Rare-earth ore (shown with a 0.75 inch US 1 cent coin for size comparison)
These rare-earth oxides are used as tracers to determine which parts of a drainage basin are eroding.
The 17 rare-earth elements are cerium (Ce), dysprosium (Dy), erbium (Er), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), holmium (Ho), lanthanum (La), lutetium (Lu), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), scandium (Sc), terbium (Tb), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and yttrium (Y).
Despite their name, rare-earth elements are – with the exception of the radioactive promethium – relatively plentiful in Earth's crust, with cerium being the 25th most abundant element at 68 parts per million, more abundant than copper. However, because of their geochemical properties, rare-earth elements are typically dispersed and not often found concentrated in rare-earth minerals; as a result economically exploitable ore deposits are less common. The first rare-earth mineral discovered (1787) was gadolinite, a mineral composed of cerium, yttrium, iron, silicon, and other elements. This mineral was extracted from a mine in the village of Ytterby in Sweden; four of the rare-earth elements bear names derived from this single location.
List
A table listing the 17 rare-earth elements, their atomic number and symbol, the etymology of their names, and their main usages
is provided here. Some of the rare-earth elements are named after the
scientists who discovered or elucidated their elemental properties, and
some after their geographical discovery.
| Z | Symbol | Name | Etymology | Selected applications | Abundance (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | from Latin Scandia (Scandinavia). | Light aluminium-scandium alloys for aerospace components, additive in metal-halide lamps and mercury-vapor lamps, radioactive tracing agent in oil refineries | 22 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | after the village of Ytterby, Sweden, where the first rare earth ore was discovered. | Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG) laser, yttrium vanadate (YVO4) as host for europium in television red phosphor, YBCO high-temperature superconductors, yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), yttrium iron garnet (YIG) microwave filters, energy-efficient light bulbs (part of triphosphor white phosphor coating in fluorescent tubes, CFLs and CCFLs, and yellow phosphor coating in white LEDs), spark plugs, gas mantles, additive to steel, cancer treatments | 33 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | from the Greek "lanthanein", meaning to be hidden. | High refractive index and alkali-resistant glass, flint, hydrogen storage, battery-electrodes, camera lenses, fluid catalytic cracking catalyst for oil refineries | 39 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | after the dwarf planet Ceres, named after the Roman goddess of agriculture. | Chemical oxidizing agent, polishing powder, yellow colors in glass and ceramics, catalyst for self-cleaning ovens, fluid catalytic cracking catalyst for oil refineries, ferrocerium flints for lighters | 66.5 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | from the Greek "prasios", meaning leek-green, and "didymos", meaning twin. | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, core material for carbon arc lighting, colorant in glasses and enamels, additive in didymium glass used in welding goggles, ferrocerium firesteel (flint) products. | 9.2 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | from the Greek "neos", meaning new, and "didymos", meaning twin. | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, violet colors in glass and ceramics, didymium glass, ceramic capacitors, electric motors of electric automobiles | 41.5 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | after the Titan Prometheus, who brought fire to mortals. | Nuclear batteries, luminous paint | 1×10−15 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | after mine official, Vasili Samarsky-Bykhovets. | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, neutron capture, masers, control rods of nuclear reactors | 7.05 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | after the continent of Europe. | Red and blue phosphors, lasers, mercury-vapor lamps, fluorescent lamps, NMR relaxation agent | 2 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | after Johan Gadolin (1760–1852), to honor his investigation of rare earths. | High refractive index glass or garnets, lasers, X-ray tubes, computer memories, neutron capture, MRI contrast agent, NMR relaxation agent, magnetostrictive alloys such as Galfenol, steel additive | 6.2 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | after the village of Ytterby, Sweden. | Additive in Neodymium based magnets, green phosphors, lasers, fluorescent lamps (as part of the white triband phosphor coating), magnetostrictive alloys such as terfenol-D, naval sonar systems, stabilizer of fuel cells | 1.2 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | from the Greek "dysprositos", meaning