European colonial officials pictured with native chiefs in Sierra Leone, 1934
European colonialism and colonization was the policy or practice of
acquiring full or partial political control over other societies and
territories, founding a colony, occupying it with settlers, and
exploiting it economically. Research suggests, the current conditions of
postcolonial countries have roots in colonial actions and policies. For example, colonial policies, such as the type of rule implemented, the nature of investments, and identity of the colonizers, are cited as impacting postcolonial states. Examination of the state-building process, economic development, and cultural norms and mores shows the direct and indirect consequences of colonialism on the postcolonial states.
History of colonisation and decolonization
The era of European colonialism
lasted from the 15th to 20th centuries and involved European powers
vastly extending their reach around the globe by establishing colonies
in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. The dismantling of European empires following World War II saw the process of decolonization begin in earnest. In 1941, President Franklin D. Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill jointly released the Atlantic Charter, which broadly outlined the goals of the U.S. and British governments. One of the main clauses of the charter acknowledged the right of all people to choose their own government. The document became the foundation for the United Nations and all of its components were integrated into the UN Charter, giving the organization a mandate to pursue global decolonization.
Varieties of colonialism
Historians generally distinguish two main varieties established by European colonials: the first is settler colonialism, where farms and towns were established by arrivals from Europe. Second, exploitation colonialism, purely extractive and exploitative colonies whose primary function was to develop economic exports. These frequently overlapped or existed on a spectrum.
Settler colonialism
Territories in the Americas claimed by a European great power in 1750
Settler colonialism is a form of colonisation where foreign citizens move into a region and create permanent or temporary settlements called colonies. The creation of settler colonies often resulted in the forced migration
of indigenous peoples to less desirable territories through forced
migration. This practice is exemplified in the colonies established in
what became the United States, New Zealand, Namibia, South Africa,
Canada, Brazil, Uruguay, Chile, Argentina, and Australia. Native
populations frequently suffered population collapse due to contact with
new diseases.
The resettlement of indigenous peoples frequently occurs along
demographic lines, but the central stimulus for resettlement is access
to desirable territory. Regions free of tropical disease with easy
access to trade routes were favorable.
When Europeans settled in these desirable territories, natives were
forced out and regional power was transferred to the colonialists. This
type of colonial behavior led to the disruption of local customary
practices and the transformation of socioeconomic systems. Ugandan academic Mahmood Mamdani
cites "the destruction of communal autonomy, and the defeat and
dispersal of tribal populations" as one primary factor in colonial
oppression.
Europeans justified settler colonialism with the belief that the
settlers were more capable of utilizing resources and land than the
indigenous populations due to the introduction of modern agricultural
practices. As agricultural expansion continued through the territories,
native populations were further displaced to clear fertile farmland.
Daron Acemoglu, James A. Robinson, and Simon Johnson
theorize that Europeans were more likely to form settler colonies in
areas where they would not face high mortality rates due to disease and
other exogenous factors.
Many settler colonies sought to establish European-like institutions
and practices that granted personal freedoms and allowed settlers to
become wealthy by engaging in trade.
Thus, jury trials, freedom from arbitrary arrest, and electoral
representation were implemented to allow settlers rights similar to
those enjoyed in Europe, though these rights were generally not extended to the indigenous people.
Exploitation colonialism
Comparison of Africa in the years 1880 and 1913
Exploitation colonialism is a form of colonisation where foreign
armies conquer a country in order to control and capitalize on its
natural resources and indigenous population. Acemoglu, Johnson, and
Robinson argue, "institutions [established by colonials] did not
introduce much protection for private property, nor did they provide
checks and balances against government expropriation. In fact, the main
purpose of the extractive state was to transfer as much of the resources
of the colony to the colonizer, with the minimum amount of investment
possible."
Since these colonies were created with the intent to extract resources,
colonial powers had no incentives to invest in institutions or
infrastructure that did not support their immediate goals. Thus,
Europeans established authoritarian regimes in these colonies, which had
no limits on state power.
The policies and practices carried out by King Leopold II of Belgium in the Congo Basin are an extreme example of exploitation colonialism. E. D. Morel
detailed the atrocities in multiple articles and books. Morel believed
the Belgian system that eliminated traditional, commercial markets in
favor of pure exploitation was the root cause of the injustice in the
Congo.
