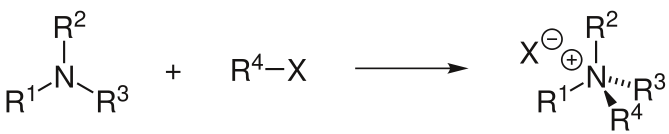Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion or a carbene (or their equivalents). An alkyl group is a piece of a molecule with the general formula CnH2n+1, where n is the integer depicting the number of carbons linked together. For example, a methyl group (n = 1, CH3) is a fragment of a methane molecule (CH4). Alkylating agents
use selective alkylation by adding the desired aliphatic carbon chain
to the previously chosen starting molecule. This is one of many known
chemical syntheses. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known
as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character.
In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline.
In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.
In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline.
In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.
Typical route for alkylation of benzene with ethylene and ZSM-5 as a heterogeneous catalyst
Nucleophilic alkylating agents
Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion (carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent bond
between the alkyl group and the electrophile. The counterion, which is a
cation such as lithium, can be removed and washed away in the work-up. Examples include the use of organometallic compounds such as Grignard (organomagnesium), organolithium, organocopper, and organosodium reagents. These compounds typically can add to an electron-deficient carbon atom such as at a carbonyl group. Nucleophilic alkylating agents can displace halide substituents on a carbon atom through the SN2 mechanism. With a catalyst, they also alkylate alkyl and aryl halides, as exemplified by Suzuki couplings.
The Kumada coupling employs both a nucleophilic alkylation step subsequent to the oxidative addition of the aryl halide (L = Ligand, Ar = Aryl).
The SN2 mechanism is not available for aryl substituents, where the
trajectory to attack the carbon atom would be inside the ring. Thus only
reactions catalyzed by organometallic catalysts are possible.
Electrophilic alkylating agents
C-alkylation
C-alkylation
is a process for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. For alkylation
at carbon, the electrophilicity of alkyl halides is enhanced by the
presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminium trichloride.
Lewis acids are particularly suited for C-alkylation. C-alkylation
can also be effected by alkenes in the presence of acids.
N-and P-alkylation
N- and P-alkylation are important processes for the formation of carbon-nitrogen and carbon-phosphorus bonds.
Amines are readily alkylated. The rate of alkylation follows the
order tertiary amine < secondary amine < primary amine. Typical
alkylating agents are alkyl halides. Industry often relies on green chemistry methods involving alkylation of amines with alcohols, the byproduct being water. Hydroamination is another green method for N-alkylation.
In the Menshutkin reaction, a tertiary amine is converted into a quaternary ammonium salt by reaction with an alkyl halide. Similar reactions occur when tertiary phosphines are treated with alkyl halides, the products being phosphonium salts.
S-alkylation
Thiols are readily alkylated to give thioethers.
The reaction is typically conducted in the presence of a base or using
the conjugate base of the thiol. Thioethers undergo alkylation to give sulfonium ions.
O-alkylation
- ROH + R'X → ROR'
When the alkylating agent is an alkyl halide, the conversion is called the Williamson ether synthesis.
Alcohols are also good alkylating agents in the presence of suitable
acid catalysts. For example, most methyl amines are prepared by
alkylation of ammonia with methanol. The alkylation of phenols is
particularly straightforward since it is subject to fewer competing
reactions.
More complex alkylation of a alcohols and phenols involve ethoxylation. Ethylene oxide is the alkylating group in this reaction.
Oxidative addition to metals
In the process called oxidative addition, low-valent metals often react with alkylating agents to give metal alkyls. This reaction is one step in the Cativa process for the synthesis of acetic acid from methyl iodide. Many cross coupling reactions proceed via oxidative addition as well.
Electrophilic alkylating agents
Electrophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl cation. Alkyl halides are typical alkylating agents. Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate and triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
are particularly strong electrophiles due to their overt positive
charge and an inert leaving group (dimethyl or diethyl ether). Dimethyl sulfate is intermediate in electrophilicity.
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is one of the most electrophilic alkylating agents.
Hazards
Electrophilic,
soluble alkylating agents are often toxic and carcinogenic, due to
their tendency to alkylate DNA. This mechanism of toxicity is relevant
to the function of anti-cancer drugs in the form of alkylating antineoplastic agents. Some chemical weapons such as mustard gas
function as alkylating agents. Alkylated DNA either does not coil or
uncoil properly, or cannot be processed by information-decoding enzymes.
Catalysts
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene is often catalyzed by aluminium trichloride.
Electrophilic alkylations use Lewis acids and Brønsted acids, sometimes both. Classically, Lewis acids, e.g., aluminium trichloride,
are employed when the alkyl halide are used. Brønsted acids are used
when alkylating with olefins. Typical catalysts are zeolites, i.e.
solid acid catalysts, and sulfuric acid. Silicotungstic acid is used to manufacture ethyl acetate by the alkylation of acetic acid by ethylene:
- C2H4 + CH3CO2H → CH3CO2C2H5
In biology
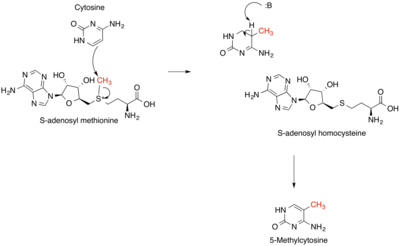
Methylation is the most common type of alkylation. Methylation in nature is often effected by vitamin B12- and radical-SAM-based enzymes.
The SN2-like methyl transfer reaction in DNA methylation. Only the SAM cofactor and cytosine base are shown for simplicity.
Commodity chemicals
Several commodity chemicals are produced by alkylation. Included are several fundamental benzene-based feedstocks such as ethylbenzene (precursor to styrene), cumene (precursor to phenol and acetone), linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (for detergents).
Sodium dodecylbenzene, obtained by alkylation of benzene with dodecene, is a precursor to linear alkylbenzene sulfonate detergents.
Oil refining
Typical acid-catalyzed route to 2,4-dimethylpentane.
In a conventional oil refinery, isobutane is alkylated with low-molecular-weight alkenes (primarily a mixture of propene and butene) in the presence of a Brønsted acid catalyst, which can include solid acids (zeolites). The catalyst protonates the alkenes (propene, butene) to produce carbocations, which alkylate isobutane. The product, called "alkylate", is composed of a mixture of high-octane, branched-chain paraffinic hydrocarbons (mostly isoheptane and isooctane). Alkylate is a premium gasoline blending stock because it has exceptional antiknock properties and is clean burning. Alkylate is also a key component of avgas. By combining fluid catalytic cracking, polymerization, and alkylation refineries can obtain a gasoline yield of 70 percent. The widespread use of sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid in refineries poses significant environmental risks.