| Radiation therapy | |
|---|---|

Radiation therapy of the pelvis, using a Varian Clinac iX linear accelerator. Lasers and a mould under the legs are used to determine exact position.
| |
| ICD-10-PCS | D |
| ICD-9-CM | 92.2-92.3 |
| MeSH | D011878 |
| OPS-301 code | 8–52 |
| MedlinePlus | 001918 |
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology.
Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue leading to cellular death. To spare normal tissues (such as skin or organs which radiation must pass through to treat the tumor), shaped radiation beams are aimed from several angles of exposure to intersect at the tumor, providing a much larger absorbed dose there than in the surrounding, healthy tissue. Besides the tumour itself, the radiation fields may also include the draining lymph nodes if they are clinically or radiologically involved with tumor, or if there is thought to be a risk of subclinical malignant spread. It is necessary to include a margin of normal tissue around the tumor to allow for uncertainties in daily set-up and internal tumor motion. These uncertainties can be caused by internal movement (for example, respiration and bladder filling) and movement of external skin marks relative to the tumor position.
Radiation oncology is the medical specialty concerned with prescribing radiation, and is distinct from radiology, the use of radiation in medical imaging and diagnosis. Radiation may be prescribed by a radiation oncologist with intent to cure ("curative") or for adjuvant therapy. It may also be used as palliative treatment (where cure is not possible and the aim is for local disease control or symptomatic relief) or as therapeutic treatment (where the therapy has survival benefit and it can be curative). It is also common to combine radiation therapy with surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy or some mixture of the four. Most common cancer types can be treated with radiation therapy in some way.
The precise treatment intent (curative, adjuvant, neoadjuvant therapeutic, or palliative) will depend on the tumor type, location, and stage, as well as the general health of the patient. Total body irradiation (TBI) is a radiation therapy technique used to prepare the body to receive a bone marrow transplant. Brachytherapy, in which a radioactive source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment, is another form of radiation therapy that minimizes exposure to healthy tissue during procedures to treat cancers of the breast, prostate and other organs. Radiation therapy has several applications in non-malignant conditions, such as the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, acoustic neuromas, severe thyroid eye disease, pterygium, pigmented villonodular synovitis, and prevention of keloid scar growth, vascular restenosis, and heterotopic ossification. The use of radiation therapy in non-malignant conditions is limited partly by worries about the risk of radiation-induced cancers.
Medical uses
Radiation therapy for a patient with a diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, with radiation dose color-coded.
Different cancers respond to radiation therapy in different ways.
The response of a cancer to radiation is described by its radiosensitivity.
Highly radiosensitive cancer cells are rapidly killed by modest doses of radiation. These include leukemias, most lymphomas and germ cell tumors.
The majority of epithelial cancers
are only moderately radiosensitive, and require a significantly higher
dose of radiation (60-70 Gy) to achieve a radical cure.
Some types of cancer are notably radioresistant, that is, much higher
doses are required to produce a radical cure than may be safe in
clinical practice. Renal cell cancer and melanoma
are generally considered to be radioresistant but radiation therapy is
still a palliative option for many patients with metastatic melanoma.
Combining radiation therapy with immunotherapy is an active area of investigation and has shown some promise for melanoma and other cancers.
It is important to distinguish the radiosensitivity of a
particular tumor, which to some extent is a laboratory measure, from the
radiation "curability" of a cancer in actual clinical practice. For
example, leukemias are not generally curable with radiation therapy,
because they are disseminated through the body. Lymphoma may be
radically curable if it is localised to one area of the body. Similarly,
many of the common, moderately radioresponsive tumors are routinely
treated with curative doses of radiation therapy if they are at an early
stage. For example: non-melanoma skin cancer, head and neck cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, cervical cancer, anal cancer, and prostate cancer. Metastatic cancers are generally incurable with radiation therapy because it is not possible to treat the whole body.
Before treatment, a CT scan is often performed to identify the
tumor and surrounding normal structures. The patient receives small skin
marks to guide the placement of treatment fields.
Patient positioning is crucial at this stage as the patient will have
to be set-up in the identical position during treatment. Many patient
positioning devices have been developed for this purpose, including
masks and cushions which can be molded to the patient.
The response of a tumor to radiation therapy is also related to its size. Due to complex radiobiology,
very large tumors respond less well to radiation than smaller tumors or
microscopic disease. Various strategies are used to overcome this
effect. The most common technique is surgical resection prior to
radiation therapy. This is most commonly seen in the treatment of breast
cancer with wide local excision or mastectomy followed by adjuvant radiation therapy. Another method is to shrink the tumor with neoadjuvant
chemotherapy prior to radical radiation therapy. A third technique is
to enhance the radiosensitivity of the cancer by giving certain drugs
during a course of radiation therapy. Examples of radiosensitizing drugs
include: Cisplatin, Nimorazole, and Cetuximab.
The impact of radiotherapy varies between different types of cancer and different groups. For example, for breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery, radiotherapy has been found to halve the rate at which the disease recurs.
Side effects
Radiation therapy is in itself painless. Many low-dose palliative treatments (for example, radiation therapy to bony metastases)
cause minimal or no side effects, although short-term pain flare-up can
be experienced in the days following treatment due to oedema
compressing nerves in the treated area. Higher doses can cause varying
side effects during treatment (acute side effects), in the months or
years following treatment (long-term side effects), or after
re-treatment (cumulative side effects). The nature, severity, and
longevity of side effects depends on the organs that receive the
radiation, the treatment itself (type of radiation, dose, fractionation,
concurrent chemotherapy), and the patient.