Under the "veil of philanthropic motive", King Leopold received the
consent of multiple international governments (including the United States, Great Britain, and France) to assume trusteeship of the vast region in order to support the elimination of the slave trade.
Leopold positioned himself as proprietor of an area totaling nearly one
million square miles, which was home to nearly 20 million Africans.
After establishing dominance in the Congo Basin, Leopold extracted large quantities of ivory, rubber, and other natural resources. It has been estimated that Leopold made 1.1 billion in today's dollars
by employing a variety of exploitative tactics. Soldiers demanded
unrealistic quantities of rubber be collected by African villagers, and
when these goals were not met, the soldiers held women hostage, beat or
killed the men, and burned crops.
These and other forced labor practices caused the birth rate to decline
as famine and disease spread. All of this was done at very little
monetary cost to Belgium. M. Crawford Young
observed, "[the Belgian companies] brought little capital – a mere 8000
pounds ... [to the Congo basin] – and instituted a reign of terror
sufficient to provoke an embarrassing public-protest campaign in Britain
and the United States at a time when the threshold of toleration for
colonial brutality was high."
The system of government implemented in the Congo by Belgium was
authoritarian and oppressive. Multiple scholars view the roots of
authoritarianism under Mobutu as the result of colonial practices.
Indirect and direct rule of the colonial political system
Systems of colonial rule can be broken into the binary
classifications of direct and indirect rule. During the era of
colonisation, Europeans were faced with the monumental task of
administrating the vast colonial territories around the globe. The
initial solution to this problem was direct rule,
which involves the establishment of a centralized European authority
within a territory run by colonial officials. In a system of direct
rule, the native population is excluded from all but the lowest level of
the colonial government. Mamdani defines direct rule as centralized despotism: a system where natives were not considered citizens.
By contrast, indirect rule integrates pre-established local elites and
native institutions into the administration of the colonial government. Indirect rule maintains good pre-colonial institutions and fosters development within the local culture.
Mamdani classifies indirect rule as “decentralized despotism,” where
day-to-day operations were handled by local chiefs, but the true
authority rested with the colonial powers.
Indirect rule
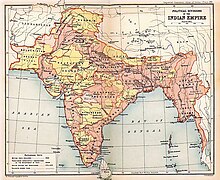
Map of the British Indian Empire. The princely states are in yellow.
In certain cases, as in India,
the colonial power directed all decisions related to foreign policy and
defense, while the indigenous population controlled most aspects of
internal administration.
This led to autonomous indigenous communities that were under the rule
of local tribal chiefs or kings. These chiefs were either drawn from the
existing social hierarchy or were newly minted by the colonial
authority. In areas under indirect rule, traditional authorities acted
as intermediaries for the “despotic” colonial rule, while the colonial government acted as an advisor and only interfered in extreme circumstances.
Often, with the support of the colonial authority, natives gained more
power under indirect colonial rule than they had in the pre-colonial
period.
Mamdani points out that indirect rule was the dominant form of
colonialism and therefore most who were colonized bore colonial rule
that was delivered by their fellow natives.
The purpose of indirect rule was to allow natives to govern their
own affairs through “customary law.” In practice though, the native
authority decided on and enforced its own unwritten rules with the
support of the colonial government. Rather than following the rule of law, local chiefs enjoyed judicial, legislative, executive, and administrative power in addition to legal arbitrariness.
Direct rule
European colonial women being carried in hammocks by natives in Ouidah, Benin (known as French Dahomey during this period).
In systems of direct rule, Europeans colonial officials oversaw all
aspects of governance, while natives were placed in an entirely
subordinate role. Unlike indirect rule, the colonial government did not
convey orders through local elites, but rather oversaw administration
directly. European laws and customs were imported to supplant
traditional power structures. Joost van Vollenhoven, Governor-General of French West Africa,
1917-1918, described the role of the traditional chiefs in by saying,
“his functions were reduced to that of a mouthpiece for orders emanating
from the outside…[The chiefs] have no power of their own of any kind.
There are not two authorities in the cercle, the French authority and the native authority; there is only one.”
The chiefs were therefore ineffective and not highly regarded by the
indigenous population. There were even instances where people under
direct colonial rule secretly elected a real chief in order to retain
traditional rights and customs.
