Modern history saw extreme changes in the way people lived including industrialization
Modern history, the modern period or the modern era, is the linear, global, historiographical approach to the time frame after post-classical history. Modern history can be further broken down into periods:
- The early modern period began approximately in the early 16th century; notable historical milestones included the European Renaissance, the Age of Discovery, and the Protestant Reformation.
- The late modern period began approximately in the mid-18th century; notable historical milestones included the American Revolution, the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, the Great Divergence, and the Russian Revolution. It took all of human history up to 1804 for the world's population to reach 1 billion; the next billion came just over a century later, in 1927.
- Contemporary history is the span of historic events from approximately 1945 that are immediately relevant to the present time.
This article primarily covers the 1800–1950 time period with a brief
summary of 1500–1800. For a more in depth article on modern times before
1800, see Early Modern period.
Terminology and usage
Pre-modern
In the pre-modern era, many people's sense of self and purpose was often expressed via a faith in some form of deity, be it that in a single God or in many gods. Pre-modern cultures have not been thought of creating a sense of distinct individuality,
though. Religious officials, who often held positions of power, were
the spiritual intermediaries to the common person. It was only through
these intermediaries that the general masses had access to the divine. Tradition was sacred to ancient cultures and was unchanging and the social order of ceremony and morals in a culture could be strictly enforced.
Modern
The term modern was coined in the 16th century to indicate present or recent times (ultimately derived from the Latin adverb modo, meaning "just now"). The European Renaissance (c. 1420–1630), which marked the transition between the Late Middle Ages and Early Modern times, started in Italy and was spurred in part by the rediscovery of classical art and literature, as well as the new perspectives gained from the Age of Discovery and the invention of the telescope and microscope, expanding the borders of thought and knowledge.
In contrast to the pre-modern era, Western civilization made a gradual transition from pre-modernity to modernity when scientific methods were developed which led many to believe that the use of science would lead to all knowledge, thus throwing back the shroud of myth under which pre-modern peoples lived. New information about the world was discovered via empirical observation, versus the historic use of reason and innate knowledge.
The term Early Modern was introduced in the English language in the 1930s to distinguish the time between what has been called the Middle Ages and time of the late Enlightenment (1800) (when the meaning of the term Modern Ages
was developing its contemporary form). It is important to note that
these terms stem from European history. In usage in other parts of the
world, such as in Asia, and in Muslim countries,
the terms are applied in a very different way, but often in the context
with their contact with European culture in the Age of Discovery.
Contemporary
In the Contemporary era, there were various socio-technological
trends. Regarding the 21st century and the late modern world, the Information Age
and computers were forefront in use, not completely ubiquitous but
often present in everyday life. The development of Eastern powers was of
note, with China and India becoming more powerful. In the Eurasian
theater, the European Union and Russian Federation
were two forces recently developed. A concern for Western world, if not
the whole world, was the late modern form of terrorism and the warfare
that has resulted from the contemporary terrorist acts.
Modern era
Significant developments
The modern period has been a period of significant development in the fields of science, politics, warfare, and technology. It has also been an age of discovery and globalization. During this time, the European powers and later their colonies, began a political, economic, and cultural colonization of the rest of the world.
By the late 19th and 20th centuries, modernist art, politics, science and culture has come to dominate not only Western Europe and North America,
but almost every civilized area on the globe, including movements
thought of as opposed to the west and globalization. The modern era is
closely associated with the development of individualism, capitalism, urbanization, and a belief in the possibilities of technological and political progress.
Wars and other perceived problems of this era, many of which come
from the effects of rapid change, and the connected loss of strength of
traditional religious and ethical norms, have led to many reactions
against modern development. Optimism and belief in constant progress has been most recently criticized by postmodernism while the dominance of Western Europe and Anglo-America over other continents has been criticized by postcolonial theory.
One common conception of modernity is the condition of Western
history since the mid-15th century, or roughly the European development
of movable type and the printing press.
In this context the "modern" society is said to develop over many
periods, and to be influenced by important events that represent breaks
in the continuity.
Early
The modern era includes the early period, called the early modern
period, which lasted from c. 1500 to around c. 1800 (most often 1815).
Particular facets of early modernity include:
- The Renaissance
- The Reformation and Counter Reformation.
- The Age of Discovery
- The Rise of capitalism
- The Golden Age of Piracy
Important events in the early modern period include:
- The invention of the printing press
- The English Civil War
- The Seven Years' War
This combination of epoch events totally changed thinking and thought
in the early modern period, and so their dates serve as well as any to
separate the old from the new modes.
As an Age of Revolutions dawned, beginning with those revolts in America and France, political changes were then pushed forward in other countries partly as a result of upheavals of the Napoleonic Wars and their impact on thought and thinking, from concepts from nationalism to organizing armies.
The early period ended in a time of political and economic change as a result of mechanization in society, the American Revolution, the first French Revolution; other factors included the redrawing of the map of Europe by the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna and the peace established by Second Treaty of Paris which ended the Napoleonic Wars.
Late
As a result of the Industrial Revolution and the earlier political revolutions, the worldviews of Modernism
emerged. The industrialization of many nations was initiated with the
industrialization of Britain. Particular facets of the late modernity
period include:
- Increasing role of science and technology
- Mass literacy and proliferation of mass media
- Spread of social movements
- Institution of representative democracy
- Individualism
- Industrialization
- Urbanization
- Total fertility rates and ecological collapses occurring at geometric rates.
Other important events in the development of the Late modern period include:
- The American Revolution
- The French Revolution
- The Colonization of Australia
- The Revolutions of 1848
- The Russian Revolution
- The First World War and the Second World War.
Our most recent era—Modern Times—begins with the end of these revolutions in the 19th century, and includes the World Wars era (encompassing World War I and World War II) and the emergence of socialist countries that led to the Cold War. The contemporary era follows shortly afterward with the explosion of research and increase of knowledge known as the Information Age in the latter 20th and the early 21st century. Today's Postmodern era is seen in widespread digitality.
Early modern period
Historians consider the early modern period to be approximately
between 1500 and 1800. It follows the Late Middle Ages and is marked by
the first European colonies, the rise of strong centralized governments,
and the beginnings of recognizable nation-states that are the direct
antecedents of today's states.
The expansion of Islam took place in North and East Africa. In
West Africa, various native nations existed. The Indian Empires and
civilizations of Southeast Asia were a vital link in the spice trade. On
the Indian subcontinent, the Mughal Empire existed. The archipelagic empires, the Sultanate of Malacca and later the Sultanate of Johor, controlled the southern areas.
Various Chinese dynasties and Japanese shogunates controlled the Asian sphere. In Japan, the Edo period
from 1600 to 1868 is also referred to as the early modern period. In
Korea, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from the
rise of the Joseon Dynasty to the enthronement of King Gojong.
In the Americas, Pre-Columbian peoples had built a large and varied
civilization, including the Aztec Empire and alliance, the Inca civilization, the Mayan Empire and cities, and the Chibcha. In the west, kingdoms of Europe moved in the direction of reformation and expansion. Russia reached the Pacific coast in 1647 and consolidated its control over the Russian Far East in the 19th century.
Later religious trends of the period saw the end of the
aforementioned Muslim expansion. Christians and Christendom saw the end
of the Crusades and of religious unity under the Roman Catholic Church.
It was during this time that the Inquisitions and the Protestant Reformation took place.
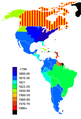
Colonial empires in 1800
During the early modern period, an age of discovery
and trade was undertaken by the Western European nations. Portugal,
Spain, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and France went on a colonial
expansion and took possession of lands and set up colonies in Africa,
southern Asia, and North and South America. Turkey colonized Southeastern Europe, and parts of the West Asia and North Africa. Russia took possession in Eastern Europe, Asia, and North America.
Asia
China
The Qing Chinese celebrate a victory over the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan. Painting was a collaboration between Chinese and European painters, 1788.
In China, urbanization increased as the population grew and as the
division of labor grew more complex. Large urban centers, such as Nanjing and Beijing,
also contributed to the growth of private industry. In particular,
small-scale industries grew up, often specializing in paper, silk,
cotton, and porcelain goods. For the most part, however, relatively
small urban centers with markets proliferated around the country. Town
markets mainly traded food, with some necessary manufactures such as
pins or oil. Despite the xenophobia and intellectual introspection characteristic of the increasingly popular new school of neo-Confucianism, China under the later Ming Dynasty became isolated, prohibiting the construction of ocean going sea vessels. Despite isolationist policies the Ming Economy still suffered from an inflation due to an overabundance of Spanish New World silver entering its economy through new European colonies such as Macao. Ming China was further strained by victorious but costly wars to protect Korea from Japanese Invasion.
The Qing dynasty (1644–1912) was founded after the fall of the Ming, the last Han Chinese dynasty, by the Manchus. The Manchus were formerly known as the Jurchens. When Beijing was captured by Li Zicheng's peasant rebels in 1644, the Chongzhen Emperor, the last Ming emperor, committed suicide. The Manchus then allied with former Ming general Wu Sangui and seized control of Beijing,
which became the new capital of the Qing dynasty. The Manchus adopted
the Confucian norms of traditional Chinese government in their rule of China proper. Schoppa, the editor of The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History
argues, "A date around 1780 as the beginning of modern China is thus
closer to what we know today as historical 'reality'. It also allows us
to have a better baseline to understand the precipitous decline of the
Chinese polity in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries."
Japan
The Great Wave off Kanagawa, art flourished in the Edo Period
In pre-modern Japan following the Sengoku period of "warring states", central government had been largely reestablished by Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hideyoshi during the Azuchi–Momoyama period. After the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, central authority fell to Tokugawa Ieyasu who completed this process and received the title of shōgun in 1603.
Society in the Japanese "Tokugawa period" (Edo society), unlike the shogunates before it, was based on the strict class hierarchy originally established by Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The daimyōs (feudal lords) were at the top, followed by the warrior-caste of samurai, with the farmers, artisans, and traders ranking below. The country was strictly closed to foreigners with few exceptions with the Sakoku policy. Literacy among the Japanese people rose in the two centuries of isolation.
