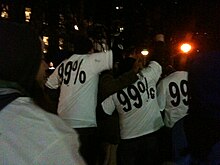The Occupy movement was an international progressive socio-political movement that expressed opposition to social and economic inequality and to the lack of "real democracy" around the world. It aimed primarily to advance social and economic justice and new forms of democracy. The movement had many different scopes, since local groups often had different focuses, but its prime concerns included how large corporations (and the global financial system) control the world in a way that disproportionately benefited a minority, undermined democracy and caused instability. It formed part of what Manfred Steger called the "global justice movement".
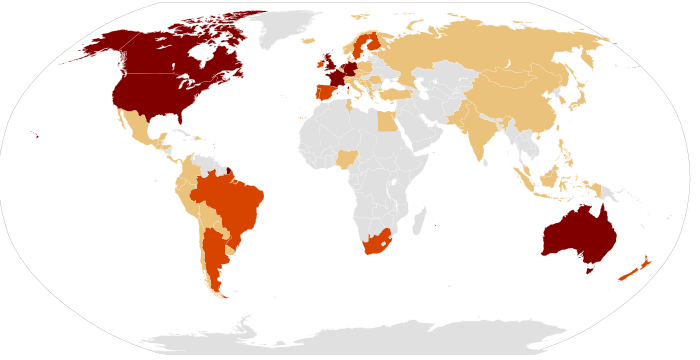
The first Occupy protest to receive widespread attention, Occupy Wall Street in New York City's Zuccotti Park, began on 17 September 2011. By 9 October, Occupy protests had taken place or were ongoing in over 951 cities across 82 countries, and in over 600 communities in the United States.
Although the movement became most active in the United States, by
October 2011 Occupy protests and occupations had started in dozens of
other countries across every widely inhabited continent. For the first
month, overt police repression remained minimal, but this began to
change by 25 October 2011, when police first attempted to forcibly
remove Occupy Oakland. By the end of 2011 authorities had cleared most of the major camps, with the last remaining high-profile sites – in Washington, D.C. and in London – evicted by February 2012.
The Occupy movement took inspiration in part from the Arab Spring, from the 2009 Iranian Green Movement, and from the Spanish Indignados Movement, as well as from the overall global wave of anti-austerity protests of 2010 and following. The movement commonly uses the slogan "We are the 99%" and the #Occupy hashtag format; it organizes through websites such as Occupy Together. According to The Washington Post, the movement, which Cornel West described as a "democratic awakening", is difficult to distill to a few demands. On 12 October 2011 Los Angeles City Council
became one of the first governmental bodies in the United States to
adopt a resolution stating its informal support of the Occupy movement. In October 2012, the Executive Director of Financial Stability at the Bank of England stated that the protesters were right to criticise and had persuaded bankers and politicians "to behave in a more moral way".
Background
In 2009 and 2010, students across the University of California occupied campus buildings in protest against budget cuts, tuition hikes, and staff cutbacks that had resulted from the Great Recession of 2008. According to Dissent Magazine, "It was in the context of the California student movement that the slogan 'Occupy Everything, Demand Nothing' first emerged." The Huffington Post
noted that "During one incident in March of 2010, 150 protesters were
arrested for trying to occupy part of Interstate 80 in protest of the
budget cuts and tuition hikes, displaying a banner that read 'Occupy
everything,' while shutting down the roadway for an hour, and were
crushed by the same kind of overwhelming police force that was later
mobilized against Occupy encampments across the country." Adbusters editor Micah White, who designed the original Occupy Wall Street concept, traveled to California for the protests and took part in the occupation of Wheeler Hall. He wrote enthusiastically for Adbusters about the "revolutionary potential of [the students] struggle".
The Spanish Indignados movement began in mid-May 2011, with camps at Madrid and elsewhere. According to sociologist Manuel Castells, by the end of the month there were already hundreds of camps around Spain and across the world.
For some journalists and commentators the camping in Spain marked the
start of the global occupy movement, though it is much more commonly
said to have begun in New York during September.
On 30 May 2011, a leader of the Indignados, inspired by the Arab Spring, 5.18 Movement of 1980, and June Democracy Movement of 1987 called for a worldwide protest on 15 October. In mid-2011, the Canadian-based group Adbusters Media Foundation, best known for its advertisement-free anti-consumerist magazine Adbusters, proposed a peaceful occupation of Wall Street to protest corporate influence on democracy, address a growing disparity in wealth, and the absence of legal repercussions behind the recent global financial crisis. Adbusters co-founder Kalle Lasn registered the OccupyWallStreet.org web address on 9 June. According to Micah White,
the senior editor of the magazine, "[we] basically floated the idea in
mid-July into our [email list] and it was spontaneously taken up by all
the people of the world, it just kind of snowballed from there."
One of the inspirations for the movement was the Democracy Village set up in 2010, outside the British Parliament in London. The protest received additional attention when the internet hacker group Anonymous encouraged its followers to take part in the protests, calling protesters to "flood lower Manhattan, set up tents, kitchens, peaceful barricades and Occupy Wall Street". They promoted the protest with a poster featuring a dancer atop Wall Street's iconic Charging Bull. The first protest was held at Zuccotti Park in New York City on 17 September 2011,
the tenth anniversary of the re-opening of Wall Street trading after
the 11 September 2001 attacks. The protests were preceded by a similar Occupy Dataran movement in Kuala Lumpur in July, seven weeks before Occupy Wall Street.
"We are the 99%" slogan
Occupy protesters with "We are the 99%" signs in Bennington, Vermont
The phrase "The 99%" is a political slogan used by participants in the Occupy movement. It was originally launched as a Tumblr blog page in late August 2011. It refers to the concentration of wealth among the top 1% of income earners compared to the other 99 percent; the top 1 percent of income earners nearly tripled after-tax income over the last thirty years according to a Congressional Budget Office (CBO) report.
The report was released just as concerns of the Occupy Wall
Street movement were beginning to enter the national political debate.
According to the CBO, between 1979 and 2007 the incomes of the top 1%
of Americans grew by an average of 275%. During the same time period,
the 60% of Americans in the middle of the income scale saw their income
rise by 40%. Since 1979 the average pre-tax income for the bottom 90% of
households has decreased by $900, while that of the top 1% increased by
over $700,000, as federal taxation became less progressive.
From 1992 to 2007 the top 400 income earners in the U.S. saw their
income increase 392% and their average tax rate reduced by 37%. In 2009, the average income of the top 1% was $960,000 with a minimum income of $343,927.
Protesters with the "99%" t-shirts at Occupy Wall Street on 17 November 2011 near the New York City Hall.
In 2007, the richest 1% of the American population owned 34.6% of the
country's total wealth, and the next 19% owned 50.5%. Thus, the top 20%
of Americans owned 85% of the country's wealth and the bottom 80% of
the population owned 15% —an example of the Pareto principle. Financial inequality (total net worth minus the value of one's home)
was greater than inequality in total wealth, with the top 1% of the
population owning 42.7%, the next 19% of Americans owning 50.3%, and the
bottom 80% owning 7%.
However, after the Great Recession
which started in 2007, the share of total wealth owned by the top 1% of
the population grew from 34.6% to 37.1%, and that owned by the top 20%
of Americans grew from 85% to 87.7%. The Great Recession also caused a
drop of 36.1% in median household wealth but a drop of only 11.1% for
the top 1%, further widening the gap between the 1% and the 99%.
During the economic expansion between 2002 and 2007, the income of the
top 1% grew 10 times faster than the income of the bottom 90%. In this
period 66% of total income gains went to the 1%, who in 2007 had a
larger share of total income than at any time since 1928.
This is in stark contrast with surveys of U.S. populations that
indicate an "ideal" distribution that is much more equal, and a
widespread ignorance of the true income inequality and wealth inequality.
Goals
During the
early weeks, the movement was frequently criticized by the news media
for having no clearly defined goals. Speaking on 7 October 2011, Kalle
Lasn of Adbusters said that, in the early stages, the lack of demands
was the "mysterious part" that allowed the movement to grow. By late October, Adbusters had been trying to "rally it around a single, clear demand" for a Robin Hood tax, with a global march in support of the Robin Hood tax planned for 29 October. Naomi Wolf
argued that the impression created by much of the media that the
protestors did not have clear demands was false. Wolf argued that they
did have clear demands including a desire to end what they saw as the corrupting effect of money on politics. The New Yorker magazine stated that the claims of Kalle Lasn and Micah M. White were specific: tighten banking-industry regulations, ban high-frequency trading,
arrest all 'financial fraudsters' responsible for the 2008 crash, and
form a Presidential commission to investigate and prosecute corruption
in politics. According to Bloomberg Businessweek,
protesters wanted more and better jobs, more equal distribution of
income, bank reform, and a reduction of the influence of corporations on
politics. The movement has also been described as broadly anticapitalist.