Direct rule deliberately removed traditional power structures in
order to implement uniformity across a region. The desire for regional
homogeneity was the driving force behind the French colonial doctrine of Assimilation. The French style of colonialism stemmed from the idea that the French Republic was a symbol of universal equality. As part of a civilizing mission,
the European principles of equality were translated into legislation
abroad. For the French colonies, this meant the enforcement of the
French penal code, the right to send a representative to parliament, and imposition of tariff
laws as a form of economic assimilation. Requiring natives to
assimilate in these and other ways, created an ubiquitous,
European-style identity that made no attempt to protect native
identities.
Indigenous people living in colonized societies were obliged to obey
European laws and customs or be deemed “uncivilized” and denied access
to any European rights.
Comparative outcomes between indirect and direct rule
Both direct and indirect rule have persistent, long term effects on the success of former colonies. Lakshmi Iyer, of Harvard Business School,
conducted research to determine the impact type of rule can have on a
region, looking at postcolonial India, where both systems were present
under British rule.
Iyer's findings suggests that regions which had previously been ruled
indirectly were generally better-governed and more capable of
establishing effective institutions than areas under direct British
rule. In the modern postcolonial period, areas formerly ruled directly
by the British perform worse economically and have significantly less
access to various public goods, such as health care, public infrastructure, and education.
In his book Citizen and Subject: Contemporary Africa and the Legacy of Colonialism, Mamdani claims the two types of rule were each sides of the same coin.
He explains that colonialists did not exclusively use one system of
rule over another. Instead, European powers divided regions along
urban-rural lines and instituted separate systems of government in each
area. Mamdani refers to the formal division of rural and urban natives
by colonizers as the “bifurcated state.” Urban areas were ruled directly
by the colonizers under an imported system of European law, which did
not recognize the validity of native institutions.
In contrast, rural populations were ruled indirectly by customary and
traditional law and were therefore subordinate to the “civilized” urban
citizenry. Rural inhabitants were viewed as “uncivilized” subjects and
were deemed unfit to receive the benefits of citizenship. The rural
subjects, Mamdani observed, had only a “modicum of civil rights,” and
were entirely excluded from all political rights.
Mamdani argues that current issues in postcolonial states are the
result of colonial government partition, rather than simply poor
governance as others have claimed.
Current systems — in Africa and elsewhere — are riddled with an
institutional legacy that reinforces a divided society. Using the
examples of South Africa
and Uganda, Mamdani observed that, rather than doing away with the
bifurcated model of rule, postcolonial regimes have reproduced it.
Although he uses only two specific examples, Mamdani maintains that
these countries are simply paradigms representing the broad
institutional legacy colonialism left on the world.
He argues that modern states have only accomplished "deracialization"
and not democratization following their independence from colonial rule.
Instead of pursuing efforts to link their fractured society,
centralized control of the government stayed in urban areas and reform
focused on “reorganizing the bifurcated power forged under colonialism.”
Native authorities that operated under indirect rule have not been
brought into the mainstream reformation process; instead, development
has been “enforced” on the rural peasantry.
In order to achieve autonomy, successful democratization, and good
governance, states must overcome their fundamental schisms: urban versus
rural, customary versus modern, and participation versus
representation.
Colonial actions and their impacts
European
colonizers engaged in various actions around the world that had both
short term and long term consequences for the colonized. Numerous
scholars have attempted to analyze and categorize colonial activities by
determining if they have positive or negative outcomes. Stanley Engerman and Kenneth Sokoloff
categorized activities, which were driven by regional factor
endowments, by determining whether they were associated with high or low
levels of economic development.
Acemoglu, Johnson, and Robinson attempted to understand what
institutional changes caused previously rich countries to become poor
after colonization.
Melissa Dell documented the persistent, damaging effects of colonial
labor exploitation under the mit'a mining system in Peru; showing
significant differences in height and road access between previous mit'a
and non-mit'a communities.
Miriam Bruhn and Francisco A. Gallego employed a simple tripartite
classification: good, bad, and ugly. Regardless of the system of
classification, the fact remains, colonial actions produced varied
outcomes which continue to be relevant.
