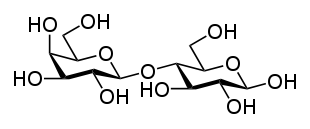
Lactose is a disaccharide found in animal milk. It consists of a molecule of D-galactose and a molecule of D-glucose bonded by beta-1-4 glycosidic linkage.
A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m may be different from n). This formula holds true for monosaccharides. Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. The carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as aldoses and ketoses.
The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of 'saccharide', a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning "sugar".
While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the
names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the
suffix -ose, as in the monosaccharides fructose (fruit sugar) and glucose (starch sugar) and the disaccharides sucrose (cane or beet sugar) and lactose (milk sugar).
Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g. starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g. ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.
Starch and sugars are the most important carbohydrates in human
diet. They are found in a wide variety of natural and processed foods.
Starch is a polysaccharide. It is abundant in cereals (wheat, maize,
rice), potatoes, and processed food based on cereal flour, such as bread, pizza or pasta. Sugars appear in human diet mainly as table sugar (sucrose, extracted from sugarcane or sugar beets), lactose (abundant in milk), glucose and fructose, both of which occur naturally in honey,
many fruits, and some vegetables. Table sugar, milk, or honey are often
added to drinks and many prepared foods such as jam, biscuits and
cakes.
Cellulose, a polysaccharide found in the cell walls of all plants, is one of the main components of insoluble dietary fiber. Although it is not digestible, insoluble dietary fiber helps to maintain a healthy digestive system by easing defecation. Other polysaccharides contained in dietary fiber include resistant starch and inulin, which feed some bacteria in the microbiota of the large intestine, and are metabolized by these bacteria to yield short-chain fatty acids.
Terminology
In scientific literature, the term "carbohydrate" has many synonyms, like "sugar" (in the broad sense), "saccharide", "ose", "glucide", "hydrate of carbon" or "polyhydroxy compounds with aldehyde or ketone". Some of these terms, specially "carbohydrate" and "sugar", are also used with other meanings.
In food science
and in many informal contexts, the term "carbohydrate" often means any
food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).
Often in lists of nutritional information, such as the USDA National Nutrient Database,
the term "carbohydrate" (or "carbohydrate by difference") is used for
everything other than water, protein, fat, ash, and ethanol. This includes chemical compounds such as acetic or lactic acid, which are not normally considered carbohydrates. It also includes dietary fiber which is a carbohydrate but which does not contribute much in the way of food energy (measured in kilocalories), even though it is often included in the calculation of total food energy just as though it were a sugar.
In the strict sense, "sugar" is applied for sweet, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food.
Structure
Formerly the name "carbohydrate" was used in chemistry for any compound with the formula Cm (H2O)n. Following this definition, some chemists considered formaldehyde (CH2O) to be the simplest carbohydrate, while others claimed that title for glycolaldehyde.
Today, the term is generally understood in the biochemistry sense,
which excludes compounds with only one or two carbons and includes many
biological carbohydrates which deviate from this formula. For example,
while the above representative formulas would seem to capture the
commonly known carbohydrates, ubiquitous and abundant carbohydrates
often deviate from this. For example, carbohydrates often display
chemical groups such as: N-acetyl (e.g. chitin), sulphate (e.g.
glycosaminoglycans), carboxylic acid (e.g. sialic acid) and deoxy
modifications (e.g. fucose and sialic acid).
Natural saccharides are generally built of simple carbohydrates called monosaccharides with general formula (CH2O)n where n is three or more. A typical monosaccharide has the structure H–(CHOH)x(C=O)–(CHOH)y–H, that is, an aldehyde or ketone with many hydroxyl groups added, usually one on each carbon atom that is not part of the aldehyde or ketone functional group. Examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and glyceraldehydes. However, some biological substances commonly called "monosaccharides" do not conform to this formula (e.g. uronic acids and deoxy-sugars such as fucose)
and there are many chemicals that do conform to this formula but are
not considered to be monosaccharides (e.g. formaldehyde CH2O and inositol (CH2O)6).
The open-chain form of a monosaccharide often coexists with a closed ring form where the aldehyde/ketone carbonyl group carbon (C=O) and hydroxyl group (–OH) react forming a hemiacetal with a new C–O–C bridge.
Monosaccharides can be linked together into what are called polysaccharides (or oligosaccharides)
in a large variety of ways. Many carbohydrates contain one or more
modified monosaccharide units that have had one or more groups replaced
or removed. For example, deoxyribose, a component of DNA, is a modified version of ribose; chitin is composed of repeating units of N-acetyl glucosamine, a nitrogen-containing form of glucose.
