| Stomach cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Gastric cancer |
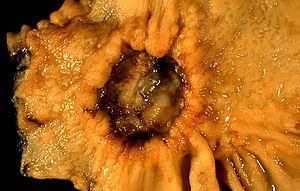 | |
| A stomach ulcer that was diagnosed as cancer on biopsy and surgically removed | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| Symptoms | Early: Heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite. Later: Weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, blood in the stool |
| Usual onset | Over years |
| Types | Gastric carcinomas, lymphoma, mesenchymal tumor |
| Causes | Helicobacter pylori, genetics |
| Risk factors | Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables, obesity |
| Diagnostic method | Biopsy done during endoscopy |
| Prevention | Mediterranean diet, stopping smoking |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate: < 10% (advanced cases), 32% (US), 71% (Japan) |
| Frequency | 3.5 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 783,000 (2018) |
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing and blood in the stool among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen and lymph nodes.
The most common cause is infection by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of H. pylori have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% of cases run in families, and between 1% and 3% of cases are due to genetic syndromes inherited from a person's parents such as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. Most of the time, stomach cancer develops in stages over years. Diagnosis is usually by biopsy done during endoscopy. This is followed by medical imaging to determine if the disease has spread to other parts of the body. Japan and South Korea, two countries that have high rates of the disease, screen for stomach cancer.
A Mediterranean diet lowers the risk of stomach cancer, as does the stopping of smoking. There is tentative evidence that treating H. pylori decreases the future risk. If stomach cancer is treated early, it can be cured. Treatments may include some combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and targeted therapy. If treated late, palliative care may be advised. Some types of lymphoma can be cured by eliminating H. pylori. Outcomes are often poor, with a less than 10% five-year survival rate in the Western world for advanced cases. This is largely because most people with the condition present with advanced disease. In the United States, five-year survival is 31.5%, while in South Korea it is over 65% and Japan over 70%, partly due to screening efforts.
Globally, stomach cancer is the fifth leading type of cancer and the third leading cause of death from cancer, making up 7% of cases and 9% of deaths. In 2018, it newly occurred in 1.03 million people and caused 783,000 deaths. Before the 1930s, in much of the world, including most Western developed countries, it was the most common cause of death from cancer. Rates of death have been decreasing in many areas of the world since then. This is believed to be due to the eating of less salted and pickled foods as a result of the development of refrigeration as a method of keeping food fresh. Stomach cancer occurs most commonly in East Asia and Eastern Europe. It occurs twice as often in males as in females.
Signs and symptoms
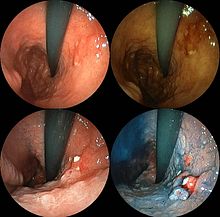
Endoscopic image of linitis plastica, a type of stomach cancer where the entire stomach is invaded, leading to a leather bottle-like appearance with blood coming out of it
Endoscopic images of the stomach cancer in early stage. Its histology was poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet ring cells. Left above: normal, right above: FICE, left low: acetate stained, right low: AIM stained
Stomach cancer is often either asymptomatic (producing no noticeable symptoms) or it may cause only nonspecific symptoms
(symptoms that may also be present in other related or unrelated
disorders) in its early stages. By the time symptoms occur, the cancer
has often reached an advanced stage (see below) and may have
metastasized (spread to other, perhaps distant, parts of the body),
which is one of the main reasons for its relatively poor prognosis. Stomach cancer can cause the following signs and symptoms:
Early cancers may be associated with indigestion or a burning sensation (heartburn). However, fewer than 1 in every 50 people referred for endoscopy due to indigestion has cancer. Abdominal discomfort and loss of appetite, especially for meat, can occur.
Gastric cancers that have enlarged and invaded normal tissue can cause weakness, fatigue, bloating of the stomach after meals, abdominal pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and occasional vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Further enlargement may cause weight loss or bleeding with vomiting blood or having blood in the stool, the latter apparent as black discolouration (melena) and sometimes leading to anemia. Dysphagia suggests a tumour in the cardia or extension of the gastric tumour into the esophagus.
Causes
Gastric cancer occurs as a result of many factors. It occurs twice as commonly in males as females. Estrogen may protect women against the development of this form of cancer.