Some commentators such as David Graeber and Judith Butler
criticized the idea that the movement must have clearly defined
demands; they argued that issuing demands is counterproductive for the
Occupy movement, because doing so would legitimize the very power
structures the movement seeks to challenge.
In late November, the London contingent of the Occupy movement released
their first statement on corporations, in which they called for
measures to end tax evasion
by wealthy firms. The reason for the delay in articulating a clear
demand was given as the time it takes to reach a consensus with the
sometimes slow processes of participatory democracy.
In November "Occupy London Stock Exchange", an offshoot of Occupy
London, said that they were working on a global collaboration of various
occupations that reflected the voices of diverse movements worldwide. The global movement has been called the reinvention of politics, revolution, and utopia in the twenty-first century.
Methods
Assembly hand signals
Activists have used web technologies and social media like IRC, Facebook, Twitter, and Meetup to coordinate events. Indymedia helped the movement with communications, saying there had been conference calls on Skype with participants from up to 80 locations. Interactive live streams of events by independent journalists such as Tim Pool were used to augment Mainstream media coverage. The progressive provider May First/People Link
offered cost-free memberships for dozens of groups, including groups in
Iran and Germany, to host websites, emails, and email lists securely.
The movement went further to attempt to promote its causes through
multi-media and art, which has been gathered and archived by
institutions such as the National Museum of American History and New York Historical Society.
The aim of much of the art produced was to visually impact the
mainstream through imagery to attempt to create solidarity and unity
among the "99%".
The Community Environmental Legal Defense Fund released a model
community bill of rights, promoting laws that strip corporations of
their personhood rights and elevating the rights of citizens, for occupy
organizers to adopt locally. In December 2011, Occupy Homes embarked on a movement to assist home owners who had lost or were scheduled to lose their homes due to foreclosure
as a result of what they called the illegal practices used by banks
that took advantage of consumers. The group planned to occupy foreclosed
homes, disrupt bank auctions, and block evictions.
Structure
The General Assembly meeting in Washington Square Park, New York City, on 8 October 2011
The movement has been described as having an "overriding commitment" to participatory democracy.
Much of the movements democratic process occurs in "working groups,"
where any protester is able to have their say. Important decisions are
often made at General assemblies, which can themselves be informed by the findings of multiple working groups. Decisions are made using the consensus model of participatory democracy. This often features the use of hand signals
to increase participation and operating with discussion facilitators
rather than leaders – a system that can be traced in part to the Quaker movement several centuries ago, to participatory democracy in ancient Athens, and to the spokescouncils of the 1999 anti-globalization movement.
At the assemblies, working group proposals are made to meeting participants, who comment upon them using a process called a stack; a queue of speakers that anyone can join. In New York City, Occupy Wall Street uses what is called a progressive stack, in which people from marginalized groups are sometimes allowed to speak before people from dominant groups, with facilitators,
or stack-keepers, urging speakers to "step forward, or step back" based
on which group they belong to, meaning that women and minorities get to
go to the front of the line, while white males must often wait for a
turn to speak. The progressive stack concept has been criticized by some outside the movement as "forced equality" and "unfair".
Nonviolence
The occupy movement began with a commitment to nonviolence. Frequent references were made to the writings of nonviolent theorist Dr. Gene Sharp whose work was reported to have influenced nonviolent struggle movements in Serbia and the Arab Spring. Study groups were organised across the US Occupy camps discussing Sharp's 198 methods of nonviolent action and his book From Dictatorship to Democracy. A subsequent film about his work How to Start a Revolution by Ruaridh Arrow which premiered in Boston on 18 September was screened in Occupy camps across the US and Europe.
Sharp himself warned that many of the tactics the movement were
employing were not effective. In an Al Jazeera interview, he said, "The
[Occupy] protesters don't have a clear objective, something they can
actually achieve. If they think they will change the economic system by
simply staying in a particular location, then they are likely to be very
disappointed. Protest alone accomplishes very little."
In late May 2011, sociologist Manuel Castells
congratulated Spanish occupiers for the fact that not a single violent
incident had been reported after 11 days of camping all over Spain.
Castells said that nonviolence was of fundamental importance, and was
echoed by various other sociologists and social historians including
Lester Kurtz, Prof. Maurice Isserman and Prof. Tom Juravich.
Juravich and others have, however, said that conflict can be important
in attracting attention, with much to be gained if occupiers are seen as
victims of the violence, providing occupiers keep their own aggression
strictly within limits.
In the words of one occupier, it can help them gain media coverage if
they "make things a little sexy and badass" . The Direct Action Working
Group of Occupy Wall Street endorsed diversity of tactics from the earliest days of the encampment.
Not all occupiers have upheld the commitment to nonviolence, with
aggressive tactics being used in Spain from as early as 15 June, and
with some journalists saying the New York branch of the movement did
initially accept protestors who had not signed up to nonviolence.
In September, sympathetic coverage given to the movement by the
media was substantially increased after the circulation of a video of
pepper spray being used by a police commander against peaceful female
protestors. In early October, Naomi Klein congratulated New York occupiers for their commitment to nonviolence.
By November 2011, media sources began to report an increase in
violence, with allegations of sexual assault and incidents of violence
from occupiers against the police, including one officer allegedly
stabbed with scissors. Some occupy camps responded by requiring that all occupiers sign a resolution to be nonviolent if they wished to stay. Rick Hampton for USA Today said the vast majority of occupy members have been nonviolent. Reviewing the global movement in December 2011, Anthony Barnett said its nonviolence remained an immense strength.
In late January 2012, the movement's commitment to nonviolence was
questioned after clashes with the police that saw about 400 arrests in
the U.S. city of Oakland.
Some protestors and witnesses said the police initiated the violence;
others said there was violence against the police; however, they blamed black bloc anarchists and agents provocateurs.
One protester who did not take part stated, "It was organized by a very
militant anarchist segment of the movement; I support the idea of
taking a building, especially for housing those who don't have housing.
But I don't support it with the kind of triumphal attitude I saw
expressed."
Social media
From
the beginning the Occupy movement relied heavily on social media to
disperse information and gather support. Occupy accounts were very
successful in achieving these goals. The social media accounts
eventually became hierarchical and failed their purpose. Some
believe, in order to have been more successful, the social media
accounts should have been more heavily regulated and kept to a standard.
In addition, a study was published that followed how Occupy user
interests changed in time from 1 June 2011 to 31 August 2012. It showed
40% of users produced Occupy related content during peak activity of the
movement. But, it was not sustained over the following year, with the
user ratio dropping to less than 5% in the last three months of the
study period.
Responses to the movement from celebrities were both in-person
and online. Some find it controversial that rich celebrities made
appearances at the Occupy Wall Street Movement, but Kanye West justified his appearance as helping give power back to the people. Other celebrities such as Yoko Ono, Mark Ruffalo, and Michael Moore tweeted and showed their support.
Many hold that the success of OWS has led to the success of Bernie Sanders and his political platform, disrupting the political conversation about environmental impact and economic equality. Some believe that there was social media blockage of Sanders' presidential campaign, in favor of more airtime for Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton.
During the 2016 Presidential Election, people used the #BernieBlackout
hashtag to boost awareness around the unfair usage of popular media to
favor some presidential candidates over others.
Chronology of events
The WikiLeaks endorsed news site WikiLeaks Central began promoting the idea of a "US Day of Rage," on 10 March 2011. The Canadian editor-in-chief Heather Marsh modeled the concept after the Days of Rage being held at that time in the Middle East and North Africa. Early promotion by the WikiLeaks Twitter and blog was reported as being instrumental in the group's success. It was renamed Occupy Wall Street after the idea publicized on an email list and online blog on 13 July 2011 by Vancouver-based non-profit Canadian group Adbusters. The Occupy Wall Street protests began on 17 September 2011 in downtown Manhattan. On 9 October 2011, activists in cities in over 25 countries repeated calls for a global protest on 15 October. A list of events for 15 October included 951 cities in 82 countries. On 15 October events were held in many cities worldwide.
17 September to 14 October 2011
On
17 September 2011, 1,000 protesters gathered in downtown Manhattan
walking up and down Wall Street. About 100 to 200 people stayed
overnight in Zucotti Park, two blocks north of Wall Street. By 19
September, seven people had been arrested.