In trying to assess the legacy of colonization, some researchers
have focused on the type of political and economic institutions that
existed before the arrival of Europeans. Heldring and Robinson conclude
that while colonization in Africa had overall negative consequences for
political and economic development in areas that had previous
centralized institutions or that hosted white settlements, it possibly
had a positive impact in areas that were virtually stateless, like South
Sudan or Somalia.
In a complementary analysis, Gerner Hariri observed that areas outside
Europe which had State-like institutions before 1500 tend to have less
open political systems today. According to the scholar, this is due to
the fact that during the colonization, European liberal institutions
were not easily implemented.
Beyond the military and political advantages, it is possible to
explain the domination of European countries over non-European areas by
the fact that capitalism did not emerge as the dominant economic
institution elsewhere. As Ugo Pipitone argues, prosperous economic
institutions that sustain growth and innovation did not prevail in areas
like China, the Arab world, or Mesoamerica because of the excessive
control of these proto-States on private matters.
Reorganization of borders
Defining borders
Throughout
the era of European colonization, those in power routinely partitioned
land masses and created borders that are still in place today. It has
been estimated that Britain and France traced almost 40% of the entire
length of today's international boundaries.
Sometimes boundaries were naturally occurring, like rivers or
mountains, but other times these borders were artificially created and
agreed upon by colonial powers. The Berlin Conference of 1884 systemized European colonization in Africa and is frequently acknowledged as the genesis of the Scramble for Africa.
The Conference implemented the Principle of Effective Occupation in
Africa which allowed European states with even the most tenuous
connection to an African region to claim dominion over its land,
resources, and people. In effect, it allowed for the arbitrary
construction of sovereign borders in a territory where they had never
previously existed.
Jeffrey Herbst
has written extensively on the impact of state organization in Africa.
He notes, because the borders were artificially created, they generally
do not conform to “typical demographic, ethnographic, and topographic
boundaries.” Instead, they were manufactured by colonialists to advance
their political goals.
This led to large scale issues, like the division of ethnic groups; and
small scale issues, such as families’ homes being separated from their
farms.
William F. S. Miles of Northeastern University,
argues that this perfunctory division of the entire continent created
expansive ungoverned borderlands. These borderlands persist today and
are havens for crimes like human trafficking and arms smuggling.
Modern preservation of the colonially defined borders
Herbst
notes a modern paradox regarding the colonial borders in Africa: while
they are arbitrary there is a consensus among African leaders that they
must be maintained. Organization of African Unity in 1963 cemented
colonial boundaries permanently by proclaiming that any changes made
were illegitimate. This, in effect, avoided readdressing the basic injustice of colonial partition,
while also reducing the likelihood of inter-state warfare as
territorial boundaries were considered immutable by the international
community.
Modern national boundaries are thus remarkably invariable, though
the stability of the nation states has not followed in suit. Some
African states are plagued by internal issues such as inability to
effectively collect taxes and weak national identities. Lacking any
external threats to their sovereignty, these countries have failed to
consolidate power, leading to weak or failed states.
Though the colonial boundaries sometimes caused internal strife
and hardship, some present day leaders benefit from the desirable
borders their former colonial overlords drew. For example, Nigeria's
inheritance of an outlet to the sea — and the trading opportunities a
port affords — gives the nation a distinct economic advantage over its
neighbor, Niger. Effectively, the early carving of colonial space turned naturally occurring factor endowments into state controlled assets.
Differing colonial investments
When
European colonials entered a region, they invariably brought new
resources and capital management. Different investment strategies were
employed, which included focuses on health, infrastructure, or
education. All colonial investments have had persistent effects on
postcolonial societies, but certain types of spending have proven to be
more beneficial than others. French economist Elise Huillery conducted research to determine specifically what types of public spending
were associated with high levels of current development. Her findings
were twofold. First, Huillery observes that the nature of colonial
investments can directly influence current levels of performance.
Increased spending in education lead to higher school attendance;
additional doctors and medical facilities decreased preventable illnesses
in children; and a colonial focus on infrastructure translated into
more modernized infrastructure today. Adding to this, Huillery also
learned that early colonial investments instituted a pattern of
continued spending that directly influenced the quality and quantity of public goods available today.
Land, property rights, and labour
Land and property rights
According to Mahmood Mamdani, prior to colonization, indigenous societies did not necessarily consider land private property.
