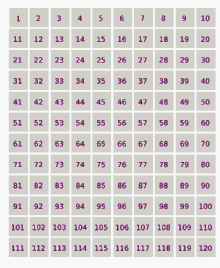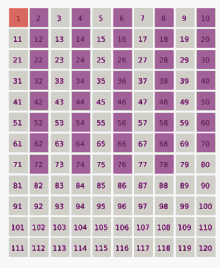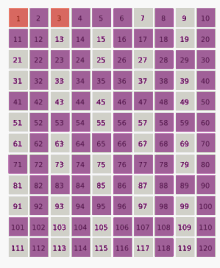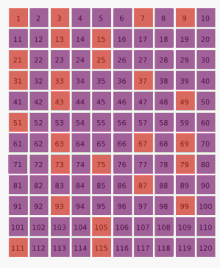
- Ulam conjecture (in Number Theory)
- Ulam conjecture (in Graph theory)
- Ulam's packing conjecture
- Ulam's game
- Ulam matrix
- Ulam numbers
- Kac, Mark; Ulam, Stanisław (1968). Mathematics and Logic: Retrospect and Prospects. New York: Praeger. ISBN 978-0-486-67085-0. OCLC 24847821.
- Ulam, Stanisław (1974). Beyer, W. A.; Mycielski and, J.; Rota, G.-C. (eds.). Sets, Numbers, and Universes: selected works. Mathematicians of Our Time. Vol. 9. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.-London. ISBN 978-0-262-02108-1. MR 0441664.
- Ulam, Stanisław (1960). A Collection of Mathematical Problems. New York: Interscience Publishers. OCLC 526673.
- Ulam, Stanisław (1983). Adventures of a Mathematician. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. ISBN 978-0-684-14391-0. OCLC 1528346. (autobiography).
- Ulam, Stanisław (1986). Science, Computers, and People: From the Tree of Mathematics. Boston: Birkhauser. ISBN 978-3-7643-3276-1. OCLC 11260216.
- Ulam, Stanisław; Ulam, Françoise (1990). Analogies Between Analogies: The Mathematical Reports of S.M. Ulam and his Los Alamos Collaborators. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-05290-1. OCLC 20318499.
Stanisław Ulam | |
|---|---|
| Born | Stanisław Marcin Ulam 13 April 1909 |
| Died | 13 May 1984 (aged 75) Santa Fe, New Mexico, U.S. |
| Nationality | Polish |
| Citizenship | Poland, United States (naturalized in 1941) |
| Education | Lwów Polytechnic Institute, Second Polish Republic |
| Known for | Mathematical formulations in the fields of Physics, Computer Science, and Biology Teller–Ulam design Monte Carlo method Fermi–Pasta–Ulam–Tsingou problem Nuclear pulse propulsion |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Mathematics |
| Institutions | Institute for Advanced Study Harvard University University of Wisconsin Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Colorado University of Florida |
| Doctoral advisor | Kazimierz Kuratowski |
| Doctoral students | Paul Kelly |
Stanisław Marcin Ulam ([sta'ɲiswaf 'mart͡ɕin 'ulam]; 13 April 1909 – 13 May 1984) was a Polish scientist in the fields of mathematics and nuclear physics. He participated in the Manhattan Project, originated the Teller–Ulam design of thermonuclear weapons, discovered the concept of the cellular automaton, invented the Monte Carlo method of computation, and suggested nuclear pulse propulsion. In pure and applied mathematics, he proved some theorems and proposed several conjectures.
Born into a wealthy Polish Jewish family, Ulam studied mathematics at the Lwów Polytechnic Institute, where he earned his PhD in 1933 under the supervision of Kazimierz Kuratowski. In 1935, John von Neumann, whom Ulam had met in Warsaw, invited him to come to the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, for a few months. From 1936 to 1939, he spent summers in Poland and academic years at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, where he worked to establish important results regarding ergodic theory. On 20 August 1939, he sailed for the United States for the last time with his 17-year-old brother Adam Ulam. He became an assistant professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1940, and a United States citizen in 1941.