At least 80 arrests were made on 24 September after protesters started
marching uptown and forcing the closure of several streets. Most of the
80 arrests were for blocking traffic, though some were also charged with
disorderly conduct and resisting arrest. Police officers also used a technique called kettling which involves using orange nets to isolate protesters into smaller groups. Videos which showed several penned-in female demonstrators being hit with pepper spray by a police official were widely disseminated, sparking controversy. That police official, later identified as Deputy Inspector Anthony Bologna, was shown in other videos hitting a photographer with a burst of spray.
Protesters rallying near New York police headquarters, with St. Andrew's Church in the background
Public attention to the pepper-sprayings resulted in a spike of news
media coverage, a pattern that was to be repeated in the coming weeks
following confrontations with police. Clyde Haberman, writing in The New York Times,
said that "If the Occupy Wall Street protesters ever choose to
recognize a person who gave their cause its biggest boost, they may want
to pay tribute to Anthony Bologna," calling the event "vital" for the
still nascent movement. On 1 October 2011, protesters set out to march across the Brooklyn Bridge. The New York Times
reported that more than 700 arrests were made. Some said the police had
tricked protesters, allowing them onto the bridge, and even escorting
them partway across. Jesse A. Myerson, a media coordinator for Occupy
Wall Street said, "The cops watched and did nothing, indeed, seemed to
guide us onto the roadway." A spokesman for the New York Police Department,
Paul Browne, said that protesters were given multiple warnings to stay
on the sidewalk and not block the street, and were arrested when they
refused.
On 4 October, a group of protesters who were arrested on the
bridge filed a lawsuit against the city, alleging that officers had
violated their constitutional rights by luring them into a trap and then
arresting them.
In June 2012, a federal judge ruled that the protesters had not
received sufficient warning of arrest pending entrance onto the Brooklyn
Bridge. Although video evidence showed the police warning protesters by
bullhorn,
after reviewing it, Judge Jed S. Rakoff sided with plaintiffs, saying,
"a reasonable officer in the noisy environment defendants occupied would
have known that a single bull horn could not reasonably communicate a
message to 700 demonstrators".
On 5 October 2011, joined by union members, students, and the
unemployed, the demonstration swelled to the largest yet with an
estimated 15,000 marchers joining the protest. Smaller protests
continued in cities and on college campuses across the country.
Thousands of union workers joined protesters marching through the
Financial District. The march was mostly peaceful—until after nightfall,
when scuffles erupted. About 200 protesters tried to storm barricades
blocking them from Wall Street and the Stock Exchange. Police responded
with pepper spray and penned the protesters in with orange netting.
Inspired by Occupy Wall Street, British protesters organized an occupation of the London Stock Exchange
to bring attention to what they saw as unethical behavior on the part
of banks. One of the organizers of the protest said the protests were to
be focused against "increasing social and economic injustice in this
country". In his opinion, "the Government has made sure to maintain the
status quo and let the people who caused this crisis get off scot-free,
whilst conversely ensuring that the people of this country pay the
price, in particular those most vulnerable."
15 October to 4 November
A crowd of protestors in Congress Square, Ljubljana, Slovenia, on 15 October 2011
On 15 October 2011 global protests
were staged around the world, with thousands of protesters staging
demonstrations in 900 cities including Auckland, Sydney, Hong Kong,
Taipei, Tokyo, São Paulo, Paris, Madrid, Berlin, Hamburg, Leipzig, and
many other cities. In Frankfurt, 5,000 people protested at the European
Central Bank and in Zurich, Switzerland's financial hub, protesters
carried banners reading "We won't bail you out yet again" and "We are
the 99 percent." Protests were largely peaceful; however, a protest in
Rome that drew thousands turned violent. Thousands of Occupy Wall Street protesters gathered in Times Square in New York City and rallied for several hours.
Several hundred protesters were arrested across the U.S., mostly for
refusing to obey police orders to leave public areas. In Chicago there
were 175 arrests, about 100 arrests in Arizona (53 in Tucson, 46 in Phoenix), and more than 70 in New York City, including at least 40 in Times Square. Multiple arrests were reported in Chicago, and about 150 people camped out by city hall in Minneapolis.
In the early morning hours of 25 October, police cleared and closed an Occupy Oakland encampment in Frank Ogawa Plaza in Oakland, California.
The raid was chaotic and violent, but Oakland Police Chief Howard
Jordan expressed his pleasure concerning the operation because neither
the police nor the public suffered any injuries.
A street march that afternoon protesting the closure culminated in a
confrontation between police and protesters, who sought to re-establish
the Ogawa Plaza encampment. During this confrontation, protester Scott
Olsen, a former Marine and Iraq War veteran, suffered a skull fracture
caused by a tear-gas projectile or smoke canister fired by police. By 29 October 2011, there were around 2,300 Occupy protest camps across around 2,000 cities worldwide. On 2 November, protesters in Oakland, California, shut down the Port of Oakland,
the fifth busiest port in the nation. Police estimated that about 3,000
demonstrators were gathered at the port and 4,500 had marched across
the city; however, a member of the Occupy movement was quoted by the BBC
as estimating as many as 30,000 may have taken part.
On 4 November 2011, "Occupy the Roads" (OTR) started traveling
throughout the U.S. to bring the message of Occupy, in order to educate
the people on various issues facing the general public and shine a light
on the inequities and political injustice. OTR has been to every major
Occupy Event in support of all occupied cities, traveling over 31,000
miles and visiting 42 States and 160 cities since inception. One side of
the RV (named the "V"- from the chant "Whose V? RV") has been decorated
with stickers, posters, and event notices from around the Country
representing a billboard for the Occupy movement. On the other side is
31 ft of graphics in support for Bradley/Chelsey Manning and WikiLeaks.
5 to 25 November
On
5 November, protesters held "Bank Transfer Day", marching on banks and
other financial institutions to urge Americans to move their money from
big corporate banks to smaller community credit unions. It was reported
that an estimated 600,000 people took their money out of major banks. On 11 November, Remembrance Day in Canada, police forcibly removed tents from Victoria Park in Halifax, Nova Scotia and arrested 15 protestors.
On the night of 14 November, a coordinated crackdown was undertaken by
authorities around the world, with several camps being forcibly cleared
including Zuccotti Park in New York, Oakland, Oregon,
Denver and Zurich. For some of the other camps such as the one at St
Pauls in London, no physical action was taken, but on 15 November
authorities stepped up legal action to gain authorization for a forcible
eviction. Financial Times editor Richard Lambert
suggested that the shift to confrontational tactics by authorities
would be more likely to spur on the movement rather than cause it to
disband. However, John Gapper, chief business commentator at the FT,
offered a different view. Gapper said that it may be advantageous that
the camps were being closed down, as they were beginning to alienate
even members of the public who were initially fully sympathetic with the
movement. During a demonstration at UC Davis on 18 November 2011, campus police Lieutenant John Pike used pepper spray on seated students. The incident drew national attention and led to further demonstrations, petitions, and calls for Chancellor Linda P.B. Katehi to resign. On 22 November, occupiers mic checked President Obama to draw his attention to the treatment they had received from the police, including thousands of arrests.
26 November to 31 December 2011
Green party leader Caroline Lucas discussing green economics with occupiers at London's Bank of Ideas on 6 December 2011
By December, occupiers had begun to divert their energies beyond protest camps
and a narrow focus on the banks, instead seeking to engage further with
mainstream politics and joining forces with established activist groups
to support causes broadly compatible with the interests of "the 99%".
Interviewing one of the informal leaders of the movement, Financial Times
journalist Shannon Bond found that issues of concern included: "the
unemployment rate, household debt, student debt, the lack of prospects
for people graduating from college and foreclosures". In the U.S., Occupy Homes
joined with other existing human rights activists groups and began to
occupy foreclosed homes, disrupt bank auctions, and block evictions.
On 1 December, two evicted activists in Portland, Oregon, planted a
table on the plaza of Portland's City Hall and lit a candle, igniting a
Prayer Vigil/Occupation of City Hall that lasted 18 months. On 22
December The Washington Post reported that some of the cities which had forcefully disbanded occupy camps were now facing legal challenges.
1 January 2012 to 2016
On 2 January 2012, Occupy Nigeria began, sparked by Nigeria's President Goodluck Jonathan
announcing the ending of fuel subsidies in the country. There was
support from the global movement, but most of the activity took place in
Nigeria itself, with a report from CSM
saying strikes were effectively shutting down whole cities. On 16
January Jonathan responded by announcing he would bring prices back down
by partially restoring the fuel subsidy.
While students have been involved with Occupy since its
inception, early 2012 has seen increasing formal interaction between the
Occupy movement and academia. In the US, universities including Columbia and Roosevelt
have begun offering courses about the movement, in the case of Columbia
the course includes field work where students join in with Occupy
activities. In Great Britain, Occupy's outwork teams are planning school
visits to give talks about the movement and related issues.