Alternately, land was a communal resources that everyone could utilize.
Once natives began interacting with colonial settlers, a long history
of land abuse followed. Extreme examples of this include Trail of Tears, a series of forced relocations of Native Americans following the Indian Removal Act of 1830, and the apartheid system in South Africa.
Australian anthropologist Patrick Wolfe points out that in these
instances, natives were not only driven off land, but the land was then
transferred to private ownership. He believes that the “frenzy for
native land” was due to economic immigrants that belonged to the ranks
of Europe's landless.
Making seemingly contradictory argument, Acemoglu, Johnson, and Robinson view strong property rights and ownership as an essential component of institutions that produce higher per capita income.
They expand on this by saying property rights give individuals the
incentive to invest, rather than stockpile, their assets. While this may
appear to further encourage colonialists to exert their rights through
exploitative behaviors, instead it offers protection to native
populations and respects their customary ownership laws. Looking broadly
at the European colonial experience, Acemoglu, Johnson, and Robinson
explain that exploitation of natives transpired when stable property
rights intentionally did not exist. These rights were never implemented
in order to facilitate the predatory extraction of resources from
indigenous populations. Bringing the colonial experience to the present
that, they maintain that broad property rights set the stage for the
effective institutions that are fundamental to strong democratic
societies. An example of Acemoglu, Robinson and Johnson hypothesis is in the work of La Porta, et al. In a study of the legal systems in various countries, La Porta, et al.
found that in those places that were colonized by the United Kingdom
and kept its common-law system, the protection of property right is
stronger compared to the countries that kept the French civil law.
In the case of India, Abhijit Banerjee and Lakshmi Iyer found
divergent legacies of the British land tenure system in India. The areas
where the property rights over the land were given to landlords
registered lower productivity and agricultural investments in
post-Colonial years compared to areas where land tenure was dominated by
cultivators. The former areas also have lower levels of investment in
health and education.
Labour exploitation
Prominent Guyanese scholar and political activist Walter Rodney wrote at length about the economic exploitation of Africa by the colonial powers. In particular, he saw labourers as an especially abused group. While a capitalist system almost always employs some form of wage labour,
the dynamic between labourers and colonial powers left the way open for
extreme misconduct. According to Rodney, African workers were more
exploited than Europeans because the colonial system produced a complete
monopoly on political power and left the working class small and
incapable of collective action. Combined with deep-seated racism,
native workers were presented with impossible circumstances. The racism
and superiority felt by the colonizers enabled them to justify the
systematic underpayment of Africans even when they were working
alongside European workers. Colonialists further defended their
disparate incomes by claiming a higher cost of living. Rodney challenged
this pretext and asserted the European quality of life and cost of living
were only possible because of the exploitation of the colonies and
African living standards were intentionally depressed in order to
maximize revenue. In its wake, Rodney argues colonialism left Africa
vastly underdeveloped and without a path forward.
Societal consequences of colonialism
Ethnic identity
The
colonial changes to ethnic identity have been explored from the
political, sociological, and psychological perspectives. In his book The Wretched of the Earth, Afro-Caribbean psychiatrist and revolutionary Frantz Fanon claims the colonized must “ask themselves the question constantly: ‘who am I?’"
Fanon uses this question to express his frustrations with fundamentally
dehumanizing character of colonialism. Colonialism in all forms, was
rarely an act of simple political control. Fanon argues the very act of
colonial domination has the power to warp the personal and ethnic
identities of natives because it operates under the assumption of
perceived superiority. Natives are thus entirely divorced from their
ethnic identities, which has been replaced by a desire to emulate their
oppressors.
Ethnic manipulation manifested itself beyond the personal and internal spheres. Scott Straus from the University of Wisconsin describes the ethnic identities that partially contributed to the Rwandan genocide. In April 1994, following the assassination of Rwanda's President Juvénal Habyarimana, Hutus of Rwanda turned on their Tutsi
neighbors and slaughtered between 500,000 and 800,000 people in just
100 days. While politically this situation was incredibly complex, the
influence ethnicity had on the violence cannot be ignored. Before the
German colonization of Rwanda, the identities of Hutu and Tutsi were not
fixed. Germany ruled Rwanda through the Tutsi dominated monarchy and
the Belgians continued this following their takeover. Belgian rule
reinforced the difference between Tutsi and Hutu. Tutsis were deemed
superior and were propped up as a ruling minority supported by the
Belgians, while the Hutu were systematically repressed. The country's
power later dramatically shifted following the so-called Hutu
Revolution, during which Rwanda gained independence from their
colonizers and formed a new Hutu-dominated government. Deep-seated
ethnic tensions did not leave with the Belgians. Instead, the new
government reinforced the cleavage.