hard to get. | Additive in Neodymium based magnets, lasers, magnetostrictive alloys such as terfenol-D, hard disk drives | 5.2 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | after Stockholm (in Latin, "Holmia"), native city of one of its discoverers. | Lasers, wavelength calibration standards for optical spectrophotometers, magnets | 1.3 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | after the village of Ytterby, Sweden. | Infrared lasers, vanadium steel, fiber-optic technology | 3.5 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | after the mythological northern land of Thule. | Portable X-ray machines, metal-halide lamps, lasers | 0.52 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | after the village of Ytterby, Sweden. | Infrared lasers, chemical reducing agent, decoy flares, stainless steel, stress gauges, nuclear medicine, monitoring earthquakes | 3.2 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | after Lutetia, the city that later became Paris. | Positron emission tomography – PET scan detectors, high-refractive-index glass, lutetium tantalate hosts for phosphors, catalyst used in refineries, LED light bulb | 0.8 |
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are often used:- RE = rare earth
- REM = rare-earth metals
- REE = rare-earth elements
- REO = rare-earth oxides
- REY = rare-earth elements and yttrium
- LREE = light rare-earth elements
- HREE = heavy rare-earth elements
Discovery and early history
The first rare-earth element discovered was the black mineral "ytterbite" (renamed to gadolinite in 1800). It was discovered by Lieutenant Carl Axel Arrhenius in 1787 at a quarry in the village of Ytterby, Sweden.Arrhenius's "ytterbite" reached Johan Gadolin, a Royal Academy of Turku professor, and his analysis yielded an unknown oxide (earth) that he called yttria. Anders Gustav Ekeberg isolated beryllium from the gadolinite but failed to recognize other elements that the ore contained. After this discovery in 1794 a mineral from Bastnäs near Riddarhyttan, Sweden, which was believed to be an iron–tungsten mineral, was re-examined by Jöns Jacob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger. In 1803 they obtained a white oxide and called it ceria. Martin Heinrich Klaproth independently discovered the same oxide and called it ochroia.
Thus by 1803 there were two known rare-earth elements, yttrium and cerium, although it took another 30 years for researchers to determine that other elements were contained in the two ores ceria and yttria (the similarity of the rare-earth metals' chemical properties made their separation difficult).
In 1839 Carl Gustav Mosander, an assistant of Berzelius, separated ceria by heating the nitrate and dissolving the product in nitric acid. He called the oxide of the soluble salt lanthana. It took him three more years to separate the lanthana further into didymia and pure lanthana. Didymia, although not further separable by Mosander's techniques, was a mixture of oxides.
In 1842 Mosander also separated the yttria into three oxides: pure yttria, terbia and erbia (all the names are derived from the town name "Ytterby"). The earth giving pink salts he called terbium; the one that yielded yellow peroxide he called erbium.
So in 1842 the number of known rare-earth elements had reached six: yttrium, cerium, lanthanum, didymium, erbium and terbium.
Nils Johan Berlin and Marc Delafontaine tried also to separate the crude yttria and found the same substances that Mosander obtained, but Berlin named (1860) the substance giving pink salts erbium, and Delafontaine named the substance with the yellow peroxide terbium. This confusion led to several false claims of new elements, such as the mosandrium of J. Lawrence Smith, or the philippium and decipium of Delafontaine. Due to the difficulty in separating the metals (and determining the separation is complete), the total number of false discoveries was dozens, with some putting the total number of discoveries at over a hundred.
Spectroscopy
There were no further discoveries for 30 years, and the element didymium was listed in the periodic table of elements with a molecular mass of 138. In 1879 Delafontaine used the new physical process of optical flame spectroscopy and found several new spectral lines in didymia. Also in 1879, the new element samarium was isolated by Paul Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran from the mineral samarskite.The samaria earth was further separated by Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1886, and a similar result was obtained by Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac by direct isolation from samarskite. They named the element gadolinium after Johan Gadolin, and its oxide was named "gadolinia".
Further spectroscopic analysis between 1886 and 1901 of samaria, yttria, and samarskite by William Crookes, Lecoq de Boisbaudran and Eugène-Anatole Demarçay yielded several new spectroscopic lines that indicated the existence of an unknown element. The fractional crystallization of the oxides then yielded europium in 1901.