On 23 January, EGT LLC (Export Grain Terminal) and the International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU) reached a tentative agreement, mediated by Washington state governor Christine Gregoire.
The agreement resolved a year-long dispute, paving the way for ILWU
Local 21 workers to work inside the $200 million grain terminal at the Port of Longview in south-west Washington state.
This came after "Occupy the Ports" protests which shut down multiple
ports on the west coast of the United States on 12 December. The goals
of those protests included support of longshoremen and truckers in
disputes with EGT and terminal operator SSA Marine (partially owned by Goldman Sachs).
"Occupy DC" sign and tents in downtown Washington, D.C. October, 2011
A worldwide poll conducted in January 2012 found that only one third
(37%) of respondents were familiar with the movement. Of the respondents
who were aware of the movement, supporters of the movement outweighed
those in opposition two to one. In late January, Occupy protested at the World Economic Forum. On 17 March, Occupy Wall Street attempted to mark six months of the movement, by reoccupying Zuccotti Park, the location of the first Occupy camp. Protestors were soon cleared away by police, who made over 70 arrests. On 1 May, the Occupy movement marked a resurgence with a May Day general strike that took place in cities across the U.S., including New York; Washington, D.C.; Chicago; and Los Angeles. This included a revival of the Free University of New York.
On the weekend of 15 and 16 September, members of the Occupy
movement gathered in Union Square, with direct action training on the
15th and a celebration of the movement on the 16th. On 17 September, the
Occupy movement celebrated its first anniversary with several marches
and general assemblies which were attended by thousands of protesters.
Occupy Portland Prayer Vigil, November 2012
The longest US "re-occupation" started on 1 December 2011, when evicted activists from the Occupy Portland camp set up a table on the plaza of Portland's City Hall and lit a candle, igniting the 24/7 Prayer Vigil to Lift the Camping Ban, referring to the city's anti-"camping" ordinances that were cited during the eviction. The activists claimed the laws, which prohibit the use of "bedding, sleeping bags, or other sleeping matter,"
are immoral and that they're obligated to challenge them. The occupiers
claim that sleep is human right and is essential for mental, physical
and emotional health, citing that human beings need to spend nearly a
third of their lives sleeping. Prohibiting sleep by making it illegal
for people to protect themselves and their belongings from the elements
causes sleep deprivation; it is inhumane, unconstitutional, and amounts to torture.
The activists said the prayer vigil would continue until "bedding
matter" was again legal. The vigil was staffed around the clock until 23
July 2013, when Mayor Charlie Hales ordered the removal of the vigil
and associated encampments on the abutting sidewalks.
The Occupy movement has "already transformed beyond recognition
from its original state" and "campaigns have emerged outside the
constraint of the trademark Occupy tactics." These campaigns include Occupy Sandy which has provided needed relief to the New York area since Hurricane Sandy hit, Occupy London's Occupy Economics group that hosted, and was praised by the Bank of England's Executive Director for Financial Stability, Occupy the SEC, which monitors US financial regulatory matters, The Rolling Jubilees program of Strike Debt, which is raising money to retire "zombie debt," debt, such as medical bills, that the individual cannot re-pay, Occupy University, which has developed and made accessible free educational materials, and the Debt Collective,
a successor of Strike Debt, worked to get students of a fraudulent
for-profit college absolved of their debt with some success.
On 3 April 2016, hundreds of supporters of Bernie Sanders protested outside of CNN's Headquarters in Los Angeles. Sanders supporters were protesting CNN's coverage of the 2016 United States presidential elections, specifically in regards to the amount of airtime Sanders has received. Known as Occupy CNN, protestors are claiming that major media networks have intentionally blacked out Sanders' presidential campaign in favor of giving much more airtime to candidates such as Hillary Clinton and Donald Trump.
In Switzerland, the Occupy spirit lives on by annual online and offline celebrations each year on 17 September in the village of St. Imier where modern anarchism began with the International Congress of 1872. The Occupy Cafe along with the Decentrale Co operative
continues to assist those wishing to participate in the continuing
"decentralisation of the power "of banks and corporate entities; and, to
encourage global activism through developing trust and value networks.
Present Day Activities
After an approximate two-year hiatus in activism on location, the Occupy Movement organized the Occupy ICE
phase in order to protest the actions of US Immigration and Customs
Enforcement office regarding the detention of undocumented immigrants
presenting themselves at the southern US border points to seek asylum.
While small groups of protesters emerged across the country in protest
against the separation of families who were detained during immigration
processing, a group swarmed the ICE facility in SoHo,
causing it to shut down temporarily. In Oregon, hundreds of Occupy ICE
activists took over a portion of the grounds of the Portland ICE
building. The blockade caused the building to shut down for several
days, with ICE staff citing "safety concerns". On 25 June, Feds ordered the protesters to vacate government environs or face arrest.
On 28 June 2018, Federal officers moved in the early morning to remove
or arrest protesters blockading the building. Eight were arrested.
On 19 August 2018, Occupy Kalamazoo began an encampment in Bronson Park to address homelessness.
The group's efforts notably received support from local Commissioner
Shannon Sykes, who criticized her colleagues in government for "failing
to create more affordable housing."
Armenia
Mashtots Park activists protesting in front of the city hall of Yerevan, Armenia
On 20 February 2012
near Margaryan Maternity Clinic, where kiosks were being built by the
city authorities. The place of protests was promptly dubbed "Mashtots
park" – a name under which it is now widely known by the Armenian
society.
The protesters faced police violence as with many other "Occupy" movements, a report was filed to the ombudsman of RA on account of the destruction of a tent with a sleeping protester inside.
"Occupy" demonstrations are still continuing in Mashtots Park, and the
leader of the Greens party Armenak Dovlatyan has named it the most
successful civic action in the history of the Republic of Armenia.
Australia
The Occupy Sydney camp in February 2012
"Occupy" demonstrations took place in Canberra, Wollongong, Perth, Sydney, Brisbane, Adelaide and Melbourne, as well as smaller towns around the country. At the Occupy Melbourne
protest on 21 October 2011, approximately 150 protesters defied police
orders to clear the area, and were subsequently removed with force. 95
arrests were made and 43 reports of police violence were filed. Occupiers returned the following day in a walk against police violence, re-occupying multiple sites since.
Occupy Sydney had an ongoing occupation in Martin Place
since their initial police eviction, marking almost 21 months in July
2013. The Occupy Sydney camp was removed on 3 July 2013 but it returned
on 4 July. It was again removed on 5 July.
Belgium
In Brussels,
a large Occupy demonstration took place on 15 October involving between
6,500 and 8,000 participants. The protest was largely peaceful,
although seven people were arrested following vandalisation of the Dexia bank headquarters and financial tower. The Occupy Antwerp
(Antwerpen) movement had its first gathering on Saturday 22 October at
the Groenplaats, next to the cathedral. About 150–200 people attended a
speakers corner. The left-wing socialist party (PVDA) was present and
served free soup as well as information about its proposed
"millionaires' tax".
To date, there have been four Occupy protests in Leuven.
Three took place on the Grand Market in the centre of the city and one
took place at a building of the city's Catholic university. The number
of protesters in these rallies varied from 100 to 250. These protests
have not included prolonged camping, but the protesters say that it is a
possibility in the future. Occupy Ghent
(Gent) began on 29 October with 400 people in the South Park
(Zuidpark). They received a visit by supporters attending the "second
day of Socialism" (de Tweede Dag van het Socialisme), also held in Ghent
on the same day.
Brazil
Protesters occupy the roof of the National Congress of Brazil in Brasília on 17 June 2013.
The 2013 protests in Brazil (also known as the Come to the street and
Brazilian Spring) are ongoing public demonstrations in several
Brazilian cities, initiated mainly by the Movimento Passe Livre (Free
Fare Movement), a local entity that advocates for free public
transportation. The most recent movement being "Ocupe Estelita"
in Recife, Pernambuco which is focused on the demolition of an
historical part of the city to make way for high-priced housing and
leisure facilities.
Canada
An Occupy Montreal demonstration on 15 October 2011
Occupy protests have taken place in at least 20 Canadian cities since
15 October 2011. On that day, 5,000 people gathered in Vancouver to
protest perceived social injustice, while 150 stayed the night in front
of the Vancouver Art Gallery. 2,000 people marched in Toronto on 15 October and around 100 continued to occupy St James Park, and 1,000 gathered in Montreal to march down Ste-Catherine Street; 85 tents were set up in Victoria square.