In October 1943, he received an invitation from Hans Bethe to join the Manhattan Project at the secret Los Alamos Laboratory in New Mexico. There, he worked on the hydrodynamic calculations to predict the behavior of the explosive lenses that were needed by an implosion-type weapon. He was assigned to Edward Teller's group, where he worked on Teller's "Super" bomb for Teller and Enrico Fermi. After the war he left to become an associate professor at the University of Southern California, but returned to Los Alamos in 1946 to work on thermonuclear weapons. With the aid of a cadre of female "computers", including his wife Françoise Aron Ulam, he found that Teller's "Super" design was unworkable. In January 1951, Ulam and Teller came up with the Teller–Ulam design, which is the basis for all thermonuclear weapons.
Ulam considered the problem of nuclear propulsion of rockets, which was pursued by Project Rover, and proposed, as an alternative to Rover's nuclear thermal rocket, to harness small nuclear explosions for propulsion, which became Project Orion. With Fermi, John Pasta, and Mary Tsingou, Ulam studied the Fermi–Pasta–Ulam–Tsingou problem, which became the inspiration for the field of non-linear science. He is probably best known for realising that electronic computers made it practical to apply statistical methods to functions without known solutions, and as computers have developed, the Monte Carlo method has become a common and standard approach to many problems.
Poland
Ulam was born in Lemberg, Galicia, on 13 April 1909. At this time, Galicia was in the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, known to Poles as the Austrian partition. In 1918, it became part of the newly restored Poland, the Second Polish Republic, and the city took its Polish name again, Lwów.
The Ulams were a wealthy Polish Jewish family of bankers, industrialists, and other professionals. Ulam's immediate family was "well-to-do but hardly rich". His father, Józef Ulam, was born in Lwów and was a lawyer, and his mother, Anna (née Auerbach), was born in Stryj. His uncle, Michał Ulam, was an architect, building contractor, and lumber industrialist. From 1916 until 1918, Józef's family lived temporarily in Vienna. After they returned, Lwów became the epicenter of the Polish–Ukrainian War, during which the city experienced a Ukrainian siege.
In 1919, Ulam entered Lwów Gymnasium Nr. VII, from which he graduated in 1927. He then studied mathematics at the Lwów Polytechnic Institute. Under the supervision of Kazimierz Kuratowski, he received his Master of Arts degree in 1932, and became a Doctor of Science in 1933. At the age of 20, in 1929, he published his first paper Concerning Function of Sets in the journal Fundamenta Mathematicae. From 1931 until 1935, he traveled to and studied in Wilno (Vilnius), Vienna, Zurich, Paris, and Cambridge, England, where he met G. H. Hardy and Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar.
Along with Stanisław Mazur, Mark Kac, Włodzimierz Stożek, Kuratowski, and others, Ulam was a member of the Lwów School of Mathematics. Its founders were Hugo Steinhaus and Stefan Banach, who were professors at the Jan Kazimierz University. Mathematicians of this "school" met for long hours at the Scottish Café, where the problems they discussed were collected in the Scottish Book, a thick notebook provided by Banach's wife. Ulam was a major contributor to the book. Of the 193 problems recorded between 1935 and 1941, he contributed 40 problems as a single author, another 11 with Banach and Mazur, and an additional 15 with others. In 1957, he received from Steinhaus a copy of the book, which had survived the war, and translated it into English. In 1981, Ulam's friend R. Daniel Maudlin published an expanded and annotated version.