Infections
Helicobacter pylori
infection is an essential risk factor in 65–80% of gastric cancers, but
only 2% of people with Helicobacter infections develop stomach cancer. The mechanism by which H. pylori induces stomach cancer potentially involves chronic inflammation, or the action of H. pylori virulence factors such as CagA. It was estimated that Epstein–Barr virus is responsible for 84,000 cases per year. AIDS is also associated with elevated risk.
Smoking
Smoking
increases the risk of developing gastric cancer significantly, from 40%
increased risk for current smokers to 82% increase for heavy smokers.
Gastric cancers due to smoking mostly occur in the upper part of the
stomach near the esophagus. Some studies show increased risk with alcohol consumption as well.
Diet
Sequence
of 123-iodine human scintiscans after an intravenous injection: (from
left) after 30 minutes, 20 hours and 48 hours. A high and rapid
concentration of radio-iodine is evident in gastric mucosa of the
stomach, in salivary glands, oral mucosa and in the periencephalic and
cerebrospinal fluid (left). In the thyroid gland, I-concentration is
more progressive, also in the reservoir (from 1% after 30 minutes to
5.8 % after 48 hours, of the total injected dose).[33]
Dietary factors are not proven causes, and the association between stomach cancer and various foods and beverages is weak. Some foods including smoked foods, salt and salt-rich foods, red meat, processed meat, pickled vegetables, and bracken are associated with a higher risk of stomach cancer. Nitrates and nitrites in cured meats can be converted by certain bacteria, including H. pylori, into compounds that have been found to cause stomach cancer in animals.
Fresh fruit and vegetable intake, citrus fruit intake, and antioxidant intake are associated with a lower risk of stomach cancer. A Mediterranean diet is associated with lower rates of stomach cancer, as is regular aspirin use.
Obesity is a physical risk factor that has been found to increase
the risk of gastric adenocarcinoma by contributing to the development
of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
The exact mechanism by which obesity causes GERD is not completely
known. Studies hypothesize that increased dietary fat leading to
increased pressure on the stomach and the lower esophageal sphincter,
due to excess adipose tissue, could play a role, yet no statistically
significant data has been collected.
However, the risk of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma, with GERD present,
has been found to increase more than 2 times for an obese person. There is a correlation between iodine deficiency and gastric cancer.
Genetics
About 10% of cases run in families and between 1% and 3% of cases are due to genetic syndromes inherited from a person's parents such as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer.
A genetic risk factor for gastric cancer is a genetic defect of the CDH1 gene known as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC). The CDH1 gene, which codes for E-cadherin, lies on the 16th chromosome. When the gene experiences a particular mutation, gastric cancer develops through a mechanism that is not fully understood.
This mutation is considered autosomal dominant meaning that half of a
carrier's children will likely experience the same mutation.
Diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer usually takes place when
at least two cases involving a family member, such as a parent or
grandparent, are diagnosed, with at least one diagnosed before the age
of 50. The diagnosis can also be made if there are at least three cases in the family, in which case age is not considered.
The International Cancer Genome Consortium is leading efforts to identify genomic changes involved in stomach cancer. A very small percentage of diffuse-type gastric cancers (see Histopathology below) arise from an inherited abnormal CDH1 gene. Genetic testing and treatment options are available for families at risk.
Other
Other risks include diabetes, pernicious anemia, chronic atrophic gastritis, Menetrier's disease (hyperplastic, hypersecretory gastropathy), and intestinal metaplasia.
Diagnosis
To
find the cause of symptoms, the doctor asks about the patient's medical
history, does a physical exam, and may order laboratory studies. The
patient may also have one or all of the following exams:
- Gastroscopic exam is the diagnostic method of choice. This involves insertion of a fibre optic camera into the stomach to visualise it.
- Upper GI series (may be called barium roentgenogram).
- Computed tomography or CT scanning of the abdomen may reveal gastric cancer. It is more useful to determine invasion into adjacent tissues or the presence of spread to local lymph nodes. Wall thickening of more than 1 cm that is focal, eccentric and enhancing favours malignancy.
In 2013, Chinese and Israeli scientists reported a successful pilot study of a breathalyzer-style breath test intended to diagnose stomach cancer by analyzing exhaled chemicals without the need for an intrusive endoscopy. A larger-scale clinical trial of this technology was completed in 2014.