Beginning on 23 October 2011 approximately 40 people occupied Memorial
Park on Minto Street in downtown Sudbury and still continue to do so. On 20 October 2011, over 100 people occupied the front of City Hall in Prince George, British Columbia. Events have been concentrated in provincial urban areas, and there have yet to be any demonstrations in the territories of Yukon, Northwest Territories, or Nunavut.
A relatively small group of occupiers successfully occupied Harbourside
Park in St John's Newfoundland for the entire 2012 Winter season. This
site, known also as "King's Beach" is symbolically significant as the
birthplace of the British Empire, and the encampment is seen by some
protesters to represent an occupation of colonialism vis-a-vis its birth
site. There are currently a number of court proceedings across Canada
on whether or not the eviction of protestors and violence from police is
an infringement of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
Colombia
Around 800 student protestors began occupying universities across Colombia on 12 November 2011.
Czech Republic
On 28 April 2012, a week after demonstrations of unions and civic associations (more than one hundred thousand protesters) the camp "Occupy Klárov" in Prague was started. Pirate Party participated in the occupation. Police dissolved the camp a month later.
Cyprus
Tents at the Occupy Buffer Zone camp in Nicosia
On 19 November 2011, protesters started the "No Borders Camp" Or
"Occupy Buffer Zone", a permanent occupation of the United Nations
controlled buffer zone in the centre of the capital, Nicosia, demanding
an end to the decades-long division of the Island. The movement used the Twitter hashtag "OccupyBufferZ". By June 2012 the occupation of the buffer zone was essentially over.
Denmark
On 15
October 2011, 2,000 protesters showed up on the square in front of the
city hall of Copenhagen, protesting in sympathy with OWS. Immediately
after the demonstration an "Occupy Copenhagen" camp was established. The
camp, internally nicknamed "Plaza One Love", lived through harsh
climate conditions and a couple of eviction attempts for two months,
until it was torn down by the Municipality of Copenhagen and Danish
police, on 21 December. The movement has shifted to a mobile camp
tactic, and still holds GA every Wednesday and other activities
throughout the week.
France
Some 300 protesters started occupying Paris's financial district, La Défense, on 4 November 2011.
Since then, their camp has been torn down by several police forces.
According to French protestors, relations with the police have varied
considerably. Some police joined them for coffee and friendly
discussion, but otherwise were hostile and confiscated blankets and
food, leaving protesters sleeping in the cold outdoors without
protection. On 11 November, following a call made on social networks,
some 400 additional people joined the occupation. Occupy protests have also begun at Nantes, Lyon, Grenoble, Marseille, Perpignan and more than 50 cities.
On 31 March 2016, students and young workers began occupying
public spaces in France in opposition to the 2016 neoliberal labor
reforms in a protest movement known as Nuit debout. As of 8 April, it has spread to dozens of cities in France as well as to Belgium, Germany, and Spain.
Germany
Occupy Berlin protests on 15 October 2011, pictured in front of the Reichstag
The Occupy movement began in Germany on 15 October 2011 with protests in Berlin, focused outside the Reichstag, as well as Frankfurt, Hamburg and Düsseldorf. Occupy Frankfurt subsequently took residence in front of the European Central Bank, and Occupy Berlin established a protest camp at St. Mary's Church. On 12 November major Occupy protests took place in Berlin and Frankfurt.
Police reported that around 9,000 people peacefully protested near the
headquarters of the European Central Bank, and that "several thousand"
people took to the streets of Berlin; organisers of the protests claimed
that turnout was around 8,000 in Berlin and 10,000 in Frankfurt.
Hong Kong
An Occupy movement in Hong Kong, named 'Occupy Central', began on 15
October 2011 with protesters occupying the plaza beneath the HSBC Main Building in Central, an iconic landmark of the territory's central business district. Despite the fact that the protesters were peaceful, HSBC filed a lawsuit for their eviction. On 13 August 2012, the High Court
ruled that the protesters must leave the occupied area. On 11 September
2012, the protesters were evicted from the plaza by court bailiffs, ending one of the world's longest continuously occupied Occupy protest camps.
Italy
On 15 October 2011, about 200,000 people gathered in Rome to protest against economic inequality and the influence of the European Commission, the European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund on government. Many other protests occurred in other Italian cities the same day. In Rome masked and hooded militants wearing makeshift body armor, in black bloc fashion, participated in the protests centered in St John Lateran square and committed numerous violent acts, throwing Molotov cocktails
and other homemade explosives, burning and blowing up cars, burning
buildings, and smashing up property such as ATMs and shop windows. The Roman Catholic church Santi Marcellino e Pietro al Laterano received extensive damage, including a statue of the Virgin Mary being thrown into the street and destroyed.
Several unexploded petrol bombs were reportedly found on several streets by Italian police. Over 1,000,000 euros of damage (equivalent to over 1.3 million dollars) was recorded.
At least 135 people were injured in the resulting clashes, including
105 police officers, several of whom were left in critical condition, and two news crews from Sky Italia. Two protesters had their fingers amputated by exploding smoke bombs. Almost 20 people have been arrested in connection with the violence. After the 15 October demonstration, people occupied the Santa Croce in Gerusalemme
square and started camping as in other cities worldwide. The name of
this Rome's group, related to international Occupy movement, is
Accampata Roma.
Malaysia
The Occupy Dataran movement first held their assembly at Dataran Merdeka (Independence Square) seven weeks before Occupy Wall Street on 30 July 2011 to create an alternative to the current representative democracy using the popular assembly model based on principles of participatory democracy. As part of the 15 October 2011 global protests, over 200 people took part in 15 October's Occupy Dataran, the largest assembly to date. In late October, the movement spread to Penang with Occupy Penang and Kelantan with Occupy Kota Bharu.
Mexico
Occupy began in Mexico City on 11 October 2011, with a hunger strike in front of the Mexican Stock Exchange
highrise. Edur Velasco, a 56-year-old labor economist and university
professor, was on a 42-day-long hunger strike sitting in a tent outside
Mexico City's stock market, demanding that the government guarantee
greater access to higher education among the youth.
Days after his initiative, it came as a surprise to see the
multiplication of tents setting up outside the stock exchange building.
Police remained discreetly around the corner sitting in their trucks.
Occupy Mexico did not achieve the level of popularity it gained
in other areas. This is attributed to the fact that Mexico's Occupy
protesters, which were focused on poverty and workers' rights, failed to
resonate with a public enthralled by the violence of the Mexican Drug War. In contrast, an anti-violence movement led by Javier Sicilia during the time that the Occupy protests occurred, drew thousands onto the streets of Mexico City. The Occupy Movement was almost entirely ignored by Mexico's mainstream politicians. By late January 2012, most of the tents were empty and only a few protesters remained outside the Stock Exchange.
Mongolia
S.
Ganbaatar, the head of Mongolia's Confederation of Trade Unions (CTU),
has announced that the association joins the worldwide occupy protests
of Wall Street and other high streets on 20 October 2011.
He claimed that bankers are charging higher interest rates from
customers and corporates. In the most recent data in September 2011, the
weighted average annual MNT lending rate is 16% in Mongolia.
Nepal
Also known as Baluwatar Satyagraha, Occupy Baluwatar is a peaceful
protest movement calling on the Nepali state to better address the
widespread problem of impunity and gender-based violence. Since 28
December 2012, protesters have gathered outside the prime minister's
official residence in Baluwatar from 9:00 to 11:00 am daily. The
protesters created a coherent set of demands, divided into short- and
long-term goals, which they presented to then prime minister Baburam
Bhattarai. The short-term demands called on the state, including the
police and the judiciary, to properly investigate and prosecute the
guilty in five specific cases which took place immediately prior to the
movement's start. The long-term demands focused on policy reform in the
arenas of migration and rape laws, among others.
Netherlands
Occupy Rotterdam on 22 October 2011 in front of the Beurs-World Trade Center
In the Netherlands, Occupy protests took place in many cities, most notably Amsterdam, The Hague, Rotterdam, and Utrecht
New Zealand
The Occupy Auckland protest camp in Aotea Square, Auckland, on 16 November 2011
In October 2011, Occupy protests began in six New Zealand cities (Auckland, New Plymouth, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill) with protests in Auckland drawing up to 3,000 supporters. A seventh Occupy protest started on 19 November in the Lower Hutt suburb of Pomare
by a group called "Pomare Community Voice" to highlight what they call
the "loss of community" caused by the demolition of state homes in the
area.
On 23 January, police moved in on four sites in Auckland. Two arrests
were made and police said campers were in breach of council bylaws
regarding camping. The sites were at Aotea Square, 360 Queen St, Victoria Park and Albert Park.