Move to the United States
In 1935, John von Neumann, whom Ulam had met in Warsaw, invited him to come to the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, for a few months. In December of that year, Ulam sailed to the US. At Princeton, he went to lectures and seminars, where he heard Oswald Veblen, James Alexander, and Albert Einstein. During a tea party at von Neumann's house, he encountered G. D. Birkhoff, who suggested that he apply for a position with the Harvard Society of Fellows. Following up on Birkhoff's suggestion, Ulam spent summers in Poland and academic years at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts from 1936 to 1939, where he worked with John C. Oxtoby to establish results regarding ergodic theory. These appeared in Annals of Mathematics in 1941. In 1938, Stanislaw's mother Anna hanna Ulam (maiden name Auerbach) died of cancer.
On 20 August 1939, in Gdynia, Józef Ulam, along with his brother Szymon, put his two sons, Stanislaw and 17 year old Adam, on a ship headed for the US. Eleven days later, the Germans invaded Poland. Within two months, the Germans completed their occupation of western Poland, and the Soviets invaded and occupied eastern Poland. Within two years, Józef Ulam and the rest of his family, including Stanislaw's sister Stefania Ulam, were victims of the Holocaust, Hugo Steinhaus was in hiding, Kazimierz Kuratowski was lecturing at the underground university in Warsaw, Włodzimierz Stożek and his two sons had been killed in the massacre of Lwów professors, and the last problem had been recorded in the Scottish Book. Stefan Banach survived the Nazi occupation by feeding lice at Rudolf Weigl's typhus research institute. In 1963, Adam Ulam, who had become an eminent kremlinologist at Harvard, received a letter from George Volsky, who hid in Józef Ulam's house after deserting from the Polish army. This reminiscence gave a chilling account of Lwów's chaotic scenes in late 1939. In later life Ulam described himself as "an agnostic. Sometimes I muse deeply on the forces that are for me invisible. When I am almost close to the idea of God, I feel immediately estranged by the horrors of this world, which he seems to tolerate".
In 1940, after being recommended by Birkhoff, Ulam became an assistant professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Here, he became a United States citizen in 1941. That year, he married Françoise Aron. She had been a French exchange student at Mount Holyoke College, whom he met in Cambridge. They had one daughter, Claire. In Madison, Ulam met his friend and colleague C. J. Everett, with whom he would collaborate on a number of papers.
Manhattan Project
In early 1943, Ulam asked von Neumann to find him a war job. In October, he received an invitation to join an unidentified project near Santa Fe, New Mexico. The letter was signed by Hans Bethe, who had been appointed as leader of the theoretical division of Los Alamos National Laboratory by Robert Oppenheimer, its scientific director. Knowing nothing of the area, he borrowed a New Mexico guide book. On the checkout card, he found the names of his Wisconsin colleagues, Joan Hinton, David Frisch, and Joseph McKibben, all of whom had mysteriously disappeared. This was Ulam's introduction to the Manhattan Project, which was the US's wartime effort to create the atomic bomb.
Hydrodynamical calculations of implosion
A few weeks after Ulam reached Los Alamos in February 1944, the project experienced a crisis. In April, Emilio Segrè discovered that plutonium made in reactors would not work in a gun-type plutonium weapon like the "Thin Man", which was being developed in parallel with a uranium weapon, the "Little Boy" that was dropped on Hiroshima. This problem threatened to waste an enormous investment in new reactors at the Hanford site and to make slow separation of uranium isotopes the only way to prepare fissile material suitable for use in bombs. To respond, Oppenheimer implemented, in August, a sweeping reorganization of the laboratory to focus on development of an implosion-type weapon and appointed George Kistiakowsky head of the implosion department. He was a professor at Harvard and an expert on precise use of explosives.