Division
Carbohydrates
are polyhydroxy aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, acids, their simple
derivatives and their polymers having linkages of the acetal type. They
may be classified according to their degree of polymerization, and may
be divided initially into three principal groups, namely sugars,
oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
| Class (DP*) | Subgroup | Components |
|---|---|---|
| Sugars (1–2) | Monosaccharides | Glucose, galactose, fructose, xylose |
| Disaccharides | Sucrose, lactose, maltose, trehalose | |
| Polyols | Sorbitol, mannitol | |
| Oligosaccharides (3–9) | Malto-oligosaccharides | Maltodextrins |
| Other oligosaccharides | Raffinose, stachyose, fructo-oligosaccharides | |
| Polysaccharides (more than 9) | Starch | Amylose, amylopectin, modified starches |
| Non-starch polysaccharides | Glycogen, Cellulose, Hemicellulose, Pectins, Hydrocolloids |
Monosaccharides
D-glucose is an aldohexose with the formula (C·H2O)6. The red atoms highlight the aldehyde group and the blue atoms highlight the asymmetric center furthest from the aldehyde; because this -OH is on the right of the Fischer projection, this is a D sugar.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates in that they cannot be hydrolyzed to smaller carbohydrates. They are aldehydes or ketones with two or more hydroxyl groups. The general chemical formula of an unmodified monosaccharide is (C•H2O)n,
literally a "carbon hydrate". Monosaccharides are important fuel
molecules as well as building blocks for nucleic acids. The smallest
monosaccharides, for which n=3, are dihydroxyacetone and D- and
L-glyceraldehydes.
Classification of monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are classified according to three different characteristics: the placement of its carbonyl group, the number of carbon atoms it contains, and its chiral handedness. If the carbonyl group is an aldehyde, the monosaccharide is an aldose; if the carbonyl group is a ketone, the monosaccharide is a ketose. Monosaccharides with three carbon atoms are called trioses, those with four are called tetroses, five are called pentoses, six are hexoses, and so on. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, glucose is an aldohexose (a six-carbon aldehyde), ribose is an aldopentose (a five-carbon aldehyde), and fructose is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketone).
Each carbon atom bearing a hydroxyl group (-OH), with the exception of the first and last carbons, are asymmetric, making them stereo centers with two possible configurations each (R or S). Because of this asymmetry, a number of isomers may exist for any given monosaccharide formula. Using Le Bel-van't Hoff rule, the aldohexose D-glucose, for example, has the formula (C·H2O)6, of which four of its six carbons atoms are stereogenic, making D-glucose one of 24=16 possible stereoisomers. In the case of glyceraldehydes, an aldotriose, there is one pair of possible stereoisomers, which are enantiomers and epimers. 1, 3-dihydroxyacetone,
the ketose corresponding to the aldose glyceraldehydes, is a symmetric
molecule with no stereo centers. The assignment of D or L is made
according to the orientation of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the
carbonyl group: in a standard Fischer projection if the hydroxyl group
is on the right the molecule is a D sugar, otherwise it is an L sugar.
The "D-" and "L-" prefixes should not be confused with "d-" or "l-",
which indicate the direction that the sugar rotates plane polarized light. This usage of "d-" and "l-" is no longer followed in carbohydrate chemistry.
Ring-straight chain isomerism
Glucose can exist in both a straight-chain and ring form.
The aldehyde or ketone group of a straight-chain monosaccharide will
react reversibly with a hydroxyl group on a different carbon atom to
form a hemiacetal or hemiketal, forming a heterocyclic ring with an oxygen bridge between two carbon atoms. Rings with five and six atoms are called furanose and pyranose forms, respectively, and exist in equilibrium with the straight-chain form.
During the conversion from straight-chain form to the cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon,
becomes a stereogenic center with two possible configurations: The
oxygen atom may take a position either above or below the plane of the
ring. The resulting possible pair of stereoisomers is called anomers. In the α anomer, the -OH substituent on the anomeric carbon rests on the opposite side (trans) of the ring from the CH2OH side branch. The alternative form, in which the CH2OH substituent and the anomeric hydroxyl are on the same side (cis) of the plane of the ring, is called the β anomer.