Nigeria
Occupy Nigeria is an anti-fuel subsidy removal protest that started
in Nigeria on 2 January 2012 in response to fuel subsidy removal by the
Federal government of Nigeria on 1 January 2012. It is a movement
against corruption in Government & public service, insensitive &
inhuman treatment of Nigerians by Government & Security agents. The
movement ended on 16 January 2012 following agreement between the
government and the organized labour leaders which saw a partial
restoration of the subsidy regime. Fuel pump price in Nigeria has since
then been fixed at the official rate of 97 naira per litre while it
practically sells for as high as 130 naira in some major cities
including Port Harcourt, one of the cities in the oil-producing states
in Nigeria.
Norway
The Occupy movement in Norway began on 15 October with protests in Oslo and Bergen as part of the Global Day of Action.
In Oslo, the movement has since then met every Saturday in the city
centre, usually at Eidsvolls plass in front of the Parliament, but
sometimes at other sites, like Spikersuppa and Youngstorget.
Republic of Ireland
The Occupy Dame Street camp in Dublin, Republic of Ireland
To date six towns and cities in Ireland have witnessed experienced
Occupy camps; Dublin, Cork, Limerick, Galway, Waterford, Letterkenny,
and Athlone. Protests were held in Dublin, Cork, Limerick and Galway. The Irish Times described the movement in the following terms: "The
group has no hierarchical structure, has set up a Facebook page and
Twitter account – with the social media links attracting a very mixed,
and sometimes critical, reaction." The protest in Dublin was
organized by "Pots & Pans – Ireland", and #OccupyDameStreet protest
group, who then invited Real Democracy Now! Shell to Sea, Tir na Saor
and many other non political groups to participate and all set up camp
outside the Central Bank of Ireland in solidarity with the Occupy Wall Street movement in New York. On 22 October it was reported that over 2,000 people took part in a demonstration organized by Occupy Dame Street.
This camp survived through the winter, but was removed by an Garda
Síochána (Irish police) on 13 March 2012, days before the annual St.
Patrick's Day Parade. On the morning of 16 May 2012 at approximately
4:30 am, the Occupy camp in Eyre Square in Galway, the longest-lasting
of the Occupy groups in Ireland, was removed by An Garda Síochána and
Galway City Council. The camp was removed because the group was
illegally occupying a public amenity. At the time the camp was
dismantled, there were only 6 protesters at the camp. The camp had
lasted for 215 days.
South Africa
In South Africa, a movement called Taking Back South Africa! sprung up as an initiative primarily aimed at protesting and inciting mass action against the economic and social inequality
in the country. It consists of a loose informal affiliation of
on-the-ground groups and individuals across South Africa as well as
internet based groups. During the 2016 Fees Must Fall movement, protest
groups also adopted the slogan #Occupy4FreeEducation in response to the
government's perceived lack of interest in dealing with the issue.
South Korea
Hundreds of protesters held rallies in the South Korean capital of Seoul
on 15 and 22 October in 2011 under the slogan of "Occupy Seoul".
Protesters focused on issues such as a recent free trade agreement with
the United States as well as costs of tuition and rent.
Although there were considerable support from public, there were
also criticisms regarding the nature of the protest. Unlike the original
Occupy movement which started out as the anti-capitalist protest, many
of the catchphrases of Occupy Seoul contained anti-government or
anti-American messages. One of the observers has argued that "South
Korea overcame the 2008 financial crisis relatively well and there was
no serious crisis in financial sector. It is hard to find the legitimate
basis of the protest."
Spain
A series of protests demands a radical change in Spanish politics,
as protesters do not consider themselves to be represented by any
traditional party nor favoured by the measures approved by politicians. Spanish media have related the protests to the economic crisis, Stéphane Hessel's Time for Outrage!, the NEET troubled generation and current protests in the Middle East and North Africa, Greece, Portugal as well as the Icelandic protest and riots in 2009. The 15-M Movement
drew inspiration from 2011 revolutions in Tunisia, Egypt and uprisings
in 1968 France, South Korea in 1980 and 1987 and Greece in 2008.
Switzerland
On 15 October 2011, between 500 to 1,000 Occupy protesters demonstrated in front of the offices of UBS and Credit Suisse on the Paradeplatz in Zurich. 100 protesters later established an occupation on the nearby Lindenhof, which was evicted by the police on 15 November.
Turkey
Some of the protesters have styled themselves as #OccupyGezi.
The initial protests in Istanbul on 28 May 2013 were led by about 50 environmentalists against replacing Taksim Gezi Park with a reconstruction of the Ottoman Era Taksim Military Barracks
(the scene of pro Sultan riots in 1909). The current protests developed
into riots after the heavy handed police intervention which featured
significant use of tear gas and water cannons. The oppressive reaction to the protests caused the protests to widen with many more people to become involved,
people from many different walks of life including a wide range of
political interest groups, secular and religious people, students, gays,
feminists, football fans, women in head scarves, whole families, all
finding reason to join the protests.
What started as an environmentalist protest against plans to
replace Taksim Gezi Park developed into wider anti-government
demonstrations. Demands issued on 4 June included
- the end of police brutality,
- the end of the sale of public facilities such as parks, forests and beaches to private investors,
- the right of public expression,
- media responsibility in informing the public of events, and other demands. The protests (up to 500.000 in İstanbul and 30.000 people in Ankara) also spread to other cities in Turkey, and protests were seen in other countries with significant Turkish communities.
England
A tent at the Occupy London encampment in the City of London
A
s part of the 15 October 2011 global protests, protesters gathered in London, Bristol, and Birmingham in England, together with Glasgow and Edinburgh in Scotland (See Scotland heading below). The London Stock Exchange in Paternoster Square was the initial target for the protesters of Occupy London on 15 October 2011. Attempts to occupy the square were thwarted by police.
Police sealed off the entrance to the square as it is private property,
and a High Court injunction had been granted against public access to
the square. 2,500–3,000 people gathered nearby outside St Paul's Cathedral, with 250 camping overnight. A canon of St. Paul's, Reverend Giles Fraser,
said he was happy for people to "exercise their right to protest
peacefully" outside the cathedral and an indefinite encampment was
established. Additional smaller protests occurred in Birmingham and Nottingham. As of 17 October an indefinite encampment had also been established on College Green in Bristol.
On 29 October a camp was also established in Victoria Gardens, Brighton, and grew from six tents to around twenty within one week. Further Occupy camps took place in Liverpool Bath, Bournemouth University, Bradford, Leeds, Sheffield, Thanet, Newcastle upon Tyne, Plymouth, Exeter, Norwich, The Occupy Thanet protests also focused on local issues, including the closure of shops in the town and the Dreamland Margate amusement park, a lack of employment opportunities and perceived disparities in the allocation of education resources. Lancaster in England and Cardiff in Wales.
On 8 January 2012, Lancaster Police arrested four members of Occupy
Lancaster who were occupying a disused hotel in the city centre.
On 11 November, police arrested 179 people believed to be EDL supporters on Armistice Day
after apparent threats to the St Paul's camp were posted on Facebook.
176 were released without charge and 3 were bailed "pending further
inquiries".
On 15 November, an Occupy camp was established in the centre of Leicester near the Highcross shopping centre. On 25 November an Occupy camp was established in Liverpool near the Walker Art Gallery. Starting on 30 November 2011 following a national strike action, a body of students occupied the University of Sheffield Arts Tower in solidarity with, but not limited to, the Occupy movement.
On 17 October 2014 a new camp was established in Parliament
Square, Westminster by a group called Occupy Democracy. The camp was
part of a campaign for greater transparency in democracy as well as an
end to lobbying.
The camp lasted two days until police swept in, giving protestors 30
minutes to leave or face arrest. Any items that could be used for
sleeping have been deemed illegal under the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, created after the original occupation. The eviction was live streamed, showing police dragging protesters away. Police said there was one arrest. Fifty to a hundred protesters remained in the park overnight.
On their website, the group says their goal is "to direct the energy
from current single issue struggles into a critical mass that can
radically challenge the corrupt and unrepresentative system".
Northern Ireland
In Northern Ireland, Occupy Belfast initiated its protest outside the offices of Invest NI on 21 October 2011. Occupy Belfast took residence at Writer's Square, in the Cathedral Quarter.
It also took control of a disused building owned by the Bank of
Ireland, renaming it the People's Bank, with plans to open a library and
homeless accommodation to be a community hub. It was expected that an Occupy Derry would take place in the near future.
Occupy Coleraine took over the University of Ulster Common Room for three weeks in December 2013.
The group protested the demolition of the historic student-teacher
shared space, due for refurbishment as a senior management corporate
dining room.