Most side effects are predictable and expected. Side effects from
radiation are usually limited to the area of the patient's body that is
under treatment. Side effects are dose- dependent; for example higher
doses of head and neck radiation can be associated with cardiovascular complications, thyroid dysfunction, and pituitary axis dysfunction.
Modern radiation therapy aims to reduce side effects to a minimum and
to help the patient understand and deal with side effects that are
unavoidable.
The main side effects reported are fatigue and skin irritation,
like a mild to moderate sun burn. The fatigue often sets in during the
middle of a course of treatment and can last for weeks after treatment
ends. The irritated skin will heal, but may not be as elastic as it was
before.
Acute side effects
- Nausea and vomiting
- This is not a general side effect of radiation therapy, and mechanistically is associated only with treatment of the stomach or abdomen (which commonly react a few hours after treatment), or with radiation therapy to certain nausea-producing structures in the head during treatment of certain head and neck tumors, most commonly the vestibules of the inner ears. As with any distressing treatment, some patients vomit immediately during radiotherapy, or even in anticipation of it, but this is considered a psychological response. Nausea for any reason can be treated with antiemetics.
- Damage to the epithelial surfaces
- Epithelial surfaces may sustain damage from radiation therapy. Depending on the area being treated, this may include the skin, oral mucosa, pharyngeal, bowel mucosa and ureter. The rates of onset of damage and recovery from it depend upon the turnover rate of epithelial cells. Typically the skin starts to become pink and sore several weeks into treatment. The reaction may become more severe during the treatment and for up to about one week following the end of radiation therapy, and the skin may break down. Although this moist desquamation is uncomfortable, recovery is usually quick. Skin reactions tend to be worse in areas where there are natural folds in the skin, such as underneath the female breast, behind the ear, and in the groin.
- Mouth, throat and stomach sores
- If the head and neck area is treated, temporary soreness and ulceration commonly occur in the mouth and throat. If severe, this can affect swallowing, and the patient may need painkillers and nutritional support/food supplements. The esophagus can also become sore if it is treated directly, or if, as commonly occurs, it receives a dose of collateral radiation during treatment of lung cancer. When treating liver malignancies and metastases, it is possible for collateral radiation to cause gastric, stomach or duodenal ulcers This collateral radiation is commonly caused by non-targeted delivery (reflux) of the radioactive agents being infused.[16] Methods, techniques and devices are available to lower the occurrence of this type of adverse side effect.
- Intestinal discomfort
- The lower bowel may be treated directly with radiation (treatment of rectal or anal cancer) or be exposed by radiation therapy to other pelvic structures (prostate, bladder, female genital tract). Typical symptoms are soreness, diarrhoea, and nausea.
- Swelling
- As part of the general inflammation that occurs, swelling of soft tissues may cause problems during radiation therapy. This is a concern during treatment of brain tumors and brain metastases, especially where there is pre-existing raised intracranial pressure or where the tumor is causing near-total obstruction of a lumen (e.g., trachea or main bronchus). Surgical intervention may be considered prior to treatment with radiation. If surgery is deemed unnecessary or inappropriate, the patient may receive steroids during radiation therapy to reduce swelling.
- Infertility
- The gonads (ovaries and testicles) are very sensitive to radiation. They may be unable to produce gametes following direct exposure to most normal treatment doses of radiation. Treatment planning for all body sites is designed to minimize, if not completely exclude dose to the gonads if they are not the primary area of treatment.
Late side effects
Late
side effects occur months to years after treatment and are generally
limited to the area that has been treated. They are often due to damage
of blood vessels and connective tissue cells. Many late effects are
reduced by fractionating treatment into smaller parts.
- Fibrosis
- Tissues which have been irradiated tend to become less elastic over time due to a diffuse scarring process.
- Epilation
- Epilation (hair loss) may occur on any hair bearing skin with doses above 1 Gy. It only occurs within the radiation field/s. Hair loss may be permanent with a single dose of 10 Gy, but if the dose is fractionated permanent hair loss may not occur until dose exceeds 45 Gy.
- Dryness
- The salivary glands and tear glands have a radiation tolerance of about 30 Gy in 2 Gy fractions, a dose which is exceeded by most radical head and neck cancer treatments. Dry mouth (xerostomia) and dry eyes (xerophthalmia) can become irritating long-term problems and severely reduce the patient's quality of life. Similarly, sweat glands in treated skin (such as the armpit) tend to stop working, and the naturally moist vaginal mucosa is often dry following pelvic irradiation.
- Lymphedema
- Lymphedema, a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling, can result from damage to the lymphatic system sustained during radiation therapy. It is the most commonly reported complication in breast radiation therapy patients who receive adjuvant axillary radiotherapy following surgery to clear the axillary lymph nodes.
- Cancer
- Radiation is a potential cause of cancer, and secondary malignancies are seen in some patients. Cancer survivors are already more likely than the general population to develop malignancies due to a number of factors including lifestyle choices, genetics, and previous radiation treatment. It is difficult to directly quantify the rates of these secondary cancers from any single cause. Studies have found radiation therapy as the cause of secondary malignancies for only a small minority of patients. New techniques such as proton beam therapy and carbon ion radiotherapy which aim to reduce dose to healthy tissues will lower these risks. It starts to occur 4 - 6 years following treatment, although some haematological malignancies may develop within 3 years. In the vast majority of cases, this risk is greatly outweighed by the reduction in risk conferred by treating the primary cancer even in pediatric malignancies which carry a higher burden of secondary malignancies.