The basic concept of implosion is to use chemical explosives to crush a chunk of fissile material into a critical mass, where neutron multiplication leads to a nuclear chain reaction, releasing a large amount of energy. Cylindrical implosive configurations had been studied by Seth Neddermeyer, but von Neumann, who had experience with shaped charges used in armor-piercing ammunition, was a vocal advocate of spherical implosion driven by explosive lenses. He realized that the symmetry and speed with which implosion compressed the plutonium were critical issues, and enlisted Ulam to help design lens configurations that would provide nearly spherical implosion. Within an implosion, because of enormous pressures and high temperatures, solid materials behave much like fluids. This meant that hydrodynamical calculations were needed to predict and minimize asymmetries that would spoil a nuclear detonation. Of these calculations, Ulam said:
The hydrodynamical problem was simply stated, but very difficult to calculate – not only in detail, but even in order of magnitude. In this discussion, I stressed pure pragmatism and the necessity to get a heuristic survey of the problem by simple-minded brute force, rather than by massive numerical work.
Nevertheless, with the primitive facilities available at the time, Ulam and von Neumann did carry out numerical computations that led to a satisfactory design. This motivated their advocacy of a powerful computational capability at Los Alamos, which began during the war years, continued through the cold war, and still exists. Otto Frisch remembered Ulam as "a brilliant Polish topologist with a charming French wife. At once he told me that he was a pure mathematician who had sunk so low that his latest paper actually contained numbers with decimal points!"
Statistics of branching and multiplicative processes
Even the inherent statistical fluctuations of neutron multiplication within a chain reaction have implications with regard to implosion speed and symmetry. In November 1944, David Hawkins and Ulam addressed this problem in a report entitled "Theory of Multiplicative Processes". This report, which invokes probability-generating functions, is also an early entry in the extensive literature on statistics of branching and multiplicative processes. In 1948, its scope was extended by Ulam and Everett.
Early in the Manhattan project, Enrico Fermi's attention was focused on the use of reactors to produce plutonium. In September 1944, he arrived at Los Alamos, shortly after breathing life into the first Hanford reactor, which had been poisoned by a xenon isotope. Soon after Fermi's arrival, Teller's "Super" bomb group, of which Ulam was a part, was transferred to a new division headed by Fermi. Fermi and Ulam formed a relationship that became very fruitful after the war.
Post war Los Alamos
In September 1945, Ulam left Los Alamos to become an associate professor at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. In January 1946, he suffered an acute attack of encephalitis, which put his life in danger, but which was alleviated by emergency brain surgery. During his recuperation, many friends visited, including Nicholas Metropolis from Los Alamos and the famous mathematician Paul Erdős, who remarked: "Stan, you are just like before." This was encouraging, because Ulam was concerned about the state of his mental faculties, for he had lost the ability to speak during the crisis. Another friend, Gian-Carlo Rota, asserted in a 1987 article that the attack changed Ulam's personality: afterwards, he turned from rigorous pure mathematics to more speculative conjectures concerning the application of mathematics to physics and biology; Rota also cites Ulam's former collaborator Paul Stein as noting that Ulam was sloppier in his clothing afterwards, and John Oxtoby as noting that Ulam before the encephalitis could work for hours on end doing calculations, while when Rota worked with him, was reluctant to solve even a quadratic equation. This assertion was not accepted by Françoise Aron Ulam.
By late April 1946, Ulam had recovered enough to attend a secret conference at Los Alamos to discuss thermonuclear weapons. Those in attendance included Ulam, von Neumann, Metropolis, Teller, Stan Frankel, and others. Throughout his participation in the Manhattan Project, Teller's efforts had been directed toward the development of a "super" weapon based on nuclear fusion, rather than toward development of a practical fission bomb. After extensive discussion, the participants reached a consensus that his ideas were worthy of further exploration. A few weeks later, Ulam received an offer of a position at Los Alamos from Metropolis and Robert D. Richtmyer, the new head of its theoretical division, at a higher salary, and the Ulams returned to Los Alamos.
