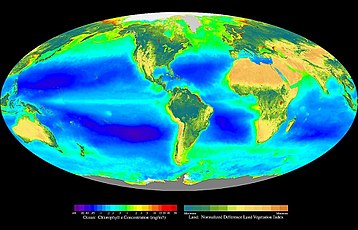
The biosphere (from Greek βίος bíos "life" and σφαῖρα sphaira "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος oîkos "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 Terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium. By the most general biophysiological definition, the biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. The biosphere is postulated to have evolved, beginning with a process of biopoiesis (life created naturally from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds) or biogenesis (life created from living matter), at least some 3.5 billion years ago.
In a general sense, biospheres are any closed, self-regulating systems containing ecosystems. This includes artificial biospheres such as Biosphere 2 and BIOS-3, and potentially ones on other planets or moons.
Origin and use of the term
The term "biosphere" was coined by geologist Eduard Suess in 1875, which he defined as the place on Earth's surface where life dwells.
While the concept has a geological origin, it is an indication of the effect of both Charles Darwin and Matthew F. Maury on the Earth sciences. The biosphere's ecological context comes from the 1920s (see Vladimir I. Vernadsky), preceding the 1935 introduction of the term "ecosystem" by Sir Arthur Tansley (see ecology history). Vernadsky defined ecology as the science of the biosphere. It is an interdisciplinary concept for integrating astronomy, geophysics, meteorology, biogeography, evolution, geology, geochemistry, hydrology and, generally speaking, all life and Earth sciences.
Narrow definition
Geochemists define the biosphere as being the total sum of living organisms (the "biomass" or "biota" as referred to by biologists and ecologists). In this sense, the biosphere is but one of four separate components of the geochemical model, the other three being geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. When these four component spheres are combined into one system, it is known as the Ecosphere. This term was coined during the 1960s and encompasses both biological and physical components of the planet.
The Second International Conference on Closed Life Systems defined biospherics as the science and technology of analogs and models of Earth's biosphere; i.e., artificial Earth-like biospheres. Others may include the creation of artificial non-Earth biospheres—for example, human-centered biospheres or a native Martian biosphere—as part of the topic of biospherics.
Earth's biosphere
Age
The earliest evidence for life on Earth includes biogenic graphite found in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks from Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone from Western Australia. More recently, in 2015, "remains of biotic life" were found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. In 2017, putative fossilized microorganisms (or microfossils) were announced to have been discovered in hydrothermal vent precipitates in the Nuvvuagittuq Belt of Quebec, Canada that were as old as 4.28 billion years, the oldest record of life on earth, suggesting "an almost instantaneous emergence of life" after ocean formation 4.4 billion years ago, and not long after the formation of the Earth 4.54 billion years ago. According to biologist Stephen Blair Hedges, "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth ... then it could be common in the universe."
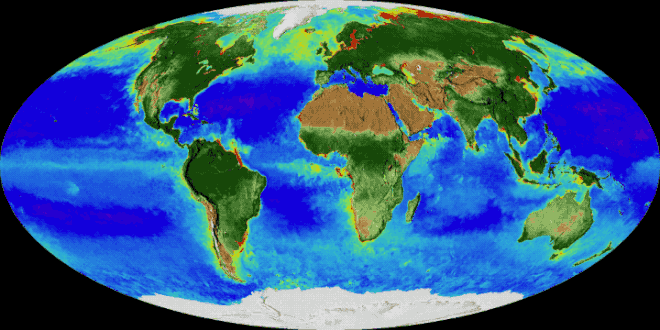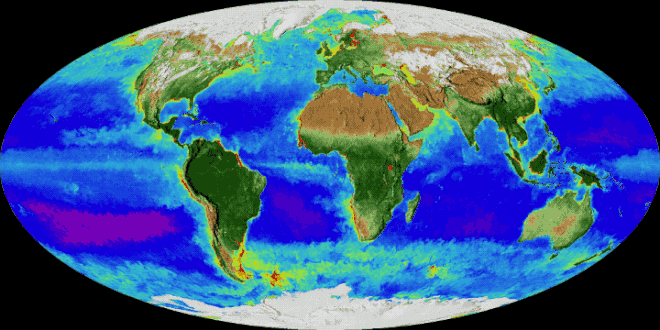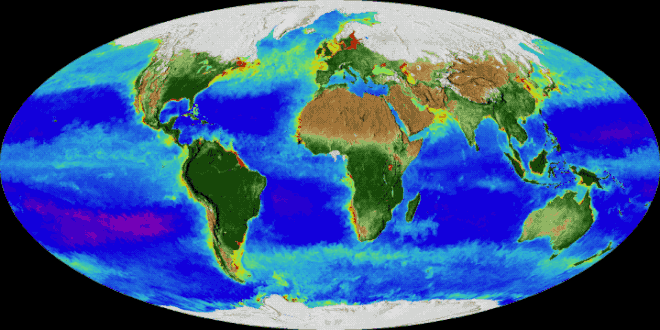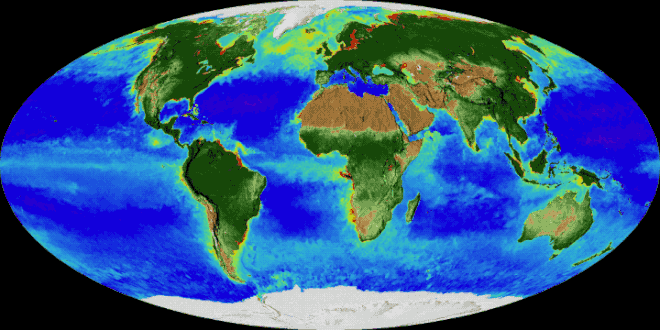
Extent
Every part of the planet, from the polar ice caps to the equator, features life of some kind. Recent advances in microbiology have demonstrated that microbes live deep beneath the Earth's terrestrial surface, and that the total mass of microbial life in so-called "uninhabitable zones" may, in biomass, exceed all animal and plant life on the surface. The actual thickness of the biosphere on earth is difficult to measure. Birds typically fly at altitudes as high as 1,800 m (5,900 ft; 1.1 mi) and fish live as much as 8,372 m (27,467 ft; 5.202 mi) underwater in the Puerto Rico Trench.