- Cardiovascular disease
- Radiation can increase the risk of heart disease and death as observed in previous breast cancer RT regimens. Therapeutic radiation increases the risk of a subsequent cardiovascular event (i.e., heart attack or stroke) by 1.5 to 4 times a person's normal rate, aggravating factors included. The increase is dose dependent, related to the RT's dose strength, volume and location.
- Cardiovascular late side effects have been termed radiation-induced heart disease (RIHD) and radiation-induced vascular disease (RIVD). Symptoms are dose dependent and include cardiomyopathy, myocardial fibrosis, valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease, heart arrhythmia and peripheral artery disease. Radiation-induced fibrosis, vascular cell damage and oxidative stress can lead to these and other late side effect symptoms. Most radiation-induced cardiovascular diseases occur 10 or more years post treatment, making causality determinations more difficult.
- Cognitive decline
- In cases of radiation applied to the head radiation therapy may cause cognitive decline. Cognitive decline was especially apparent in young children, between the ages of 5 to 11. Studies found, for example, that the IQ of 5-year-old children declined each year after treatment by several IQ points.
- Radiation enteropathy
- The gastrointestinal tract can be damaged following abdominal and pelvic radiotherapy. Atrophy, fibrosis and vascular changes produce malabsorption, diarrhea, steatorrhea and bleeding with bile acid diarrhea and vitamin B12 malabsorption commonly found due to ileal involvement. Pelvic radiation disease includes radiation proctitis, producing bleeding, diarrhoea and urgency, and can also cause radiation cystitis when the bladder is affected.
- Radiation-induced polyneuropathy
- Radiation treatments are vitally necessary but may damage nerves near the target area or within the delivery path as nerve tissue is also radiosensitive. Nerve damage from ionizing radiation occurs in phases, the initial phase from microvascular injury, capillary damage and nerve demyelination. Subsequent damage occurs from vascular constriction and nerve compression due to uncontrolled fibrous tissue growth caused by radiation. Radiation-induced polyneuropathy, ICD-10-CM Code G62.82, occurs in approximately 1-5% of those receiving radiation therapy.
- Depending upon the irradiated zone, late effect neuropathy may occur in either the central nervous system (CNS) or the peripheral nervous system (PNS). In the CNS for example, cranial nerve injury typically presents as a visual acuity loss 1-14 years post treatment.[31] In the PNS, injury to the plexus nerves presents as radiation-induced brachial plexopathy or radiation-induced lumbosacral plexopathy appearing up to 3 decades post treatment.
Cumulative side effects
Cumulative
effects from this process should not be confused with long-term
effects—when short-term effects have disappeared and long-term effects
are subclinical, reirradiation can still be problematic.
These doses are calculated by the radiation oncologist and many factors
are taken into account before the subsequent radiation takes place.
Effects on reproduction
During the first two weeks after fertilization, radiation therapy is lethal but not teratogenic. High doses of radiation during pregnancy induce anomalies, impaired growth and intellectual disability, and there may be an increased risk of childhood leukemia and other tumours in the offspring.
In males previously having undergone radiotherapy, there appears
to be no increase in genetic defects or congenital malformations in
their children conceived after therapy. However, the use of assisted reproductive technologies and micromanipulation techniques might increase this risk.
Effects on pituitary system
Hypopituitarism
commonly develops after radiation therapy for sellar and parasellar
neoplasms, extrasellar brain tumours, head and neck tumours, and
following whole body irradiation for systemic malignancies. Radiation-induced hypopituitarism mainly affects growth hormone and gonadal hormones. In contrast, adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) deficiencies are the least common among people with radiation-induced hypopituitarism. Changes in prolactin-secretion is usually mild, and vasopressin deficiency appears to be very rare as a consequence of radiation.
Radiation therapy accidents
There
are rigorous procedures in place to minimise the risk of accidental
overexposure of radiation therapy to patients. However, mistakes do
occasionally occur; for example, the radiation therapy machine Therac-25
was responsible for at least six accidents between 1985 and 1987, where
patients were given up to one hundred times the intended dose; two
people were killed directly by the radiation overdoses. From 2005 to
2010, a hospital in Missouri
overexposed 76 patients (most with brain cancer) during a five-year
period because new radiation equipment had been set up incorrectly.
Although medical errors are exceptionally rare, radiation
oncologists, medical physicists and other members of the radiation
therapy treatment team are working to eliminate them. ASTRO has launched
a safety initiative called Target Safely
that, among other things, aims to record errors nationwide so that
doctors can learn from each and every mistake and prevent them from
happening. ASTRO also publishes a list of questions for patients to ask
their doctors about radiation safety to ensure every treatment is as
safe as possible.
Use in non-cancerous diseases
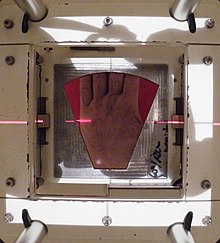
The beam's eye view of the radiotherapy portal on the hand's surface with the lead shield cut-out placed in the machine's gantry
Radiation therapy is used to treat early stage Dupuytren's disease and Ledderhose disease.
When Dupuytren's disease is at the nodules and cords stage or fingers
are at a minimal deformation stage of less than 10 degrees, then
radiation therapy is used to prevent further progress of the disease.