Monte Carlo method
Late in the war, under the sponsorship of von Neumann, Frankel and Metropolis began to carry out calculations on the first general-purpose electronic computer, the ENIAC at the Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland. Shortly after returning to Los Alamos, Ulam participated in a review of results from these calculations. Earlier, while playing solitaire during his recovery from surgery, Ulam had thought about playing hundreds of games to estimate statistically the probability of a successful outcome. With ENIAC in mind, he realized that the availability of computers made such statistical methods very practical. John von Neumann immediately saw the significance of this insight. In March 1947 he proposed a statistical approach to the problem of neutron diffusion in fissionable material. Because Ulam had often mentioned his uncle, Michał Ulam, "who just had to go to Monte Carlo" to gamble, Metropolis dubbed the statistical approach "The Monte Carlo method". Metropolis and Ulam published the first unclassified paper on the Monte Carlo method in 1949.
Fermi, learning of Ulam's breakthrough, devised an analog computer known as the Monte Carlo trolley, later dubbed the FERMIAC. The device performed a mechanical simulation of random diffusion of neutrons. As computers improved in speed and programmability, these methods became more useful. In particular, many Monte Carlo calculations carried out on modern massively parallel supercomputers are embarrassingly parallel applications, whose results can be very accurate.
Teller–Ulam design
On 29 August 1949, the Soviet Union tested its first fission bomb, the RDS-1. Created under the supervision of Lavrentiy Beria, who sought to duplicate the US effort, this weapon was nearly identical to Fat Man, for its design was based on information provided by spies Klaus Fuchs, Theodore Hall, and David Greenglass. In response, on 31 January 1950, President Harry S. Truman announced a crash program to develop a fusion bomb.
To advocate an aggressive development program, Ernest Lawrence and Luis Alvarez came to Los Alamos, where they conferred with Norris Bradbury, the laboratory director, and with George Gamow, Edward Teller, and Ulam. Soon, these three became members of a short-lived committee appointed by Bradbury to study the problem, with Teller as chairman. At this time, research on the use of a fission weapon to create a fusion reaction had been ongoing since 1942, but the design was still essentially the one originally proposed by Teller. His concept was to put tritium and/or deuterium in close proximity to a fission bomb, with the hope that the heat and intense flux of neutrons released when the bomb exploded, would ignite a self-sustaining fusion reaction. Reactions of these isotopes of hydrogen are of interest because the energy per unit mass of fuel released by their fusion is much larger than that from fission of heavy nuclei.
Because the results of calculations based on Teller's concept were discouraging, many scientists believed it could not lead to a successful weapon, while others had moral and economic grounds for not proceeding. Consequently, several senior people of the Manhattan Project opposed development, including Bethe and Oppenheimer. To clarify the situation, Ulam and von Neumann resolved to do new calculations to determine whether Teller's approach was feasible. To carry out these studies, von Neumann decided to use electronic computers: ENIAC at Aberdeen, a new computer, MANIAC, at Princeton, and its twin, which was under construction at Los Alamos. Ulam enlisted Everett to follow a completely different approach, one guided by physical intuition. Françoise Ulam was one of a cadre of women "computers" who carried out laborious and extensive computations of thermonuclear scenarios on mechanical calculators, supplemented and confirmed by Everett's slide rule. Ulam and Fermi collaborated on further analysis of these scenarios. The results showed that, in workable configurations, a thermonuclear reaction would not ignite, and if ignited, it would not be self-sustaining. Ulam had used his expertise in combinatorics to analyze the chain reaction in deuterium, which was much more complicated than the ones in uranium and plutonium, and he concluded that no self-sustaining chain reaction would take place at the (low) densities that Teller was considering. In late 1950, these conclusions were confirmed by von Neumann's results.