In some parts of the country, particularly smaller regions, daimyōs and samurai were more or less identical, since daimyōs might be trained as samurai, and samurai might act as local lords. Otherwise, the largely inflexible nature of this social stratification system unleashed disruptive forces over time. Taxes on the peasantry were set at fixed amounts which did not account for inflation or other changes in monetary
value. As a result, the tax revenues collected by the samurai
landowners were worth less and less over time. This often led to
numerous confrontations between noble but impoverished samurai and
well-to-do peasants. None, however, proved compelling enough to
seriously challenge the established order until the arrival of foreign
powers.
India
The Mughal ambassador Khan’Alam in 1618 negotiating with Shah Abbas the Great of Iran.
On the Indian subcontinent, the Mughal Empire ruled most of India in the early 18th century. The "classic period" ended with the death and defeat of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707 by the rising Hindu Maratha Empire,
although the dynasty continued for another 150 years. During this
period, the Empire was marked by a highly centralized administration
connecting the different regions. All the significant monuments of the
Mughals, their most visible legacy, date to this period which was
characterised by the expansion of Persian cultural influence in the
Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and
architectural results. The Maratha Empire was located in the south west
of present-day India and expanded greatly under the rule of the Peshwas, the prime ministers of the Maratha empire. In 1761, the Maratha army lost the Third Battle of Panipat which halted imperial expansion and the empire was then divided into a confederacy of Maratha states.
British and Dutch colonization
The development of New Imperialism saw the conquest of nearly all eastern hemisphere territories by colonial powers. The commercial colonization of India commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey, when the Nawab of Bengal surrendered his dominions to the British East India Company, in 1765, when the Company was granted the diwani, or the right to collect revenue, in Bengal and Bihar, or in 1772, when the Company established a capital in Calcutta, appointed its first Governor-General, Warren Hastings, and became directly involved in governance.
Robert Clive and Mir Jafar after the Battle of Plassey, 1757 by Francis Hayman
The Maratha states, following the Anglo-Maratha wars, eventually lost to the British East India Company in 1818 with the Third Anglo-Maratha War. The rule lasted until 1858, when, after the Indian rebellion of 1857 and consequent of the Government of India Act 1858, the British government assumed the task of directly administering India in the new British Raj. In 1819 Stamford Raffles established Singapore as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an Anglo-Dutch treaty
demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. From the 1850s
onwards, the pace of colonization shifted to a significantly higher
gear.
The Dutch East India Company (1800) and British East India Company (1858) were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies. Only Thailand
was spared the experience of foreign rule, although, Thailand itself
was also greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers.
Colonial rule had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the
colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large
market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent.
Europe
Ferdinand Pauwels – Martin Luther hammers his 95 theses to the door
Many major events caused Europe to change around the start of the 16th century, starting with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the fall of Muslim Spain and the discovery of the Americas in 1492, and Martin Luther's Protestant Reformation in 1517. In England the modern period is often dated to the start of the Tudor period with the victory of Henry VII over Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. Early modern European history is usually seen to span from the start of the 15th century, through the Age of Enlightenment in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century.
Tsardom of Russia
Russia experienced territorial growth through the 17th century, which was the age of Cossacks. Cossacks were warriors organized into military communities, resembling pirates and pioneers of the New World. The native land of the Cossacks is defined by a line of Russian/Ruthenian town-fortresses located on the border with the steppe
and stretching from the middle Volga to Ryazan and Tula, then breaking
abruptly to the south and extending to the Dnieper via Pereyaslavl. This
area was settled by a population of free people practicing various
trades and crafts.
Cossacks became the backbone of the early Russian Army.
In 1648, the peasants of Ukraine joined the Zaporozhian Cossacks in rebellion against Poland-Lithuania during the Khmelnytsky Uprising, because of the social and religious oppression they suffered under Polish rule. In 1654 the Ukrainian leader, Bohdan Khmelnytsky, offered to place Ukraine under the protection of the Russian Tsar, Aleksey I. Aleksey's acceptance of this offer led to another Russo-Polish War (1654–1667). Finally, Ukraine was split along the river Dnieper, leaving the western part (or Right-bank Ukraine) under Polish rule and eastern part (Left-bank Ukraine and Kiev) under Russian. Later, in 1670–71 the Don Cossacks led by Stenka Razin
initiated a major uprising in the Volga region, but the Tsar's troops
were successful in defeating the rebels. In the east, the rapid Russian
exploration and colonisation of the huge territories of Siberia was led
mostly by Cossacks hunting for valuable furs and ivory. Russian explorers pushed eastward primarily along the Siberian river routes, and by the mid-17th century there were Russian settlements in the Eastern Siberia, on the Chukchi Peninsula, along the Amur River, and on the Pacific coast. In 1648 the Bering Strait between Asia and North America was passed for the first time by Fedot Popov and Semyon Dezhnyov.
Reason and Enlightenment
"If
there is something you know, communicate it. If there is something you
don't know, search for it." An engraving from the 1772 edition of the Encyclopédie; Truth (center) is surrounded by light and unveiled by the figures to the right, Philosophy and Reason
Traditionally, the European intellectual transformation of and after
the Renaissance bridged the Middle Ages and the Modern era. The Age of Reason in the Western world is generally regarded as being the start of modern philosophy, and a departure from the medieval approach, especially Scholasticism.
Early 17th-century philosophy is often called the Age of Rationalism
and is considered to succeed Renaissance philosophy and precede the Age
of Enlightenment, but some consider it as the earliest part of the
Enlightenment era in philosophy, extending that era to two centuries.
The 18th century saw the beginning of secularization in Europe, rising to notability in the wake of the French Revolution.
The Age of Enlightenment is a time in Western philosophy
and cultural life centered upon the 18th century in which reason was
advocated as the primary source and legitimacy for authority.
Enlightenment gained momentum more or less simultaneously in many parts
of Europe and America. Developing during the Enlightenment era, Renaissance humanism
as an intellectual movement spread across Europe. The basic training of
the humanist was to speak well and write (typically, in the form of a
letter). The term umanista comes from the latter part of the 15th century. The people were associated with the studia humanitatis, a novel curriculum that was competing with the quadrivium and scholastic logic.
Renaissance humanism took a close study of the Latin and Greek classical texts, and was antagonistic to the values of scholasticism
with its emphasis on the accumulated commentaries; and humanists were
involved in the sciences, philosophies, arts and poetry of classical
antiquity. They self-consciously imitated classical Latin and deprecated the use of medieval Latin. By analogy with the perceived decline of Latin, they applied the principle of ad fontes, or back to the sources, across broad areas of learning.
Model for the Three Superior Planets and Venus from Georg von Peuerbach, Theoricae novae planetarum.
The quarrel of the Ancients and the Moderns was a literary and artistic quarrel that heated up in the early 1690s and shook the Académie française. The opposing two sides were, the Ancients (Anciens) who constrain choice of subjects to those drawn from the literature of Antiquity and the Moderns (Modernes), who supported the merits of the authors of the century of Louis XIV. Fontenelle quickly followed with his Digression sur les anciens et les modernes
(1688), in which he took the Modern side, pressing the argument that
modern scholarship allowed modern man to surpass the ancients in
knowledge.
Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a period when European ideas in classical physics, astronomy, biology, human anatomy, chemistry, and other classical sciences were rejected and led to doctrines supplanting those that had prevailed from Ancient Greece to the Middle Ages which would lead to a transition to modern science. This period saw a fundamental transformation in scientific ideas across physics, astronomy, and biology, in institutions supporting scientific investigation, and in the more widely held picture of the universe.
Individuals started to question all manners of things and it was this
questioning that led to the Scientific Revolution, which in turn formed
the foundations of contemporary sciences and the establishment of
several modern scientific fields.
The French Revolutions
Eugène Delacroix's La liberté guidant le peuple. The French Revolution inspired a wave of revolutions across Europe. Liberalism and Nationalism were popular ideas that challenged Absolute Monarchies in the 19th century.
Toward the middle and latter stages of the Age of Revolution, the
French political and social revolutions and radical change saw the
French governmental structure, previously an absolute monarchy with
feudal privileges for the aristocracy and Catholic clergy transform,
changing to forms based on Enlightenment principles of citizenship and
inalienable rights. The first revolution led to government by the National Assembly, the second by the Legislative Assembly, and the third by the Directory.
The changes were accompanied by violent turmoil which included
the trial and execution of the king, vast bloodshed and repression
during the Reign of Terror, and warfare involving every other major
European power. Subsequent events that can be traced to the Revolution
include the Napoleonic Wars, two separate restorations of the monarchy,
and two additional revolutions as modern France took shape. In the
following century, France would be governed at one point or another as a
republic, constitutional monarchy, and two different empires.
National and Legislative Assembly
During the French Revolution, the National Assembly, which existed
from June 17 to July 9 of 1789, was a transitional body between the
Estates-General and the National Constituent Assembly.
The Legislative Assembly was the legislature of France from
October 1, 1791, to September 1792. It provided the focus of political
debate and revolutionary law-making between the periods of the National
Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention.
The Directory and Napoleonic Era
Napoleon at the Battle of the Pyramids 1810 by Baron Antoine-Jean Gros
The Executive Directory was a body of five Directors that held
executive power in France following the Convention and preceding the
Consulate. The period of this regime (2 November 1795 until 10 November
1799), commonly known as the Directory (or Directoire) era, constitutes
the second to last stage of the French Revolution. Napoleon, before
seizing the title of Emperor, was elected as First Consul of the
Consulate of France.
The campaigns of French Emperor and General Napoleon Bonaparte
characterized the Napoleonic Era. Born on Corsica as the French invaded,
and dying suspiciously on the tiny British Island of St. Helena, this
brilliant commander, controlled a French Empire that, at its height,
ruled a large portion of Europe directly from Paris, while many of his
friends and family ruled countries such as Spain, Poland, several parts
of Italy and many other Kingdoms Republics and dependencies. The
Napoleonic Era changed the face of Europe forever, and old Empires and
Kingdoms fell apart as a result of the mighty and "Glorious" surge of Republicanism.
