| Cushing's syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hypercortisolism, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, hyperadrenocorticism |
 | |
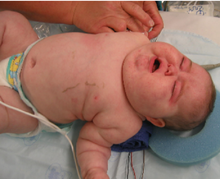
| Person's facial appearance 3 months after treatment with inhaled fluticasone | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
| Symptoms | High blood pressure, abdominal obesity with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, round red face, fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, acne, fragile skin |
| Usual onset | 20–50 years |
| Causes | Prolonged exposure to cortisol |
| Diagnostic method | Requires a number of steps |
| ment | Based on underlying cause |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | 2–3 per million people per year |
Cushing's syndrome is the collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness.
Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors may also cause Cushing's. Some of these are associated with inherited disorders such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 and Carney complex. Diagnosis requires a number of steps. The first step is to check the medications a person takes. The second step is to measure levels of cortisol in the urine, saliva or in the blood after taking dexamethasone. If this test is abnormal, the cortisol may be measured late at night. If the cortisol remains high, a blood test for ACTH may be done.
Most cases can be treated and cured. If due to medications, these can often be slowly decreased if still required or slowly stopped. If caused by a tumor, it may be treated by a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation. If the pituitary was affected, other medications may be required to replace its lost function. With treatment, life expectancy is usually normal. Some, in whom surgery is unable to remove the entire tumor, have an increased risk of death.
About two to three people per million are affected each year. It most commonly affects people who are 20 to 50 years of age. Women are affected three times more often than men. A mild degree of overproduction of cortisol without obvious symptoms, however, is more common. Cushing's syndrome was first described by American neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing in 1932. Cushing's syndrome may also occur in other animals including cats, dogs, and horses.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms include rapid weight gain, particularly of the trunk and face with sparing of the limbs (central obesity). Common signs include the growth of fat pads along the collarbone, on the back of the neck ("buffalo hump" or lipodystrophy), and on the face ("moon face"). Other symptoms include excess sweating, dilation of capillaries, thinning of the skin (which causes easy bruising and dryness, particularly the hands) and mucous membranes, purple or red striae (the weight gain in Cushing's syndrome stretches the skin, which is thin and weakened, causing it to hemorrhage) on the trunk, buttocks, arms, legs, or breasts, proximal muscle weakness (hips, shoulders), and hirsutism (facial male-pattern hair growth), baldness and/or extremely dry and brittle hair. In rare cases, Cushing's can cause hypocalcemia. The excess cortisol may also affect other endocrine systems and cause, for example, insomnia, inhibited aromatase, reduced libido, impotence in men, and amenorrhoea, oligomenorrhea and infertility in women due to elevations in androgens. Studies have also shown that the resultant amenorrhea is due to hypercortisolism, which feeds back onto the hypothalamus resulting in decreased levels of GnRH release.
Many of the features of Cushing's are those seen in metabolic syndrome, including insulin resistance, hypertension, obesity, and elevated blood levels of triglycerides.
Cognitive conditions, including memory and attention dysfunctions, as well as depression, are commonly associated with elevated cortisol, and may be early indicators of exogenous or endogenous Cushing's. Depression and anxiety disorders are also common.
Other striking and distressing skin changes that may appear in Cushing's syndrome include facial acne, susceptibility to superficial fungus (dermatophyte and malassezia) infections, and the characteristic purplish, atrophic striae on the abdomen.
Other signs include increased urination (and accompanying increased thirst), persistent high blood pressure (due to cortisol's enhancement of epinephrine's vasoconstrictive effect) and insulin resistance (especially common with ACTH production outside the pituitary), leading to high blood sugar and insulin resistance which can lead to diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance is accompanied by skin changes such as acanthosis nigricans in the axilla and around the neck, as well as skin tags in the axilla. Untreated Cushing's syndrome can lead to heart disease and increased mortality. Cortisol can also exhibit mineralocorticoid activity in high concentrations, worsening the hypertension and leading to hypokalemia (common in ectopic ACTH secretion) and hypernatremia (increased Na+ ions concentration in plasma). Furthermore, excessive cortisol may lead to gastrointestinal disturbances, opportunistic infections, and impaired wound healing related to cortisol's suppression of the immune and inflammatory responses. Osteoporosis is also an issue in Cushing's syndrome since osteoblast activity is inhibited. Additionally, Cushing's syndrome may cause sore and aching joints, particularly in the hip, shoulders, and lower back.
Brain changes such as cerebral atrophy may occur. This atrophy is associated with areas of high glucocorticoid receptor concentrations such as the hippocampus and correlates highly with psychopathological personality changes.