Radiation therapy is also used post surgery in some cases to prevent the
disease continuing to progress. Low doses of radiation are used
typically three gray of radiation for five days, with a break of three
months followed by another phase of three gray of radiation for five
days.
Technique
Mechanism of action
Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cancerous cells. This DNA damage is caused by one of two types of energy, photon or charged particle. This damage is either direct or indirect ionization of the atoms which make up the DNA chain. Indirect ionization happens as a result of the ionization of water, forming free radicals, notably hydroxyl radicals, which then damage the DNA.
In photon therapy, most of the radiation effect is through free
radicals. Cells have mechanisms for repairing single-strand DNA damage
and double-stranded DNA
damage. However, double-stranded DNA breaks are much more difficult to
repair, and can lead to dramatic chromosomal abnormalities and genetic
deletions. Targeting double-stranded breaks increases the probability
that cells will undergo cell death. Cancer cells are generally less differentiated and more stem cell-like; they reproduce more than most healthy differentiated
cells, and have a diminished ability to repair sub-lethal damage.
Single-strand DNA damage is then passed on through cell division; damage
to the cancer cells' DNA accumulates, causing them to die or reproduce
more slowly.
One of the major limitations of photon radiation therapy is that the cells of solid tumors become deficient in oxygen. Solid tumors can outgrow their blood supply, causing a low-oxygen state known as hypoxia. Oxygen is a potent radiosensitizer,
increasing the effectiveness of a given dose of radiation by forming
DNA-damaging free radicals. Tumor cells in a hypoxic environment may be
as much as 2 to 3 times more resistant to radiation damage than those in
a normal oxygen environment.
Much research has been devoted to overcoming hypoxia including the use of high pressure oxygen tanks, hyperthermia therapy
(heat therapy which dilates blood vessels to the tumor site), blood
substitutes that carry increased oxygen, hypoxic cell radiosensitizer
drugs such as misonidazole and metronidazole, and hypoxic cytotoxins (tissue poisons), such as tirapazamine. Newer research approaches are currently being studied, including preclinical and clinical investigations into the use of an oxygen diffusion-enhancing compound such as trans sodium crocetinate (TSC) as a radiosensitizer.
Charged particles such as protons and boron, carbon, and neon ions can cause direct damage to cancer cell DNA through high-LET (linear energy transfer)
and have an antitumor effect independent of tumor oxygen supply because
these particles act mostly via direct energy transfer usually causing
double-stranded DNA breaks. Due to their relatively large mass, protons
and other charged particles have little lateral side scatter in the
tissue—the beam does not broaden much, stays focused on the tumor shape,
and delivers small dose side-effects to surrounding tissue. They also
more precisely target the tumor using the Bragg peak effect. See proton therapy for a good example of the different effects of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) vs. charged particle therapy.
This procedure reduces damage to healthy tissue between the charged
particle radiation source and the tumor and sets a finite range for
tissue damage after the tumor has been reached. In contrast, IMRT's use
of uncharged particles causes its energy to damage healthy cells when it
exits the body. This exiting damage is not therapeutic, can increase
treatment side effects, and increases the probability of secondary
cancer induction.
This difference is very important in cases where the close proximity of
other organs makes any stray ionization very damaging (example: head and neck cancers).
This x-ray exposure is especially bad for children, due to their growing
bodies, and they have a 30% chance of a second malignancy after 5 years
post initial RT.
Dose
The amount of radiation used in photon radiation therapy is measured in grays
(Gy), and varies depending on the type and stage of cancer being
treated. For curative cases, the typical dose for a solid epithelial
tumor ranges from 60 to 80 Gy, while lymphomas are treated with 20 to
40 Gy.
Preventive (adjuvant) doses are typically around 45–60 Gy in
1.8–2 Gy fractions (for breast, head, and neck cancers.) Many other
factors are considered by radiation oncologists
when selecting a dose, including whether the patient is receiving
chemotherapy, patient comorbidities, whether radiation therapy is being
administered before or after surgery, and the degree of success of
surgery.
Delivery parameters of a prescribed dose are determined during treatment planning (part of dosimetry).
Treatment planning is generally performed on dedicated computers using
specialized treatment planning software. Depending on the radiation
delivery method, several angles or sources may be used to sum to the
total necessary dose. The planner will try to design a plan that
delivers a uniform prescription dose to the tumor and minimizes dose to
surrounding healthy tissues.
In radiation therapy, three-dimensional dose distributions may be evaluated using the dosimetry technique known as gel dosimetry.
- Fractionation
The total dose is fractionated (spread out over time) for several
important reasons. Fractionation allows normal cells time to recover,
while tumor cells are generally less efficient in repair between
fractions. Fractionation also allows tumor cells that were in a
relatively radio-resistant phase of the cell cycle during one treatment
to cycle into a sensitive phase of the cycle before the next fraction is
given. Similarly, tumor cells that were chronically or acutely hypoxic
(and therefore more radioresistant) may reoxygenate between fractions,
improving the tumor cell kill.
Fractionation regimens are individualised between different
radiation therapy centers and even between individual doctors. In North
America, Australia, and Europe, the typical fractionation schedule for
adults is 1.8 to 2 Gy per day, five days a week. In some cancer types,
prolongation of the fraction schedule over too long can allow for the
tumor to begin repopulating, and for these tumor types, including
head-and-neck and cervical squamous cell cancers, radiation treatment is
preferably completed within a certain amount of time. For children, a
typical fraction size may be 1.5 to 1.8 Gy per day, as smaller fraction
sizes are associated with reduced incidence and severity of late-onset
side effects in normal tissues.
