A booby trap is a device or setup that is intended to kill, harm or surprise a human or another animal. It is triggered by the presence or actions of the victim and sometimes has some form of bait designed to lure the victim towards it. The trap may be set to act upon trespassers that enter restricted areas, and it can be triggered when the victim performs an action (e.g., opening a door, picking something up, or switching something on). It can also be triggered by vehicles driving along a road, as in the case of improvised explosive devices (IEDs).
Booby traps should not be confused with mantraps which are designed to catch a person. Lethal booby traps are often used in warfare, particularly guerrilla warfare, and traps designed to cause injury or pain are also sometimes used by criminals wanting to protect drugs or other illicit property, and by some owners of legal property who wish to protect it from theft. Booby traps which merely cause discomfort or embarrassment are a popular form of practical joke.
Etymology
The Spanish word bobo translates to "stupid, daft, naïve, simple, fool, idiot, clown, funny man, one who is easily cheated" and similar pejorative terms. The slang of bobo, bubie, translates to "dunce". Variations of this word exist in other languages (such as Latin), with their meaning being "to stammer".
In approximately 1590, the word began appearing in the English language as booby, meaning "stupid person, slow bird". The seabird in question was the genus Sula, with their common name being boobies. These birds have large flat feet and wide wingspans for marine habitats but are clumsy and slow on shore making them easy to catch. The birds are also known for landing aboard seagoing vessels, whereupon they have been eaten by the crew.
The phrase booby trap originally applied to schoolboy pranks, but took on its more serious connotation during World War I.
Military booby traps




A military booby trap is designed to kill or injure a person who activates its trigger, or employed to reveal the location of an enemy by setting off a signalling device. Most, but not all, military booby traps involve explosives.
Part of the skill in placing booby traps lies in exploiting natural human behaviors such as habit, self–preservation, curiosity or acquisitiveness. A common trick is to provide victims with a simple solution to a problem, for example, leaving only one door open in an otherwise secure building, luring them straight toward the firing mechanism.
An example that exploits an instinct for self–preservation was used in the Vietnam War. Spikes known as punji sticks were hidden in grassy areas. When fired upon, soldiers instinctively sought to take cover by throwing themselves down on the ground, impaling themselves on the spikes.
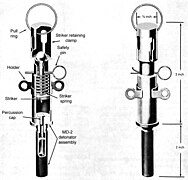
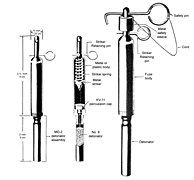
Many purpose–built booby–trap firing devices exist such as the highly versatile M142 universal firing device (identical to the British L5A1 or Australian F1A1), or Yugoslavian UMNOP-1 which allow a variety of different ways of triggering explosives e.g. via trip wire (either pulling it or releasing the tension on it), direct pressure on an object (e.g. standing on it), or pressure release (lift/shift something) etc.
Most explosive booby traps use between 250 g and 1 kg of explosive. Since most booby traps are rigged to detonate within a metre of the victim's body, this is adequate to kill or severely wound.
Effects
Booby traps are indiscriminate weapons. Like anti-personnel mines, they can harm civilians and noncombatants during and after the conflict. The use against civilians is prohibited by the Protocol on Mines, Booby-Traps and Other Devices, and the protocol also prohibits boobytrapping e.g. the wounded or dead, medical equipment, food, and drink.
History
A type of booby trap was referred to in an 1839 news story in The Times.
During the Vietnam War, motorcycles were rigged with explosives by the National Liberation Front and abandoned. U.S. soldiers would be tempted to ride the motorcycle and thus trigger the explosives. In addition, NLF soldiers would rig rubber band grenades and place them in huts that US soldiers would likely burn. Another popular booby trap was the "Grenade in a Can", a grenade with the safety pin removed in a container and a string attached, sometimes with the grenade's fuse mechanism modified to give a much shorter delay than the four to seven seconds typical with grenade fuses. The NLF soldiers primarily used these on doors and attached them to tripwires on jungle paths.
The CIA and Green Berets countered by booby trapping the enemy's ammunition supplies, in an operation code–named "Project Eldest Son". The propellant in a rifle or machine–gun cartridge was replaced with high explosive. Upon being fired, the sabotaged round would destroy the gun and kill or injure the shooter. Mortar shells were similarly rigged to explode when dropped down the tube, instead of launching properly. This ammunition was then carefully re–packed to eliminate any evidence of tampering, and planted in enemy munitions dumps by covert insertion teams. A sabotaged round might also be planted in a rifle magazine or machine–gun belt and left on the body of a dead NLF soldier, in anticipation that the deceased's ammo would be picked up and used by his comrades. No more than one sabotaged round would be planted in any case, magazine, or belt of ammunition, to reduce the chances of the enemy finding it no matter how diligently they inspected their supplies. False rumors and forged documents were circulated to make it appear that the Communist Chinese were supplying the NLF with defective weapons and ammunition.
Northern Ireland
During the Troubles, an ethnonationalist conflict in Northern Ireland, booby traps were used by Irish republican and Ulster loyalist paramilitaries to target British security forces and civilians. The Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) was the most prolific user of the booby traps during the conflict; according to the Sutton Index of Deaths, 180 people were killed during the Troubles as the result of booby trap bombs, the vast majority of them laid by the IRA. A common type of booby trap was the car bomb, which involved attaching a bomb to a car so that starting or driving it would detonate the explosive.
Middle East
Lebanese media reported on the phenomenon of intentionally concealed bombs in children's toys in 1997, citing a number of examples. Israel occupied southern Lebanon between 1982 and 2000 and during that period planted hundreds of thousands of landmines and bomblets. A report by the UK Foreign Affairs Committee in 2000 warned of the dangers of unexploded bombs in southern Lebanon, mentioning the use of "booby-trapped toys, allegedly dropped by the Israeli air force near Lebanese villages adjacent to the so-called security zone".
During the Al-Aqsa Intifada (2000—2005), some Arab–Palestinian groups made wide use of booby traps to prevent the Israeli army from entering their cities on Palestinian territories. The largest use of booby traps was in the Battle of Jenin during Operation Defensive Shield where a large number (1000–2000 bombs and booby traps according to a Palestinian militant who surrendered to Israeli forces in Jenin) of explosive devices were planted by insurgents. Booby traps had been laid in the streets of both the camp and the town, ready to be triggered if a foot snagged a tripwire or a vehicle rolled over a mine. Some of the bombs were huge, containing as much as 250 lb (110 kg) of explosives. To counter the booby traps, anti–tank and anti–personnel mines the Israeli army sent armored Caterpillar D9 bulldozers to clear the area out of any explosive device and booby trap planted. Eventually, a dozen D9 bulldozers went into action, razing the center of the refugee camp and forcing the Palestinian militants inside to surrender.
In the Israel–Hamas war, Israel's use of pagers and walkie-talkies detonations to target the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah that killed 42 people and injured 3,500 more, was condemned by some as illegal.
Gallery
-
Simple Trou de loup booby trap: concealed pitfall with sharp spike at the bottom
-
-
Alternative design of USSR booby trap firing device - pull fuze: normally connected to tripwire
-
USSR booby-trap firing device - pressure fuze: victim steps on loose floorboard with fuze concealed underneath
Civilian use and legal ramifications
Booby traps have been applied as defensive weapons against non-military trespassers, but most jurisdictions consider the practice illegal.