 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epigen, Glycyron |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic and by intestinal bacteria |
| Elimination half-life | 6.2-10.2 hours |
| Excretion | Faeces, urine (0.31-0.67%) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | E958 (glazing agents, ...) |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.350 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
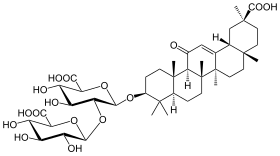
| Formula | C42H62O16 |
| Molar mass | 822.942 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Solubility in water | 1-10 mg/mL (20 °C) |
Glycyrrhizin (or glycyrrhizic acid or glycyrrhizinic acid) is the chief sweet-tasting constituent of Glycyrrhiza glabra (liquorice) root. Structurally, it is a saponin used as an emulsifier and gel-forming agent in foodstuffs and cosmetics. Its aglycone is enoxolone.
Adverse effects
The most widely reported side effect of glycyrrhizin use via consumption of black licorice is reduction of blood potassium levels, which can affect body fluid balance and function of nerves. Chronic consumption of black licorice, even in moderate amounts, is associated with an increase in blood pressure, may cause irregular heart rhythm, and may have adverse interactions with prescription drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral ingestion, glycyrrhizin is first hydrolysed
to 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (enoxolone) by intestinal bacteria. After
complete absorption from the gut, 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid is metabolised
to 3β-monoglucuronyl-18β-glycyrrhetinic acid in the liver. This
metabolite then circulates in the bloodstream. Consequently, its oral
bioavailability is poor. The main part is eliminated by bile and only a minor part (0.31–0.67%) by urine.
After oral ingestion of 600 mg of glycyrrhizin the metabolite appeared
in urine after 1.5 to 14 hours. Maximal concentrations (0.49 to
2.69 mg/l) were achieved after 1.5 to 39 hours and metabolite can be
detected in the urine after 2 to 4 days.
Flavouring properties
Glycyrrhizin is obtained as an extract from licorice root after maceration and boiling in water. Licorice extract (glycyrrhizin) is sold in the United States as a liquid, paste, or spray-dried powder. When in specified amounts, it is approved for use as a flavor and aroma in manufactured foods, beverages, candies, dietary supplements, and seasonings. It is 30 to 50 times as sweet as sucrose (table sugar).