Abnormal tissue seen in a gastroscope examination will be biopsied by the surgeon or gastroenterologist. This tissue is then sent to a pathologist for histological
examination under a microscope to check for the presence of cancerous
cells. A biopsy, with subsequent histological analysis, is the only sure
way to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Various gastroscopic modalities have been developed to increase
yield of detected mucosa with a dye that accentuates the cell structure
and can identify areas of dysplasia. Endocytoscopy involves
ultra-high magnification to visualise cellular structure to better
determine areas of dysplasia. Other gastroscopic modalities such as optical coherence tomography are being tested investigationally for similar applications.
A number of cutaneous conditions are associated with gastric cancer. A condition of darkened hyperplasia of the skin, frequently of the axilla and groin, known as acanthosis nigricans, is associated with intra-abdominal cancers such as gastric cancer. Other cutaneous manifestations of gastric cancer include tripe palms (a similar darkening hyperplasia of the skin of the palms) and the Leser-Trelat sign, which is the rapid development of skin lesions known as seborrheic keratoses.
Various blood tests may be done including a complete blood count (CBC) to check for anaemia, and a fecal occult blood test to check for blood in the stool.
Histopathology
- Gastric adenocarcinoma is a malignant epithelial tumour, originating from glandular epithelium of the gastric mucosa. Stomach cancers are about 90% adenocarcinomas. Histologically, there are two major types of gastric adenocarcinoma (Lauren classification): intestinal type or diffuse type. Adenocarcinomas tend to aggressively invade the gastric wall, infiltrating the muscularis mucosae, the submucosa and then the muscularis propria. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma tumour cells describe irregular tubular structures, harbouring pluristratification, multiple lumens, reduced stroma ("back to back" aspect). Often, it associates intestinal metaplasia in neighbouring mucosa. Depending on glandular architecture, cellular pleomorphism and mucosecretion, adenocarcinoma may present 3 degrees of differentiation: well, moderate and poorly differentiated. Diffuse type adenocarcinoma (mucinous, colloid, linitis plastica or leather-bottle stomach) tumour cells are discohesive and secrete mucus, which is delivered in the interstitium, producing large pools of mucus/colloid (optically "empty" spaces). It is poorly differentiated. If the mucus remains inside the tumour cell, it pushes the nucleus to the periphery: "signet-ring cell".
- Around 5% of gastric cancers are lymphomas. These may include extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas (MALT type) and to a lesser extent diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. MALT type make up about half of stomach lymphomas.
- Carcinoid and stromal tumors may occur.
- Poor to moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach. H&E stain.
- Gastric signet ring cell carcinoma. H&E stain.
Staging
T stages of stomach cancer
If cancer cells are found in the tissue sample, the next step is to stage,
or find out the extent of the disease. Various tests determine whether
the cancer has spread and, if so, what parts of the body are affected.
Because stomach cancer can spread to the liver, the pancreas, and other
organs near the stomach as well as to the lungs, the doctor may order a CT scan, a PET scan, an endoscopic ultrasound exam, or other tests to check these areas. Blood tests for tumor markers, such as carcinoembryonic antigen
(CEA) and carbohydrate antigen (CA) may be ordered, as their levels
correlate to extent of metastasis, especially to the liver, and the cure
rate.
Staging may not be complete until after surgery. The surgeon
removes nearby lymph nodes and possibly samples of tissue from other
areas in the abdomen for examination by a pathologist.
The clinical stages of stomach cancer are:
- Stage 0. Limited to the inner lining of the stomach. Treatable by endoscopic mucosal resection when found very early (in routine screenings); otherwise by gastrectomy and lymphadenectomy without need for chemotherapy or radiation.
- Stage I. Penetration to the second or third layers of the stomach (Stage 1A) or to the second layer and nearby lymph nodes (Stage 1B). Stage 1A is treated by surgery, including removal of the omentum. Stage 1B may be treated with chemotherapy (5-fluorouracil) and radiation therapy.
- Stage II. Penetration to the second layer and more distant lymph nodes, or the third layer and only nearby lymph nodes, or all four layers but not the lymph nodes. Treated as for Stage I, sometimes with additional neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
- Stage III. Penetration to the third layer and more distant lymph nodes, or penetration to the fourth layer and either nearby tissues or nearby or more distant lymph nodes. Treated as for Stage II; a cure is still possible in some cases.