In some cases, two fractions per day are used near the end of a
course of treatment. This schedule, known as a concomitant boost regimen
or hyperfractionation, is used on tumors that regenerate more quickly
when they are smaller. In particular, tumors in the head-and-neck
demonstrate this behavior.
Patients receiving palliative radiation to treat uncomplicated painful bone metastasis should not receive more than a single fraction of radiation.
A single treatment gives comparable pain relief and morbidity outcomes
to multiple-fraction treatments, and for patients with limited life
expectancy, a single treatment is best to improve patient comfort.
- Schedules for fractionation
One fractionation schedule that is increasingly being used and
continues to be studied is hypofractionation. This is a radiation
treatment in which the total dose of radiation is divided into large
doses. Typical doses vary significantly by cancer type, from
2.2 Gy/fraction to 20 Gy/fraction, the latter being typical of
stereotactic treatments (stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy, or
SABR – also known as SBRT, or stereotactic body radiotherapy) for
subcranial lesions, or SRS (stereotactic radiosurgery) for intracranial
lesions. The rationale of hypofractionation is to reduce the probability
of local recurrence by denying clonogenic cells the time they require
to reproduce and also to exploit the radiosensitivity of some tumors. In particular, stereotactic treatments are intended to destroy clonogenic cells by a process of ablation – i.e.
the delivery of a dose intended to destroy clonogenic cells directly,
rather than to interrupt the process of clonogenic cell division
repeatedly (apoptosis), as in routine radiotherapy.
Estimation of dose based on target sensitivity
Different
cancer types have different radiation sensitivity. However, predicting
the sensitivity based on genomic or proteomic analyses of biopsy samples
has proved difficult.
An alternative approach to genomics and proteomics was offered by the
discovery that radiation protection in microbes is offered by
non-enzymatic complexes of manganese and small organic metabolites. The content and variation of manganese (measurable by electron paramagnetic resonance) were found to be good predictors of radiosensitivity, and this finding extends also to human cells.
An association was confirmed between total cellular manganese contents
and their variation, and clinically-inferred radioresponsiveness in
different tumor cells, a finding that may be useful for more precise
radiodosages and improved treatment of cancer patients.
Types
Historically, the three main divisions of radiation therapy are :
- external beam radiation therapy (EBRT or XRT) or teletherapy;
- brachytherapy or sealed source radiation therapy; and
- systemic radioisotope therapy or unsealed source radiotherapy.
The differences relate to the position of the radiation source;
external is outside the body, brachytherapy uses sealed radioactive
sources placed precisely in the area under treatment, and systemic
radioisotopes are given by infusion or oral ingestion. Brachytherapy can
use temporary or permanent placement of radioactive sources. The
temporary sources are usually placed by a technique called afterloading.
In afterloading a hollow tube or applicator is placed surgically in the
organ to be treated, and the sources are loaded into the applicator
after the applicator is implanted. This minimizes radiation exposure to
health care personnel.
Particle therapy is a special case of external beam radiation therapy where the particles are protons or heavier ions.
External beam radiation therapy
The following three sections refer to treatment using x-rays.
Conventional external beam radiation therapy
A teletherapy radiation capsule composed of the following:
- an international standard source holder (usually lead),
- a retaining ring, and
- a teletherapy "source" composed of
- two nested stainless steel canisters welded to
- two stainless steel lids surrounding
- a protective internal shield (usually uranium metal or a tungsten alloy) and
- a cylinder of radioactive source material, often but not always cobalt-60. The diameter of the "source" is 30 mm.
Historically conventional external beam radiation therapy (2DXRT) was
delivered via two-dimensional beams using kilovoltage therapy x-ray
units or medical linear accelerators which generate high energy x-rays.
2DXRT mainly consists of a single beam of radiation delivered to the
patient from several directions: often front or back, and both sides.
Conventional refers to the way the treatment is planned or simulated
on a specially calibrated diagnostic x-ray machine known as a simulator
because it recreates the linear accelerator actions (or sometimes by
eye), and to the usually well-established arrangements of the radiation
beams to achieve a desired plan. The aim of simulation is to
accurately target or localize the volume which is to be treated. This
technique is well established and is generally quick and reliable. The
worry is that some high-dose treatments may be limited by the radiation
toxicity capacity of healthy tissues which lie close to the target tumor
volume.
An example of this problem is seen in radiation of the prostate
gland, where the sensitivity of the adjacent rectum limited the dose
which could be safely prescribed using 2DXRT planning to such an extent
that tumor control may not be easily achievable. Prior to the invention
of the CT, physicians and physicists had limited knowledge about the
true radiation dosage delivered to both cancerous and healthy tissue.
For this reason, 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy has become
the standard treatment for almost all tumor sites. More recently other
forms of imaging are used including MRI, PET, SPECT and Ultrasound.
Stereotactic radiation
Stereotactic radiation is a specialized type of external beam
radiation therapy. It uses focused radiation beams targeting a
well-defined tumor using extremely detailed imaging scans. Radiation
oncologists perform stereotactic treatments, often with the help of a
neurosurgeon for tumors in the brain or spine.
There are two types of stereotactic radiation. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is when doctors use a single or several stereotactic radiation treatments of the brain or spine. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) refers to one or several stereotactic radiation treatments with the body, such as the lungs.
