An emergent virus (or emerging virus) is a virus that is either newly appeared, notably increasing in incidence/geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious diseases and raise public health challenges globally, given their potential to cause outbreaks of disease which can lead to epidemics and pandemics. As well as causing disease, emergent viruses can also have severe economic implications. Recent examples include the SARS-related coronaviruses, which have caused the 2002-2004 outbreak of SARS (SARS-CoV-1) and the 2019–21 pandemic of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Other examples include the human immunodeficiency virus which causes HIV/AIDS; the viruses responsible for Ebola; the H5N1 influenza virus responsible for avian flu; and H1N1/09, which caused the 2009 swine flu pandemic (an earlier emergent strain of H1N1 caused the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic). Viral emergence in humans is often a consequence of zoonosis, which involves a cross-species jump of a viral disease into humans from other animals. As zoonotic viruses exist in animal reservoirs, they are much more difficult to eradicate and can therefore establish persistent infections in human populations.
Emergent viruses should not be confused with re-emerging viruses or newly detected viruses. A re-emerging virus is generally considered to be a previously appeared virus that is experiencing a resurgence, for example measles. A newly detected virus is a previously unrecognized virus that had been circulating in the species as endemic or epidemic infections. Newly detected viruses may have escaped classification because they left no distinctive clues, and/or could not be isolated or propagated in cell culture. Examples include human rhinovirus (a leading cause of common colds which was first identified in 1956), hepatitis C (eventually identified in 1989), and human metapneumovirus (first described in 2001, but thought to have been circulating since the 19th century). As the detection of such viruses is technology driven, the number reported is likely to expand.
Zoonosis
Given the rarity of spontaneous development of new virus species, the most frequent cause of emergent viruses in humans is zoonosis. This phenomenon is estimated to account for 73% of all emerging or re-emerging pathogens, with viruses playing a disproportionately large role. RNA viruses are particularly frequent, accounting for 37% of emerging and re-emerging pathogens. A broad range of animals - including wild birds, rodents and bats - are associated with zoonotic viruses. It is not possible to predict specific zoonotic events that may be associated with a particular animal reservoir at any given time.
Zoonotic spillover can either result in self-limited 'dead-end' infections, in which no further human-human transmission occurs (as with the rabies virus), or in infectious cases, in which the zoonotic pathogen is able to sustain human-human transmission (as with the Ebola virus). If the zoonotic virus is able to maintain successful human-human transmission, an outbreak may occur. Some spillover events can also result in the virus adapting exclusively for human infection (as occurred with the HIV virus), in which case humans become a new reservoir for the pathogen.
A successful zoonotic 'jump' depends on human contact with an animal harbouring a virus variant that is able to infect humans. In order to overcome host-range restrictions and sustain efficient human-human transmission, viruses originating from an animal reservoir will normally undergo mutation, genetic recombination and reassortment. Due to their rapid replication and high mutation rates, RNA viruses are more likely to successfully adapt for invasion of a new host population.
Examples of animal sources
Bats
While bats are essential members of many ecosystems, they are also frequently implicated as frequent sources of emerging virus infections. Their immune systems have evolved in such a way as to suppress any inflammatory response to viral infections, thereby allowing them to become tolerant hosts for evolving viruses, and consequently provide major reservoirs of zoonotic viruses. They are associated with more zoonotic viruses per host species than any other mammal, and molecular studies have demonstrated that they are the natural hosts for several high-profile zoonotic viruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronaviruses and Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever filoviruses. In terms of their potential for spillover events, bats have taken over the leading role previously assigned to rodents. Viruses can be transmitted from bats via several mechanisms, including bat bite, aerosolization of saliva (e.g. during echolocation) and faeces/urine.
Due to their distinct ecology/behaviour, bats are naturally more susceptible to viral infection and transmission. Several bat species (e.g. brown bats) aggregate in crowded roosts, which promotes intra- and interspecies viral transmission. Moreover, as bats are widespread in urban areas, humans occasionally encroach on their habitats which are contaminated with guano and urine. Their ability to fly and migration patterns also means that bats are able to spread disease over a large geographic area, while also acquiring new viruses. Additionally, bats experience persistent viral infections which, together with their extreme longevity (some bat species have lifespans of 35 years), helps to maintain viruses and transmit them to other species. Other bat characteristics which contribute to their potency as viral hosts include: their food choices, torpor/hibernation habits and susceptibility to reinfection.