Civil society
Joel Migdal of the University of Washington
believes weak postcolonial states have issues rooted in civil society.
Rather than seeing the state as a singular dominant entity, Migdal
describes “weblike societies” composed of social organizations. These
organizations are a melange of ethnic, cultural, local, and familial
groups and they form the basis of our society. The state is simply one
actor in a much larger framework. Strong states are able to effectively
navigate the intricate societal framework and exert social control over
people's behavior. Weak states, on the other hand, are lost amongst the
fractionalized authority of a complex society.
Migdal expands his theory of state-society relations by examining Sierra Leone. At the time of Migdal's publication (1988), the country's leader, President Joseph Saidu Momoh, was widely viewed as weak and ineffective. Just three years later, the country erupted into civil war,
which continued for nearly 11 years. The basis for this tumultuous
time, in Migdal's estimation, was the fragmented social control
implemented by British colonizers. Using the typical British system of
indirect rule, colonizers empowered local chiefs to mediate British rule
in the region, and in turn, the chiefs exercised social control. After
achieving independence from Great Britain, the chiefs remained deeply
entrenched and did not allow for the necessary consolidation of power
needed to build a strong state. Migdal remarked, “Even with all the
resources at their disposal, even with the ability to eliminate any
single strongman, state leaders found themselves severely limited.”
It is necessary for the state and society to form a mutually
beneficially symbiotic relationship in order for each to thrive. The
peculiar nature of postcolonial politics makes this increasingly
difficult.
Linguistic Discrimination
In settler colonies, indigenous languages were often lost either as
indigenous populations were decimated by war and disease, or as
aboriginal tribes mixed with colonists. On the other hand, in exploitation colonies such as India, colonial languages were usually only taught to a small local elite.
The linguistic differences between the local elite and other locals
exacerbated class stratification, and also increased inequality in
access to education, industry and civic society in postcolonial states.
Ecological impacts of colonialism
European colonialism spread contagious diseases between Europeans and subjugated peoples.
Countering disease
The Dutch Public Health Service provides medical care for the native people of the Dutch East Indies, May 1946
The Spanish Crown organised a mission (the Balmis expedition) to transport the smallpox vaccine and establish mass vaccination programs in colonies in 1803. By 1832, the federal government of the United States established a smallpox vaccination program for Native Americans. Under the direction of Mountstuart Elphinstone a program was launched to increase smallpox vaccination in India.
From the beginning of the 20th century onwards, the elimination
or control of disease in tropical countries became a necessity for all
colonial powers. The sleeping sickness epidemic in Africa was arrested due to mobile teams systematically screening millions of people at risk. The biggest population increases in human history occurred during the 20th century due to the decreasing mortality rate in many countries due to medical advances.
Colonial policies contributing to indigenous deaths from disease
St. Paul's Indian Industrial School, Middlechurch, Manitoba, Canada, 1901. This school was part of the Canadian Indian residential school system.
John S. Milloy published evidence indicating that Canadian
authorities had intentionally concealed information on the spread of
disease in his book A National Crime: The Canadian Government and the Residential School System, 1879 to 1986 (1999). According to Milloy, the Government of Canada
was aware of the origins of many diseases but maintained a secretive
policy. Medical professionals had knowledge of this policy, and further,
knew it was causing a higher death rate among indigenous people, yet
the policy continued.
Evidence suggests, government policy was not to treat natives
infected with tuberculosis or smallpox, and native children infected
with smallpox and tuberculosis
were deliberately sent back to their homes and into native villages by
residential school administrators. Within the residential schools, there
was no segregation of sick students from healthy students, and students
infected with deadly illnesses were frequently admitted to the schools,
where infections spread among the healthy students and resulted in
deaths; death rates were at least 24% and as high as 69%.