Some doctors say an advantage to stereotactic treatments is that
they deliver the right amount of radiation to the cancer in a shorter
amount of time than traditional treatments, which can often take 6 to 11
weeks. Plus treatments are given with extreme accuracy, which should
limit the effect of the radiation on healthy tissues. One problem with
stereotactic treatments is that they are only suitable for certain small
tumors.
Stereotactic treatments can be confusing because many hospitals
call the treatments by the name of the manufacturer rather than calling
it SRS or SBRT. Brand names for these treatments include Axesse, Cyberknife, Gamma Knife, Novalis, Primatom, Synergy, X-Knife, TomoTherapy, Trilogy and Truebeam. This list changes as equipment manufacturers continue to develop new, specialized technologies to treat cancers.
Virtual simulation, and 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy
The
planning of radiation therapy treatment has been revolutionized by the
ability to delineate tumors and adjacent normal structures in three
dimensions using specialized CT and/or MRI scanners and planning
software.
Virtual simulation, the most basic form of planning, allows more
accurate placement of radiation beams than is possible using
conventional X-rays, where soft-tissue structures are often difficult to
assess and normal tissues difficult to protect.
An enhancement of virtual simulation is 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT), in which the profile of each radiation beam is shaped to fit the profile of the target from a beam's eye view (BEV) using a multileaf collimator
(MLC) and a variable number of beams. When the treatment volume
conforms to the shape of the tumor, the relative toxicity of radiation
to the surrounding normal tissues is reduced, allowing a higher dose of
radiation to be delivered to the tumor than conventional techniques
would allow.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
Varian TruBeam Linear Accelerator, used for delivering IMRT
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced type of
high-precision radiation that is the next generation of 3DCRT. IMRT also improves the ability to conform the treatment volume to concave tumor shapes, for example when the tumor is wrapped around a vulnerable structure such as the spinal cord or a major organ or blood vessel.
Computer-controlled x-ray accelerators distribute precise radiation
doses to malignant tumors or specific areas within the tumor. The
pattern of radiation delivery is determined using highly tailored
computing applications to perform optimization and treatment simulation (Treatment Planning).
The radiation dose is consistent with the 3-D shape of the tumor by
controlling, or modulating, the radiation beam's intensity. The
radiation dose intensity is elevated near the gross tumor volume while
radiation among the neighboring normal tissues is decreased or avoided
completely. This results in better tumor targeting, lessened side
effects, and improved treatment outcomes than even 3DCRT.
3DCRT is still used extensively for many body sites but the use
of IMRT is growing in more complicated body sites such as CNS, head and
neck, prostate, breast, and lung. Unfortunately, IMRT is limited by its
need for additional time from experienced medical personnel. This is
because physicians must manually delineate the tumors one CT image at a
time through the entire disease site which can take much longer than
3DCRT preparation. Then, medical physicists and dosimetrists must be
engaged to create a viable treatment plan. Also, the IMRT technology has
only been used commercially since the late 1990s even at the most
advanced cancer centers, so radiation oncologists who did not learn it
as part of their residency programs must find additional sources of
education before implementing IMRT.
Proof of improved survival benefit from either of these two
techniques over conventional radiation therapy (2DXRT) is growing for
many tumor sites, but the ability to reduce toxicity is generally
accepted. This is particularly the case for head and neck cancers in a
series of pivotal trials performed by Professor Christopher Nutting
of the Royal Marsden Hospital. Both techniques enable dose escalation,
potentially increasing usefulness. There has been some concern,
particularly with IMRT,
about increased exposure of normal tissue to radiation and the
consequent potential for secondary malignancy. Overconfidence in the
accuracy of imaging may increase the chance of missing lesions that are
invisible on the planning scans (and therefore not included in the
treatment plan) or that move between or during a treatment (for example,
due to respiration or inadequate patient immobilization). New
techniques are being developed to better control this uncertainty—for
example, real-time imaging combined with real-time adjustment of the
therapeutic beams. This new technology is called image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) or four-dimensional radiation therapy.
Another technique is the real-time tracking and localization of
one or more small implantable electric devices implanted inside or close
to the tumor. There are various types of medical implantable devices
that are used for this purpose. It can be a magnetic transponder which
senses the magnetic field generated by several transmitting coils, and
then transmits the measurements back to the positioning system to
determine the location.
The implantable device can also be a small wireless transmitter sending
out an RF signal which then will be received by a sensor array and used
for localization and real-time tracking of the tumor position.
A well-studied issue with IRMT is the "tongue and groove effect"
which results in unwanted underdosing, due to irradiating through
extended tongues and grooves of overlapping MLC (multileaf collimator)
leaves.
While solutions to this issue have been developed, which either reduce
the TG effect to negligible amounts or remove it completely, they
depend upon the method of IMRT being used and some of them carry costs
of their own.
Some texts distinguish "tongue and groove error" from "tongue or
groove error", according as both or one side of the aperture is
occluded.
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT)
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is a radiation technique introduced in 2007
which can achieve highly conformal dose distributions on target volume
coverage and sparing of normal tissues. The specificity of this
technique is to modify three parameters during the treatment. VMAT
delivers radiation by rotating gantry (usually 360° rotating fields with
one or more arcs), changing speed and shape of the beam with a multileaf collimator
(MLC) ("sliding window" system of moving) and fluence output rate (dose
rate) of the medical linear accelerator. VMAT has an advantage in
patient treatment, compared with conventional static field intensity
modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), of reduced radiation delivery times.