- Rapid weight gain
- Moodiness, irritability, or depression
- Muscle and bone weakness
- Memory and attention dysfunction
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Immune suppression
- Sleep disturbances
- Menstrual disorders such as amenorrhea in women
- Infertility in women
- Impotence in men
- Hirsutism
- Baldness
- Hypercholesterolemia
Hyperpigmentation
Cushing's syndrome due to excess ACTH may also result in hyperpigmentation. This is due to melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone production as a byproduct of ACTH synthesis from pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC). Alternatively, it is proposed that the high levels of ACTH, β-lipotropin, and γ-lipotropin, which contain weak MSH function, can act on the melanocortin 1 receptor. A variant of Cushing's disease can be caused by ectopic, i.e. extrapituitary, ACTH production from, for example, a small-cell lung cancer.
When Cushing's syndrome is caused by an increase of cortisol at the level of the adrenal glands (via an adenoma or hyperplasia), negative feedback ultimately reduces ACTH production in the pituitary. In these cases, ACTH levels remain low and no hyperpigmentation develops.
Causes
Cushing's syndrome may result from any cause of increased glucocorticoid levels, whether due to medication or internal processes. Some sources however do not consider the glucocorticoid medication-induced condition as "Cushing's syndrome" proper, instead using the term "Cushingoid" to describe the medication's side effects which mimic the endogenous condition.
Cushing's disease is a specific type of Cushing's syndrome caused by a pituitary tumor leading to excessive production of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). Excessive ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce high levels of cortisol, producing the disease state. While all Cushing's disease gives Cushing's syndrome, not all Cushing's syndrome is due to Cushing's disease. Several possible causes of Cushing's syndrome are known.
Exogenous
The most common cause of Cushing's syndrome is the use of prescribed glucocorticoids to treat other diseases (iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome). Glucocorticoids are used in treatment of a variety of disorders, including asthma and rheumatoid arthritis, and also used for immunosuppression after organ transplants. Administration of synthetic ACTH is also possible, but ACTH is less often prescribed due to cost and lesser utility. Rarely, Cushing's syndrome can also be due to the use of medroxyprogesterone acetate. In exogenous Cushing's, the adrenal glands may often gradually atrophy due to lack of stimulation by ACTH, the production of which is suppressed by glucocorticoid medication. Abruptly stopping the medication can thus result in acute and potentially life-threatening adrenal insufficiency and the dose must hence be slowly and carefully tapered off to allow internal cortisol production to pick up. In some cases, patients never recover sufficient levels of internal production and must continue taking glucocorticoids at physiological doses for life.
Cushing's syndrome in childhood is especially rare and usually results from use of glucocorticoid medication.
Endogenous
Endogenous Cushing's syndrome results from some derangement of the body's own system of cortisol secretion. Normally, ACTH is released from the pituitary gland when necessary to stimulate the release of cortisol from the adrenal glands.
- In pituitary Cushing's, a benign pituitary adenoma secretes ACTH. This is also known as Cushing's disease and is responsible for 70% of endogenous Cushing's syndrome.
- In adrenal Cushing's, excess cortisol is produced by adrenal gland tumors, hyperplastic adrenal glands, or adrenal glands with nodular adrenal hyperplasia.
- Tumors outside the normal pituitary-adrenal system can produce ACTH (occasionally with CRH) that affects the adrenal glands. This etiology is called ectopic or paraneoplastic Cushing's disease and is seen in diseases such as small cell lung cancer.
- Finally, rare cases of CRH-secreting tumors (without ACTH secretion) have been reported, which stimulates pituitary ACTH production.
Pseudo-Cushing's syndrome
Elevated levels of total cortisol can also be due to estrogen found in oral contraceptive pills that contain a mixture of estrogen and progesterone, leading to pseudo-Cushing's syndrome. Estrogen can cause an increase of cortisol-binding globulin and thereby cause the total cortisol level to be elevated. However, the total free cortisol, which is the active hormone in the body, as measured by a 24-hour urine collection for urinary free cortisol, is normal.
Pathophysiology
The hypothalamus is in the brain and the pituitary gland sits just below it. The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropin (ACTH). ACTH travels via the blood to the adrenal gland, where it stimulates the release of cortisol. Cortisol is secreted by the cortex of the adrenal gland from a region called the zona fasciculata in response to ACTH. Elevated levels of cortisol exert negative feedback on CRH in the hypothalamus, which decreases the amount of ACTH released from the anterior pituitary gland.
Strictly, Cushing's syndrome refers to excess cortisol of any etiology (as syndrome means a group of symptoms). One of the causes of Cushing's syndrome is a cortisol-secreting adenoma in the cortex of the adrenal gland (primary hypercortisolism/hypercorticism). The adenoma causes cortisol levels in the blood to be very high, and negative feedback on the pituitary from the high cortisol levels causes ACTH levels to be very low.