In 1839 the third source for rare earths became available. This is a mineral similar to gadolinite, uranotantalum (now called "samarskite"). This mineral from Miass in the southern Ural Mountains was documented by Gustav Rose. The Russian chemist R. Harmann proposed that a new element he called "ilmenium" should be present in this mineral, but later, Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand, Galissard de Marignac, and Heinrich Rose found only tantalum and niobium (columbium) in it.
The exact number of rare-earth elements that existed was highly unclear, and a maximum number of 25 was estimated. The use of X-ray spectra (obtained by X-ray crystallography) by Henry Gwyn Jeffreys Moseley made it possible to assign atomic numbers to the elements. Moseley found that the exact number of lanthanides had to be 15, and that element 61 had yet to be discovered.
Using these facts about atomic numbers from X-ray crystallography, Moseley also showed that hafnium (element 72) would not be a rare-earth element. Moseley was killed in World War I in 1915, years before hafnium was discovered. Hence, the claim of Georges Urbain that he had discovered element 72 was untrue. Hafnium is an element that lies in the periodic table immediately below zirconium, and hafnium and zirconium are very similar in their chemical and physical properties.
During the 1940s, Frank Spedding and others in the United States (during the Manhattan Project) developed the chemical ion-exchange procedures for separating and purifying the rare-earth elements. This method was first applied to the actinides for separating plutonium-239 and neptunium from uranium, thorium, actinium, and the other actinides in the materials produced in nuclear reactors. The plutonium-239 was very desirable because it is a fissile material.
The principal sources of rare-earth elements are the minerals bastnäsite, monazite, and loparite and the lateritic ion-adsorption clays. Despite their high relative abundance, rare-earth minerals are more difficult to mine and extract than equivalent sources of transition metals (due in part to their similar chemical properties), making the rare-earth elements relatively expensive. Their industrial use was very limited until efficient separation techniques were developed, such as ion exchange, fractional crystallization and liquid–liquid extraction during the late 1950s and early 1960s.
Some ilmenite concentrates contain small amounts scandium and other rare-earth elements, which could be analysed by XRF .
Early classification
Before the time that ion-exchange methods and elution were available, the separation of the rare earths was primarily achieved by repeated precipitation or crystallisation. In those days, the first separation was into two main groups, the cerium earths (scandium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, and samarium) and the yttrium earths (yttrium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium). Europium, gadolinium, and terbium were either considered as a separate group of rare-earth elements (the terbium group), or europium was included in the cerium group, and gadolinium and terbium were included in the yttrium group. The reason for this division arose from the difference in solubility of rare-earth double sulfates with sodium and potassium. The sodium double sulfates of the cerium group are difficultly soluble, those of the terbium group slightly, and those of the yttrium group are very soluble. Sometimes, the yttrium group was further split into the erbium group (dysprosium, holmium, erbium, and thulium) and the ytterbium group (ytterbium and lutetium), but today the main grouping is between the cerium and the yttrium groups. Today, the rare-earth elements are classified as light or heavy rare-earth elements, rather than in cerium and yttrium groups.Light versus heavy classification
The classification of rare-earth elements is inconsistent between authors. The most common distinction between rare-earth elements is made by atomic numbers; those with low atomic numbers are referred to as light rare-earth elements (LREE), those with high atomic numbers are the heavy rare-earth elements (HREE), and those that fall in between are typically referred to as the middle rare-earth elements (MREE). Commonly, rare-earth elements with atomic numbers 57 to 61 are classified as light and those with atomic numbers greater than 62 (corresponding to europium) are classified as heavy-rare earth elements. Increasing atomic numbers between light and heavy rare-earth elements and decreasing atomic radii throughout the series causes chemical variations. Europium is exempt of this classification as it has two valence states: Eu+2 and Eu+3. Yttrium is grouped as heavy rare-earth element due to chemical similarities.Origin
Rare-earth elements, except scandium, are heavier than iron and thus are produced by supernova nucleosynthesis or the s-process in asymptotic giant branch stars. In nature, spontaneous fission of uranium-238 produces trace amounts of radioactive promethium, but most promethium is synthetically produced in nuclear reactors.Due to their chemical similarity, the concentrations of rare earths in rocks are only slowly changed by geochemical processes, making their proportions useful for geochronology and dating fossils.
