The Pleistocene ( /ˈplaɪstəˌsiːn,
The Pleistocene is the first epoch of the Quaternary Period or sixth epoch of the Cenozoic Era. In the ICS timescale, the Pleistocene is divided into four stages or ages, the Gelasian, Calabrian, Middle Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Chibanian') and Upper Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Tarantian'). In addition to this international subdivision, various regional subdivisions are often used.
Before a change finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the time boundary between the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being at 1.806 million years Before Present (BP), as opposed to the currently accepted 2.588 million years BP: publications from the preceding years may use either definition of the period.
The Pleistocene is the first epoch of the Quaternary Period or sixth epoch of the Cenozoic Era. In the ICS timescale, the Pleistocene is divided into four stages or ages, the Gelasian, Calabrian, Middle Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Chibanian') and Upper Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Tarantian'). In addition to this international subdivision, various regional subdivisions are often used.
Before a change finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the time boundary between the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being at 1.806 million years Before Present (BP), as opposed to the currently accepted 2.588 million years BP: publications from the preceding years may use either definition of the period.
Etymology
Dating
The Pleistocene has been dated from 2.588 million (±0.005) to 11,700 years BP with the end date expressed in radiocarbon years as 10,000 carbon-14 years BP. It covers most of the latest period of repeated glaciation, up to and including the Younger Dryas cold spell. The end of the Younger Dryas has been dated to about 9640 BC (11,654 calendar years BP). It was not until after the development of radiocarbon dating, however, that Pleistocene archaeological excavations shifted to stratified caves and rock-shelters as opposed to open-air river-terrace sites.In 2009 the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) confirmed a change in time period for the Pleistocene, changing the start date from 1.806 to 2.588 million years BP, and accepted the base of the Gelasian as the base of the Pleistocene, namely the base of the Monte San Nicola GSSP. The IUGS has yet to approve a type section, Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP), for the upper Pleistocene/Holocene boundary (i.e. the upper boundary). The proposed section is the North Greenland Ice Core Project ice core 75° 06' N 42° 18' W. The lower boundary of the Pleistocene Series is formally defined magnetostratigraphically as the base of the Matuyama (C2r) chronozone, isotopic stage 103. Above this point there are notable extinctions of the calcareous nanofossils: Discoaster pentaradiatus and Discoaster surculus.
The Pleistocene covers the recent period of repeated glaciations. The name Plio-Pleistocene has, in the past, been used to mean the last ice age. The revised definition of the Quaternary, by pushing back the start date of the Pleistocene to 2.58 Ma, results in the inclusion of all the recent repeated glaciations within the Pleistocene.
Paleogeography and climate
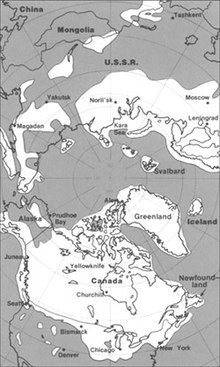
The maximum extent of glacial ice in the north polar area during the Pleistocene period.
The modern continents were essentially at their present positions during the Pleistocene, the plates upon which they sit probably having moved no more than 100 km relative to each other since the beginning of the period.
According to Mark Lynas (through collected data), the Pleistocene's overall climate could be characterized as a continuous El Niño with trade winds in the south Pacific weakening or heading east, warm air rising near Peru, warm water spreading from the west Pacific and the Indian Ocean to the east Pacific, and other El Niño markers.
Glacial features
Pleistocene climate was marked by repeated glacial cycles in which continental glaciers pushed to the 40th parallel in some places. It is estimated that, at maximum glacial extent, 30% of the Earth's surface was covered by ice. In addition, a zone of permafrost stretched southward from the edge of the glacial sheet, a few hundred kilometres in North America, and several hundred in Eurasia. The mean annual temperature at the edge of the ice was −6 °C (21 °F); at the edge of the permafrost, 0 °C (32 °F).Each glacial advance tied up huge volumes of water in continental ice sheets 1,500 to 3,000 metres (4,900–9,800 ft) thick, resulting in temporary sea-level drops of 100 metres (300 ft) or more over the entire surface of the Earth. During interglacial times, such as at present, drowned coastlines were common, mitigated by isostatic or other emergent motion of some regions.
The effects of glaciation were global. Antarctica was ice-bound throughout the Pleistocene as well as the preceding Pliocene. The Andes were covered in the south by the Patagonian ice cap. There were glaciers in New Zealand and Tasmania. The current decaying glaciers of Mount Kenya, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Ruwenzori Range in east and central Africa were larger. Glaciers existed in the mountains of Ethiopia and to the west in the Atlas mountains.
In the northern hemisphere, many glaciers fused into one. The Cordilleran ice sheet covered the North American northwest; the east was covered by the Laurentide. The Fenno-Scandian ice sheet rested on northern Europe, including Great Britain; the Alpine ice sheet on the Alps. Scattered domes stretched across Siberia and the Arctic shelf. The northern seas were ice-covered.