Scotland
Occupy Edinburgh protesters in St Andrew Square, Edinburgh
Occupy camps were established in the financial district of St. Andrew Square, Edinburgh on 15 October 2011. St. Andrews Square is the home of the Royal Bank of Scotland headquarters in the Dundas House mansion. Edinburgh City Council subsequently officially backed Occupy Edinburgh and the Occupy movement worldwide. Protesters from Occupy Glasgow set up in the civic George Square on 15 October but after the council obtained a court order moved to Kelvingrove Park, where the council agreed to provide running water, toilets and safety fences.
Wales
In Wales, Occupy Cardiff
originally set its camp-site outside Cardiff Castle but it was
disbanded by police, and some protesters were arrested. Charges were
later dropped following calls from trade unionists, lawyers and
politicians including Plaid Cymru leader Leanne Wood, Labour Party politician Tony Benn and demonstrations outside Cardiff magistrates court. Occupy Cardiff set up a new camp in the city, outside the offices of Welsh Labour and a number of trade unions at the Transport House, Cathedral Road.
United States
One of the marches to the Port of Oakland during the 2011 Oakland General Strike on 2 November 2011
The Occupy Wall Street protests began in New York City on 17 September 2011. By 9 October, similar demonstrations were either ongoing or had been held in 70 major cities and over 600 communities across the U.S.
The movement rejects existing political institutions and attempts to
create alternative ones through direct action and direct democracy.
Occupy protesters' slogan, "We are the 99%", asserts that the "99%" pay
for the mistakes of the "1%".
The original location of choice by the protesters was 1 Chase Plaza, the
site of the "Charging Bull" statue, but when police discovered the
planned site, it was fenced off and nearby Zuccotti Park was chosen.
There was scant media coverage till 24 September when a large march
forcing the closure of several streets resulted in 80 arrests. Police
used a technique called "netting", the use of orange plastic nets to
corral protesters, and the march received extensive media coverage when a
video of several "netted" young women being pepper sprayed was widely
circulated.
Media coverage was again sparked on 1 October, when New York City protesters attempted to march across the Brooklyn Bridge
and more than 700 arrests were made. Some said the police had tricked
protesters, allowing them onto the bridge and even escorting them
partway across before they began to make mass arrests. On 25 October, police officers cleared two Occupy Oakland protest camp sites. Police fired tear gas canisters at the protestors, allegedly in response to objects being thrown at them. Protest organizers said that many of the troublemakers were not part of the Occupy movement. The raid was described as "violent and chaotic at times" and resulted in over 102 arrests. Scott Olsen, a former Marine and Iraq War veteran, suffered a skull fracture caused by a projectile that witnesses believed was a tear gas or smoke canister fired by the police. On 2 November, protesters in Oakland, California, shut down the Port of Oakland,
the fifth busiest port in the nation. Police estimated that about 3,000
demonstrators were gathered at the port and 4,500 had marched across
the city.
Zuccotti Park closed to overnight camping on 15 November 2011
At about 1:00 am on 15 November, police cleared the Zuccotti Park
encampment. Many journalists complained that the police had made a
deliberate decision to keep journalists away from the park during the
raid.
New York City journalists responded to what they perceived as "alarming
suppression, abuse and arrests of reporters" by forming "The Coalition
for the First Amendment" to "monitor police-press relations as a way of
spotlighting police activities that threaten constitutional
protections". Executive Director Alison Bethel McKenzie of the International Press Institute
commented: "It is completely unacceptable to hinder reporting on a
subject that is undoubtedly of public interest. Such reporting is vital
to democracy, and authorities at every level of government – federal,
state and local – must honour their constitutional obligation not to
infringe upon the freedom of the press."
On 6 December, Occupy Homes,
an offshoot of Occupy Wall Street, embarked on a "national day of
action" to protest the mistreatment of homeowners by big banks, who they
say made billions of dollars off the housing bubble by offering predatory loans
and indulging in practices that allegedly took advantage of consumers.
In more than two dozen cities across the nation the movement took on the
housing crisis by re-occupying foreclosed homes, disrupting bank
auctions and blocking evictions. On 17 September 2012, protesters returned to Zuccotti Park to mark the one-year anniversary of the beginning of the occupation.
Reactions
Political
- Brazil—President Dilma Rousseff said, "We agree with some of the expressions that some movements have used around the world [in] demonstrations like the ones we see in the US and other countries."
- Canada—Finance Minister Jim Flaherty expressed sympathy with the protests, stating "There's growing worry about a lack of opportunities for the younger generation – particularly in the United States – and it's up to governments to ensure youth are able to capitalize on their education and find good jobs." He later commented, "I can understand some legitimate frustration arising out of that."
- India—Prime Minister Manmohan Singh described the protests as "a warning for all those who are in charge of the processes of governance".
- Iran—Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei voiced his support for the Occupy Movement saying, "Ultimately, it will grow so that it will bring down the capitalist system and the West."
- United Kingdom—On 21 October 2011, former Prime Minister Gordon Brown said the protests were about fairness. "There are voices in the middle who say, 'Look, we can build a better financial system that is more sustainable, that is based on a better and proportionate sense of what's just and fair and where people don't take reckless risks or, if they do, they're penalized for doing so.'" On 6 November 2011, Opposition leader Ed Miliband: "The challenge is that they reflect a crisis of concern for millions of people about the biggest issue of our time: the gap between their values and the way our country is run." He mentioned that he is "determined that mainstream politics, and the Labour Party in particular, speaks to that crisis and rises to the challenge". On Saturday 26 November 2011, Edinburgh City Council set a worldwide precedent by voting in favour of the motion to support the aims and sentiments of Occupy Edinburgh and the Occupy movement as a whole. This motion was presented by the Scottish Green Party, was seconded by the Scottish Labour Party and was slightly amended by the Scottish National Party (SNP) and Scottish Liberal Democrats. The only party not to back the motion was the Scottish Conservative Party. "We regard this as a fantastic step forward in the opening of dialogue with the Scottish government.", stated Occupy Edinburgh.
- United States—President Barack Obama spoke in support of the movement, but also asked protesters not to "demonize" finance workers. Local authorities in the United States have collaborated to develop strategies to respond to the Occupy movement and its encampments, and political leaders in eighteen United States cities consulted on cracking down on the Occupy movement, according to Oakland Mayor Jean Quan, who participated in a conference call. Within a span of less than 24 hours, municipal authorities in Denver, Salt Lake City, Portland, Oakland, and New York City sent in police to crack down on the encampments of the Occupy movement. In a markedly different approach, the city administration and police in New Haven, Connecticut, have worked with Occupy New Haven to ensure the safety of protesters occupying the upper section of the New Haven Green. Until 18 April 2012, Occupy New Haven, has been running continuously on the Green for 186 days until they were removed by police.
- Venezuela—President Hugo Chávez condemned the "horrible repression" of the activists and expressed solidarity with the movement.
Media
Foreign Affairs has had various articles covering the movement. In the January/February 2012 issue, Francis Fukuyama
argued that the Occupy movement was not as influential as the
right-wing Tea Party movement. "One of the most puzzling features of the
world in the aftermath of the financial crisis," he wrote, "is that so
far, populism has taken primarily a right-wing form, not a left-wing
one." In contrast, a survey for the think tank Center for American Progress
suggested that the Occupy movement has succeeded in substantially
boosting the coverage of the job crisis in the American media.
Other
Egyptian protesters from Tahrir Square
have lent their support of the movement. A message of solidarity issued
by a collective of Cairo-based protesters declared: "As the interests
of government increasingly cater to the interests and comforts of
private, transnational capital, our cities and homes have become
progressively more abstract and violent places, subject to the casual
ravages of the next economic development or urban renewal scheme. An
entire generation across the globe has grown up realizing, rationally
and emotionally, that we have no future in the current order of things."
In early December 2011, business magnate Richard Branson
said the movement is a "good start", that they have been protesting for
valid reasons, and that if the business community takes some of their
concerns on board they will have made a difference.
On 15 December 2011, Jesse Jackson said that Jesus Christ, Gandhi, and Martin Luther King
were all occupiers, and that: "Occupy is a global spirit, which is now
sweeping the nation and the world, fighting for justice for all of God's
children". A global survey of 23 countries published by Ipsos
on 20 January 2012 found that around 40% of the world's citizens are
familiar with the movement. Over twice as many reported a favourable
response to the movement compared to those who dislike it. Support for
the movement varied markedly among countries, with South Korea (67%),
Indonesia (65%), and India (64%) reporting the highest sympathy – while
Australia (41%), Japan (41%), and Poland (37%) reporting the lowest.