Drivers of viral emergence
Viral emergence is often a consequence of both nature and human activity. In particular, ecological changes can greatly facilitate the emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic viruses. Factors such as deforestation, reforestation, habitat fragmentation and irrigation can all impact the ways in which humans come into contact with wild animal species, and consequently promote virus emergence. Additionally, climate change can affect ecosystems and vector distribution, which in turn can affect the emergence of vector-borne viruses. Other ecological changes - for example, species introduction and predator loss - can also affect virus emergence and prevalence. Some agricultural practices, for example livestock intensification and inappropriate management/disposal of farm animal faeces, are also associated with an increased risk of zoonosis.
Viruses may also emerge due to the establishment of human populations that are vulnerable to infection. For example, a virus may emerge following loss of cross-protective immunity, which may occur due to loss of a wild virus or termination of vaccination programmes. Well-developed countries also have higher proportions of aging citizens and obesity-related disease, thus meaning that their populations may be more immunosuppressed and therefore at risk of infection. Contrastingly, poorer nations may have immunocompromised populations due to malnutrition or chronic infection; these countries are also unlikely to have stable vaccination programmes. Additionally, changes in human demographics – for example, the birth and/or migration of immunologically naïve individuals – can lead to the development of a susceptible population that enables large-scale virus infection.
Other factors which can promote viral emergence include globalisation; in particular, international trade and human travel/migration can result in the introduction of viruses into new areas. Moreover, as densely populated cities promote rapid pathogen transmission, uncontrolled urbanization (i.e. the increased movement and settling of individuals in urban areas) can promote viral emergence. Animal migration can also lead to the emergence of viruses, as was the case for the West Nile virus which was spread by migrating bird populations. Additionally, human practices regarding food production and consumption can also contribute to the risk of viral emergence. In particular, wet markets (i.e. live animal markets) are an ideal environment for virus transfer, due to the high density of people and wild/farmed animals present. Consumption of bush meat is also associated with pathogen emergence.
Prevention
Control and prevention of zoonotic diseases depends on appropriate global surveillance at various levels, including identification of novel pathogens, public health surveillance (including serological surveys), and analysis of the risks of transmission. The complexity of zoonotic events around the world predicates a multidisciplinary approach to prevention. The One Health Model has been proposed as a global strategy to help prevent the emergence of zoonotic diseases in humans, including novel viral diseases. The One Health concept aims to promote the health of animals, humans, and the environment, both locally and globally, by fostering understanding and collaboration between practitioners of different interrelated disciplines, including wildlife biology, veterinary science, medicine, agriculture, ecology, microbiology, epidemiology, and biomedical engineering.
Virulence of emergent viruses
As hosts are immunologically naïve to pathogens they have not encountered before, emergent viruses are often extremely virulent in terms of their capacity to cause disease. Their high virulence is also due to a lack of adaptation to the new host; viruses normally exert strong selection pressure on the immune systems of their natural hosts, which in turn exerts a strong selection pressure on viruses. This coevolution means that the natural host is able to manage infection. However, when the virus jumps to a new host (e.g. humans), the new host is unable to deal with infection due to a lack of coevolution, which results in mismatch between host immunoeffectors and virus immunomodulators.
Additionally, in order to maximise transmission, viruses often naturally undergo attenuation (i.e. virulence is reduced) so that infected animals can survive long enough to infect other animals more efficiently. However, as attenuation takes time to achieve, new host populations will not initially benefit from this phenomenon. Moreover, as zoonotic viruses also naturally exist in animal reservoirs, their survival is not dependent on transmission between new hosts; this means that emergent viruses are even more unlikely to attenuate for the purpose of maximal transmission, and they remain virulent.
Although emergent viruses are frequently highly virulent, they are limited by several host factors including: innate immunity, natural antibodies and receptor specificity. If the host has previously been infected by a pathogen that is similar to the emergent virus, the host may also benefit from cross-protective immunity.
Examples of emergent viruses
Influenza A
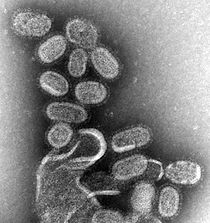
Influenza is a highly contagious respiratory infection, which affects approximately 9% of the global population and causes 300,000 to 500,000 deaths annually. Based on their core proteins, influenza viruses are classified into types A, B, C and D. While both influenza A and B can cause epidemics in humans, influenza A also has pandemic potential and a higher mutation rate, therefore is most significant to public health.