Use in living organisms
Monosaccharides are the major source of fuel for metabolism, being used both as an energy source (glucose being the most important in nature) and in biosynthesis. When monosaccharides are not immediately needed by many cells they are often converted to more space-efficient forms, often polysaccharides. In many animals, including humans, this storage form is glycogen, especially in liver and muscle cells. In plants, starch is used for the same purpose. The most abundant carbohydrate, cellulose, is a structural component of the cell wall of plants and many forms of algae. Ribose is a component of RNA. Deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Lyxose is a component of lyxoflavin found in the human heart. Ribulose and xylulose occur in the pentose phosphate pathway. Galactose, a component of milk sugar lactose, is found in galactolipids in plant cell membranes and in glycoproteins in many tissues. Mannose occurs in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Fructose,
or fruit sugar, is found in many plants and in humans, it is
metabolized in the liver, absorbed directly into the intestines during digestion, and found in semen. Trehalose, a major sugar of insects, is rapidly hydrolyzed into two glucose molecules to support continuous flight.
Disaccharides
Sucrose, also known as table sugar, is a common disaccharide. It is composed of two monosaccharides: D-glucose (left) and D-fructose (right).
Two joined monosaccharides are called a disaccharide and these are the simplest polysaccharides. Examples include sucrose and lactose. They are composed of two monosaccharide units bound together by a covalent bond known as a glycosidic linkage formed via a dehydration reaction, resulting in the loss of a hydrogen atom from one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group from the other. The formula of unmodified disaccharides is C12H22O11. Although there are numerous kinds of disaccharides, a handful of disaccharides are particularly notable.
Sucrose,
pictured to the right, is the most abundant disaccharide, and the main
form in which carbohydrates are transported in plants. It is composed of
one D-glucose molecule and one D-fructose molecule. The systematic name for sucrose, O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-D-fructofuranoside, indicates four things:
- Its monosaccharides: glucose and fructose
- Their ring types: glucose is a pyranose and fructose is a furanose
- How they are linked together: the oxygen on carbon number 1 (C1) of α-D-glucose is linked to the C2 of D-fructose.
- The -oside suffix indicates that the anomeric carbon of both monosaccharides participates in the glycosidic bond.
Lactose, a disaccharide composed of one D-galactose molecule and one D-glucose molecule, occurs naturally in mammalian milk. The systematic name for lactose is O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucopyranose. Other notable disaccharides include maltose
(two D-glucoses linked α-1,4) and cellulobiose (two D-glucoses linked
β-1,4). Disaccharides can be classified into two types: reducing and
non-reducing disaccharides. If the functional group is present in
bonding with another sugar unit, it is called a reducing disaccharide or
biose.
Nutrition
Grain products: rich sources of carbohydrates
Carbohydrate consumed in food yields 3.87 kilocalories of energy per gram for simple sugars, and 3.57 to 4.12 kilocalories per gram for complex carbohydrate in most other foods.
Relatively high levels of carbohydrate are associated with processed
foods or refined foods made from plants, including sweets, cookies and
candy, table sugar, honey, soft drinks, breads and crackers, jams and
fruit products, pastas and breakfast cereals. Lower amounts of
carbohydrate are usually associated with unrefined foods, including
beans, tubers, rice, and unrefined fruit. Animal-based foods generally have the lowest carbohydrate levels, although milk does contain a high proportion of lactose.
Organisms typically cannot metabolize all types of carbohydrate
to yield energy. Glucose is a nearly universal and accessible source of
energy. Many organisms also have the ability to metabolize other monosaccharides and disaccharides but glucose is often metabolized first. In Escherichia coli, for example, the lac operon will express enzymes for the digestion of lactose when it is present, but if both lactose and glucose are present the lac operon is repressed, resulting in the glucose being used first. Polysaccharides
are also common sources of energy. Many organisms can easily break down
starches into glucose; most organisms, however, cannot metabolize cellulose or other polysaccharides like chitin and arabinoxylans. These carbohydrate types can be metabolized by some bacteria and protists. Ruminants and termites,
for example, use microorganisms to process cellulose. Even though these
complex carbohydrates are not very digestible, they represent an
important dietary element for humans, called dietary fiber. Fiber enhances digestion, among other benefits.
Based on the effects on risk of heart disease and obesity in otherwise healthy middle-aged adults, the Institute of Medicine recommends that American and Canadian adults get between 45–65% of dietary energy from whole-grain carbohydrates. The Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization
jointly recommend that national dietary guidelines set a goal of 55–75%
of total energy from carbohydrates, but only 10% directly from sugars
(their term for simple carbohydrates). A 2017 Cochrane Systematic Review concluded that there was insufficient evidence to support the claim that whole grain diets can affect cardiovascular disease.
Classification
Nutritionists
often refer to carbohydrates as either simple or complex. However, the
exact distinction between these groups can be ambiguous. The term complex carbohydrate was first used in the U.S. Senate Select Committee on Nutrition and Human Needs publication Dietary Goals for the United States
(1977) where it was intended to distinguish sugars from other
carbohydrates (which were perceived to be nutritionally superior).
