| Wheat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Subfamily: | Pooideae |
| Tribe: | Triticeae |
| Genus: | Triticum L. |
| Species | |
| |
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain which is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus Triticum; the most widely grown is common wheat (T. aestivum).
The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis.
Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (220.4 million hectares, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2016, world production of wheat was 749 million tonnes, making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is increasing as a result of the worldwide industrialization process and the westernization of the diet.
Wheat is an important source of carbohydrates. Globally, it is the leading source of vegetal protein in human food, having a protein content of about 13%, which is relatively high compared to other major cereals but relatively low in protein quality for supplying essential amino acids. When eaten as the whole grain, wheat is a source of multiple nutrients and dietary fiber.
In a small part of the general population, gluten – the major part of wheat protein – can trigger coeliac disease, noncoeliac gluten sensitivity, gluten ataxia, and dermatitis herpetiformis.
Origin and history
Spikelets of a hulled wheat, einkorn
Cultivation and repeated harvesting and sowing of the grains of wild
grasses led to the creation of domestic strains, as mutant forms
('sports') of wheat were preferentially chosen by farmers. In
domesticated wheat, grains are larger, and the seeds (inside the
spikelets) remain attached to the ear by a toughened rachis during harvesting. In wild strains, a more fragile rachis allows the ear to easily shatter and disperse the spikelets.
Selection for these traits by farmers might not have been deliberately
intended, but simply have occurred because these traits made gathering
the seeds easier; nevertheless such 'incidental' selection was an
important part of crop domestication.
As the traits that improve wheat as a food source also involve the loss
of the plant's natural seed dispersal mechanisms, highly domesticated
strains of wheat cannot survive in the wild.
Cultivation of wheat began to spread beyond the Fertile Crescent after about 8000 BCE. Jared Diamond traces the spread of cultivated emmer wheat starting in the Fertile Crescent sometime before 8800 BCE. Archaeological analysis of wild emmer indicates that it was first cultivated in the southern Levant, with finds dating back as far as 9600 BCE. Genetic analysis of wild einkorn wheat suggests that it was first grown in the Karacadag Mountains in southeastern Turkey. Dated archeological remains of einkorn wheat in settlement sites near this region, including those at Abu Hureyra in Syria, suggest the domestication of einkorn near the Karacadag Mountain Range. With the anomalous exception of two grains from Iraq ed-Dubb, the earliest carbon-14 date for einkorn wheat remains at Abu Hureyra is 7800 to 7500 years BCE.
Remains of harvested emmer from several sites near the Karacadag Range have been dated to between 8600 (at Cayonu) and 8400 BCE (Abu Hureyra), that is, in the Neolithic period.
With the exception of Iraq ed-Dubb, the earliest carbon-14 dated
remains of domesticated emmer wheat were found in the earliest levels of
Tell Aswad, in the Damascus basin, near Mount Hermon in Syria. These remains were dated by Willem van Zeist
and his assistant Johanna Bakker-Heeres to 8800 BCE. They also
concluded that the settlers of Tell Aswad did not develop this form of
emmer themselves, but brought the domesticated grains with them from an
as yet unidentified location elsewhere.
The cultivation of emmer reached Greece, Cyprus and India by
6500 BCE, Egypt shortly after 6000 BCE, and Germany and Spain by
5000 BCE.
"The early Egyptians were developers of bread and the use of the oven
and developed baking into one of the first large-scale food production
industries." By 3000 BCE, wheat had reached the British Isles and Scandinavia. A millennium later it reached China.
The oldest evidence for hexaploid wheat has been confirmed
through DNA analysis of wheat seeds, dating to around 6400-6200 BCE,
recovered from Çatalhöyük. The first identifiable bread wheat (Triticum aestivum)
with sufficient gluten for yeasted breads has been identified using DNA
analysis in samples from a granary dating to approximately 1350 BCE at Assiros in Macedonia.
From Asia, wheat continued to spread across Europe. In the
British Isles, wheat straw (thatch) was used for roofing in the Bronze
Age, and was in common use until the late 19th century.
Farming techniques
Green wheat a month before harvest
Young wheat crop in a field near Solapur, Maharashtra, India
Technological advances in soil preparation and seed placement at planting time, use of crop rotation
and fertilizers to improve plant growth, and advances in harvesting
methods have all combined to promote wheat as a viable crop. When the
use of seed drills replaced broadcasting sowing of seed in the 18th century, another great increase in productivity occurred.
Yields of pure wheat per unit area increased as methods of crop rotation were applied to long cultivated land, and the use of fertilizers became widespread. Improved agricultural husbandry has more recently included threshing machines and reaping machines (the 'combine harvester'), tractor-drawn cultivators and planters, and better varieties (see Green Revolution and Norin 10 wheat).