Italian unification
Rome or Death, Italian Patriotic Painting, 1863
Italian unification was the political and social movement that annexed different states of the Italian peninsula
into the single state of Italy in the 19th century. There is a lack of
consensus on the exact dates for the beginning and the end of this
period, but many scholars agree that the process began with the end of
Napoleonic rule and the Congress of Vienna in 1815, and approximately ended with the Franco-Prussian War in 1871, though the last città irredente did not join the Kingdom of Italy until after World War I.
End of the early modern period
Toward
the end of the early modern period, Europe was dominated by the
evolving system of mercantile capitalism in its trade and the New
Economy. European states and politics had the characteristic of
Absolutism. The French power and English revolutions dominated the
political scene. There eventually evolved an international balance of
power that held at bay a great conflagration until years later.
The end date of the early modern period is usually associated
with the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in about 1750.
Another significant date is 1789, the beginning of the French
Revolution, which drastically transformed the state of European politics
and ushered in the Prince Edward Era and modern Europe.
North America
John Trumbull's Declaration of Independence, showing the five-man committee in charge of drafting the Declaration in 1776 as it presents its work to the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia
The French and Indian Wars
were a series of conflicts in North America that represented the
actions there that accompanied the European dynastic wars. In Quebec,
the wars are generally referred to as the Intercolonial Wars. While some
conflicts involved Spanish and Dutch forces, all pitted Great Britain,
its colonies and American Indian allies on one side and France, its
colonies and Indian allies on the other.
The expanding French and British colonies were contending for
control of the western, or interior, territories. Whenever the European
countries went to war, there were actions within and by these colonies
although the dates of the conflict did not necessarily exactly coincide
with those of the larger conflicts.
Beginning the Age of Revolution, the American Revolution
and the ensuing political upheaval during the last half of the 18th
century saw the Thirteen Colonies of North America overthrow the
governance of the Parliament of Great Britain, and then reject the
British monarchy itself to become the sovereign United States of
America. In this period the colonies first rejected the authority of the
Parliament to govern them without representation, and formed
self-governing independent states. The Second Continental Congress then
joined together against the British to defend that self-governance in
the armed conflict from 1775 to 1783 known as the American Revolutionary War (also called American War of Independence).
North America 1797
The American Revolution began with fighting at Lexington and Concord.
On July 4, 1776, they issued the Declaration of Independence, which
proclaimed their independence from Great Britain and their formation of a
cooperative union. In June 1776, Benjamin Franklin was appointed a member of the Committee of Five that drafted the Declaration of Independence.
Although he was temporarily disabled by gout and unable to attend most
meetings of the Committee, Franklin made several small changes to the
draft sent to him by Thomas Jefferson.
The rebellious states defeated Great Britain in the American
Revolutionary War, the first successful colonial war of independence.
While the states had already rejected the governance of Parliament,
through the Declaration the new United States now rejected the
legitimacy of the monarchy to demand allegiance. The war raged for seven
years, with effective American victory, followed by formal British
abandonment of any claim to the United States with the Treaty of Paris.
The Philadelphia Convention set up the current United States; the United States Constitution ratification the following year made the states part of a single republic with a limited central government. The Bill of Rights, comprising ten constitutional amendments guaranteeing many fundamental civil rights and freedoms, was ratified in 1791.
Decolonization of North and South Americas
The
decolonization of the Americas was the process by which the countries
in the Americas gained their independence from European rule.
Decolonization began with a series of revolutions in the late 18th and
early-to-mid-19th centuries. The Spanish American wars of independence
were the numerous wars against Spanish rule in Spanish America that took
place during the early 19th century, from 1808 until 1829, directly
related to the Napoleonic French invasion of Spain. The conflict started
with short-lived governing juntas established in Chuquisaca and Quito
opposing the composition of the Supreme Central Junta of Seville.
|
|
|
When the Central Junta fell to the French, numerous new Juntas
appeared all across the Americas, eventually resulting in a chain of
newly independent countries stretching from Argentina and Chile in the
south, to Mexico in the north. After the death of the king Ferdinand
VII, in 1833, only Cuba and Puerto Rico remained under Spanish rule,
until the Spanish–American War in 1898. Unlike the Spanish, the
Portuguese did not divide their colonial territory in America. The
captaincies they created were subdued to a centralized administration in
Salvador (later relocated to Rio de Janeiro) which reported directly to
the Portuguese Crown until its independence in 1822, becoming the Empire of Brazil.
Late modern period
Timeline
Industrial revolutions
Maquina vapor Watt ETSIIM
The development of the steam engine started the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The steam engine was created to pump water from coal mines, enabling them to be deepened beyond groundwater levels. The date of the Industrial Revolution is not exact. Eric Hobsbawm held that it "broke out" in the 1780s and was not fully felt until the 1830s or 1840s, while T.S. Ashton held that it occurred roughly between 1760 and 1830 (in effect the reigns of George III, The Regency, and George IV).
The great changes of centuries before the 19th were more connected with
ideas, religion or military conquest, and technological advance had
only made small changes in the material wealth of ordinary people.
The first Industrial Revolution merged into the Second Industrial
Revolution around 1850, when technological and economic progress gained
momentum with the development of steam-powered ships and railways, and
later in the 19th century with the internal combustion engine and electric power
generation. The Second Industrial Revolution was a phase of the
Industrial Revolution; labeled as the separate Technical Revolution.
From a technological and a social point of view there is no clean break
between the two. Major innovations during the period occurred in the
chemical, electrical, petroleum, and steel industries. Specific
advancements included the introduction of oil fired steam turbine and
internal combustion driven steel ships, the development of the airplane,
the practical commercialization of the automobile, mass production of
consumer goods, the perfection of canning, mechanical refrigeration and
other food preservation techniques, and the invention of the telephone.
Industrialization
Industrialization
is the process of social and economic change whereby a human group is
transformed from a pre-industrial society into an industrial one. It is a
subdivision of a more general modernization process, where social change and economic development are closely related with technological innovation,
particularly with the development of large-scale energy and metallurgy
production. It is the extensive organization of an economy for the
purpose of manufacturing. Industrialization also introduces a form of
philosophical change, where people obtain a different attitude towards
their perception of nature.
Revolution in manufacture and power
Liverpool and Manchester Railway from 1830, world's first railway.
An economy based on manual labor was replaced by one dominated by industry and the manufacture of machinery. It began with the mechanization of the textile industries and the development of iron-making techniques, and trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of canals, improved roads, and then railways.
The introduction of steam power (fuelled primarily by coal) and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing) underpinned the dramatic increases in production capacity. The development of all-metal machine tools
in the first two decades of the 19th century facilitated the
manufacture of more production machines for manufacturing in other
industries.
The modern petroleum industry started in 1846 with the discovery of the process of refining kerosene from coal by Nova Scotian Abraham Pineo Gesner. Ignacy Łukasiewicz improved Gesner's method to develop a means of refining kerosene from the more readily available "rock oil" ("petr-oleum") seeps in 1852 and the first rock oil mine was built in Bóbrka, near Krosno in Galicia in the following year. In 1854, Benjamin Silliman, a science professor at Yale University in New Haven, was the first to fractionate petroleum by distillation. These discoveries rapidly spread around the world.
Notable engineers
Nikola Tesla with his high-frequency transformer at East Houston Street, New York
Engineering achievements of the revolution ranged from
electrification to developments in materials science. The advancements
made a great contribution to the quality of life. In the first
revolution, Lewis Paul was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill. Matthew Boulton and James Watt's
improvements to the steam engine were fundamental to the changes
brought by the Industrial Revolution in both the Kingdom of Great
Britain and the world.
In the latter part of the second revolution, Thomas Alva Edison
developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world
and is often credited with the creation of the first industrial research
laboratory. In 1882, Edison switched on the world's first large-scale electrical supply network
that provided 110 volts direct current to fifty-nine customers in lower
Manhattan. Also toward the end of the second industrial revolution, Nikola Tesla made many contributions in the field of electricity and magnetism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Social effects and classes
The Industrial Revolutions were major technological, socioeconomic, and cultural
changes in late 18th and early 19th centuries that began in Britain and
spread throughout the world. The effects spread throughout Western Europe and North America during the 19th century, eventually affecting the majority of the world. The impact of this change on society was enormous and is often compared to the Neolithic revolution, when mankind developed agriculture and gave up its nomadic lifestyle.
It has been argued that GDP
per capita was much more stable and progressed at a much slower rate
until the industrial revolution and the emergence of the modern capitalist economy, and that it has since increased rapidly in capitalist countries.
Mid-19th-century European revolts
German Revolution, Berlin 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848,
known in some countries as the Spring of Nations or the Year of
Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout the European
continent. Described as a revolutionary wave, the period of unrest
began in France and then, further propelled by the French Revolution of
1848, soon spread to the rest of Europe.
Although most of the revolutions were quickly put down, there was a
significant amount of violence in many areas, with tens of thousands of
people tortured and killed. While the immediate political effects of the
revolutions were reversed, the long-term reverberations of the events
were far-reaching.
Industrial age reformism
Industrial age reform movements
began the gradual change of society rather than with episodes of rapid
fundamental changes. The reformists' ideas were often grounded in
liberalism, although they also possessed aspects of utopian, socialist
or religious concepts. The Radical movement campaigned for electoral
reform, a reform of the Poor Laws, free trade, educational reform,
postal reform, prison reform, and public sanitation.
Following the Enlightenment's ideas, the reformers looked to the Scientific Revolution
and industrial progress to solve the social problems which arose with
the Industrial Revolution. Newton's natural philosophy combined a
mathematics of axiomatic proof with the mechanics of physical
observation, yielding a coherent system of verifiable predictions and
replacing a previous reliance on revelation and inspired truth. Applied
to public life, this approach yielded several successful campaigns for
changes in social policy.