Geological distribution
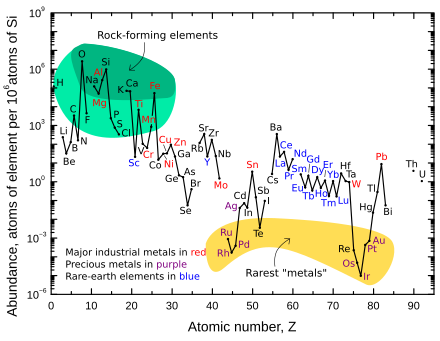
Abundance of elements in Earth's crust per million Si atoms (y axis is logarithmic)
The rare-earth elements are often found together. The longest-lived isotope of promethium has a half-life of 17.7 years, so the element exists in nature in only negligible amounts (approximately 572 g in the entire Earth's crust). Promethium is one of the two elements that do not have stable (non-radioactive) isotopes and are followed by (i.e. with higher atomic number) stable elements (the other being technetium).
During the sequential accretion of the Earth, the dense rare-earth elements were incorporated into the deeper portions of the planet. Early differentiation of molten material largely incorporated the rare-earths into Mantle rocks. The high field strength and large ionic radii of rare-earths make them incompatible with the crystal lattices of most rock-forming minerals, so REE will undergo strong partitioning into a melt phase if one is present. REE are chemically very similar and have always been difficult to separate, but a gradual decrease in ionic radius from LREE to HREE, called lanthanide contraction, can produce a broad separation between light and heavy REE. The larger ionic radii of LREE make them generally more incompatible than HREE in rock-forming minerals, and will partition more strongly into a melt phase, while HREE may prefer to remain in the crystalline residue, particularly if it contains HREE-compatible minerals like garnet. The result is that all magma formed from partial melting will always have greater concentrations of LREE than HREE, and individual minerals may be dominated by either HREE or LREE, depending on which range of ionic radii best fits the crystal lattice.
Among the anhydrous rare-earth phosphates, it is the tetragonal mineral xenotime that incorporates yttrium and the HREE, whereas the monoclinic monazite phase incorporates cerium and the LREE preferentially. The smaller size of the HREE allows greater solid solubility in the rock-forming minerals that make up Earth's mantle, and thus yttrium and the HREE show less enrichment in Earth's crust relative to chondritic abundance than does cerium and the LREE. This has economic consequences: large ore bodies of LREE are known around the world and are being exploited. Ore bodies for HREE are more rare, smaller, and less concentrated. Most of the current supply of HREE originates in the "ion-absorption clay" ores of Southern China. Some versions provide concentrates containing about 65% yttrium oxide, with the HREE being present in ratios reflecting the Oddo–Harkins rule: even-numbered REE at abundances of about 5% each, and odd-numbered REE at abundances of about 1% each. Similar compositions are found in xenotime or gadolinite.
Well-known minerals containing yttrium, and other HREE, include gadolinite, xenotime, samarskite, euxenite, fergusonite, yttrotantalite, yttrotungstite, yttrofluorite (a variety of fluorite), thalenite, yttrialite. Small amounts occur in zircon, which derives its typical yellow fluorescence from some of the accompanying HREE. The zirconium mineral eudialyte, such as is found in southern Greenland, contains small but potentially useful amounts of yttrium. Of the above yttrium minerals, most played a part in providing research quantities of lanthanides during the discovery days. Xenotime is occasionally recovered as a byproduct of heavy-sand processing, but is not as abundant as the similarly recovered monazite (which typically contains a few percent of yttrium). Uranium ores from Ontario have occasionally yielded yttrium as a byproduct.
Well-known minerals containing cerium, and other LREE, include bastnäsite, monazite, allanite, loparite, ancylite, parisite, lanthanite, chevkinite, cerite, stillwellite, britholite, fluocerite, and cerianite. Monazite (marine sands from Brazil, India, or Australia; rock from South Africa), bastnäsite (from Mountain Pass, California, or several localities in China), and loparite (Kola Peninsula, Russia) have been the principal ores of cerium and the light lanthanides.