Great expansion of wheat production occurred as new arable land was
farmed in the Americas and Australia in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Physiology
Leaves emerge from the shoot apical meristem in a telescoping fashion until the transition to reproduction ie. flowering. The last leaf produced by a wheat plant is known as the flag leaf. It is denser and has a higher photosynthetic rate than other leaves, to supply carbohydrate
to the developing ear. In temperate countries the flag leaf, along with
the second and third highest leaf on the plant, supply the majority of
carbohydrate in the grain and their condition is paramount to yield
formation. Wheat is unusual among plants in having more stomata on the upper (adaxial) side of the leaf, than on the under (abaxial) side. It has been theorised that this might be an effect of it having been domesticated and cultivated longer than any other plant. Winter wheat generally produces up to 15 leaves per shoot and spring wheat up to 9 and winter crops may have up to 35 tillers (shoots) per plant (depending on cultivar).
Wheat roots are among the deepest of arable crops, extending as far down as 2m. While the roots of a wheat plant are growing, the plant also accumulates an energy store in its stem, in the form of fructans, which helps the plant to yield under drought and disease pressure, but it has been observed that there is a trade-off between root growth and stem non-structural carbohydrate reserves. Root growth is likely to be prioritised in drought-adapted
crops, while stem non-structural carbohydrate is prioritised in
varieties developed for countries where disease is a bigger issue.
Depending on variety, wheat may be awned or not awned. Producing awns
incurs a cost in grain number, but wheat awns photosynthesise more water-use-efficiently than their leaves,
so awns are much more frequent in varieties of wheat grown in hot
drought-prone countries than those generally seen in temperate
countries. For this reason, awned varieties could become more widely
grown due to climate change. In Europe, however, a decline in climate resilience of wheat has been observed.
Genetics
Wheat genetics is more complicated than that of most other domesticated species. Some wheat species are diploid, with two sets of chromosomes, but many are stable polyploids, with four sets of chromosomes (tetraploid) or six (hexaploid).
- Einkorn wheat (T. monococcum) is diploid (AA, two complements of seven chromosomes, 2n=14).
- Most tetraploid wheats (e.g. emmer and durum wheat) are derived from wild emmer, T. dicoccoides. Wild emmer is itself the result of a hybridization between two diploid wild grasses, T. urartu and a wild goatgrass such as Aegilops searsii or Ae. speltoides. The unknown grass has never been identified among now surviving wild grasses, but the closest living relative is Aegilops speltoides. The hybridization that formed wild emmer (AABB) occurred in the wild, long before domestication, and was driven by natural selection.
- Hexaploid wheats evolved in farmers' fields. Either domesticated emmer or durum wheat hybridized with yet another wild diploid grass (Aegilops tauschii) to make the hexaploid wheats, spelt wheat and bread wheat. These have three sets of paired chromosomes, three times as many as in diploid wheat.
The presence of certain versions of wheat genes has been important
for crop yields. Apart from mutant versions of genes selected in
antiquity during domestication, there has been more recent deliberate
selection of alleles that affect growth characteristics. Genes for the 'dwarfing' trait, first used by Japanese wheat breeders to produce short-stalked wheat, have had a huge effect on wheat yields worldwide, and were major factors in the success of the Green Revolution in Mexico and Asia, an initiative led by Norman Borlaug.
Dwarfing genes enable the carbon that is fixed in the plant during
photosynthesis to be diverted towards seed production, and they also
help prevent the problem of lodging. 'Lodging' occurs when an ear stalk
falls over in the wind and rots on the ground, and heavy nitrogenous
fertilization of wheat makes the grass grow taller and become more
susceptible to this problem. By 1997, 81% of the developing world's
wheat area was planted to semi-dwarf wheats, giving both increased
yields and better response to nitrogenous fertilizer.
Wild grasses in the genus Triticum and related genera, and grasses such as rye have been a source of many disease-resistance traits for cultivated wheat breeding since the 1930s.
Heterosis,
or hybrid vigor (as in the familiar F1 hybrids of maize), occurs in
common (hexaploid) wheat, but it is difficult to produce seed of hybrid
cultivars on a commercial scale (as is done with maize) because wheat flowers are perfect and normally self-pollinate.
Commercial hybrid wheat seed has been produced using chemical
hybridizing agents; these chemicals selectively interfere with pollen
development, or naturally occurring cytoplasmic male sterility systems.
Hybrid wheat has been a limited commercial success in Europe
(particularly France), the United States and South Africa.