Imperial Russia
Russian Peasant Girls, 1900
Under Peter the Great,
Russia was proclaimed an Empire in 1721 and became recognized as a
world power. Ruling from 1682 to 1725, Peter defeated Sweden in the Great Northern War, forcing it to cede West Karelia and Ingria (two regions lost by Russia in the Time of Troubles), as well as Estland and Livland, securing Russia's access to the sea and sea trade. On the Baltic Sea Peter founded a new capital called Saint Petersburg, later known as Russia's Window to Europe. Peter the Great's reforms brought considerable Western European cultural influences to Russia. Catherine II (the Great),
who ruled in 1762–96, extended Russian political control over the
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and incorporated most of its territories
into Russia during the Partitions of Poland, pushing the Russian frontier westward and southward. Russia would colonize the vast Asian lands of Siberia expanding by land to the Pacific Coast of Asia, and North America. As the large realm embraced Absolute Monarchy
Russia remained more conservative than its western neighbors. In the
19th century, Russia was invaded by France in 1812 but emerged as a more
powerful superpower afterwards. Nonetheless industrialization did not
come to Russia until the 1870s. The Medieval practice of serfdom was abolished
in 1861 freeing over thirty million Russian peasants. A market economy
finally emerged in the Russian Empire. However class warfare rose, and
the nation was vulnerable due to rivalries with the United Kingdom, the Ottoman Empire, and the Japanese Empire.
European dominance and the 19th century
Historians define the 19th century historical era as stretching from 1815 (the Congress of Vienna) to 1914 (the outbreak of the First World War). Alternatively, Eric Hobsbawm defined the "Long Nineteenth Century" as spanning the years 1789 to 1914.
Imperialism and empires
"The World's Sovereigns", 1889
In the 1800s and early 1900s, once great and powerful Empires such as
Spain, Ottoman Turkey, the Mughal Empire, and the Kingdom of Portugal
began to break apart. Spain, which was at one time unrivaled in Europe,
had been declining for a long time when it was crippled by Napoleon
Bonaparte's invasion. Sensing the time was right, Spain's vast colonies
in South America began a series of rebellions that ended with almost all
of the Spanish territories gaining their independence.
The once mighty Ottoman Empire was wracked with a series of
revolutions, resulting with the Ottoman's only holding a small region
that surrounded the capital, Istanbul.
Montage that depicts European wars of imperialism. By clockwise, wars include French Algerian War, Opium War, Russian Conquest of Central Asia and Zulu War
The Mughal empire, which was descended from the Mongol Khanate, was bested by the upcoming Maratha Confederacy. All was going well for the Marathas
until the British took an interest in the riches of India and the
British ended up ruling not just the boundaries of Modern India, but
also Pakistan, Burma, Nepal, Bangladesh and some Southern Regions of
Afghanistan.
The King of Portugal's vast territory of Brazil reformed into the
independent Empire of Brazil. With the defeat of Napoleonic France,
Britain became undoubtedly the most powerful country in the world, and
by the end of the First World War controlled a Quarter of the world's
population and a third of its surface. However, the power of the British
Empire did not end on land, since it had the greatest navy on the
planet. Electricity, steel, and petroleum enabled Germany to become a
great international power that raced to create empires of its own.
The Meiji Restoration
was a chain of events that led to enormous changes in Japan's political
and social structure that was taking a firm hold at the beginning of
the Meiji Era which coincided the opening of Japan by the arrival of the Black Ships of Commodore Matthew Perry and made Imperial Japan a great power. Russia and Qing Dynasty
China failed to keep pace with the other world powers which led to
massive social unrest in both empires. The Qing Dynasty's military power
weakened during the 19th century, and faced with international
pressure, massive rebellions and defeats in wars, the dynasty declined after the mid-19th century.
European powers controlled parts of Oceania, with French New Caledonia from 1853 and French Polynesia from 1889; the Germans established colonies in New Guinea in 1884, and Samoa in 1900. The United States expanded into the Pacific with Hawaii becoming a U.S. territory from 1898. Disagreements between the US, Germany and UK over Samoa led to the Tripartite Convention of 1899.
British Victorian era
The British Empire in 1897, marked in the traditional colour for imperial British dominions on maps
The Victorian era of the United Kingdom was the period of Queen Victoria's
reign from June 1837 to January 1901. This was a long period of
prosperity for the British people, as profits gained from the overseas
British Empire, as well as from industrial improvements at home, allowed
a large, educated middle class to develop. Some scholars would extend
the beginning of the period—as defined by a variety of sensibilities and
political games that have come to be associated with the
Victorians—back five years to the passage of the Reform Act 1832.
Fleet Street in London capital of the British Empire, 1890
In Britain's "imperial century",
victory over Napoleon left Britain without any serious international
rival, other than Russia in central Asia. Unchallenged at sea, Britain
adopted the role of global policeman, a state of affairs later known as
the Pax Britannica, and a foreign policy of "splendid isolation".
Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies,
Britain's dominant position in world trade meant that it effectively
controlled the economies of many nominally independent countries, such
as China, Argentina and Siam, which has been generally characterized as "informal empire". Of note during this time was the Anglo-Zulu War, which was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Empire.
British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship and the telegraph,
new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century,
allowing it to control and defend the Empire. By 1902, the British
Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, the
so-called All Red Line. Growing until 1922, around 13,000,000 square miles (34,000,000 km2) of territory and roughly 458 million people were added to the British Empire. The British established colonies in Australia in 1788, New Zealand in 1840 and Fiji in 1872, with much of Oceania becoming part of the British Empire.
French governments and conflicts
The Bourbon Restoration
followed the ousting of Napoleon I of France in 1814. The Allies
restored the Bourbon Dynasty to the French throne. The ensuing period is
called the Restoration, following French usage, and is characterized by
a sharp conservative reaction and the re-establishment of the Roman
Catholic Church as a power in French politics. The July Monarchy
was a period of liberal constitutional monarchy in France under King
Louis-Philippe starting with the July Revolution (or Three Glorious
Days) of 1830 and ending with the Revolution of 1848. The Second Empire
was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870,
between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.
Napoleon III and Bismarck after the Battle of Sedan
The Franco-Prussian War
was a conflict between France and Prussia, while Prussia was backed up
by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the
South German states of Baden, Württemberg and Bavaria. The complete
Prussian and German victory brought about the final unification of
Germany under King Wilhelm I of Prussia. It also marked the downfall of
Napoleon III and the end of the Second French Empire, which was replaced
by the Third Republic. As part of the settlement, almost all of the
territory of Alsace-Lorraine was taken by Prussia to become a part of
Germany, which it would retain until the end of World War I.
The French Third Republic
was the republican government of France between the end of the Second
French Empire following the defeat of Louis-Napoléon in the
Franco-Prussian war in 1870 and the Vichy Regime after the invasion of
France by the German Third Reich in 1940. The Third Republic endured
seventy years, making it the most long-lasting regime in France since
the collapse of the Ancien Régime in the French Revolution of 1789.
Slavery and abolition
Slavery was greatly reduced around the world in the 19th century. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti, Britain forced the Barbary pirates to halt their practice of kidnapping and enslaving Europeans, banned slavery throughout its domain, and charged its navy with ending the global slave trade. Slavery was then abolished in Russia, America, and Brazil.
African colonization
Following the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 and propelled by economic exploitation, the Scramble for Africa was initiated formally at the Berlin West Africa Conference
in 1884–1885. The Berlin Conference attempted to avoid war among the
European powers by allowing the European rival countries to carve up the
continent of Africa into national colonies. Africans were not
consulted.
The major European powers laid claim to the areas of Africa
where they could exhibit a sphere of influence over the area. These
claims did not have to have any substantial land holdings or treaties to
be legitimate. The European power that demonstrated its control over a
territory accepted the mandate to rule that region as a national colony.
The European nation that held the claim developed and benefited from
their colony's commercial interests without having to fear rival
European competition. With the colonial claim came the underlying
assumption that the European power that exerted control would use its
mandate to offer protection and provide welfare for its colonial
peoples, however, this principle remained more theory than practice.
There were many documented instances of material and moral conditions
deteriorating for native Africans in the late nineteenth and early
twentieth centuries under European colonial rule, to the point where the
colonial experience for them has been described as "hell on earth."
European officials staking claims to Africa in the Congress of Berlin
At the time of the Berlin Conference,
Africa contained one-fifth of the world's population living in
one-quarter of the world's land area. However, from Europe's
perspective, they were dividing an unknown continent. European countries
established a few coastal colonies in Africa by the mid-nineteenth
century, which included Cape Colony (Great Britain), Angola (Portugal), and Algeria
(France), but until the late nineteenth century Europe largely traded
with free African states without feeling the need for territorial
possession. Until the 1880s most of Africa remained uncharted, with
western maps from the period generally showing blank spaces for the
continent's interior.
From the 1880s to 1914, the European powers expanded their
control across the African continent, competing with each other for
Africa's land and resources. Great Britain
controlled various colonial holdings in East Africa that spanned the
length of the African continent from Egypt in the north to South Africa.
The French gained major ground in West Africa, and the Portuguese held colonies in southern Africa. Germany, Italy, and Spain
established a small number of colonies at various points throughout the
continent, which included German East Africa (Tanganyika) and German
Southwest Africa for Germany, Eritrea and Libya for Italy, and the
Canary Islands and Rio de Oro in northwestern Africa for Spain. Finally,
for King Leopold (ruled from 1865 to 1909), there was the large “piece of that great African cake” known as the Congo, which became his personal fiefdom. By 1914, almost the entire continent was under European control. Liberia, which was settled by freed American slaves in the 1820s, and Abyssinia (Ethiopia) in eastern Africa were the last remaining independent African states.
Meiji Japan
Kobe Japan and its harbor, 1865. Hand colored.
Around the end of the 19th century and into the 20th century, the Meiji era occurred during the reign of the Meiji Emperor. During this time, Japan started its modernization and rose to world power status. This era name
means "Enlightened Rule". In Japan, the Meiji Restoration started in
the 1860s, marking the rapid modernization by the Japanese themselves
along European lines. Much research has focused on the issues of
discontinuity versus continuity with the previous Tokugawa Period.
It was not until the beginning of the Meiji Era that the Japanese
government began taking modernization seriously. Japan expanded its
military production base by opening arsenals in various locations. The hyobusho (war office) was replaced with a War Department and a Naval Department. The samurai class suffered great disappointment the following years.