Comparisons between VMAT and conventional IMRT for their sparing of
healthy tissues and Organs at Risk (OAR) depends upon the cancer type.
In the treatment of nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinomas VMAT provides equivalent or better OAR protection. In the treatment of prostate cancer the OAR protection result is mixed with some studies favoring VMAT, others favoring IMRT.
Automated planning
Automated
treatment planning has become an integrated part of radiotherapy
treatment planning. There are in general two approaches of automated
planning. 1) Knowledge based planning where the treatment planning
system has a library of high quality plans, from which it can predict
the target and OAR DVH.
2) The other approach is commonly called protocol based planning, where
the treatment planning system tried to mimic an experienced treatment
planner and through an iterative process evaluates the plan quality from
on the basis of the protocol.
Particle therapy
In particle therapy (proton therapy being one example), energetic ionizing particles (protons or carbon ions) are directed at the target tumor. The dose increases while the particle penetrates the tissue, up to a maximum (the Bragg peak) that occurs near the end of the particle's range,
and it then drops to (almost) zero. The advantage of this energy
deposition profile is that less energy is deposited into the healthy
tissue surrounding the target tissue.
Auger therapy
Auger therapy (AT) makes use of a very high dose
of ionizing radiation in situ that provides molecular modifications at
an atomic scale. AT differs from conventional radiation therapy in
several aspects; it neither relies upon radioactive nuclei to cause
cellular radiation damage at a cellular dimension, nor engages multiple
external pencil-beams from different directions to zero-in to deliver a
dose to the targeted area with reduced dose outside the targeted
tissue/organ locations. Instead, the in situ delivery of a very high
dose at the molecular level using AT aims for in situ molecular
modifications involving molecular breakages and molecular
re-arrangements such as a change of stacking structures as well as
cellular metabolic functions related to the said molecule structures.
Contact x-ray brachytherapy
Contact
x-ray brachytherapy (also called "CXB", "electronic brachytherapy" or
the "Papillon Technique") is a type of radiation therapy using
kilovoltage X-rays applied close to the tumour to treat rectal cancer. The process involves inserting the x-ray tube through the anus into the rectum and placing it against the cancerous tissue, then high doses of X-rays are emitted directly into the tumor
at two weekly intervals. It is typically used for treating early
rectal cancer in patients who may not be candidates for surgery.
A 2015 NICE review found the main side effect to be bleeding that
occurred in about 38% of cases, and radiation-induced ulcer which
occurred in 27% of cases.
Brachytherapy (sealed source radiotherapy)
A SAVI brachytherapy device
Brachytherapy is delivered by placing radiation source(s) inside or
next to the area requiring treatment. Brachytherapy is commonly used as
an effective treatment for cervical, prostate, breast, and skin cancer and can also be used to treat tumours in many other body sites.
In brachytherapy, radiation sources are precisely placed directly
at the site of the cancerous tumour. This means that the irradiation
only affects a very localized area – exposure to radiation of healthy
tissues further away from the sources is reduced. These characteristics
of brachytherapy provide advantages over external beam radiation therapy
– the tumour can be treated with very high doses of localized
radiation, whilst reducing the probability of unnecessary damage to
surrounding healthy tissues.
A course of brachytherapy can often be completed in less time than
other radiation therapy techniques. This can help reduce the chance of
surviving cancer cells dividing and growing in the intervals between
each radiation therapy dose.
As one example of the localized nature of breast brachytherapy,
the SAVI device delivers the radiation dose through multiple catheters,
each of which can be individually controlled. This approach decreases
the exposure of healthy tissue and resulting side effects, compared both
to external beam radiation therapy and older methods of breast
brachytherapy.
Unsealed source radiotherapy (systemic radioisotope therapy)
Systemic radioisotope therapy (RIT) is a form of targeted therapy.
Targeting can be due to the chemical properties of the isotope such as
radioiodine which is specifically absorbed by the thyroid gland a
thousandfold better than other bodily organs. Targeting can also be
achieved by attaching the radioisotope to another molecule or antibody
to guide it to the target tissue. The radioisotopes are delivered
through infusion (into the bloodstream) or ingestion. Examples are the infusion of metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) to treat neuroblastoma, of oral iodine-131 to treat thyroid cancer or thyrotoxicosis, and of hormone-bound lutetium-177 and yttrium-90 to treat neuroendocrine tumors (peptide receptor radionuclide therapy).
Another example is the injection of radioactive yttrium-90 or holmium-166 microspheres into the hepatic artery to radioembolize liver tumors or liver metastases. These microspheres are used for the treatment approach known as selective internal radiation therapy. The microspheres are approximately 30 µm
in diameter (about one-third of a human hair) and are delivered
directly into the artery supplying blood to the tumors. These treatments
begin by guiding a catheter
up through the femoral artery in the leg, navigating to the desired
target site and administering treatment. The blood feeding the tumor
will carry the microspheres directly to the tumor enabling a more
selective approach than traditional systemic chemotherapy. There are
currently three different kinds of microspheres: SIR-Spheres, TheraSphere and QuiremSpheres.
A major use of systemic radioisotope therapy is in the treatment of bone metastasis
from cancer. The radioisotopes travel selectively to areas of damaged
bone, and spare normal undamaged bone. Isotopes commonly used in the
treatment of bone metastasis are radium-223, strontium-89 and samarium (153Sm) lexidronam.