F1 hybrid wheat cultivars should not be confused with the standard
method of breeding inbred wheat cultivars by crossing two lines using
hand emasculation, then selfing or inbreeding the progeny many (ten or
more) generations before release selections are identified to be
released as a variety or cultivar.
Synthetic hexaploids made by crossing the wild goatgrass wheat ancestor Aegilops tauschii and various durum wheats are now being deployed, and these increase the genetic diversity of cultivated wheats.
Stomata
(or leaf pores) are involved in both uptake of carbon dioxide gas from
the atmosphere and water vapor losses from the leaf due to water transpiration. Basic physiological investigation of these gas exchange processes has yielded valuable carbon isotope
based methods that are used for breeding wheat varieties with improved
water-use efficiency. These varieties can improve crop productivity in
rain-fed dry-land wheat farms.
In 2010, a team of UK scientists funded by BBSRC
announced they had decoded the wheat genome for the first time (95% of
the genome of a variety of wheat known as Chinese Spring line 42).
This genome was released in a basic format for scientists and plant
breeders to use but was not a fully annotated sequence which was
reported in some of the media.
On 29 November 2012, an essentially complete gene set of bread wheat was published. Random shotgun libraries of total DNA and cDNA from the T. aestivum
cv. Chinese Spring (CS42) were sequenced in Roche 454 pyrosequencer
using GS FLX Titanium and GS FLX+ platforms to generate 85 Gb of
sequence (220 million reads), equivalent to 5X genome coverage and
identified between 94,000 and 96,000 genes.
This sequence data provides direct access to about 96,000 genes,
relying on orthologous gene sets from
other cereals. and represents an essential step towards a systematic
understanding of biology and engineering the cereal crop for valuable
traits. Its implications in cereal genetics and breeding includes the
examination of genome variation, association mapping using natural
populations, performing wide crosses and alien introgression, studying
the expression and nucleotide polymorphism in transcriptomes, analyzing
population genetics and evolutionary biology, and studying the
epigenetic modifications. Moreover, the availability of large-scale
genetic markers generated through NGS technology will facilitate trait
mapping and make marker-assisted breeding much feasible.
Moreover, the data not only facilitate in deciphering the complex
phenomena such as heterosis and epigenetics, it may also enable
breeders to predict which fragment of a chromosome is derived from which
parent in the progeny line, thereby recognizing crossover events
occurring in every progeny line and inserting markers on genetic and
physical maps without ambiguity. In due course, this will assist in
introducing specific chromosomal segments from one cultivar to another.
Besides, the researchers had identified diverse classes of genes
participating in energy production, metabolism and growth that were
probably linked with crop yield, which can now be utilized for the
development of transgenic wheat. Thus whole genome sequence of wheat and
the availability of thousands of SNPs will inevitably permit the
breeders to stride towards identifying novel traits, providing
biological knowledge and empowering biodiversity-based breeding.
Plant breeding
Sheaved and stooked wheat
Wheat field in Punjab
In traditional agricultural systems wheat populations often consist of landraces,
informal farmer-maintained populations that often maintain high levels
of morphological diversity. Although landraces of wheat are no longer
grown in Europe and North America, they continue to be important
elsewhere. The origins of formal wheat breeding lie in the nineteenth
century, when single line varieties were created through selection of
seed from a single plant noted to have desired properties. Modern wheat
breeding developed in the first years of the twentieth century and was
closely linked to the development of Mendelian genetics.
The standard method of breeding inbred wheat cultivars is by crossing
two lines using hand emasculation, then selfing or inbreeding the
progeny. Selections are identified (shown to have the genes
responsible for the varietal differences) ten or more generations before
release as a variety or cultivar.
The major breeding objectives include high grain yield, good
quality, disease and insect resistance and tolerance to abiotic
stresses, including mineral, moisture and heat tolerance. The major
diseases in temperate environments include the following, arranged in a
rough order of their significance from cooler to warmer climates: eyespot, Stagonospora nodorum blotch (also known as glume blotch), yellow or stripe rust, powdery mildew, Septoria tritici blotch (sometimes known as leaf blotch), brown or leaf rust, Fusarium head blight, tan spot and stem rust. In tropical areas, spot blotch (also known as Helminthosporium leaf blight) is also important.
Wheat has also been the subject of mutation breeding,
with the use of gamma, x-rays, ultraviolet light, and sometimes harsh
chemicals. The varieties of wheat created through these methods are in
the hundreds (going as far back as 1960), more of them being created in
higher populated countries such as China. Bread wheat with high grain iron and zinc content was developed through gamma radiation breeding. Modern bread wheat varieties have been cross-bred to contain greater amounts of gluten, which affords significant advantages for improving the quality of breads and pastas from a functional point of view. Gluten is appreciated for its unique viscoelastic properties. It gives elasticity to dough and is responsible for dough's gas-retaining properties.