Cushing's disease refers only to hypercortisolism secondary to excess production of ACTH from a corticotroph pituitary adenoma (secondary hypercortisolism/hypercorticism) or due to excess production of hypothalamus CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone) (tertiary hypercortisolism/hypercorticism). This causes the blood ACTH levels to be elevated along with cortisol from the adrenal gland. The ACTH levels remain high because the tumor is unresponsive to negative feedback from high cortisol levels.
When Cushing's syndrome is due to extra ACTH it is known as ectopic Cushing syndrome. This may be seen in a paraneoplastic syndrome.
When Cushing's syndrome is suspected, either a dexamethasone suppression test (administration of dexamethasone and frequent determination of cortisol and ACTH level), or a 24-hour urinary measurement for cortisol offers equal detection rates. Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid and simulates the effects of cortisol, including negative feedback on the pituitary gland. When dexamethasone is administered and a blood sample is tested, cortisol levels >50 nmol/l (1.81 μg/dl) would be indicative of Cushing's syndrome because an ectopic source of cortisol or ACTH (such as adrenal adenoma) exists which is not inhibited by the dexamethasone. A novel approach, recently cleared by the US FDA, is sampling cortisol in saliva over 24 hours, which may be equally sensitive, as late-night levels of salivary cortisol are high in cushingoid patients. Other pituitary hormone levels may need to be ascertained. Performing a physical examination to determine any visual field defect may be necessary if a pituitary lesion is suspected, which may compress the optic chiasm, causing typical bitemporal hemianopia.
When any of these tests is positive, CT scanning of the adrenal gland and MRI of the pituitary gland are performed to detect the presence of any adrenal or pituitary adenomas or incidentalomas (the incidental discovery of harmless lesions). Scintigraphy of the adrenal gland with iodocholesterol scan is occasionally necessary. Occasionally, determining the ACTH levels in various veins in the body by venous catheterization, working towards the pituitary (petrosal sinus sampling) is necessary. In many cases, the tumors causing Cushing's disease are less than 2 mm in size and difficult to detect using MRI or CT imaging. In one study of 261 patients with confirmed pituitary Cushing's disease, only 48% of pituitary lesions were identified using MRI prior to surgery.
Plasma CRH levels are inadequate at diagnosis (with the possible exception of tumors secreting CRH) because of peripheral dilution and binding to CRHBP.
Diagnosis
Cushing's syndrome can be ascertained via a variety of test which include the following:
- Dexamethasone suppression test
- Saliva cortisol level
Treatment
Most cases of Cushingoid symptoms are caused by corticosteroid medications, such as those used for asthma, arthritis, eczema and other inflammatory conditions. Consequently, most patients are effectively treated by carefully tapering off (and eventually stopping) the medication that causes the symptoms.
If an adrenal adenoma is identified, it may be removed by surgery. An ACTH-secreting corticotrophic pituitary adenoma should be removed after diagnosis. Regardless of the adenoma's location, most patients require steroid replacement postoperatively at least in the interim, as long-term suppression of pituitary ACTH and normal adrenal tissue does not recover immediately. Clearly, if both adrenals are removed, replacement with hydrocortisone or prednisolone is imperative.
In those patients not suited for or unwilling to undergo surgery, several drugs have been found to inhibit cortisol synthesis (e.g. ketoconazole, metyrapone) but they are of limited efficacy. Mifepristone is a powerful glucocorticoid type II receptor antagonist and, since it does not interfere with normal cortisol homeostasis type I receptor transmission, may be especially useful for treating the cognitive effects of Cushing's syndrome. However, the medication faces considerable controversy due to its use as an abortifacient. In February 2012, the FDA approved mifepristone to control high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) in adult patients who are not candidates for surgery, or who did not respond to prior surgery, with the warning that mifepristone should never be used by pregnant women. In March 2020, Isturisa (osilodrostat) oral tablets a 11-beta-hydroxylase enzyme inhibitor was approved by FDA for treating those patients who cannot undergo pituitary surgery or for patients who underwent surgery but continues to have the disease.
Removal of the adrenals in the absence of a known tumor is occasionally performed to eliminate the production of excess cortisol. In some occasions, this removes negative feedback from a previously occult pituitary adenoma, which starts growing rapidly and produces extreme levels of ACTH, leading to hyperpigmentation. This clinical situation is known as Nelson's syndrome.
Epidemiology
Cushing's syndrome caused by treatment with corticosteroids is the most common form. Cushing's disease is rare; a Danish study found an incidence of less than one case per million people per year. However, asymptomatic microadenomas (less than 10 mm in size) of the pituitary are found in about one in six individuals.
People with Cushing's syndrome have increased morbidity and mortality as compared to the general population. The most common cause of mortality in Cushing's syndrome is cardiovascular events. People with Cushing's syndrome have nearly 4 times increased cardiovascular mortality as compared to the general population.