Influenza A viruses are further classified into subtypes, based on the combinations of the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). The primary natural reservoir for most influenza A subtypes are wild aquatic birds; however, through a series of mutations, a small subset of these viruses have adapted for infection of humans (and other animals). A key determinant of whether a particular influenza A subtype can infect humans is its binding specificity. Avian influenza A preferentially binds to cell surface receptors with a terminal α2,3‐linked sialic acid, while human influenza A preferentially binds to cell surface receptors with a terminal α2,6‐linked sialic acid. Via mutation, some avian influenza A viruses have successfully altered their binding specificity from α2,3‐ to α2,6‐linked sialic acid. However, in order to emerge in humans, avian influenza A viruses must also adapt their RNA polymerases for function in mammalian cells, as well as mutating for stability in the acidic respiratory tract of humans.
Following adaptation and host switch, influenza A viruses have the potential to cause epidemics and pandemics in humans. Minor changes in HA and NA structure (antigenic drift) occur frequently, which enables the virus to cause repetitive outbreaks (i.e. seasonal influenza) by evading immune recognition. Major changes in HA and NA structure (antigenic shift), which are caused by genetic reassortment between different influenza A subtypes (e.g. between human and animal subtypes), can instead cause large regional/global pandemics. Due to the emergence of antigenically different influenza A strains in humans, four pandemics occurred in the 20th century alone.
Additionally, although animal influenza A viruses (e.g. swine influenza) are distinct from human influenza viruses, they can still cause zoonotic infection in humans. These infections are largely acquired following direct contact with infected animals or contaminated environments, but do not result in efficient human-human transmission; examples of this include H5N1 influenza and H7N9 influenza.
SARS-CoV
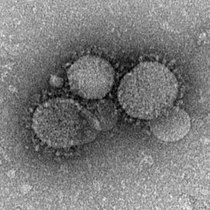
In 2002, a highly pathogenic SARS-CoV (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus) strain emerged from a zoonotic reservoir; approximately 8000 people were infected worldwide, and mortality rates approached 50% or more in the elderly. As SARS-CoV is most contagious post-symptoms, the introduction of strict public health measures effectively halted the pandemic. The natural reservoir host for SARS-CoV is thought to be horseshoe bats, although the virus has also been identified in several small carnivores (e.g. palm civets and racoon dogs). The emergence of SARS-CoV is believed to have been facilitated by Chinese wet markets, in which civets positive for the virus acted as intermediate hosts and passed SARS-CoV onto humans (and other species). However, more recent analysis suggests that SARS-CoV may have directly jumped from bats to humans, with subsequent cross-transmission between humans and civets.
In order to infect cells, SARS-CoV uses the spike surface glycoprotein to recognise and bind to host ACE-2, which it uses as a cellular entry receptor; the development of this characteristic was crucial in enabling SARS-CoV to ‘jump’ from bats to other species.
MERS-CoV
First reported in 2012, MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus) marks the second known introduction of a highly pathogenic coronavirus from a zoonotic reservoir into humans. The case mortality rate of this emergent virus is approximately 35%, with 80% of all cases reported by Saudi Arabia. Although MERS-CoV is likely to have originated in bats, dromedary camels have been implicated as probable intermediate hosts. MERS-CoV is believed to have been circulating in these mammals for over 20 years, and it is thought that novel camel farming practices drove the spillover of MERS-CoV into humans. Studies have shown that humans can be infected with MERS-CoV via direct or indirect contact within infected dromedary camels, while human-human transmission is limited.
MERS-CoV gains cellular entry by using a spike surface protein to bind to the host DPP4 surface receptor; the core subdomain of this spike surface protein shares similarities with that of SARS-CoV, but its receptor binding subdomain (RBSD) significantly differs.
Bluetongue disease
Bluetongue disease is a non-contagious vector-borne disease caused by bluetongue virus, which affects species of ruminants (particularly sheep). Climate change has been implicated in the emergence and global spread of this disease, due to its impact on vector distribution. The natural vector of the bluetongue virus is the African midge C. imicola, which is normally limited to Africa and subtropical Asia. However, global warming has extended the geographic range of C. imicola, so that it now overlaps with a different vector (C. pulcaris or C. obsoletus) with a much more northward geographic range. This change enabled the bluetongue virus to jump vector, thus causing the northward spread of bluetongue disease into Europe.
See also
- Biosecurity
- Emerging infectious disease
- History of emerging infectious diseases
- Laboratory biosafety
- Viral quasispecies