International wheat breeding is led by CIMMYT in Mexico. ICARDA is another major public sector international wheat breeder, but it was forced to relocate from Syria in the Syrian Civil War. The world record wheat yield is about 17t/ha, reached in New Zealand in 2017. A project in the UK, led by Rothamsted Research
has aimed to raise wheat yields in the country to 20t/ha by 2020, but
in 2018 the UK record stood at 16t/ha, and the average yield was just
8t/ha.
Hybrid wheat
Because wheat self-pollinates, creating hybrid varieties
is extremely labor-intensive; the high cost of hybrid wheat seed
relative to its moderate benefits have kept farmers from adopting them
widely despite nearly 90 years of effort. F1 hybrid wheat cultivars should not be confused with wheat cultivars deriving from standard plant breeding. Heterosis
or hybrid vigor (as in the familiar F1 hybrids of maize) occurs in
common (hexaploid) wheat, but it is difficult to produce seed of hybrid
cultivars on a commercial scale as is done with maize because wheat flowers are perfect in the botanical sense, meaning they have both male and female parts, and normally self-pollinate. Commercial hybrid wheat seed has been produced using chemical hybridizing agents, plant growth regulators that selectively interfere with pollen development, or naturally occurring cytoplasmic male sterility systems. Hybrid wheat has been a limited commercial success in Europe (particularly France), the United States and South Africa.
Hulled versus free-threshing wheat
Left: Naked wheat, Bread wheat Triticum aestivum; Right: Hulled wheat, Einkorn, Triticum monococcum. Note how the einkorn ear breaks down into intact spikelets.
The four wild species of wheat, along with the domesticated varieties einkorn, emmer, and spelt,
have hulls. This more primitive morphology (in evolutionary terms)
consists of toughened glumes that tightly enclose the grains, and (in
domesticated wheats) a semi-brittle rachis that breaks easily on
threshing. The result is that when threshed, the wheat ear breaks up
into spikelets. To obtain the grain, further processing, such as milling
or pounding, is needed to remove the hulls or husks. In contrast, in
free-threshing (or naked) forms such as durum wheat and common wheat,
the glumes are fragile and the rachis tough. On threshing, the chaff
breaks up, releasing the grains. Hulled wheats are often stored as
spikelets because the toughened glumes give good protection against
pests of stored grain.
Naming
Sack of wheat
Model of a wheat grain, Botanical Museum Greifswald
There are many botanical classification systems used for wheat species, discussed in a separate article on wheat taxonomy. The name of a wheat species from one information source may not be the name of a wheat species in another.
Within a species, wheat cultivars are further classified by wheat breeders and farmers in terms of:
- Growing season, such as winter wheat vs. spring wheat.
- Protein content. Bread wheat protein content ranges from 10% in some soft wheats with high starch contents, to 15% in hard wheats.
- The quality of the wheat protein gluten. This protein can determine the suitability of a wheat to a particular dish. A strong and elastic gluten present in bread wheats enables dough to trap carbon dioxide during leavening, but elastic gluten interferes with the rolling of pasta into thin sheets. The gluten protein in durum wheats used for pasta is strong but not elastic.
- Grain color (red, white or amber). Many wheat varieties are reddish-brown due to phenolic compounds present in the bran layer which are transformed to pigments by browning enzymes. White wheats have a lower content of phenolics and browning enzymes, and are generally less astringent in taste than red wheats. The yellowish color of durum wheat and semolina flour made from it is due to a carotenoid pigment called lutein, which can be oxidized to a colorless form by enzymes present in the grain.
Major cultivated species of wheat
Hexaploid species
- Common wheat or bread wheat (T. aestivum) – A hexaploid species that is the most widely cultivated in the world.
- Spelt (T. spelta) – Another hexaploid species cultivated in limited quantities. Spelt is sometimes considered a subspecies of the closely related species common wheat (T. aestivum), in which case its botanical name is considered to be T. aestivum ssp. spelta.
Tetraploid species
- Durum (T. durum) – A tetraploid form of wheat widely used today, and the second most widely cultivated wheat.
- Emmer (T. dicoccon) – A tetraploid species, cultivated in ancient times but no longer in widespread use.
- Khorasan (T. turgidum ssp. turanicum, also called T. turanicum) is a tetraploid wheat species. It is an ancient grain type; Khorasan refers to a historical region in modern-day Afghanistan and the northeast of Iran. This grain is twice the size of modern-day wheat and is known for its rich nutty flavor.