- Stage IV. Cancer has spread to nearby tissues and more distant lymph nodes, or has metastasized to other organs. A cure is very rarely possible at this stage. Some other techniques to prolong life or improve symptoms are used, including laser treatment, surgery, and/or stents to keep the digestive tract open, and chemotherapy by drugs such as 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, epirubicin, etoposide, docetaxel, oxaliplatin, capecitabine or irinotecan.
Stomach cancer metastasized to the lungs
The TNM staging system is also used.
In a study of open-access endoscopy in Scotland, patients were diagnosed 7% in Stage I 17% in Stage II, and 28% in Stage III. A Minnesota population was diagnosed 10% in Stage I, 13% in Stage II, and 18% in Stage III. However, in a high-risk population in the Valdivia Province of southern Chile, only 5% of patients were diagnosed in the first two stages and 10% in stage III.
Prevention
Getting rid of H. pylori in those who are infected decreases the risk of stomach cancer, at least in those who are Asian. A 2014 meta-analysis of observational studies found that a diet high in fruits, mushrooms, garlic, soybeans, and green onions was associated with a lower risk of stomach cancer in the Korean population. Low doses of vitamins, especially from a healthy diet, decrease the risk of stomach cancer. A previous review of antioxidant supplementation did not find supporting evidence and possibly worse outcomes.
Management
Cancer
of the stomach is difficult to cure unless it is found at an early
stage (before it has begun to spread). Unfortunately, because early
stomach cancer causes few symptoms, the disease is usually advanced when
the diagnosis is made.
Treatment for stomach cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. New treatment approaches such as immunotherapy or gene therapy and improved ways of using current methods are being studied in clinical trials.
Surgery
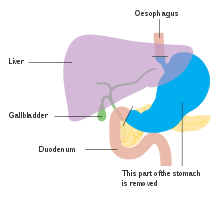
Anatomy before Roux-en-y surgery to resect stomach cancer.
Surgery remains the only curative therapy for stomach cancer. Of the different surgical techniques, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is a treatment for early gastric cancer (tumor only involves the mucosa) that was pioneered in Japan and is available in the United States at some centers.
In this procedure, the tumor, together with the inner lining of stomach
(mucosa), is removed from the wall of the stomach using an electrical
wire loop through the endoscope. The advantage is that it is a much
smaller operation than removing the stomach. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is a similar technique pioneered in Japan, used to resect a large area of mucosa in one piece.
If the pathologic examination of the resected specimen shows incomplete
resection or deep invasion by tumor, the patient would need a formal
stomach resection. A 2016 Cochrane review
found low quality evidence of no difference in short-term mortality
between laparoscopic and open gastrectomy (removal of stomach), and that
benefits or harms of laparoscopic gastrectomy cannot be ruled out.
Post-operatively, up to 70% of people undergoing total gastrectomy
develop complications such as dumping syndrome and reflux esophagitis.
Construction of a "pouch", which serves as a "stomach substitute",
reduced the incidence of dumping syndrome and reflux esophagitis by 73%
and 63% respectively, and led to improvements in quality-of-life,
nutritional outcomes, and body mass index.
Those with metastatic disease at the time of presentation may
receive palliative surgery and while it remains controversial, due to
the possibility of complications from the surgery itself and the fact
that it may delay chemotherapy the data so far is mostly positive, with
improved survival rates being seen in those treated with this approach.
Chemotherapy
The use of chemotherapy to treat stomach cancer has no firmly established standard of care.
Unfortunately, stomach cancer has not been particularly sensitive to
these drugs, and chemotherapy, if used, has usually served to
palliatively reduce the size of the tumor, relieve symptoms of the
disease and increase survival time. Some drugs used in stomach cancer treatment have included: 5-FU (fluorouracil) or its analog capecitabine, BCNU (carmustine), methyl-CCNU (semustine) and doxorubicin (Adriamycin), as well as mitomycin C, and more recently cisplatin and taxotere, often using drugs in various combinations. The relative benefits of these different drugs, alone and in combination, are unclear.
Clinical researchers are exploring the benefits of giving chemotherapy
before surgery to shrink the tumor, or as adjuvant therapy after surgery
to destroy remaining cancer cells.
Targeted therapy
Recently, treatment with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) inhibitor, trastuzumab, has been demonstrated to increase overall survival in inoperable locally advanced or metastatic gastric carcinoma over-expressing the HER2/neu gene. In particular, HER2 is overexpressed in 13–22% of patients with gastric cancer. Of note, HER2
overexpression in gastric neoplasia is heterogeneous and comprises a
minority of tumor cells (less than 10% of gastric cancers overexpress HER2 in more than 5% of tumor cells). Hence, this heterogeneous expression should be taken into account for HER2 testing, particularly in small samples such as biopsies, requiring the evaluation of more than one bioptic sample.