Tuberculosis was the leading cause of death in Europe and North
America in the 19th century, accounting for about 40% of working-class
deaths in cities,
and by 1918 one in six deaths in France were still caused by
tuberculosis. European governments, and medical professionals in Canada,
were well aware that tuberculosis and smallpox were highly contagious,
and that deaths could be prevented by taking measures to quarantine
patients and inhibit the spread of the disease. They failed to do this,
however, and imposed laws that in fact ensured that these deadly
diseases spread quickly among the indigenous population. Despite the
high death rate among students from contagious disease, in 1920 the
Canadian government made attendance at residential schools mandatory for
native children, threatening non-compliant parents with fines and
imprisonment. John S. Milloy argued that these policies regarding
disease were not conventional genocide, but rather policies of neglect
aimed at assimilating natives.
Some historians, such as Roland Chrisjohn, director of Native Studies at St. Thomas University,
have argued that some European colonists, having discovered that
indigenous populations were not immune to certain diseases, deliberately
spread diseases to gain military advantages and subjugate local
peoples. In his book The Circle Game: Shadows and Substance in the Indian Residential School Experience in Canada, Chrisjohn argues that the Canadian government followed a deliberate policy amounting to genocide against native populations. British officers, including the top British commanding generals Amherst and Gage, ordered, sanctioned, paid for and conducted the use of smallpox against the Native Americans during the siege of Fort Pitt.
Historian David Dixon recognized, "there is no doubt that British
military authorities approved of attempts to spread smallpox among the
enemy." Russell Thornton went further by saying, "it was deliberate British policy to infect the indians with smallpox".
While the exact effectiveness of the British attempts at infecting
Native Americans is unknown, the outbreak of smallpox among the Indians
has been documented.
Letters and journals from the colonial period show that British
authorities discussed and agreed to the deliberate distribution of
blankets infected with smallpox among Indian tribes in 1763, and an incident involving William Trent
and Captain Ecuyer has been regarded as one of the first instances of
the use of smallpox as a biological weapon in the history of warfare.
Historic debates surrounding colonialism
Bartolomé de Las Casas (1484–1566) was the first Protector of the Indians appointed by the Spanish crown.
During his time in the Spanish West Indies, he witnessed many of the
atrocities committed by Spanish colonists against the natives.
After this experience, he reformed his view on colonialism and
determined the Spanish people would suffer divine punishment if the
gross mistreatment in the Indies continued. De Las Casas detailed his
opinion in his book The Destruction of the Indies: A Brief Account (1552).
During the sixteenth century, Spanish priest and philosopher Francisco Suarez (1548–1617) expressed his objections to colonialism in his work De Bello et de Indis (On War and the Indies). In this text and others, Suarez supported natural law
and conveyed his beliefs that all humans had rights to life and
liberty. Along these lines, he argued for the limitation of the imperial
powers of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor by underscoring the natural rights of indigenous people. Accordingly, native inhabitants of the colonial Spanish West Indies deserved independence and each island should be considered a sovereign state with all the legal powers of Spain.
Denis Diderot was openly critical of ethnocentrism and the colonisation of Tahiti. In a series of philosophical dialogues entitled Supplément au voyage de Bougainville
(1772), Diderot imagines several conversations between Tahitians and
Europeans. The two speakers discuss their cultural differences, which
acts as a critique of European culture.
Modern theories of colonialism
The
effects of European colonialism have consistently drawn academic
attention in the decades since decolonization. New theories continue to
emerge. The field of colonial and postcolonial studies has been
implemented as a major in multiple universities around the globe.
Dependency theory
Dependency theory is an economic theory
which postulated that advanced and industrialized “metropolitan”
nations have been able to develop because of the existence of
less-developed “satellite” states. Satellite nations are anchored to,
and subordinate to, metropolitan countries because of the international
division of labor. Satellite countries are thus dependent on
metropolitan states and incapable of charting their own economic path.
The theory was introduced in the 1950s by Raul Prebisch, Director
of the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America after
observing that economic growth in wealthy countries did not translate
into economic growth in poor countries. Dependency theorists believe this is due to the import-export relationship between rich and poor countries. Walter Rodney, in his book How Europe Underdeveloped Africa,
used this framework when observing the relationship between European
trading companies and African peasants living in postcolonial states.