In January 1951, Ulam had another idea: to channel the mechanical shock of a nuclear explosion so as to compress the fusion fuel. On the recommendation of his wife, Ulam discussed this idea with Bradbury and Mark before he told Teller about it. Almost immediately, Teller saw its merit, but noted that soft X-rays from the fission bomb would compress the thermonuclear fuel more strongly than mechanical shock and suggested ways to enhance this effect. On 9 March 1951, Teller and Ulam submitted a joint report describing these innovations. A few weeks later, Teller suggested placing a fissile rod or cylinder at the center of the fusion fuel. The detonation of this "spark plug" would help to initiate and enhance the fusion reaction. The design based on these ideas, called staged radiation implosion, has become the standard way to build thermonuclear weapons. It is often described as the "Teller–Ulam design".
In September 1951, after a series of differences with Bradbury and other scientists, Teller resigned from Los Alamos, and returned to the University of Chicago. At about the same time, Ulam went on leave as a visiting professor at Harvard for a semester. Although Teller and Ulam submitted a joint report on their design and jointly applied for a patent on it, they soon became involved in a dispute over who deserved credit. After the war, Bethe returned to Cornell University, but he was deeply involved in the development of thermonuclear weapons as a consultant. In 1954, he wrote an article on the history of the H-bomb, which presents his opinion that both men contributed very significantly to the breakthrough. This balanced view is shared by others who were involved, including Mark and Fermi, but Teller persistently attempted to downplay Ulam's role. "After the H-bomb was made," Bethe recalled, "reporters started to call Teller the father of the H-bomb. For the sake of history, I think it is more precise to say that Ulam is the father, because he provided the seed, and Teller is the mother, because he remained with the child. As for me, I guess I am the midwife."
With the basic fusion reactions confirmed, and with a feasible design in hand, there was nothing to prevent Los Alamos from testing a thermonuclear device. On 1 November 1952, the first thermonuclear explosion occurred when Ivy Mike was detonated on Enewetak Atoll, within the US Pacific Proving Grounds. This device, which used liquid deuterium as its fusion fuel, was immense and utterly unusable as a weapon. Nevertheless, its success validated the Teller–Ulam design, and stimulated intensive development of practical weapons.
Fermi–Pasta–Ulam–Tsingou problem
When Ulam returned to Los Alamos, his attention turned away from weapon design and toward the use of computers to investigate problems in physics and mathematics. With John Pasta, who helped Metropolis to bring MANIAC on line in March 1952, he explored these ideas in a report "Heuristic Studies in Problems of Mathematical Physics on High Speed Computing Machines", which was submitted on 9 June 1953. It treated several problems that cannot be addressed within the framework of traditional analytic methods: billowing of fluids, rotational motion in gravitating systems, magnetic lines of force, and hydrodynamic instabilities.
Soon, Pasta and Ulam became experienced with electronic computation on MANIAC, and by this time, Enrico Fermi had settled into a routine of spending academic years at the University of Chicago and summers at Los Alamos. During these summer visits, Pasta, Ulam, and Mary Tsingou, a programmer in the MANIAC group, joined him to study a variation of the classic problem of a string of masses held together by springs that exert forces linearly proportional to their displacement from equilibrium. Fermi proposed to add to this force a nonlinear component, which could be chosen to be proportional to either the square or cube of the displacement, or to a more complicated "broken linear" function. This addition is the key element of the Fermi–Pasta–Ulam–Tsingou problem, which is often designated by the abbreviation FPUT.
A classical spring system can be described in terms of vibrational modes, which are analogous to the harmonics that occur on a stretched violin string. If the system starts in a particular mode, vibrations in other modes do not develop. With the nonlinear component, Fermi expected energy in one mode to transfer gradually to other modes, and eventually, to be distributed equally among all modes. This is roughly what began to happen shortly after the system was initialized with all its energy in the lowest mode, but much later, essentially all the energy periodically reappeared in the lowest mode. This behavior is very different from the expected equipartition of energy. It remained mysterious until 1965, when Kruskal and Zabusky showed that, after appropriate mathematical transformations, the system can be described by the Korteweg–de Vries equation, which is the prototype of nonlinear partial differential equations that have soliton solutions. This means that FPUT behavior can be understood in terms of solitons.