Diploid species
- Einkorn (T. monococcum) – A diploid species with wild and cultivated variants. Domesticated at the same time as emmer wheat.
Classes used in North America
The
named classes of wheat in English are more or less the same in Canada
as in the US, as broadly the same commercial cash crop strains can be
found in both.
The classes used in the United States are:
- Durum – Very hard, translucent, light-colored grain used to make semolina flour for pasta & bulghur; high in protein, specifically, gluten protein.
- Hard Red Spring – Hard, brownish, high-protein wheat used for bread and hard baked goods. Bread Flour and high-gluten flours are commonly made from hard red spring wheat. It is primarily traded at the Minneapolis Grain Exchange.
- Hard Red Winter – Hard, brownish, mellow high-protein wheat used for bread, hard baked goods and as an adjunct in other flours to increase protein in pastry flour for pie crusts. Some brands of unbleached all-purpose flours are commonly made from hard red winter wheat alone. It is primarily traded on the Kansas City Board of Trade. One variety is known as "turkey red wheat", and was brought to Kansas by Mennonite immigrants from Russia.
- Soft Red Winter – Soft, low-protein wheat used for cakes, pie crusts, biscuits, and muffins. Cake flour, pastry flour, and some self-rising flours with baking powder and salt added, for example, are made from soft red winter wheat. It is primarily traded on the Chicago Board of Trade.
- Hard White – Hard, light-colored, opaque, chalky, medium-protein wheat planted in dry, temperate areas. Used for bread and brewing.
- Soft White – Soft, light-colored, very low protein wheat grown in temperate moist areas. Used for pie crusts and pastry. Pastry flour, for example, is sometimes made from soft white winter wheat.
Red wheats may need bleaching; therefore, white wheats usually command higher prices than red wheats on the commodities market.
As a food
Wheat is used in a wide variety of foods.
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1,368 kJ (327 kcal) |
71.18 g
| |
| Sugars | 0.41 |
| Dietary fiber | 12.2 g |
1.54 g
| |
12.61 g
| |
| Vitamins | Quantity %DV† |
| Thiamine (B1) |
33%
0.383 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
10%
0.115 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
36%
5.464 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
19%
0.954 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
23%
0.3 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
10%
38 μg |
| Choline |
6%
31.2 mg |
| Vitamin E |
7%
1.01 mg |
| Vitamin K |
2%
1.9 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity %DV† |
| Calcium |
3%
29 mg |
| Iron |
25%
3.19 mg |
| Magnesium |
35%
126 mg |
| Manganese |
190%
3.985 mg |
| Phosphorus |
41%
288 mg |
| Potassium |
8%
363 mg |
| Sodium |
0%
2 mg |
| Zinc |
28%
2.65 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 13.1 g |
| Selenium | 70.7 µg |
| |
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database | |
Raw wheat can be ground into flour or, using hard durum wheat only, can be ground into semolina; germinated and dried creating malt; crushed or cut into cracked wheat; parboiled (or steamed), dried, crushed and de-branned into bulgur also known as groats. If the raw wheat is broken into parts at the mill, as is usually done, the outer husk or bran can be used several ways.
Wheat is a major ingredient in such foods as bread, porridge, crackers, biscuits, Muesli, pancakes, pasta and noodles, pies, pastries, pizza, polenta and semolina, cakes, cookies, muffins, rolls, doughnuts, gravy, beer, vodka, boza (a fermented beverage), and breakfast cereals.
In manufacturing wheat products, gluten is valuable to impart viscoelastic functional qualities in dough, enabling the preparation of diverse processed foods such as breads, noodles, and pasta that facilitate wheat consumption.
Nutrition
In 100 grams, wheat provides 327 kilocalories and is a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV) of multiple essential nutrients, such as protein, dietary fiber, manganese, phosphorus and niacin (table). Several B vitamins and other dietary minerals are in significant content. Wheat is 13% water, 71% carbohydrates, and 1.5% fat. Its 13% protein content is mostly gluten (75-80% of the protein in wheat).
Wheat proteins have a low quality for human nutrition, according to the new protein quality method (DIAAS) promoted by the Food and Agriculture Organization.
Though they contain adequate amounts of the other essential amino
acids, at least for adults, wheat proteins are deficient in the essential amino acid, lysine. Because the proteins present in the wheat endosperm (gluten proteins) are particularly poor in lysine, white flours are more deficient in lysine compared with whole grains. Significant efforts in plant breeding are being made to develop lysine-rich wheat varieties, without success as of 2017. Supplementation with proteins from other food sources (mainly legumes) is commonly used to compensate for this deficiency,
since the limitation of a single essential amino acid causes the others
to break down and become excreted, which is especially important during
the period of growth.