There are more extreme examples for life on the planet: Rüppell's vulture has been found at altitudes of 11,300 m (37,100 ft; 7.0 mi); bar-headed geese migrate at altitudes of at least 8,300 m (27,200 ft; 5.2 mi); yaks live at elevations as high as 5,400 m (17,700 ft; 3.4 mi) above sea level; mountain goats live up to 3,050 m (10,010 ft; 1.90 mi). Herbivorous animals at these elevations depend on lichens, grasses, and herbs.
Life forms live in every part of the Earth's biosphere, including soil, hot springs, inside rocks at least 19 km (12 mi) deep underground, the deepest parts of the ocean, and at least 64 km (40 mi) high in the atmosphere. Microorganisms, under certain test conditions, have been observed to survive the vacuum of outer space. The total amount of soil and subsurface bacterial carbon is estimated as 5 × 1017 g, or the "weight of the United Kingdom". The mass of prokaryote microorganisms—which includes bacteria and archaea, but not the nucleated eukaryote microorganisms—may be as much as 0.8 trillion tons of carbon (of the total biosphere mass, estimated at between 1 and 4 trillion tons). Barophilic marine microbes have been found at more than a depth of 10,000 m (33,000 ft; 6.2 mi) in the Mariana Trench, the deepest spot in the Earth's oceans. In fact, single-celled life forms have been found in the deepest part of the Mariana Trench, by the Challenger Deep, at depths of 11,034 m (36,201 ft; 6.856 mi). Other researchers reported related studies that microorganisms thrive inside rocks up to 580 m (1,900 ft; 0.36 mi) below the sea floor under 2,590 m (8,500 ft; 1.61 mi) of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States, as well as 2,400 m (7,900 ft; 1.5 mi) beneath the seabed off Japan. Culturable thermophilic microbes have been extracted from cores drilled more than 5,000 m (16,000 ft; 3.1 mi) into the Earth's crust in Sweden, from rocks between 65–75 °C (149–167 °F). Temperature increases with increasing depth into the Earth's crust. The rate at which the temperature increases depends on many factors, including type of crust (continental vs. oceanic), rock type, geographic location, etc. The greatest known temperature at which microbial life can exist is 122 °C (252 °F) (Methanopyrus kandleri Strain 116), and it is likely that the limit of life in the "deep biosphere" is defined by temperature rather than absolute depth. On 20 August 2014, scientists confirmed the existence of microorganisms living 800 m (2,600 ft; 0.50 mi) below the ice of Antarctica. According to one researcher, "You can find microbes everywhere – they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are."
Our biosphere is divided into a number of biomes, inhabited by fairly similar flora and fauna. On land, biomes are separated primarily by latitude. Terrestrial biomes lying within the Arctic and Antarctic Circles are relatively barren of plant and animal life, while most of the more populous biomes lie near the equator.
Annual variation
Artificial biospheres
Experimental biospheres, also called closed ecological systems, have been created to study ecosystems and the potential for supporting life outside the Earth. These include spacecraft and the following terrestrial laboratories:
- Biosphere 2 in Arizona, United States, 3.15 acres (13,000 m2).
- BIOS-1, BIOS-2 and BIOS-3 at the Institute of Biophysics in Krasnoyarsk, Siberia, in what was then the Soviet Union.
- Biosphere J (CEEF, Closed Ecology Experiment Facilities), an experiment in Japan.
- Micro-Ecological Life Support System Alternative (MELiSSA) at Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
Extraterrestrial biospheres
No biospheres have been detected beyond the Earth; therefore, the existence of extraterrestrial biospheres remains hypothetical. The rare Earth hypothesis suggests they should be very rare, save ones composed of microbial life only. On the other hand, Earth analogs may be quite numerous, at least in the Milky Way galaxy, given the large number of planets. Three of the planets discovered orbiting TRAPPIST-1 could possibly contain biospheres. Given limited understanding of abiogenesis, it is currently unknown what percentage of these planets actually develop biospheres.
Based on observations by the Kepler Space Telescope team, it has been calculated that provided the probability of abiogenesis is higher than 1 to 1000, the closest alien biosphere should be within 100 light-years from the Earth.
It is also possible that artificial biospheres will be created in the future, for example with the terraforming of Mars.