Nuclear propulsion
Starting in 1955, Ulam and Frederick Reines considered nuclear propulsion of aircraft and rockets. This is an attractive possibility, because the nuclear energy per unit mass of fuel is a million times greater than that available from chemicals. From 1955 to 1972, their ideas were pursued during Project Rover, which explored the use of nuclear reactors to power rockets. In response to a question by Senator John O. Pastore at a congressional committee hearing on "Outer Space Propulsion by Nuclear Energy", on January 22, 1958, Ulam replied that "the future as a whole of mankind is to some extent involved inexorably now with going outside the globe."
Ulam and C. J. Everett also proposed, in contrast to Rover's continuous heating of rocket exhaust, to harness small nuclear explosions for propulsion. Project Orion was a study of this idea. It began in 1958 and ended in 1965, after the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty of 1963 banned nuclear weapons tests in the atmosphere and in space. Work on this project was spearheaded by physicist Freeman Dyson, who commented on the decision to end Orion in his article, "Death of a Project".
Bradbury appointed Ulam and John H. Manley as research advisors to the laboratory director in 1957. These newly created positions were on the same administrative level as division leaders, and Ulam held his until he retired from Los Alamos. In this capacity, he was able to influence and guide programs in many divisions: theoretical, physics, chemistry, metallurgy, weapons, health, Rover, and others.
In addition to these activities, Ulam continued to publish technical reports and research papers. One of these introduced the Fermi–Ulam model, an extension of Fermi's theory of the acceleration of cosmic rays. Another, with Paul Stein and Mary Tsingou, titled "Quadratic Transformations", was an early investigation of chaos theory and is considered the first published use of the phrase "chaotic behavior".
Return to academia
During his years at Los Alamos, Ulam was a visiting professor at Harvard from 1951 to 1952, MIT from 1956 to 1957, the University of California, San Diego, in 1963, and the University of Colorado at Boulder from 1961 to 1962 and 1965 to 1967. In 1967, the last of these positions became permanent, when Ulam was appointed as professor and Chairman of the Department of Mathematics at Boulder, Colorado. He kept a residence in Santa Fe, New Mexico, which made it convenient to spend summers at Los Alamos as a consultant.
In Colorado, where he rejoined his friends Gamow, Richtmyer, and Hawkins, Ulam's research interests turned toward biology. In 1968, recognizing this emphasis, the University of Colorado School of Medicine appointed Ulam as Professor of Biomathematics, and he held this position until his death. With his Los Alamos colleague Robert Schrandt he published a report, "Some Elementary Attempts at Numerical Modeling of Problems Concerning Rates of Evolutionary Processes", which applied his earlier ideas on branching processes to biological inheritance. Another, report, with William Beyer, Temple F. Smith, and M. L. Stein, titled "Metrics in Biology", introduced new ideas about biometric distances.
When he retired from Colorado in 1975, Ulam had begun to spend winter semesters at the University of Florida, where he was a graduate research professor. Except for sabbaticals at the University of California, Davis from 1982 to 1983, and at Rockefeller University from 1980 to 1984, this pattern of spending summers in Colorado and Los Alamos and winters in Florida continued until Ulam died of an apparent heart attack in Santa Fe on 13 May 1984. Paul Erdős noted that "he died suddenly of heart failure, without fear or pain, while he could still prove and conjecture." In 1987, Françoise Ulam deposited his papers with the American Philosophical Society Library in Philadelphia. She continued to live in Santa Fe until she died on 30 April 2011, at the age of 93. Both Françoise and her husband are buried with her French family in Montparnasse Cemetery in Paris.