100 g (3.5 oz) of hard red winter wheat contain about 12.6 g (0.44 oz) of protein, 1.5 g (0.053 oz) of total fat, 71 g (2.5 oz) of carbohydrate (by difference), 12.2 g (0.43 oz) of dietary fiber, and 3.2 mg (0.00011 oz) of iron
(17% of the daily requirement); the same weight of hard red spring
wheat contains about 15.4 g (0.54 oz) of protein, 1.9 g (0.067 oz) of
total fat, 68 g (2.4 oz) of carbohydrate (by difference), 12.2 g
(0.43 oz) of dietary fiber, and 3.6 mg (0.00013 oz) of iron (20% of the
daily requirement).
Worldwide consumption
Wheat is grown on more than 218,000,000 hectares (540,000,000 acres),
a larger area than for any other crop. World trade in wheat is greater
than for all other crops combined. With rice, wheat is the world's most
favored staple food. It is a major diet component because of the wheat
plant's agronomic adaptability with the ability to grow from near arctic
regions to equator, from sea level to plains of Tibet, approximately
4,000 m (13,000 ft) above sea level. In addition to agronomic
adaptability, wheat offers ease of grain storage and ease of converting
grain into flour for making edible, palatable, interesting and
satisfying foods. Wheat is the most important source of carbohydrate in a
majority of countries.
The most common forms of wheat are white and red wheat. However,
other natural forms of wheat exist. Other commercially minor but
nutritionally promising species of naturally evolved wheat species
include black, yellow and blue wheat.
Health effects
Consumed worldwide by billions of people, wheat is a significant food for human nutrition, particularly in the least developed countries where wheat products are primary foods. When eaten as the whole grain, wheat is a healthy food source of multiple nutrients and dietary fiber
recommended for children and adults, in several daily servings
containing a variety of foods that meet whole grain-rich criteria. Dietary fiber may also help people feel full and therefore help with a healthy weight. Further, wheat is a major source for natural and biofortified nutrient supplementation, including dietary fiber, protein and dietary minerals.
Manufacturers of foods containing wheat as a whole grain in specified amounts are allowed a health claim
for marketing purposes in the United States, stating: "low fat diets
rich in fiber-containing grain products, fruits, and vegetables may
reduce the risk of some types of cancer,
a disease associated with many factors" and "diets low in saturated fat
and cholesterol and rich in fruits, vegetables, and grain products that
contain some types of dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, may reduce the risk of heart disease, a disease associated with many factors". The scientific opinion of the European Food Safety Authority
(EFSA) related to health claims on gut health/bowel function, weight
control, blood glucose/insulin levels, weight management, blood
cholesterol, satiety, glycaemic index, digestive function and
cardiovascular health is "that the food constituent, whole grain, (...)
is not sufficiently characterised in relation to the claimed health
effects" and "that a cause and effect relationship cannot be established
between the consumption of whole grain and the claimed effects
considered in this opinion."
Concerns
In genetically susceptible people, gluten – a major part of wheat protein – can trigger coeliac disease. Coeliac disease affects about 1% of the general population in developed countries. There is evidence that most cases remain undiagnosed and untreated. The only known effective treatment is a strict lifelong gluten-free diet.
While coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to wheat proteins, it is not the same as a wheat allergy. Other diseases triggered by eating wheat are non-coeliac gluten sensitivity which is estimated to affect 0.5% to 13% of the general population, and may result from a sensitivity to the fructan component of wheat. Other gluten-related disorders include gluten ataxia and dermatitis herpetiformis.
Commercial use
Harvested wheat grain that enters trade is classified according to grain properties for the purposes of the commodity markets.
Wheat buyers use these to decide which wheat to buy, as each class has
special uses, and producers use them to decide which classes of wheat
will be most profitable to cultivate.
Wheat is widely cultivated as a cash crop because it produces a good yield per unit area, grows well in a temperate climate even with a moderately short growing season, and yields a versatile, high-quality flour that is widely used in baking. Most breads are made with wheat flour, including many breads named for the other grains they contain, for example, most rye and oat
breads. The popularity of foods made from wheat flour creates a large
demand for the grain, even in economies with significant food surpluses.
Utensil made of wheat straw for loaves of bread
In recent years, low international wheat prices have often encouraged
farmers in the United States to change to more profitable crops. In
1998, the price at harvest of a 60 pounds (27 kg) bushel was $2.68 per. Some information providers, following CBOT practice, quote the wheat market in per ton denomination. A USDA report revealed that in 1998, average operating costs were $1.43 per bushel and total costs were $3.97 per bushel.