Laws were instituted that required every able-bodied male
Japanese citizen, regardless of class, to serve a mandatory term of
three years with the first reserves and two additional years with the
second reserves. This action, the deathblow for the samurai warriors and
their daimyōs, initially met resistance from both the peasant
and warrior alike. The peasant class interpreted the term for military
service, ketsu-eki ("blood tax") literally, and attempted to avoid
service by any means necessary. The Japanese government began modelling
their ground forces after the French military. The French government
contributed greatly to the training of Japanese officers. Many were
employed at the military academy in Kyoto, and many more still were
feverishly translating French field manuals for use in the Japanese
ranks. Japan's modernized military gave Japan the opportunity to engage
in Imperialism with its victory against the Qing Empire in the First Sino-Japanese War Japan annexed Taiwan, Korea and the Chinese province of Shangdong.
After the death of the Meiji Emperor, the Taishō Emperor took the throne, theTaishō period
was a time of democratic reform granting democratic rights to all
Japanese men. Foreigners would instrumental in aiding in Japan's
modernization. A key foreign observer of the remarkable and rapid
changes in Japanese society in this period was Ernest Mason Satow.
United States
Antebellum expansion
American westward expansion is idealized in Emanuel Leutze's famous painting Westward the Course of Empire Takes its Way (1861).
The Antebellum Age was a period of increasing division in the country based on the growth of slavery in the American South and in the western territories of Kansas and Nebraska that eventually led to the Civil War in 1861. The Antebellum Period is often considered to have begun with the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854,
although it may have begun as early as 1812. This period is also
significant because it marked the transition of American manufacturing
to the industrial revolution.
"Manifest destiny"
was the belief that the United States was destined to expand across the
North American continent, from the Atlantic seaboard to the Pacific
Ocean. During this time, the United States expanded to the Pacific
Ocean—"from sea to shining sea"—largely defining the borders of the
contiguous United States as they are today.
Civil War and Reconstruction
Battle of Gettysburg – Restoration by Adam Cuerden 0.5
The American Civil War began when seven Southern slave states declared their secession from the U.S. and formed the Confederate States of America, the Confederacy (four more states joinged the Confederacy later). Led by Jefferson Davis, they fought against the U.S. federal government (the Union) under President Abraham Lincoln, which was supported by all the free states and the five border slave states in the north.
Northern leaders agreed that victory would require more than the
end of fighting. Secession and Confederate nationalism had to be totally
repudiated and all forms of slavery or quasi-slavery had to be
eliminated. Lincoln proved effective in mobilizing support for the war
goals, raising large armies and supplying them, avoiding foreign
interference, and making the end of slavery a war goal. The Confederacy
had a larger area than it could defend, and it failed to keep its ports
open and its rivers clear as was the case in the Battle of Vickysburg. The North
kept up the pressure as the South could barely feed and clothe its
soldiers. Its soldiers, especially those in the East under the command
of General Robert E. Lee proved highly resourceful until they finally were overwhelmed by Generals Ulysses S. Grant and William T. Sherman in 1864–65. The Reconstruction Era (1863–77) began with the Emancipation proclamation
in 1863, and included freedom, full citizenship and voting rights for
Southern blacks. It was followed by a reaction that left the blacks in a
second class status legally, politically, socially and economically
until the 1960s.
The Gilded Age and legacy
During the Gilded Age, there was substantial growth in population in
the United States and extravagant displays of wealth and excess of
America's upper-class during the post-Civil War and post-Reconstruction
era, in the late 19th century. The wealth polarization derived primarily
from industrial and population expansion. The businessmen of the Second Industrial Revolution created industrial towns and cities in the Northeast with new factories, and contributed to the creation of an ethnically diverse industrial working class which produced the wealth owned by rising super-rich industrialists and financiers called the "robber barons". An example is the company of John D. Rockefeller,
who was an important figure in shaping the new oil industry. Using
highly effective tactics and aggressive practices, later widely
criticized, Standard Oil absorbed or destroyed most of its competition.
The creation of a modern industrial economy took place. With the creation of a transportation and communication infrastructure, the corporation became the dominant form of business organization and a managerial revolution transformed business operations. In 1890, Congress passed the Sherman Antitrust Act—the
source of all American anti-monopoly laws. The law forbade every
contract, scheme, deal, or conspiracy to restrain trade, though the
phrase "restraint of trade" remained subjective. By the beginning of the
20th century, per capita income and industrial production
in the United States exceeded that of any other country except Britain.
Long hours and hazardous working conditions led many workers to attempt
to form labor unions
despite strong opposition from industrialists and the courts. But the
courts did protect the marketplace, declaring the Standard Oil group to
be an "unreasonable" monopoly under the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1911. It ordered Standard to break up into 34 independent companies with different boards of directors.
Science and philosophy
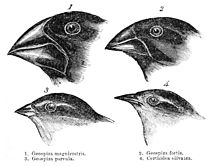
Charles Darwin's finches by Gould, 1882. Charles Darwin used the example of finches in the Galapagos Islands as evidence for the Theory of Evolution.
Replacing the classical physics in use since the end of the scientific revolution, modern physics arose in the early 20th century with the advent of quantum physics, substituting mathematical studies for experimental studies and examining equations to build a theoretical structure. The old quantum theory was a collection of results which predate modern quantum mechanics, but were never complete or self-consistent. The collection of heuristic prescriptions for quantum mechanics were the first corrections to classical mechanics. Outside the realm of quantum physics, the various aether theories in classical physics, which supposed a "fifth element" such as the Luminiferous aether, were nullified by the Michelson–Morley experiment—an attempt to detect the motion of earth through the aether. In biology, Darwinism gained acceptance, promoting the concept of adaptation in the theory of natural selection. The fields of geology, astronomy and psychology also made strides and gained new insights. In medicine, there were advances in medical theory and treatments.
Starting one-hundred years before the 20th century, the enlightenment spiritual philosophy was challenged in various quarters around the 1900s. Developed from earlier secular traditions, modern Humanist ethical philosophies
affirmed the dignity and worth of all people, based on the ability to
determine right and wrong by appealing to universal human qualities,
particularly rationality, without resorting to the supernatural or alleged divine authority from religious texts. For liberal humanists such as Rousseau and Kant, the universal law of reason guided the way toward total emancipation from any kind of tyranny. These ideas were challenged, for example by the young Karl Marx, who criticized the project of political emancipation (embodied in the form of human rights), asserting it to be symptomatic of the very dehumanization it was supposed to oppose. For Friedrich Nietzsche, humanism was nothing more than a secular version of theism. In his Genealogy of Morals,
he argues that human rights exist as a means for the weak to
collectively constrain the strong. On this view, such rights do not
facilitate emancipation of life, but rather deny it. In the 20th
century, the notion that human beings are rationally autonomous was
challenged by the concept that humans were driven by unconscious
irrational desires.
Notable persons
Albert Einstein in 1921
Sigmund Freud is renowned for his redefinition of sexual desire as the primary motivational energy of human life, as well as his therapeutic techniques, including the use of free association, his theory of transference in the therapeutic relationship, and the interpretation of dreams as sources of insight into unconscious desires.
Albert Einstein is known for his theories of special relativity and general relativity. He also made important contributions to statistical mechanics, especially his mathematical treatment of Brownian motion, his resolution of the paradox of specific heats, and his connection of fluctuations and dissipation. Despite his reservations about its interpretation, Einstein also made contributions to quantum mechanics and, indirectly, quantum field theory, primarily through his theoretical studies of the photon.
Social Darwinism
At the end of the 19th century, Social Darwinism
was promoted and included the various ideologies based on a concept
that competition among all individuals, groups, nations, or ideas was a
"natural" framework for social evolution in human societies. In this
view, society's advancement is dependent on the "survival of the fittest", the term was in fact coined by Herbert Spencer and referred to in "The Gospel of Wealth" written by Andrew Carnegie.
Marxist society
Pyramid of Capitalist System, produced in the United States
Karl Marx summarized his approach to history and politics in the opening line of the first chapter of The Communist Manifesto (1848). He wrote:
- The history of all hitherto existing society is the history of class struggles.
The Manifesto went through a number of editions from 1872 to
1890; notable new prefaces were written by Marx and Engels for the 1872
German edition, the 1882 Russian edition, the 1883 German edition, and
the 1888 English edition. In general, Marxism identified five (and one transitional) successive stages of development in Western Europe.
- Primitive Communism: as seen in cooperative tribal societies.
- Slave Society: which develops when the tribe becomes a city-state. Aristocracy is born.
- Feudalism: aristocracy is the ruling class. Merchants develop into capitalists.
- Capitalism: capitalists are the ruling class, who create and employ the true working class.
- Dictatorship of the proletariat: workers gain class consciousness, overthrow the capitalists and take control over the state.
- Communism: a classless and stateless society.
European decline and the 20th century
Though still tied to Great Britain in the commonwealth Australia achieved peaceful independence in 1901.
Major political developments saw the former British Empire lose most of its remaining political power over commonwealth countries. The Trans-Siberian Railway, crossing Asia by train, was complete by 1916. Other events include the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, two world wars, and the Cold War.
Australian Constitution
In 1901, the Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia
formed one nation. They kept the systems of government that they had
developed as separate colonies but also would have a federal government
that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia came into force, the colonies collectively became states of the Commonwealth of Australia.
Revolution and Warlords in China
Xinhai Revolution in Shanghai; Chen Qimei organized Shanghainese civilians to start the uprising and was successful. The picture above is Nanjing Road after the uprising, hung with the Five Races Under One Union Flags then used by the revolutionaries.
The last days of the Qing dynasty were marked with civil unrest, failed reforms and foreign invasions such as the Boxer rebellion.
Responding to these civil failures and discontent, the Qing Imperial
Court did attempt to reform the government in various ways, as the
decision to draft a constitution in 1906, the establishment of
provincial legislatures in 1909, and the preparation for a national
parliament in 1910. However, many of these measures were opposed by the
conservatives of the Qing Court, and many reformers were either
imprisoned or executed outright. The failures of the Imperial Court to
enact such reforming measures of political liberalization and
modernization caused the reformists to steer toward the road of
revolution.
The assertions of Chinese philosophy began to integrate concepts of Western philosophy, as steps toward modernization. By the time of the Xinhai Revolution in 1911, there were many calls, such as the May Fourth Movement, to completely abolish the old imperial institutions and practices of China. There were attempts to incorporate democracy, republicanism, and industrialism into Chinese philosophy, notably by Sun Yat-sen at the beginning of the 20th century.