South of the ice sheets large lakes accumulated because outlets were blocked and the cooler air slowed evaporation. When the Laurentide ice sheet retreated, north-central North America was totally covered by Lake Agassiz. Over a hundred basins, now dry or nearly so, were overflowing in the North American west. Lake Bonneville, for example, stood where Great Salt Lake now does. In Eurasia, large lakes developed as a result of the runoff from the glaciers. Rivers were larger, had a more copious flow, and were braided. African lakes were fuller, apparently from decreased evaporation. Deserts, on the other hand, were drier and more extensive. Rainfall was lower because of the decreases in oceanic and other evaporation.
It has been estimated that during the Pleistocene, the East Antarctic Ice Sheet thinned by at least 500 meters, and that thinning since the Last Glacial Maximum is less than 50 meters and probably started after ca 14 ka.
Major events
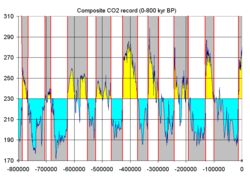
Ice ages as reflected in atmospheric CO2, stored in bubbles from glacial ice of Antarctica.
Over 11 major glacial events have been identified, as well as many minor glacial events. A major glacial event is a general glacial excursion, termed a "glacial." Glacials are separated by "interglacials". During a glacial, the glacier experiences minor advances and retreats. The minor excursion is a "stadial"; times between stadials are "interstadials".
These events are defined differently in different regions of the glacial range, which have their own glacial history depending on latitude, terrain and climate. There is a general correspondence between glacials in different regions. Investigators often interchange the names if the glacial geology of a region is in the process of being defined. However, it is generally incorrect to apply the name of a glacial in one region to another.
For most of the 20th century only a few regions had been studied and the names were relatively few. Today the geologists of different nations are taking more of an interest in Pleistocene glaciology. As a consequence, the number of names is expanding rapidly and will continue to expand. Many of the advances and stadials remain unnamed. Also, the terrestrial evidence for some of them has been erased or obscured by larger ones, but evidence remains from the study of cyclical climate changes.
The glacials in the following tables show historical usages, are a simplification of a much more complex cycle of variation in climate and terrain, and are generally no longer used. These names have been abandoned in favor of numeric data because many of the correlations were found to be either inexact or incorrect and more than four major glacials have been recognized since the historical terminology was established.
| Region | Glacial 1 | Glacial 2 | Glacial 3 | Glacial 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alps | Günz | Mindel | Riss | Würm |
| North Europe | Eburonian | Elsterian | Saalian | Weichselian |
| British Isles | Beestonian | Anglian | Wolstonian | Devensian |
| Midwest U.S. | Nebraskan | Kansan | Illinoian | Wisconsinan |
| Region | Interglacial 1 | Interglacial 2 | Interglacial 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alps | Günz-Mindel | Mindel-Riss | Riss-Würm |
| North Europe | Waalian | Holsteinian | Eemian |
| British Isles | Cromerian | Hoxnian | Ipswichian |
| Midwest U.S. | Aftonian | Yarmouthian | Sangamonian |
Corresponding to the terms glacial and interglacial, the terms pluvial and interpluvial are in use (Latin: pluvia, rain). A pluvial is a warmer period of increased rainfall; an interpluvial, of decreased rainfall. Formerly a pluvial was thought to correspond to a glacial in regions not iced, and in some cases it does. Rainfall is cyclical also. Pluvials and interpluvials are widespread.
There is no systematic correspondence of pluvials to glacials, however. Moreover, regional pluvials do not correspond to each other globally. For example, some have used the term "Riss pluvial" in Egyptian contexts. Any coincidence is an accident of regional factors. Only a few of the names for pluvials in restricted regions have been stratigraphically defined.
Palaeocycles
The sum of transient factors acting at the Earth's surface is cyclical: climate, ocean currents and other movements, wind currents, temperature, etc. The waveform response comes from the underlying cyclical motions of the planet, which eventually drag all the transients into harmony with them. The repeated glaciations of the Pleistocene were caused by the same factors.Milankovitch cycles
Glaciation in the Pleistocene was a series of glacials and interglacials, stadials and interstadials, mirroring periodic changes in climate. The main factor at work in climate cycling is now believed to be Milankovitch cycles. These are periodic variations in regional and planetary solar radiation reaching the Earth caused by several repeating changes in the Earth's motion.Milankovitch cycles cannot be the sole factor responsible for the variations in climate since they explain neither the long term cooling trend over the Plio-Pleistocene, nor the millennial variations in the Greenland Ice Cores. Milankovitch pacing seems to best explain glaciation events with periodicity of 100,000, 40,000, and 20,000 years. Such a pattern seems to fit the information on climate change found in oxygen isotope cores.