In that study, farm wheat yields averaged 41.7 bushels per acre (2.2435
metric ton/hectare), and typical total wheat production value was
$31,900 per farm, with total farm production value (including other
crops) of $173,681 per farm, plus $17,402 in government payments. There
were significant profitability differences between low- and high-cost
farms, mainly due to crop yield differences, location, and farm size.
Production and consumption
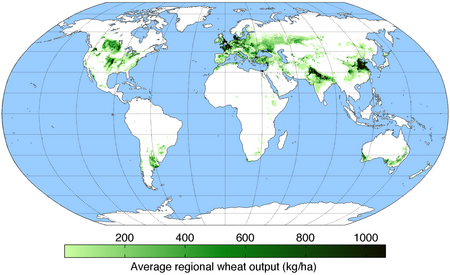
A map of worldwide wheat production.
The combine Claas Lexion 584 06833 is threshing the wheat. The combine crushes the chaff and blows it across the field.
The combine Claas Lexion 584 06833 mows, threshes, shreds the chaff and blows it across the field. At the same time the combine loads the threshed wheat onto a trailer while moving at full speed.
In 2016, global wheat production was 749 million tonnes.
Wheat is the primary food staple in North Africa and the Middle East,
and is growing in uses in Asia. Unlike rice, wheat production is more
widespread globally, though 47% of the world total in 2014 was produced
by just four countries – China, India, Russia and the United States
(table).
Historical factors
In
the 20th century, global wheat output expanded by about 5-fold, but
until about 1955 most of this reflected increases in wheat crop area,
with lesser (about 20%) increases in crop yields per unit area. After
1955 however, there was a ten-fold increase in the rate of wheat yield
improvement per year, and this became the major factor allowing global
wheat production to increase. Thus technological innovation and
scientific crop management with synthetic nitrogen fertilizer,
irrigation and wheat breeding were the main drivers of wheat output
growth in the second half of the century. There were some significant
decreases in wheat crop area, for instance in North America.
Better seed storage and germination ability (and hence a smaller
requirement to retain harvested crop for next year's seed) is another
20th-century technological innovation. In Medieval England, farmers
saved one-quarter of their wheat harvest as seed for the next crop,
leaving only three-quarters for food and feed consumption. By 1999, the
global average seed use of wheat was about 6% of output.
Several factors are currently slowing the rate of global
expansion of wheat production: population growth rates are falling while
wheat yields continue to rise, and the better economic profitability of
other crops such as soybeans and maize, linked with investment in
modern genetic technologies, has promoted shifts to other crops.
Farming systems
In 2014, the most productive crop yields for wheat were in Ireland, producing 10 tonnes per hectare.
In addition to gaps in farming system technology and knowledge, some
large wheat grain-producing countries have significant losses after
harvest at the farm and because of poor roads, inadequate storage
technologies, inefficient supply chains and farmers' inability to bring
the produce into retail markets dominated by small shopkeepers. Various
studies in India, for example, have concluded that about 10% of total
wheat production is lost at farm level, another 10% is lost because of
poor storage and road networks, and additional amounts lost at the
retail level.
In the Punjab region of India and Pakistan,
as well as North China, irrigation has been a major contributor to
increased grain output. More widely over the last 40 years, a massive
increase in fertilizer use together with the increased availability of
semi-dwarf varieties in developing countries, has greatly increased
yields per hectare.
In developing countries, use of (mainly nitrogenous) fertilizer
increased 25-fold in this period. However, farming systems rely on much
more than fertilizer and breeding to improve productivity. A good
illustration of this is Australian wheat growing in the southern winter
cropping zone, where, despite low rainfall (300 mm), wheat cropping is
successful even with relatively little use of nitrogenous fertilizer.
This is achieved by 'rotation cropping' (traditionally called the ley
system) with leguminous pastures and, in the last decade, including a canola crop in the rotations has boosted wheat yields by a further 25%.
In these low rainfall areas, better use of available soil-water (and
better control of soil erosion) is achieved by retaining the stubble
after harvesting and by minimizing tillage.
Geographical variation
| Country | millions of tonnes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
There are substantial differences in wheat farming, trading, policy,
sector growth, and wheat uses in different regions of the world.
The largest exporters of wheat in 2013 were, in order of exported
quantities: United States (33.2 million tonnes), Canada (19.8 million
tonnes), France (19.6 million tonnes), Australia (18 million tonnes),
and the Russian Federation (13.8 million tonnes).
The largest importers of wheat in 2013 were, in order of imported
quantities: Egypt (10.3 million tonnes), Brazil (7.3 million tonnes),
Indonesia (6.7 million tonnes), Algeria (6.3 million tonnes) and Japan
(6.2 million tonnes).