In 1912, the Republic of China was established and Sun Yat-sen was inaugurated in Nanjing as the first Provisional President. But power in Beijing already had passed to Yuan Shikai, who had effective control of the Beiyang Army, the most powerful military force in China at the time. To prevent civil war
and possible foreign intervention from undermining the infant republic,
leaders agreed to Army's demand that China be united under a Beijing
government. On March 10, in Beijing, Shikai was sworn in as the second
Provisional President of the Republic of China.
After the early 20th century revolutions, shifting alliances of China's regional warlords
waged war for control of the Beijing government. Despite the fact that
various warlords gained control of the government in Beijing during the
warlord era, this did not constitute a new era of control or governance,
because other warlords did not acknowledge the transitory governments
in this period and were a law unto themselves. These military-dominated
governments were collectively known as the Beiyang government. The warlord era ended around 1927.
World Wars era
Start of the 20th century
The World in 1898 color coded for major empires. The British Empire, the Russian Empire, the Qing Dynasty and the United States were the largest countries at the time.
The Russo-Japanese War was the first time a European Country was defeated by an Asian Country in modern times. The Japanese Victory shocked the world.
In 1900 the World's Population had approached approximately 1.6 billion.
Four years into the 20th century saw the Russo-Japanese War with the Battle of Port Arthur establishing the Empire of Japan as a world power. The Russians were in constant pursuit of a warm water port on the Pacific Ocean, for their navy as well as for maritime trade. The Manchurian Campaign of the Russian Empire was fought against the Japanese over Manchuria and Korea. The major theatres of operations were Southern Manchuria, specifically the area around the Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden, and the seas around Korea, Japan, and the Yellow Sea.
The resulting campaigns, in which the fledgling Japanese military
consistently attained victory over the Russian forces arrayed against
them, were unexpected by world observers. These victories, as time
transpired, would dramatically transform the distribution of power in
East Asia, resulting in a reassessment of Japan's recent entry onto the
world stage. The embarrassing string of defeats increased Russian
popular dissatisfaction with the inefficient and corrupt Tsarist
government.
The Russian Revolution of 1905 was a wave of mass political unrest through vast areas of the Russian Empire. Some of it was directed against the government, while some was undirected. It included terrorism, worker strikes, peasant unrests, and military mutinies. It led to the establishment of the limited constitutional monarchy, the establishment of State Duma of the Russian Empire, and the multi-party system.
In China, the Qing Dynasty was overthrown following the Xinhai Revolution. The Xinhai Revolution began with the Wuchang Uprising on October 10, 1911, and ended with the abdication of Emperor Puyi on February 12, 1912. The primary parties to the conflict were the Imperial forces of the Qing dynasty (1644–1911), and the revolutionary forces of the Chinese Revolutionary Alliance (Tongmenghui).
Edwardian Britain
The Titanic was the largest ship constructed in its time. Deemed invincible, it was sunk by icebergs off the coast of Labrador, Canada.
The Edwardian era in the United Kingdom is the period spanning the reign of King Edward VII up to the end of the First World War, including the years surrounding the sinking of the RMS Titanic. In the early years of the period, the Second Boer War
in South Africa split the country into anti- and pro-war factions. The
imperial policies of the Conservatives eventually proved unpopular and
in the general election of 1906
the Liberals won a huge landslide. The Liberal government was unable to
proceed with all of its radical programme without the support of the House of Lords, which was largely Conservative. Conflict between the two Houses of Parliament over the People's Budget led to a reduction in the power of the peers in 1910. The general election in January that year returned a hung parliament with the balance of power held by Labour and Irish Nationalist members.
World War I
The causes of World War I included many factors, including the conflicts and antagonisms of the four decades leading up to the war. The Triple Entente was the name given to the loose alignment between the United Kingdom, France, and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907. The alignment of the three powers, supplemented by various agreements with Japan, the United States, and Spain, constituted a powerful counterweight to the Triple Alliance of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy,
the third having concluded an additional secret agreement with France
effectively nullifying her Alliance commitments. Militarism, alliances,
imperialism, and nationalism played major roles in the conflict. The
immediate origins of the war lay in the decisions taken by statesmen and
generals during the July Crisis of 1914, the spark (or casus belli) for which was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
However, the crisis did not exist in a void; it came after a long
series of diplomatic clashes between the Great Powers over European and
colonial issues in the decade prior to 1914 which had left tensions
high. The diplomatic clashes can be traced to changes in the balance of
power in Europe since 1870. An example is the Baghdad Railway which was planned to connect the Ottoman Empire cities of Konya and Baghdad
with a line through modern-day Turkey, Syria and Iraq. The railway
became a source of international disputes during the years immediately
preceding World War I. Although it has been argued that they were
resolved in 1914 before the war began, it has also been argued that the
railroad was a cause of the First World War. Fundamentally the war was sparked by tensions over territory in the Balkans.
Austria-Hungary competed with Serbia and Russia for territory and
influence in the region and they pulled the rest of the great powers
into the conflict through their various alliances and treaties. The Balkan Wars were two wars in South-eastern Europe in 1912–1913 in the course of which the Balkan League
(Bulgaria, Montenegro, Greece, and Serbia) first captured Ottoman-held
remaining part of Thessaly, Macedonia, Epirus, Albania and most of
Thrace and then fell out over the division of the spoils, with
incorporation of Romania this time.
Various
periods of World War I; 1914.07.28 (Tsar Nicholas II of Russia orders a
partial mobilization against Austria-Hungary), 1914.08.01 (Germany
declares war on Russia), 1914.08.03 (Germany declares war on Russia's
ally France), 1914.08.04 (Britain declares war on Germany), 1914.12
(British and German Christmas truce), 1915.12 (French and German Christmas truce), 1916.12 (Battle of Magdhaba),
1917.12 (British troops take Jerusalem from the Ottoman Empire), and
1918.11.11 (World War I ends: Germany signs an armistice agreement with
the Allies).Allies and Central Powers in the First World War
Allied powers and areas
Central powers and colonies or occupied territory
Neutral countries
Allied powers and areas
Central powers and colonies or occupied territory
Neutral countries
French Army, 1918
The First World War began in 1914 and lasted to the final Armistice in 1918. The Allied Powers, led by the British Empire, France, Russia until March 1918, Japan and the United States after 1917, defeated the Central Powers, led by the German Empire, Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
The war caused the disintegration of four empires—the Austro-Hungarian,
German, Ottoman, and Russian ones—as well as radical change in the
European and West Asian maps. The Allied powers before 1917 are referred
to as the Triple Entente, and the Central Powers are referred to as the Triple Alliance.
Italian Arditi troops using gas-masks to protect themselves from Chemical Warfare, used for the first time in WWI.
Much of the fighting in World War I took place along the Western Front, within a system of opposing manned trenches and fortifications (separated by a "No man's land") running from the North Sea to the border of Switzerland. On the Eastern Front,
the vast eastern plains and limited rail network prevented a trench
warfare stalemate from developing, although the scale of the conflict
was just as large. Hostilities also occurred on and under the sea
and—for the first time—from the air. More than 9 million soldiers died
on the various battlefields, and nearly that many more in the
participating countries' home fronts on account of food shortages and genocide committed under the cover of various civil wars and internal conflicts. Notably, more people died of the worldwide influenza outbreak
at the end of the war and shortly after than died in the hostilities.
The unsanitary conditions engendered by the war, severe overcrowding in
barracks, wartime propaganda interfering with public health warnings,
and migration of so many soldiers around the world helped the outbreak
become a pandemic.
Ultimately, World War I created a decisive break with the old world order that had emerged after the Napoleonic Wars,
which was modified by the mid-19th century's nationalistic revolutions.
The results of World War I would be important factors in the
development of World War II approximately 20 years later. More immediate
to the time, the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
was a political event that redrew the political boundaries of West
Asia. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples formerly ruled
by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new
nations. The partitioning brought the creation of the modern Arab world and the Republic of Turkey. The League of Nations granted France mandates over Syria and Lebanon and granted the United Kingdom mandates over Mesopotamia and Palestine (which was later divided into two regions: Palestine and Transjordan). Parts of the Ottoman Empire on the Arabian Peninsula became parts of what are today Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
Revolutions and war in Eurasia
Lenin
The Russian Revolution is the series of revolutions in Russia in 1917, which destroyed the Tsarist autocracy and led to the creation of the Soviet Union. Following the abdication of Nicholas II of Russia, the Russian Provisional Government was established. In October 1917, a red faction revolution occurred in which the Red Guard, armed groups of workers and deserting soldiers directed by the Bolshevik Party, seized control of Saint Petersburg (then known as Petrograd) and began an immediate armed takeover of cities and villages throughout the former Russian Empire.
Another action in 1917 that is of note was the armistice signed between Russia and the Central Powers at Brest-Litovsk. As a condition for peace, the treaty by the Central Powers conceded huge portions of the former Russian Empire to Imperial Germany and the Ottoman Empire, greatly upsetting nationalists and conservatives. The Bolsheviks made peace with the German Empire and the Central Powers,
as they had promised the Russian people prior to the Revolution.
Vladimir Lenin's decision has been attributed to his sponsorship by the
foreign office of Wilhelm II, German Emperor,
offered by the latter in hopes that with a revolution, Russia would
withdraw from World War I. This suspicion was bolstered by the German
Foreign Ministry's sponsorship of Lenin's return to Petrograd. The Western Allies expressed their dismay at the Bolsheviks, upset at:
- the withdrawal of Russia from the war effort,
- worried about a possible Russo-German alliance, and
- galvanized by the prospect of the Bolsheviks making good their threats to assume no responsibility for, and so default on, Imperial Russia's massive foreign loans.
Two contrasting visions of the Russian Civil War. To the left is propaganda from the White Army, to the right is propaganda from the Bolsheviks.
In addition, there was a concern, shared by many Central Powers
as well, that the socialist revolutionary ideas would spread to the
West. Hence, many of these countries expressed their support for the
Whites, including the provision of troops and supplies. Winston Churchill declared that Bolshevism must be "strangled in its cradle".