Oxygen isotope ratio cycles
In oxygen isotope ratio analysis, variations in the ratio of 18O to 16O (two isotopes of oxygen) by mass (measured by a mass spectrometer) present in the calcite of oceanic core samples is used as a diagnostic of ancient ocean temperature change and therefore of climate change. Cold oceans are richer in 18O, which is included in the tests of the microorganisms (foraminifera) contributing the calcite.A more recent version of the sampling process makes use of modern glacial ice cores. Although less rich in 18O than sea water, the snow that fell on the glacier year by year nevertheless contained 18O and 16O in a ratio that depended on the mean annual temperature.
Temperature and climate change are cyclical when plotted on a graph of temperature versus time. Temperature coordinates are given in the form of a deviation from today's annual mean temperature, taken as zero. This sort of graph is based on another of isotope ratio versus time. Ratios are converted to a percentage difference from the ratio found in standard mean ocean water (SMOW).
The graph in either form appears as a waveform with overtones. One half of a period is a Marine isotopic stage (MIS). It indicates a glacial (below zero) or an interglacial (above zero). Overtones are stadials or interstadials.
According to this evidence, Earth experienced 102 MIS stages beginning at about 2.588 Ma BP in the Early Pleistocene Gelasian. Early Pleistocene stages were shallow and frequent. The latest were the most intense and most widely spaced.
By convention, stages are numbered from the Holocene, which is MIS1. Glacials receive an even number; interglacials, odd. The first major glacial was MIS2-4 at about 85–11 ka BP. The largest glacials were 2, 6, 12, and 16; the warmest interglacials, 1, 5, 9 and 11. For matching of MIS numbers to named stages, see under the articles for those names.
Fauna
Both marine and continental faunas were essentially modern but with many more large land mammals such as Mammoths, Mastodons, Diprotodon, Smilodon, tiger, lion, Aurochs, Short-faced bear, giant sloths, Gigantopithecus and others. Isolated places such as Australia, Madagascar, New Zealand and islands in the Pacific saw the evolution of large birds and even reptiles such as the Elephant bird, moa, Haast's eagle, Quinkana, Megalania and Meiolania.
Pleistocene of Northern Spain showing woolly mammoth, cave lions eating a reindeer, tarpans, and woolly rhinoceros.
The severe climatic changes during the ice age had major impacts on the fauna and flora. With each advance of the ice, large areas of the continents became totally depopulated, and plants and animals retreating southwards in front of the advancing glacier faced tremendous stress. The most severe stress resulted from drastic climatic changes, reduced living space, and curtailed food supply. A major extinction event of large mammals (megafauna), which included mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed cats, glyptodons, the woolly rhinoceros, various giraffids, such as the Sivatherium; ground sloths, Irish elk, cave bears, Gomphothere, dire wolves, and short-faced bears, began late in the Pleistocene and continued into the Holocene. Neanderthals also became extinct during this period. At the end of the last ice age, cold-blooded animals, smaller mammals like wood mice, migratory birds, and swifter animals like whitetail deer had replaced the megafauna and migrated north.
The extinctions hardly affected Africa but were especially severe in North America where native horses and camels were wiped out.
- Asian land mammal ages (ALMA) include Zhoukoudianian, Nihewanian, and Yushean.
- European land mammal ages (ELMA) include Gelasian (2.5—1.8 Ma).
- North American land mammal ages (NALMA) include Blancan (4.75–1.8), Irvingtonian (1.8–0.24) and Rancholabrean (0.24–0.01) in millions of years. The Blancan extends significantly back into the Pliocene.
- South American land mammal ages (SALMA) include Uquian (2.5–1.5), Ensenadan (1.5–0.3) and Lujanian (0.3–0.01) in millions of years. The Uquian previously extended significantly back into the Pliocene, although the new definition places it entirely within the Pleistocene.
Humans
The evolution of anatomically modern humans took place during the Pleistocene. In the beginning of the Pleistocene Paranthropus species are still present, as well as early human ancestors, but during the lower Palaeolithic they disappeared, and the only hominin species found in fossilic records is Homo erectus for much of the Pleistocene. Acheulean lithics appear along with Homo erectus, some 1.8 million years ago, replacing the more primitive Oldowan industry used by A. garhi and by the earliest species of Homo. The Middle Paleolithic saw more varied speciation within Homo, including the appearance of Homo sapiens about 200,000 years ago.According to mitochondrial timing techniques, modern humans migrated from Africa after the Riss glaciation in the Middle Palaeolithic during the Eemian Stage, spreading all over the ice-free world during the late Pleistocene. A 2005 study posits that humans in this migration interbred with archaic human forms already outside of Africa by the late Pleistocene, incorporating archaic human genetic material into the modern human gene pool.
 |