Enriched deposits of rare-earth elements at the surface of the Earth, carbonatites and pegmatites, are related to alkaline plutonism, an uncommon kind of magmatism that occurs in tectonic settings where there is rifting or that are near subduction zones. In a rift setting, the alkaline magma is produced by very small degrees of partial melting (l.t. 1%) of garnet peridotite in the upper mantle (200 to 600 km depth). This melt becomes enriched in incompatible elements, like the rare-earth elements, by leaching them out of the crystalline residue. The resultant magma rises as a diapir, or diatreme, along pre-existing fractures, and can be emplaced deep in the crust, or erupted at the surface. Typical REE enriched deposits types forming in rift settings are carbonatites, and A- and M-Type granitoids. Near subduction zones, partial melting of the subducting plate within the asthenosphere (80 to 200 km depth) produces a volatile-rich magma (high concentrations of CO2 and water), with high concentrations of alkaline elements, and high element mobility that the rare-earths are strongly partitioned into. This melt may also rise along pre-existing fractures, and be emplaced in the crust above the subducting slab or erupted at the surface. REE enriched deposits forming from these melts are typically S-Type granitoids.
Alkaline magmas enriched with rare-earth elements include carbonatites, peralkaline granites (pegmatites), and nepheline syenite. Carbonatites crystallize from CO2-rich fluids, which can be produced by partial melting of hydrous-carbonated lherzolite to produce a CO2-rich primary magma, by fractional crystallization of an alkaline primary magma, or by separation of a CO2-rich immiscible liquid from. These liquids are most commonly forming in association with very deep Precambrian Cratons, like the ones found in Africa and the Canadian Shield. Ferrocarbonatites are the most common type of carbonatite to be enriched in REE, and are often emplaced as late-stage, brecciated pipes at the core of igneous complexes; they consist of fine-grained calcite and hematite, sometimes with significant concentrations of ankerite and minor concentrations of siderite. Large carbonatite deposits enriched in rare-earth elements include Mount Weld in Australia, Thor Lake in Canada, Zandkopsdrift in South Africa, and Mountain Pass in the USA. Peralkaline granites (A-Type granitoids) have very high concentrations of alkaline elements and very low concentrations of phosphorus; they are deposited at moderate depths in extensional zones, often as igneous ring complexes, or as pipes, massive bodies, and lenses. These fluids have very low viscosities and high element mobility, which allows for crystallization of large grains, despite a relatively short crystallization time upon emplacement; their large grain size is why these deposits are commonly referred to as pegmatites. Economically viable pegmatites are divided into Lithium-Cesium-Tantalum (LCT) and Niobium-Yttrium-Fluorine (NYF) types; NYF types are enriched in rare-earth minerals. Examples of rare-earth pegmatite deposits include Strange Lake in Canada, and Khaladean-Buregtey in Mongolia. Nepheline syenite (M-Type granitoids) deposits are 90% feldspar and feldspathoid minerals, and are deposited in small, circular massifs. They contain high concentrations of rare-earth-bearing accessory minerals. For the most part these deposits are small but important examples include Illimaussaq-Kvanefeld in Greenland, and Lovozera in Russia.
Rare-earth elements can also be enriched in deposits by secondary alteration either by interactions with hydrothermal fluids or meteoric water or by erosion and transport of resistate REE-bearing minerals. Argillization of primary minerals enriches insoluble elements by leaching out silica and other soluble elements, recrystallizing feldspar into clay minerals such kaolinite, halloysite and montmorillonite. In tropical regions where precipitation is high, weathering forms a thick argillized regolith, this process is called supergene enrichment and produces laterite deposits; heavy rare-earth elements are incorporated into the residual clay by absorption. This kind of deposit is only mined for REE in Southern China, where the majority of global heavy rare-earth element production occurs. REE-laterites do form elsewhere, including over the carbonatite at Mount Weld in Australia. REE may also by extracted from placer deposits if the sedimentary parent lithology contained REE-bearing, heavy resistate minerals.
In 2011, Yasuhiro Kato, a geologist at the University of Tokyo who led a study of Pacific Ocean seabed mud, published results indicating the mud could hold rich concentrations of rare-earth minerals. The deposits, studied at 78 sites, came from "[h]ot plumes from hydrothermal vents pull[ing] these materials out of seawater and deposit[ing] them on the seafloor, bit by bit, over tens of millions of years. One square patch of metal-rich mud 2.3 kilometers wide might contain enough rare earths to meet most of the global demand for a year, Japanese geologists report July 3 in Nature Geoscience." "I believe that rare[-]earth resources undersea are much more promising than on-land resources," said Kato. "[C]oncentrations of rare earths were comparable to those found in clays mined in China. Some deposits contained twice as much heavy rare earths such as dysprosium, a component of magnets in hybrid car motors."