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed and the Soviets under the domination of the Bolshevik party assumed power, first in Petrograd (St. Petersburg) and then in other places. In the wake of the October Revolution,
the old Russian Imperial Army had been demobilized; the volunteer-based
Red Guard was the Bolsheviks' main military force, augmented by an
armed military component of the Cheka,
the Bolshevik state security apparatus. There was an instituted
mandatory conscription of the rural peasantry into the Red Army.
Opposition of rural Russians to Red Army conscription units was
overcome by taking hostages and shooting them when necessary in order to
force compliance. Former Tsarist officers were utilized as "military specialists" (voenspetsy), taking their families hostage in order to ensure loyalty. At the start of the war, three-fourths of the Red Army officer corps was composed of former Tsarist officers. By its end, 83% of all Red Army divisional and corps commanders were ex-Tsarist soldiers.
In the Russian Civil War, over eleven nations intervened in favor of the White Movement. Here Japanese occupy Vladivostok.
The principal fighting occurred between the Bolshevik Red Army and the forces of the White Army. Many foreign armies warred against the Red Army, notably the Allied Forces,
yet many volunteer foreigners fought in both sides of the Russian Civil
War. Other nationalist and regional political groups also participated
in the war, including the Ukrainian nationalist Green Army, the Ukrainian anarchist Black Army and Black Guards, and warlords such as Ungern von Sternberg.
The most intense fighting took place from 1918 to 1920. Major military
operations ended on 25 October 1922 when the Red Army occupied Vladivostok, previously held by the Provisional Priamur Government. The last enclave of the White Forces was the Ayano-Maysky District on the Pacific coast. The majority of the fighting ended in 1920 with the defeat of General Pyotr Wrangel in the Crimea, but a notable resistance in certain areas continued until 1923 (e.g., Kronstadt Uprising, Tambov Rebellion, Basmachi Revolt, and the final resistance of the White movement in the Far East).
While the early 1920s was a time of flux for revolutionary Russia and Central Asia, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was proclaimed in 1922 as the successor state to the fallen Russian Empire. Revolutionary leader Vladimir Lenin died of natural causes and was succeeded by Joseph Stalin.
The Early Republic of China
In 1917, China declared war on Germany in the hope of recovering its lost province, then under Japanese control. The New Culture Movement occupied the period from 1917 to 1923. Chinese representatives refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles, due to intense pressure from the student protesters and public opinion alike.
Student Demonstrations, June 4th and 5th, 1919
The May Fourth Movement helped to rekindle the then-fading cause of republican revolution. In 1917 Sun Yat-sen had become commander-in-chief of a rival military government in Guangzhou
in collaboration with southern warlords. Sun's efforts to obtain aid
from the Western democracies were ignored, however, and in 1920 he
turned to the Soviet Union, which had recently achieved its own
revolution. The Soviets sought to befriend the Chinese revolutionists by
offering scathing attacks on Western imperialism. But for political
expediency, the Soviet leadership initiated a dual policy of support for
both Sun and the newly established Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
With Sino-German cooperation until 1941, Chinese industry and military was improved just prior to the war against Japan.
In early 1927, the Kuomintang-CCP rivalry led to a split in the
revolutionary ranks. The CCP and the left wing of the Kuomintang had
decided to move the seat of the Nationalist government from Guangzhou to
Wuhan. But Chiang Kai-shek, whose Northern Expedition
was proving successful, set his forces to destroying the Shanghai CCP
apparatus and established an anti-Communist government at Nanjing in April 1927.
Nanjing period in China
The
"Nanjing Decade" of 1928–37 was one of consolidation and accomplishment
under the leadership of the Nationalists, with a mixed but generally
positive record in the economy, social progress, development of democracy,
and cultural creativity. Some of the harsh aspects of foreign
concessions and privileges in China were moderated through diplomacy.
The 1920s and the Depression
The world in 1920, part of the interwar period. Great Britain and France expanded greatly at the expense of the former German Empire
The interwar period was the period between the end of the First World
War and the beginning of the Second World War. This period was marked by
turmoil in much of the world, as Europe struggled to recover from the
devastation of the First World War.
American, Flapper Girl. In the 1920s women experienced a degree of liberation.
In
North America, especially the first half of this period, people
experienced considerable prosperity in the Roaring Twenties. The social
and societal upheaval known as the Roaring Twenties began in North
America and spread to Europe in the aftermath of World War I. The Roaring Twenties, often called "The Jazz Age", saw an exposition of social, artistic, and cultural dynamism. "Normalcy" returned to politics, jazz music blossomed, the flapper redefined modern womanhood, Art Deco
peaked. The spirit of the Roaring Twenties was marked by a general
feeling of discontinuity associated with modernity, a break with
traditions. Everything seemed to be feasible through modern technology.
New technologies, especially automobiles, movies and radio proliferated
'modernity' to a large part of the population. The 1920s saw the general
favor of practicality, in architecture as well as in daily life. The
1920s was further distinguished by several inventions and discoveries,
extensive industrial growth and the rise in consumer demand and
aspirations, and significant changes in lifestyle.
Europe spent these years rebuilding and coming to terms with the vast
human cost of the conflict. The economy of the United States became
increasingly intertwined with that of Europe. In Germany, the Weimar Republic gave way to episodes of political and economic turmoil, which culminated with the German hyperinflation of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch
of that same year. When Germany could no longer afford war payments,
Wall Street invested heavily in European debts to keep the European
economy afloat as a large consumer market for American mass-produced
goods. By the middle of the decade, economic development
soared in Europe, and the Roaring Twenties broke out in Germany,
Britain and France, the second half of the decade becoming known as the "Golden Twenties". In France and francophone Canada, they were also called the "années folles" ("Crazy Years")., 1935. German Nazis created large public performances to earn public support.
Great Depression, Breadlines-long line of people waiting to be fed, New York City, United States
Worldwide prosperity changed dramatically with the onset of the Great Depression in 1929. The Wall Street Crash of 1929 served to punctuate the end of the previous era, as The Great Depression set in. The Great Depression was a worldwide economic downturn starting in most places in 1929 and ending at different times in the 1930s or early 1940s for different countries. It was the largest and most important economic depression in the 20th century, and is used in the 21st century as an example of how far the world's economy can fall.
The depression had devastating effects in virtually every
country, rich or poor. International trade plunged by half to
two-thirds, as did personal income, tax revenue, prices and profits. Cities all around the world were hit hard, especially those dependent on heavy industry.
Construction was virtually halted in many countries. Farming and rural
areas suffered as crop prices fell by roughly 60 percent. Facing plummeting demand with few alternate sources of jobs, areas dependent on primary sector industries suffered the most.
The Great Depression ended at different times in different countries with the effect lasting into the next era. America's Great Depression ended in 1941 with America's entry into World War II.
The majority of countries set up relief programs, and most underwent
some sort of political upheaval, pushing them to the left or right. In
some world states, the desperate citizens turned toward nationalist demagogues—the most infamous being Adolf Hitler—setting the stage for the next era of war. The convulsion brought on by the worldwide depression resulted in the rise of Nazism. In Asia, Japan became an ever more assertive power, especially with regards to China.
The League and crises
The interwar period was also marked by a radical change in the international order, away from the balance of power that had dominated pre–World War I Europe. One main institution that was meant to bring stability was the League of Nations,
which was created after the First World War with the intention of
maintaining world security and peace and encouraging economic growth
between member countries. The League was undermined by the bellicosity
of Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, the Soviet Union, and Mussolini's Italy, and by the non-participation of the United States, leading many to question its effectiveness and legitimacy.
Nationalist Chinese soldiers defending at the Battle at Great Wall, Laiyuan, Hebei, China autumn 1937. The Second Sino-Japanese war cost at least twenty millions lives.
A series of international crises strained the League to its limits, the earliest being the invasion of Manchuria by Japan and the Abyssinian crisis of 1935/36 in which Italy invaded Abyssinia, one of the only free African nations at that time.
The signatories Munich Agreement where British Prime Minister Nevil Chamberline appeased to the Axis Powers regarding territorial claims in Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia to avoid conflict.
The League tried to enforce economic sanctions upon Italy, but to no
avail. The incident highlighted French and British weakness, exemplified
by their reluctance to alienate Italy and lose her as their ally. The
limited actions taken by the Western powers pushed Mussolini's Italy
towards alliance with Hitler's Germany anyway. The Abyssinian war showed
Hitler how weak the League was and encouraged the remilitarization of
the Rhineland in flagrant disregard of the Treaty of Versailles. This
was the first in a series of provocative acts culminating in the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the beginning of the Second World War.
Few Chinese had any illusions about Japanese designs on China.
Hungry for raw materials and pressed by a growing population, Japan
initiated the seizure of Manchuria in September 1931 and established ex-Qing emperor Puyi as head of the puppet state of Manchukuo in 1932. During the Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945),
the loss of Manchuria, and its vast potential for industrial
development and war industries, was a blow to the Kuomintang economy.
The League of Nations,
established at the end of World War I, was unable to act in the face of
the Japanese defiance. After 1940, conflicts between the Kuomintang and
Communists became more frequent in the areas not under Japanese control.
The Communists expanded their influence wherever opportunities
presented themselves through mass organizations, administrative reforms,
and the land- and tax-reform measures favoring the peasants—while the
Kuomintang attempted to neutralize the spread of Communist influence.
Tripartite Pact
Japanese poster advocating for Tripartite Pact, 1941.
The Second Sino-Japanese War had seen tensions rise between Imperial Japan and the United States; events such as the Panay incident and the Nanking Massacre turned American public opinion against Japan. With the occupation of French Indochina in the years of 1940–41, and with the continuing war in China, the United States placed embargoes on Japan of strategic materials
such as scrap metal and oil, which were vitally needed for the war
effort. The Japanese were faced with the option of either withdrawing
from China and losing face or seizing and securing new sources of raw
materials in the resource-rich, European-controlled colonies of South East Asia—specifically British Malaya and the Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia). In 1940, Imperial Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy.
World War II
World War II at the height of Axis expansion (black) fighting against the Allies (blue) and Comintern (red). It is important to note that the Empire of Japan was not at war with the Soviet Union despite being part of the Tripartite Pact.