Through the labour of peasants, African countries are able to gather
large quantities of raw materials.
Rather than being able to export these materials directly to Europe,
states must work with a number of trading companies, who collaborated to
keep purchase prices low. The trading companies then sold the materials
to European manufactures at inflated prices. Finally the manufactured
goods were returned to Africa, but with prices so high, that labourers
were unable to afford them. This led to a situation where the
individuals who labored extensively to gather raw materials were unable
to benefit from the finished goods.
Neocolonialism
Neocolonialism is the continued economic and cultural control of
countries that have been decolonized. The first documented use of the
term was by Former President of Ghana Kwame Nkrumah in the 1963 preamble of the Organization of African States. Nkrumah expanded the concept of neocolonialism in the book Neo-Colonialism, the Last Stage of Imperialism
(1965). In Nkrumah's estimation, traditional forms of colonialism have
ended, but many African states are still subject to external political
and economic control by Europeans. Neocolonialism is related to dependency theory in that they both acknowledge the financial exploitation of poor counties by the rich, but neocolonialism also includes aspects of cultural imperialism. Rejection of cultural neocolonialism formed the basis of négritude
philosophy, which sought to eliminate colonial and racist attitudes by
affirming the values of "the black world" and embracing "blackness".
Benign colonialism
Dutch colonial administrator of the South Moluccas, picture taken 1940.
Benign colonialism is a form of colonialism in which benefits
allegedly outweigh the negatives for indigenous populations whose lands,
resources, rights and freedoms come under the control of a colonising
nation-state. The historical source for the concept of benign
colonialism resides with John Stuart Mill (1806-1873), who served as chief examiner of the British East India Company - dealing with British interests in India
- in the 1820s and 1830s. Mill's most well-known essays on benign
colonialism appear in "Essays on some Unsettled Questions of Political
Economy."
Mill's view contrasted with Burkean orientalists.
Mill promoted the training of a corps of bureaucrats indigenous to
India who could adopt the modern liberal perspective and values of
19th-century Britain. Mill predicted this group's eventual governance of India would be based on British values and perspectives.
Advocates of the concept of benign colonialism cite improved
standards in health and education, in employment opportunities, in
liberal markets, in the development of natural resources and in
introduced governance.
The first wave of benign colonialism lasted from c. 1790-1960,
according to Mill's concept. The second wave included neocolonial
policies exemplified in Hong Kong, where unfettered expansion of the market created a new form of benign colonialism. Political interference and military intervention in independent nation-states, such as Iraq,
is also discussed under the rubric of benign colonialism in which a
foreign power preempts national governance to protect a higher concept
of freedom. The term is also used in the 21st century to refer to US, French and Chinese market activities in African countries with massive quantities of underdeveloped nonrenewable.
These views have support from some academics. Economic historian Niall Ferguson (born 1964) argues that empires
can be a good thing provided that they are "liberal empires". He cites
the British Empire as being the only example of a "liberal empire" and
argues that it maintained the rule of law, benign government, free trade and, with the abolition of slavery, free labour.
Historian Rudolf von Albertini agrees that, on balance, colonialism can
be good. He argues that colonialism was a mechanism for modernisation
in the colonies and imposed a peace by putting an end to tribal warfare.
Historians L. H. Gann and Peter Duignan have also argued that
Africa probably benefited from colonialism on balance. Although it had
its faults, colonialism was probably "one of the most efficacious
engines for cultural diffusion in world history".
These views, however, are controversial and are rejected by some who,
on balance, see colonialism as bad. The economic historian David Kenneth Fieldhouse
has taken a kind of middle position, arguing that the effects of
colonialism were actually limited and their main weakness was not in
deliberate underdevelopment but in what it failed to do. Niall Ferguson agrees with his last point, arguing that colonialism's main weaknesses were sins of omission. Marxist historian Bill Warren has argued that whilst colonialism may be bad because it relies on force, he views it as being the genesis of Third World development.
History records few cases where two or more peoples have met and
mingled without generating some sort of friction. The clearest cases of
"benign" colonialism occur where the target exploited land is minimally
populated (as with Iceland in the 9th century) or completely terra nullius (such as the Falkland Islands).