Challenge to economics
Alfred Marshall and his disciples dominated economic theory until the end of WWII. With the Cold War, the theory changed, emphasizing that a market economy was superior and the only sensible way. In Paul Samuelson's "Economics: An Introductory Analysis", 1948, Adam Smith's "invisible hand" was only a footnote. In later editions, it became the central theme. As Samuelson remembers, all this was challenged by Stanislaw Ulam: "[Y]ears ago... I was in the Society of Fellows at Harvard along with the mathematician Stanislaw Ulam. Ulam, who was to become an originator of the Monte Carlo method and co-discoverer of the hydrogen-bomb,... used to tease me by saying, 'Name me one proposition in all of the social sciences which is both true and non-trivial.' This was the test that I always failed. But now, some thirty years later ... an appropriate answer occurs to me: The Ricardian theory of comparative advantage ... That it is logically true need not be argued before a mathematician; that it is not trivial is attested by the thousands of important and intelligent men who have never been able to grasp the doctrine for themselves or to believe it after it was explained to them."
Impact and legacy
From the publication of his first paper as a student in 1929 until his death, Ulam was constantly writing on mathematics. The list of Ulam's publications includes more than 150 papers. Topics represented by a significant number of papers are: set theory (including measurable cardinals and abstract measures), topology, transformation theory, ergodic theory, group theory, projective algebra, number theory, combinatorics, and graph theory. In March 2009, the Mathematical Reviews database contained 697 papers with the name "Ulam".
Notable results of this work are:
|
|
With his pivotal role in the development of thermonuclear weapons, Stanislaw Ulam changed the world. According to Françoise Ulam: "Stan would reassure me that, barring accidents, the H-bomb rendered nuclear war impossible." In 1980, Ulam and his wife appeared in the television documentary The Day After Trinity.
The Monte Carlo method has become a ubiquitous and standard approach to computation, and the method has been applied to a vast number of scientific problems. In addition to problems in physics and mathematics, the method has been applied to finance, social science, environmental risk assessment, linguistics, radiation therapy, and sports.
The Fermi–Pasta–Ulam–Tsingou problem is credited not only as "the birth of experimental mathematics", but also as inspiration for the vast field of Nonlinear Science. In his Lilienfeld Prize lecture, David K. Campbell noted this relationship and described how FPUT gave rise to ideas in chaos, solitons, and dynamical systems. In 1980, Donald Kerr, laboratory director at Los Alamos, with the strong support of Ulam and Mark Kac, founded the Center for Nonlinear Studies (CNLS). In 1985, CNLS initiated the Stanislaw M. Ulam Distinguished Scholar program, which provides an annual award that enables a noted scientist to spend a year carrying out research at Los Alamos.
The fiftieth anniversary of the original FPUT paper was the subject of the March 2005 issue of the journal Chaos, and the topic of the 25th Annual International Conference of CNLS. The University of Southern Mississippi and the University of Florida supported the Ulam Quarterly, which was active from 1992 to 1996, and which was one of the first online mathematical journals. Florida's Department of Mathematics has sponsored, since 1998, the annual Ulam Colloquium Lecture, and in March 2009, the Ulam Centennial Conference.
Ulam's work on non-Euclidean distance metrics in the context of molecular biology made a significant contribution to sequence analysis and his contributions in theoretical biology are considered watersheds in the development of cellular automata theory, population biology, pattern recognition, and biometrics generally (David Sankoff, however, challenged conclusions of Walter by writing that Ulam had only modest influence on early development of sequence alignment methods.). Colleagues noted that some of his greatest contributions were in clearly identifying problems to be solved and general techniques for solving them.
In 1987, Los Alamos issued a special issue of its Science publication, which summarized his accomplishments, and which appeared, in 1989, as the book From Cardinals to Chaos. Similarly, in 1990, the University of California Press issued a compilation of mathematical reports by Ulam and his Los Alamos collaborators: Analogies Between Analogies. During his career, Ulam was awarded honorary degrees by the Universities of New Mexico, Wisconsin, and Pittsburgh.
In 2021, German film director Thorsten Klein made the film adaptation of the book Adventures of a Mathematician about Ulam's life