The German Invasion of Poland in 1939 is the official start of WWII
The Second World War was a global military conflict that took place
in 1939–1945. It was the largest and deadliest war in history,
culminating in the Holocaust and ending with the dropping of the atom bomb.
Even though Japan had been invading in China since 1937, the conventional view is that the war began on September 1, 1939, when Nazi Germany invaded Poland, the Drang nach Osten.
Within two days the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany,
even though the fighting was confined to Poland. Pursuant to a
then-secret provision of its non-aggression Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, the Soviet Union joined with Germany on September 17, 1939, to conquer Poland and to divide Eastern Europe.
The Allies were initially made up of Poland, the United Kingdom, France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, as well as British Commonwealth countries which were controlled directly by the UK, such as the Indian Empire. All of these countries declared war on Germany in September 1939.
Following the lull in fighting, known as the "Phoney War",
Germany invaded western Europe in May 1940. Six weeks later, France, in
the mean time attacked by Italy as well, surrendered to Germany, which
then tried unsuccessfully to conquer Britain. On September 27, Germany,
Italy, and Japan signed a mutual defense agreement, the Tripartite Pact, and were known as the Axis Powers.Nine
months later, on June 22, 1941, Germany launched a massive invasion of
the Soviet Union, which promptly joined the Allies. Germany was now
engaged in fighting a war on two fronts. This proved to be a mistake by
Germany – Germany had not successfully carried out the invasion of
Britain and the war turned against the Axis.
On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the United States at Pearl Harbor,
bringing it too into the war on the Allied side. China also joined the
Allies, as eventually did most of the rest of the world. China was in
turmoil at the time, and attacked Japanese armies through guerilla-type
warfare. By the beginning of 1942, the major combatants were aligned as
follows: the British Commonwealth, the United States, and the Soviet
Union were fighting Germany and Italy; and the British Commonwealth,
China, and the United States were fighting Japan. The United Kingdom,
the United States, the Soviet Union and China were referred as a
"trusteeship of the powerful" during the World War II and were recognized as the Allied "Big Four" in Declaration by United Nations These four countries were considered as the "Four Policemen" or "Four Sheriffs" of the Allies power and primary victors of World War II. From then through August 1945, battles raged across all of Europe, in the North Atlantic Ocean, across North Africa, throughout Southeast Asia, throughout China, across the Pacific Ocean and in the air over Japan.
Italy surrendered in September 1943 and was split into a northern Germany-occupied puppet state and an Allies-friendly state in the South; Germany surrendered in May 1945. Following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan surrendered, marking the end of the war on September 2, 1945.
It is possible that around 62 million people died in the war; estimates vary greatly. About 60% of all casualties were civilians, who died as a result of disease, starvation, genocide (in particular, the Holocaust),
and aerial bombing. The former Soviet Union and China suffered the most
casualties. Estimates place deaths in the Soviet Union at around 23
million, while China suffered about 10 million. No country lost a
greater portion of its population than Poland: approximately 5.6
million, or 16%, of its pre-war population of 34.8 million died.
The Holocaust (which roughly means "burnt whole") was the deliberate and
systematic murder of millions of Jews and other "unwanted" during World
War II by the Nazi regime in Germany. Several differing views exist
regarding whether it was intended to occur from the war's beginning, or
if the plans for it came about later. Regardless, persecution of Jews
extended well before the war even started, such as in the Kristallnacht (Night of Broken Glass). The Nazis used propaganda to great effect to stir up anti-Semitic feelings within ordinary Germans.
After World War II, Europe was informally split into Western and Soviet spheres of influence. Western Europe later aligned as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and Eastern Europe as the Warsaw Pact. There was a shift in power from Western Europe and the British Empire to the two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union. These two rivals would later face off in the Cold War. In Asia, the defeat of Japan led to its democratization. China's civil war continued through and after the war, resulting eventually in the establishment of the People's Republic of China. The former colonies of the European powers began their road to independence.
End of the Period – Postwar World
During Pax Americana, the popular music industry flourished.Pictured here is the Beatles Group.
The mid-20th century is distinguished from most of human history in
that its most significant changes were directly or indirectly economic
and technological in nature. Economic development was the force behind
vast changes in everyday life, to a degree which was unprecedented in
human history.
Over the course of the 20th century, the world's per-capita gross domestic product grew by a factor of five,
much more than all earlier centuries combined (including the 19th with
its Industrial Revolution). Many economists make the case that this
understates the magnitude of growth, as many of the goods and services
consumed at the end of the 20th century, such as improved medicine
(causing world life expectancy to increase by more than two decades) and
communications technologies, were not available at any price at its
beginning. However, the gulf between the world's rich and poor grew
wider, and the majority of the global population remained in the poor side of the divide.
Still, advancing technology and medicine has had a great impact even in the Global South. Large-scale industry and more centralized media
made brutal dictatorships possible on an unprecedented scale in the
middle of the century, leading to wars that were also unprecedented.
However, the increased communications contributed to democratization. Technological developments included the development of airplanes and space exploration, nuclear technology, advancement in genetics, and the dawning of the Information Age.
American Peace
Pax Americana is an appellation applied to the historical concept of
relative liberal peace in the Western world, resulting from the
preponderance of power enjoyed by the United States of America starting
around the start of the 20th century. Although the term finds its
primary utility in the latter half of the 20th century, it has been used
in various places and eras. Its modern connotations concern the peace
established after the end of World War II in 1945.
Cold War era
The Cold War began in the mid-1940s and lasted into the early 1990s.
Throughout this period, the conflict was expressed through military
coalitions, espionage, weapons development, invasions, propaganda, and
competitive technological development. The conflict included costly
defense spending, a massive conventional and nuclear arms race, and numerous proxy wars; the two superpowers never fought one another directly.
Borders of NATO (blue) and Warsaw Pact (red) states during the Cold war era.
The Soviet Union created the Eastern Bloc of countries that it occupied, annexing some as Soviet Socialist Republics and maintaining others as satellite states that would later form the Warsaw Pact. The United States and various western European countries began a policy of "containment" of communism and forged myriad alliances to this end, including NATO.
Several of these western countries also coordinated efforts regarding
the rebuilding of western Europe, including western Germany, which the
Soviets opposed. In other regions of the world, such as Latin America
and Southeast Asia, the Soviet Union fostered communist revolutionary movements, which the United States and many of its allies opposed and, in some cases, attempted to "roll back".
Many countries were prompted to align themselves with the nations that
would later form either NATO or the Warsaw Pact, though other movements
would also emerge.
US and USSR nuclear stockpiles
In China Mao Zedong (Máo zé dōng) utilized Marxist-Leninist thought. When the Communist Party of China assumed power in 1959, previous schools of Chinese thought, excepting notably Legalism, were denounced as backward. Many parts of China's past were even purged during the Cultural Revolution. Though initially friendly with the Soviet Union the Chinese and Soviet communists diverged in the Sino-Soviet split
of 1960. Through the end of the Cold-War, China would continue on its
own path from other communist countries, building better relations with
the United States after 1972. China's economy would recover from the
Cultural Revolution due to market-oriented reforms led by Deng Xiaoping.
The Cold War saw periods of both heightened tension and relative calm. International crises arose, such as the Berlin Blockade (1948–1949), the Korean War (1950–1953), the Berlin Crisis of 1961, the Vietnam War (1955–1975), the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962), the Soviet–Afghan War (1979–1989) and NATO exercises in November 1983. There were also periods of reduced tension as both sides sought détente. Direct military attacks on adversaries were deterred by the potential for mutual assured destruction using deliverable nuclear weapons.
European trade blocs as of the late 1980s. EEC member states are marked in blue, EFTA – green, and Comecon – red.

East
and West in 1980, as defined by the Cold War. The Cold War had divided
Europe politically into East and West, with the Iron Curtain splitting Central Europe.
|
The Cold War drew to a close in the late 1980s and the early 1990s. The United States under President Ronald Reagan increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressure on the Soviet Union, which was already suffering from severe economic stagnation. In the second half of the 1980s, newly appointed Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the perestroika and glasnost reforms. The Soviet Union collapsed
in 1991, leaving the United States as the dominant military power,
though Russia retained much of the massive Soviet nuclear arsenal.
Latin America polarization
In
Latin America in the 1970s, leftists acquired a significant political
influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a
large portion of the individual country's upper class to support coups
d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was
further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a
political polarization. Most South American countries were in some
periods ruled by military dictatorships that were supported by the United States of America. In the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone collaborated in Operation Condor killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas. However, by the early 1990s all countries had restored their democracies.
Space Age
The Blue Marble, a photograph of Earth as seen from Apollo 17. The second half of the 20th century saw an increase of interest in both space exploration and the environmental movement.
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration,
space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these
events. The Space Age began with the development of several technologies
that culminated with the launch of Sputnik 1
by the Soviet Union in October 1957. This was the world's first
artificial satellite, orbiting the Earth in 98.1 minutes and weighing in
at 83 kg. The launch of Sputnik 1 ushered a new era of political,
scientific and technological achievements that became known as the Space
Age. The Space Age was characterized by rapid development of new
technology in a close race mostly between the United States and the
Soviet Union. The Space Age brought the first human spaceflight during
the Vostok programme and reached its peak with the Apollo program which captured the imagination of much of the world's population. The landing of Apollo 11
was an event watched by over 500 million people around the world and is
widely recognized as one of the defining moments of the 20th century.
Since then and with the end of the space race due to the dissolution of the Soviet Union, public attention has largely moved to other areas.
Education and schools
The humanities are academic disciplines which study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytic, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural and social sciences.
Although many of the subjects of modern history coincide with that of
standard history, the subject is taught independently by various systems
of education in the world.
British education
Students
can choose the subject at university. The material covered includes
from the mid-18th century, to analysis of the present day. Virtually all
colleges and sixth forms that do teach modern history do it alongside
standard history; very few teach the subject exclusively.
Universities
At the University of Oxford
'Modern History' has a somewhat different meaning. The contrast is not
with the Middle Ages but with Antiquity. The earliest period that can be
studied in the Final Honour School of Modern History begins in 285.