In the rapidly developing countries of Asia and Africa,
westernization of diets associated with increasing prosperity is leading
to growth in per capita demand for wheat at the expense of the other food staples.
In the past, there has been significant governmental intervention
in wheat markets, such as price supports in the US and farm payments in
the EU. In the EU, these subsidies have encouraged heavy use of
fertilizer inputs with resulting high crop yields. In Australia and
Argentina, direct government subsidies are much lower.
Most productive
The average annual world farm yield for wheat in 2014 was 3.3 tonnes per hectare (330 grams per square meter).
Ireland wheat farms were the most productive in 2014, with a nationwide
average of 10.0 tonnes per hectare, followed by the Netherlands (9.2),
and Germany, New Zealand and the United Kingdom (each with 8.6).
Futures contracts
Wheat futures are traded on the Chicago Board of Trade, Kansas City Board of Trade, and Minneapolis Grain Exchange, and have delivery dates in March (H), May (K), July (N), September (U), and December (Z).
Agronomy
Wheat spikelet with the three anthers sticking out
Crop development
Wheat
normally needs between 110 and 130 days between sowing and harvest,
depending upon climate, seed type, and soil conditions (winter wheat
lies dormant during a winter freeze). Optimal crop management requires
that the farmer have a detailed understanding of each stage of
development in the growing plants. In particular, spring fertilizers, herbicides, fungicides, and growth regulators
are typically applied only at specific stages of plant development. For
example, it is currently recommended that the second application of
nitrogen is best done when the ear (not visible at this stage) is about
1 cm in size (Z31 on Zadoks scale).
Knowledge of stages is also important to identify periods of higher
risk from the climate. For example, pollen formation from the mother
cell, and the stages between anthesis and maturity are susceptible to high temperatures, and this adverse effect is made worse by water stress.
Farmers also benefit from knowing when the 'flag leaf' (last leaf)
appears, as this leaf represents about 75% of photosynthesis reactions
during the grain filling period, and so should be preserved from disease
or insect attacks to ensure a good yield.
Several systems exist to identify crop stages, with the Feekes and Zadoks scales
being the most widely used. Each scale is a standard system which
describes successive stages reached by the crop during the agricultural
season.
Wheat at the anthesis stage. Face view (top) and side view (bottom) and wheat ear at the late milk
Diseases
Rust-affected wheat seedlings
There are many wheat diseases, mainly caused by fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Plant breeding
to develop new disease-resistant varieties, and sound crop management
practices are important for preventing disease. Fungicides, used to
prevent the significant crop losses from fungal disease, can be a
significant variable cost in wheat production. Estimates of the amount
of wheat production lost owing to plant diseases vary between 10–25% in
Missouri. A wide range of organisms infect wheat, of which the most important are viruses and fungi.
The main wheat-disease categories are:
- Seed-borne diseases: these include seed-borne scab, seed-borne Stagonospora (previously known as Septoria), common bunt (stinking smut), and loose smut. These are managed with fungicides.
- Leaf- and head- blight diseases: Powdery mildew, leaf rust, Septoria tritici leaf blotch, Stagonospora (Septoria) nodorum leaf and glume blotch, and Fusarium head scab.
- Crown and root rot diseases: Two of the more important of these are 'take-all' and Cephalosporium stripe. Both of these diseases are soil borne.
- Stem rust diseases: Caused by basidiomycete fungi e.g. Ug99
- Viral diseases: Wheat spindle streak mosaic (yellow mosaic) and barley yellow dwarf are the two most common viral diseases. Control can be achieved by using resistant varieties.
Pests
Wheat is used as a food plant by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (butterfly and moth) species including the flame, rustic shoulder-knot, setaceous Hebrew character and turnip moth.
Early in the season, many species of birds, including the long-tailed widowbird,
and rodents feed upon wheat crops. These animals can cause significant
damage to a crop by digging up and eating newly planted seeds or young
plants. They can also damage the crop late in the season by eating the
grain from the mature spike. Recent post-harvest losses in cereals
amount to billions of dollars per year in the United States alone, and
damage to wheat by various borers, beetles and weevils is no exception.
Rodents can also cause major losses during storage, and in major grain
growing regions, field mice numbers can sometimes build up explosively
to plague proportions because of the ready availability of food. To reduce the amount of wheat lost to post-harvest pests, Agricultural Research Service
scientists have developed an "insect-o-graph," which can detect insects
in wheat that are not visible to the naked eye. The device uses
electrical signals to detect the insects as the wheat is being milled.
The new technology is so precise that it can detect 5–10 infested seeds
out of 300,000 good ones. Tracking insect infestations in stored grain is critical for food safety as well as for the marketing value of the crop.