folate). For women, the values
are 199, 153 and 459 μg/day, respectively. This means that fortification
led to a bigger increase in folic acid intake than first projected, and
that more than half the adults are consuming more than the RDA of 400
μg (as DFEs). Even so, fewer than half of pregnant women are exceeding
the pregnancy RDA of 600 μg/day.
Before folic acid fortification, about 4,100 pregnancies were
affected by a neural tube defect each year in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
reported in 2015 that since the addition of folic acid in grain-based
foods as mandated by the FDA, the rate of neural tube defects dropped by
35%. This translates to an annual saving in total direct costs of
approximately $508 million for the NTD-affected births that were
prevented.
In 2016, folate was the 96th most prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8 million prescriptions.
History
In the 1920s, scientists believed folate deficiency and anemia were the same condition. In 1931, researcher Lucy Wills made a key observation that led to the identification of folate as the nutrient required to prevent anemia during pregnancy. Wills demonstrated that anemia could be reversed with brewer's yeast.
In the late 1930s, folate was identified as the corrective substance in
brewer's yeast. It was first isolated via extraction from spinach leaves by Herschel K. Mitchell, Esmond E. Snell, and Roger J. Williams in 1941. The term "folic" is from the Latin word folium (which means leaf) because it was found in dark-green leafy vegetables. Historic names included L.casei, factor vitamin Bc after research done in chicks and vitamin M after research done in monkeys.
Bob Stokstad isolated the pure crystalline form in 1943, and was
able to determine its chemical structure while working at the Lederle
Laboratories of the American Cyanamid Company.
This historical research project, of obtaining folic acid in a pure
crystalline form in 1945, was done by the team called the "folic acid
boys," under the supervision and guidance of Director of Research Dr. Yellapragada Subbarow, at the Lederle Lab, Pearl River, NY. This research subsequently led to the synthesis of the antifolate aminopterin, which was used to treat childhood leukemia by Sidney Farber in 1948.
In the 1950s and 1960s, scientists began to discover the biochemical mechanisms of action for folate. In 1960, researchers linked folate deficiency to risk of neural tube defects.
In the late 1990s, the U.S. and Canadian governments decided that
despite public education programs and the availability of folic acid
supplements, there was still a challenge for women of child-bearing age
to meet the daily folate recommendations, which is when those two
countries implemented folate fortification programs. As of December 2018, 62 countries mandated food fortification with folic acid.
Other animals
Veterinarians
may test cats and dogs if a risk of folate deficiency is indicated.
Cats with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, moreso than dogs, may have
low serum folate. In dog breeds at risk for cleft lip and cleft palate
dietary folic acid supplementation significantly decreased incidence.