In 2002, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin), which is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody conjugated to yttrium-90.
In 2003, the FDA approved the tositumomab/iodine (131I)
tositumomab regimen (Bexxar), which is a combination of an iodine-131
labelled and an unlabelled anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
These medications were the first agents of what is known as radioimmunotherapy, and they were approved for the treatment of refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Intraoperative radiotherapy
Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) is applying therapeutic levels of radiation to a target area, such as a cancer tumor, while the area is exposed during surgery.
Rationale
The
rationale for IORT is to deliver a high dose of radiation precisely to
the targeted area with minimal exposure of surrounding tissues which are
displaced or shielded during the IORT. Conventional radiation
techniques such as external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) following surgical
removal of the tumor have several drawbacks: The tumor bed where the
highest dose should be applied is frequently missed due to the complex
localization of the wound cavity even when modern radiotherapy planning
is used. Additionally, the usual delay between the surgical removal of
the tumor and EBRT may allow a repopulation of the tumor cells. These
potentially harmful effects can be avoided by delivering the radiation
more precisely to the targeted tissues leading to immediate
sterilization of residual tumor cells. Another aspect is that wound
fluid has a stimulating effect on tumor cells. IORT was found to inhibit
the stimulating effects of wound fluid.
Deep inspiration breath-hold
Deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) is a method of delivering radiotherapy while limiting radiation exposure to the heart and lungs.
It is used primarily for treating left-sided breast cancer. The
technique involves a patient holding their breath during treatment.
There are two basic methods of performing DIBH: free-breathing
breath-hold and spirometry-monitored deep inspiration breath hold.
History
X-ray treatment of tuberculosis in 1910. Before the 1920s, the hazards of radiation were not understood, and it was used to treat a wide range of diseases.
Medicine has used radiation therapy as a treatment for cancer for
more than 100 years, with its earliest roots traced from the discovery
of x-rays in 1895 by Wilhelm Röntgen. Emil Grubbe of Chicago was possibly the first American physician to use x-rays to treat cancer, beginning in 1896.
The field of radiation therapy began to grow in the early 1900s largely due to the groundbreaking work of Nobel Prize–winning scientist Marie Curie (1867–1934), who discovered the radioactive elements polonium and radium in 1898. This began a new era in medical treatment and research.
Through the 1920s the hazards of radiation exposure were not
understood, and little protection was used. Radium was believed to have
wide curative powers and radiotherapy was applied to many diseases.
Prior to World War 2, the only practical sources of radiation for radiotherapy were radium, its "emanation", radon gas, and the x-ray tube. External beam radiotherapy
(teletherapy) began at the turn of the century with relatively low
voltage (<150 a="" be="" beams="" body="" could="" energy="" found="" higher="" href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orthovoltage_X-rays" inside="" it="" kv="" low="" machines.="" more="" nbsp="" penetrating="" reach="" required="" requiring="" superficial="" that="" the="" title="Orthovoltage X-rays" to="" treated="" tumors="" voltage="" voltages.="" was="" were="" while="" with="" x-ray="" x-rays="">Orthovoltage X-rays
,
which used tube voltages of 200-500 kV, began to be used during the
1920s. To reach the most deeply buried tumors without exposing
intervening skin and tissue to dangerous radiation doses required rays
with energies of 1 MV or above, called "megavolt" radiation. Producing
megavolt x-rays required voltages on the x-ray tube of 3 to 5 million volts,
which required huge expensive installations. Megavoltage x-ray units
were first built in the late 1930s but because of cost were limited to a
few institutions. One of the first, installed at St. Bartholomew's hospital, London in 1937 and used until 1960, used a 30 foot long x-ray tube and weighed 10 tons. Radium produced megavolt gamma rays,
but was extremely rare and expensive due to its low occurrence in ores.
In 1937 the entire world supply of radium for radiotherapy was 50
grams, valued at £800,000, or $50 million in 2005 dollars.
The invention of the nuclear reactor in the Manhattan Project during World War 2 made possible the production of artificial radioisotopes for radiotherapy. Cobalt therapy, teletherapy machines using megavolt gamma rays emitted by cobalt-60,
a radioisotope produced by irradiating ordinary cobalt metal in a
reactor, revolutionized the field between the 1950s and the early 1980s.
Cobalt machines were relatively cheap, robust and simple to use,
although due to its 5.27 year half-life the cobalt had to be replaced about every 5 years.
Medical linear particle accelerators,
developed since the 1940s, began replacing x-ray and cobalt units in
the 1980s and these older therapies are now declining. The first medical
linear accelerator was used at the Hammersmith Hospital in London in 1953.
Linear accelerators can produce higher energies, have more collimated
beams, and do not produce radioactive waste with its attendant disposal
problems like radioisotope therapies.
With Godfrey Hounsfield’s invention of computed tomography
(CT) in 1971, three-dimensional planning became a possibility and
created a shift from 2-D to 3-D radiation delivery. CT-based planning
allows physicians to more accurately determine the dose distribution
using axial tomographic images of the patient's anatomy. The advent of
new imaging technologies, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the 1970s and positron emission tomography (PET) in the 1980s, has moved radiation therapy from 3-D conformal to intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and to image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) tomotherapy.
These advances allowed radiation oncologists to better see and target
tumors, which have resulted in better treatment outcomes, more organ
preservation and fewer side effects.
While access to radiotherapy is improving globally, more than half of patients in low and middle income countries still do not have available access to the therapy as of 2017.