However, the report put "fruit, vegetables and whole-grains" in the
complex carbohydrate column, despite the fact that these may contain
sugars as well as polysaccharides. This confusion persists as today some
nutritionists use the term complex carbohydrate to refer to any sort of
digestible saccharide present in a whole food, where fiber, vitamins
and minerals are also found (as opposed to processed carbohydrates,
which provide energy but few other nutrients). The standard usage,
however, is to classify carbohydrates chemically: simple if they are
sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) and complex if they are polysaccharides (or oligosaccharides).
In any case, the simple vs. complex chemical distinction has
little value for determining the nutritional quality of carbohydrates. Some simple carbohydrates (e.g. fructose)
raise blood glucose slowly, while some complex carbohydrates
(starches), especially if processed, raise blood sugar rapidly. The
speed of digestion is determined by a variety of factors including which
other nutrients are consumed with the carbohydrate, how the food is
prepared, individual differences in metabolism, and the chemistry of the
carbohydrate.
The USDA's Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010
call for moderate- to high-carbohydrate consumption from a balanced
diet that includes six one-ounce servings of grain foods each day, at
least half from whole grain sources and the rest from enriched.
The glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load
concepts have been developed to characterize food behavior during human
digestion. They rank carbohydrate-rich foods based on the rapidity and
magnitude of their effect on blood glucose levels. Glycemic index is a measure of how quickly food glucose is absorbed, while glycemic load is a measure of the total absorbable glucose in foods. The insulin index is a similar, more recent classification method that ranks foods based on their effects on blood insulin levels, which are caused by glucose (or starch) and some amino acids in food.
Effects of dietary carbohydrate restriction
Carbohydrates are a common source of energy in living organisms; however, no single carbohydrate is an essential nutrient in humans.
Humans are able to obtain all of their energy requirement from protein
and fats, though the potential for some negative health effects of
extreme carbohydrate restriction remains, as the issue has not been
studied extensively yet. However, in the case of dietary fiber –
indigestible carbohydrates which are not a source of energy –
inadequate intake can lead to significant increases in mortality.
Following a diet consisting of very low amounts of daily
carbohydrate for several days will usually result in higher levels of
blood ketone bodies than an isocaloric diet with similar protein content. This relatively high level of ketone bodies is commonly known as ketosis and is very often confused with the potentially fatal condition often seen in type 1 diabetics known as diabetic ketoacidosis.
Somebody suffering ketoacidosis will have much higher levels of blood
ketone bodies along with high blood sugar, dehydration and electrolyte
imbalance.
Long-chain fatty acids cannot cross the blood–brain barrier,
but the liver can break these down to produce ketones. However, the
medium-chain fatty acids octanoic and heptanoic acids can cross the
barrier and be used by the brain, which normally relies upon glucose for
its energy.
Gluconeogenesis allows humans to synthesize some glucose from specific amino acids: from the glycerol backbone in triglycerides and in some cases from fatty acids.
Metabolism
Carbohydrate metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the formation, breakdown and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms.
The most important carbohydrate is glucose, a simple sugar (monosaccharide)
that is metabolized by nearly all known organisms. Glucose and other
carbohydrates are part of a wide variety of metabolic pathways across
species: plants synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water by photosynthesis storing the absorbed energy internally, often in the form of starch or lipids. Plant components are consumed by animals and fungi, and used as fuel for cellular respiration. Oxidation of one gram of carbohydrate yields approximately 9 kJ (4 kcal) of energy,
while the oxidation of one gram of lipids yields about 38 kJ (9 kcal).
The human body stores between 300 to 500 g of carbohydrates depending on
body weight, with the skeletal muscle contributing to a large portion
of the storage. Energy obtained from metabolism (e.g., oxidation of glucose) is usually stored temporarily within cells in the form of ATP. Organisms capable of anaerobic and aerobic respiration metabolize glucose and oxygen (aerobic) to release energy, with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
Catabolism
Catabolism is the metabolic reaction which cells undergo to break down larger molecules, extracting energy. There are two major metabolic pathways of monosaccharide catabolism: glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
In glycolysis, oligo- and polysaccharides are cleaved first to smaller monosaccharides by enzymes called glycoside hydrolases.
The monosaccharide units can then enter into monosaccharide catabolism.
A 2 ATP investment is required in the early steps of glycolysis to
phosphorylate Glucose to Glucose 6-Phosphate (G6P) and Fructose 6-Phosphate (F6P) to Fructose 1,6-biphosphate (FBP), thereby pushing the reaction forward irreversibly.
In some cases, as with humans, not all carbohydrate types are usable as
the digestive and metabolic enzymes necessary are not present.