Impact
Some known impacts to date include the following:
Social impact
In
the United States, the protests have helped shift the focus of national
dialogue from the federal budget deficit to economic problems many
ordinary Americans face, such as unemployment, the large amount of student and other personal debt that burdens middle class and working class Americans, and other major issues of social inequality, such as homelessness.
The movement appears to have generated a national conversation about
income inequality, as evidenced by the fact that print and broadcast
news mentioned the term "income inequality" more than five times more
often during the last week of October 2011 than during the week before
the occupation began.
Longer term effects are much less clear, as according to Google search
trends, in the years since 2012 interest has waned. Occupy movement
raised awareness regarding what organizers consider undeserved wealth
and lack of fairness in American society.
Labor unions have become bolder in the tactics they employ and have
been using digital social media more effectively thanks to the Occupy
movement.
In New York City, the Occupy Wall Street protest has also provided
hundreds of protesters to help in picket actions conducted by labor
unions.
Offshoots of the Occupy movement, such as Rolling Jubilee,
a project of Strike Debt, have bought millions in "zombie debt," money
that individuals owe that they have no financial means to pay, including
medical debt, to free the debtors from the obligation to pay it off.
As of September 2014, Rolling Jubilee claims to have cancelled more
than $15 million in medical debt and $4 million in private student loan
debt. Noam Chomsky
argues that the movement "spontaneously created something that doesn't
really exist in the country: communities of mutual support, cooperation,
open spaces for discussion . . . just people doing things and helping
each other". As of April 2015, Rolling Jubilee reports it has cleared nearly $32 million in debt.
On 10 November 2011, The Daily Telegraph
reported that the word "occupy" had been the "most commonly used
English word on the internet and in print" over the past 12 months
according to a top ten list published by media analysis company Global Language Monitor. In January 2012, members of the American Dialect Society voted with an overwhelming majority for "Occupy" as the word of the year for 2011. Numerous news shows and radio shows have been using the term "1%" and "99%" TV shows such as The Middle, Revenge and, The Office
have made references to Occupy, and, in July 2012, the City of
Vancouver added the word to its list of reserve names for civic assets
such as streets and buildings. In December 2012, the Television show Conan launched a contest called "Occupy Conan".
Political impact
On 27 December 2011, the Financial Times argued that the movement had had a global impact, altering "the terms of the political debate".
However, some sympathetic commentators such as Anthony Barnett have
suggested that in Spain, where the movement once had the support of well
over 70% of the population with millions taking part, the popularity of
Occupy is now past its peak and has achieved no consequences of any significance. However, there were numerous successes at local levels, and The Economist
has reported that Spanish protesters caused their government to pass
various laws including new limits on the amounts banks can "claw back" from defaulting borrowers.
In November 2011, U.S. Congressman Ted Deutch, member of the House Judiciary Committee,
introduced the "Outlawing Corporate Cash Undermining the Public
Interest in our Elections and Democracy (OCCUPIED) Constitutional
Amendment," which would overturn the United States Supreme Court decision in Citizens United v. FEC recognizing corporate constitutionally protected free speech rights and would ban corporate money from the electoral process.
In March 2012, former U.S. Vice President Al Gore
called on activists to "occupy democracy", explaining that "Our
democracy has been hacked. It no longer works to serve the best
interests of the people of this country." Also in November 2011, Paul Mason said that the Occupy movement had started to dynamically shape the global policy response to the Late-2000s financial crisis, being mentioned so often at the 2011 G20 summit that if Occupy had been a brand "it would have a profile to die for among the super-elite". Various journalists along with Jared Bernstein former chief economist and economic adviser to Vice President Joe Biden, have suggested that Occupy influenced the President's January 2012 State of the Union address,
with the movement creating the political space for Obama to shift to
the economic left and speak about the desirability of the rich paying a
greater share of the tax burden. Inequality has remained a central theme
of President Obama's reelection campaign, yet he no longer mentions the
Occupy movement by name, which analysts say reflects the fact that by
early 2012 Occupy had become a divisive issue, unpopular with some of
the public.
Three years later, income inequality had become a major part of the political discourse and The Atlantic Magazine declared "The Triumph of Occupy Wall Street"
National monitoring and crackdown
Government documents released in December 2012 pursuant to Freedom of Information Act requests by the Partnership for Civil Justice Fund
reveal FBI monitoring of what became known as the Occupy movement since
at least August 2011, a month before the protests began. The FBI, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, local police, regional law enforcement "counterterrorism" fusion centers, and private security forces of major banks formed the Domestic Security Alliance Council
(DSAC) to collect and share information about, and to share plans to
target and to arrest Occupy protesters. Banks met with the FBI to pool
information about participants of the Occupy movement collected by
corporate security, and the FBI offered to bank officials its plans to
prevent Occupy events that were scheduled for a month later.
FBI officials met with New York Stock Exchange representatives on 19 August 2011, notifying them of planned peaceful protests. FBI officials later met with representatives of the Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond and Zions Bank about planned protests.
The FBI used informants to infiltrate and monitor protests; information
from informants and military intelligence units was passed to DSAC,
which then gave updates to financial companies. Surveillance of protestors was also carried out by the Joint Terrorism Task Force. DSAC also coordinated with security firms hired by banks to target OWS leaders.
Lawsuits
Following
actions by police and municipal officials to use force in closing
various Occupy tent camps in public spaces, lawsuits have been filed,
while others are being planned.
Civil liberties organizations filed separate law suits against the FBI
for refusing to turn over documents requested pursuant to the Freedom of Information Act
(FOIA) regarding the FBI's role in surveillance of the Occupy movement
and the FBI's sharing of intelligence about Occupy events with private
corporate security officials.
The FBI withheld documents requested under the FOIA citing the reason
that the withholding was "in the interest of national defense or foreign
policy".
In 2013, MIT doctoral student Ryan Shapiro,
collecting research on the role of the FBI in the Occupy movement, sent
the FBI three FOIA requests regarding "a potential plan to gather
intelligence against the leaders of [Occupy Wall Street-related protests
in Houston] and obtain photographs, then formulate a plan to kill the leadership [of the protests] via suppressed sniper
rifles". When the FBI refused the request, Shapiro filed a federal
complaint in Washington, D.C., and subsequently obtained 17 pages (most
of the requested documentation was ruled withheld due to the possibility
to "disclose the identity of a confidential source".) The redacted FBI
document confirmed the Houston plot and contradicted an earlier claim by
the FBI that it had never opened an investigation on the Occupy
movement.
Criticism
Apart from the dismissals made by political conservatives, there have also been appreciative criticisms from more left-wing
scholars. One such critique concerns itself with the way in which the
Occupy movement has focused its demands around a narrowly modern
understanding of freedom that differs little from the claims of
mainstream liberal pluralism:
The modern ideology of freedom ... provides its point of departure. This singular dominance of the modern becomes clear in the long list of demands that follow. Practicality dominates and there is not a single demand for relief from the ontological dominance of modern practices and subjectivities that abstract, codify, rationalize and objectify our lives. Though the ideals and demands ... are laudable, they are not that much different in form from the Millennium Goals of the United Nations.
International activists involved in the Occupy Movement have seen it
stall due a lack of synergy to work with other alternative movements
calling for change. The biggest criticism is that the movement is
without depth, without a lasting vision of an alternative future.
In her critique of the Occupy movement, American political philosopher Jodi Dean
argues that the focus on autonomy, leaderlessness and horizontality
paved the way for conflicts and disillusionment within the movement:
Emphasis on autonomy encouraged people to pursue multiple, separate and even conflicting goals rather than work toward common ones. Celebration of horizontality heightened skepticism toward organizing structures like the General Assembly and the Spokes Council, ultimately leading to the dissolution of both. assertions of leaderlessness as a principle incited a kind of paranoia around leaders who emerged but could not be acknowledged or held accountable as leaders. So rather than solving the problem of left political organization by focusing on process and immediate questions of action, as anarchism suggests, Occupy Wall Street in fact poses it anew. It pushes us to think again about the role of a communist party.
Remarks from Occupy Wall Street participant Justine Tunney, a Google software engineer, who called on President Obama to appoint Eric Schmidt
"CEO of America", have also sparked criticism, including from the vast
majority of other Occupy participants, many of whom have observed that
her politics are inconsistent with horizontalism.
Many Occupy Wall Street protests have included anti-zionist and anti semitic
slogans and signage such as "Jews control Wall Street" or "Zionist Jews
who are running the big banks and the Federal Reserve". As a result,
the Occupy Wall Street Movement has been consistently confronted with
accusations of anti-Semitism. However, Abraham Foxman, national director of the Anti-Defamation League
stated that "it's not surprising that in a movement that deals with
economic issues you're going to get bigots that believe in this
stereotype...[however] they are not expressing or representing a larger
view."