Geochemistry applications
The application of rare-earth elements to geology is important to understanding the petrological processes of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock formation. In geochemistry, rare-earth elements can be used to infer the petrological mechanisms that have affected a rock due to the subtle atomic size differences between the elements, which causes preferential fractionation of some rare earths relative to others depending on the processes at work.In geochemistry, rare-earth elements are typically presented in normalized "spider" diagrams, in which concentration of rare-earth elements are normalized to a reference standard and are then expressed as the logarithm to the base 10 of the value. Commonly, the rare-earth elements are normalized to chondritic meteorites, as these are believed to be the closest representation of unfractionated solar system material. However, other normalizing standards can be applied depending on the purpose of the study. Normalization to a standard reference value, especially of a material believed to be unfractionated, allows the observed abundances to be compared to initial abundances of the element. Normalization also removes the pronounced ‘zig-zag’ pattern caused by the differences in abundance between even and odd atomic numbers. The trends that are observed in "spider" diagrams are typically referred to as "patterns", which may be diagnostic of petrological processes that have affected the material of interest.
The rare-earth elements patterns observed in igneous rocks are primarily a function of the chemistry of the source where the rock came from, as well as the fractionation history the rock has undergone. Fractionation is in turn a function of the partition coefficients of each element. Partition coefficients are responsible for the fractionation of a trace elements (including rare-earth elements) into the liquid phase (the melt/magma) into the solid phase (the mineral). If an element preferentially remains in the solid phase it is termed ‘compatible’, and it preferentially partitions into the melt phase it is described as ‘incompatible’. Each element has a different partition coefficient, and therefore fractionates into solid and liquid phases distinctly. These concepts are also applicable to metamorphic and sedimentary petrology.
In igneous rocks, particularly in felsic melts, the following observations apply: anomalies in europium are dominated by the crystallization of feldspars. Hornblende, controls the enrichment of MREE compared to LREE and HREE. Depletion of LREE relative to HREE may be due to the crystallization of olivine, orthopyroxene, and clinopyroxene. On the other hand, depletion of HREE relative to LREE may be due to the presence of garnet, as garnet preferentially incorporates HREE into its crystal structure. The presence of zircon may also cause a similar effect.
In sedimentary rocks, rare-earth elements in clastic sediments are a representation provenance. The rare-earth element concentrations are not typically affected by sea and river waters, as rare-earth elements are insoluble and thus have very low concentrations in these fluids. As a result, when a sediment is transported, rare-earth element concentrations are unaffected by the fluid and instead the rock retains the rare-earth element concentration from its source.
Sea and river waters typically have low rare-earth element concentrations. However, aqueous geochemistry is still very important. In oceans, rare-earth elements reflect input from rivers, hydrothermal vents, and aeolian sources; this is important in the investigation of ocean mixing and circulation.
Rare-earth elements are also useful for dating rocks, as some radioactive isotopes display long half-lives. Of particular interest are the 138La-138Ce, 147Sm-143Nd, and 176Lu-176Hf systems.
Global rare-earth production
Global production 1950–2000
Increased demand has strained supply, and there is growing concern that the world may soon face a shortage of the rare earths. In several years from 2009 worldwide demand for rare-earth elements is expected to exceed supply by 40,000 tonnes annually unless major new sources are developed. In 2013, it was stated that the demand for REEs would increase due to the dependence of the EU on these elements, the fact that rare earth elements cannot be substituted by other elements and that REEs have a low recycling rate. Furthermore, due to the increased demand and low supply, future prices are expected to increase and there is a chance that countries other than China will open REE mines. REE is increasing in demand due to the fact that they are essential for new and innovative technology that is being created. These new products that need REEs to be produced are high technology equipment such as smart phones, digital cameras, computer parts, etc. In addition, these elements are more prevalent is production in the renewable energy technology industry, military equipment industry, glass making and metallurgy.