Radiation
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) may be used to treat stomach cancer, often as an adjuvant to chemotherapy and/or surgery.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma of the MALT type can often be fully treated by treating an underlying H. pylori infection. This results in remission in about 80% of cases.
Prognosis
The
prognosis of stomach cancer is generally poor, due to the fact the
tumour has often metastasised by the time of discovery and the fact that
most people with the condition are elderly (median age is between 70
and 75 years) at presentation.
The average life expectancy after being diagnosed is around 24 months,
and the five-year survival rate for stomach cancer is less than 10
percent.
Almost 300 genes are related to outcomes in stomach cancer with
both unfavorable genes where high expression related to poor survival
and favorable genes where high expression associated with longer
survival times. Examples of poor prognosis genes include ITGAV and DUSP1.
Epidemiology
Stomach cancer deaths per million persons in 2012
0–11
12–16
17–24
25–33
34–51
52–76
77–102
103–128
129–175
176–400
Worldwide, stomach cancer is the fifth most-common cancer with 952,000 cases diagnosed in 2012. It is more common both in men and in developing countries. In 2012, it represented 8.5% of cancer cases in men, making it the fourth most-common cancer in men.
Also in 2012, the number of deaths was 700,000 having decreased
slightly from 774,000 in 1990, making it the third-leading cause of
cancer-related death (after lung cancer and liver cancer).
Less than 5% of stomach cancers occur in people under 40 years of
age with 81.1% of that 5% in the age-group of 30 to 39 and 18.9% in the
age-group of 20 to 29.
In 2014, stomach cancer resulted in 0.61% of deaths (13,303 cases) in the U.S. In China, stomach cancer accounted for 3.56% of all deaths (324,439 cases). The highest rate of stomach cancer was in Mongolia, at 28 cases per 100,000 people.
In the United Kingdom, stomach cancer is the fifteenth
most-common cancer (around 7,100 people were diagnosed with stomach
cancer in 2011), and it is the tenth most-common cause of cancer-related
deaths (around 4,800 people died in 2012).
Incidence and mortality rates of gastric cancer vary greatly in
Africa. The GLOBOCAN system is currently the most widely used method to
compare these rates between countries, but African incidence and
mortality rates are seen to differ among countries, possibly due to the
lack of universal access to a registry system for all countries. Variation as drastic as estimated rates from 0.3/100000 in Botswana to 20.3/100000 in Mali have been observed. In Uganda, the incidence of gastric cancer has increased from the 1960s measurement of 0.8/100000 to 5.6/100000.
Gastric cancer, though present, is relatively low when compared to
countries with high incidence like Japan and China. One suspected cause
of the variation within Africa and between other countries is due to
different strains of the Helicobacter pylori bacteria. The trend
commonly-seen is that H. pylori infection increases the risk for gastric
cancer. However, this is not the case in Africa, giving this phenomenon
the name the “African enigma.”
Although this bacteria is found in Africa, evidence has supported that
different strains with mutations in the bacterial genotype may
contribute to the difference in cancer development between African
countries and others outside the continent.
However, increasing access to health care and treatment measures have
been commonly-associated with the rising incidence, particularly in
Uganda.
Other animals
The stomach is a muscular organ of the gastrointestinal tract that holds food and begins the digestive process by secreting gastric juice. The most common cancers of the stomach are adenocarcinomas
but other histological types have been reported. Signs vary but may
include vomiting (especially if blood is present), weight loss, anemia,
and lack of appetite. Bowel movements may be dark and tarry in nature.
In order to determine whether cancer is present in the stomach, special
X-rays and/or abdominal ultrasound may be performed. Gastroscopy,
a test using an instrument called endoscope to examine the stomach, is a
useful diagnostic tool that can also take samples of the suspected mass
for histopathological analysis to confirm or rule out cancer. The most
definitive method of cancer diagnosis is through open surgical biopsy.
Most stomach tumors are malignant with evidence of spread to lymph
nodes or liver, making treatment difficult. Except for lymphoma, surgery
is the most frequent treatment option for stomach cancers but it is
associated with significant risks.