China
These concerns have intensified due to the actions of China, the predominant supplier. Specifically, China has announced regulations on exports and a crackdown on smuggling. On September 1, 2009, China announced plans to reduce its export quota to 35,000 tons per year in 2010–2015 to conserve scarce resources and protect the environment. On October 19, 2010, China Daily, citing an unnamed Ministry of Commerce official, reported that China will "further reduce quotas for rare[-]earth exports by 30 percent at most next year to protect the precious metals from over-exploitation." The government in Beijing further increased its control by forcing smaller, independent miners to merge into state-owned corporations or face closure. At the end of 2010, China announced that the first round of export quotas in 2011 for rare earths would be 14,446 tons, which was a 35% decrease from the previous first round of quotas in 2010. China announced further export quotas on 14 July 2011 for the second half of the year with total allocation at 30,184 tons with total production capped at 93,800 tonnes. In September 2011, China announced the halt in production of three of its eight major rare-earth mines, responsible for almost 40% of China's total rare-earth production. In March 2012, the US, EU, and Japan confronted China at WTO about these export and production restrictions. China responded with claims that the restrictions had environmental protection in mind. In August 2012, China announced a further 20% reduction in production. These restrictions have damaged industries in other countries and forced producers of rare-earth products to relocate their operations to China. The Chinese restrictions on supply failed in 2012, as prices dropped in response to the opening of other sources. The price of dysprosium oxide was 994 USD/kg in 2011, but dropped to 265 USD/kg by 2014.On August 29, 2014, the WTO ruled that China had broken free-trade agreements, and the WTO said in the summary of key findings that "the overall effect of the foreign and domestic restrictions is to encourage domestic extraction and secure preferential use of those materials by Chinese manufacturers." China declared that it would implement the ruling on September 26, 2014, but would need some time to do so. By January 5, 2015, China had lifted all quotas from the export of rare earths, however export licences will still be required.
Outside of China
As a result of the increased demand and tightening restrictions on exports of the metals from China, some countries are stockpiling rare-earth resources. Searches for alternative sources in Australia, Brazil, Canada, South Africa, Tanzania, Greenland, and the United States are ongoing. Mines in these countries were closed when China undercut world prices in the 1990s, and it will take a few years to restart production as there are many barriers to entry. One example is the Mountain Pass mine in California, which announced its resumption of operations on a start-up basis on August 27, 2012. Other significant sites under development outside of China include the Nolans Project in Central Australia, the remote Hoidas Lake project in northern Canada, and the Mount Weld project in Australia. The Hoidas Lake project has the potential to supply about 10% of the $1 billion of REE consumption that occurs in North America every year. Vietnam signed an agreement in October 2010 to supply Japan with rare earths from its northwestern Lai Châu Province.Also under consideration for mining are sites such as Thor Lake in the Northwest Territories, various locations in Vietnam, and a site in southeast Nebraska in the US, where NioCorp Development Ltd is seeking $1 billion in funding toward opening a niobium, scandium and titanium mine. Additionally, in 2010, a large deposit of rare-earth minerals was discovered in Kvanefjeld in southern Greenland. Pre-feasibility drilling at this site has confirmed significant quantities of black lujavrite, which contains about 1% rare-earth oxides (REO). The European Union has urged Greenland to restrict Chinese development of rare-earth projects there, but as of early 2013, the government of Greenland has said that it has no plans to impose such restrictions. Many Danish politicians have expressed concerns that other nations, including China, could gain influence in thinly populated Greenland, given the number of foreign workers and investment that could come from Chinese companies in the near future because of the law passed December 2012.
Adding to potential mine sites, ASX listed Peak Resources announced in February 2012, that their Tanzanian-based Ngualla project contained not only the 6th largest deposit by tonnage outside of China, but also the highest grade of rare-earth elements of the 6.
North Korea has been reported to have sold rare-earth metals to China. During May and June 2014, North Korea sold over 1.88 million USD worth of rare-earth metals to China. Other sources suggest that North Korea has the world's second largest reserve of rare-earth metals, with potentially over 20 million tons in total. Rare-earth elements may be a factor behind the 2018 thaw in North Korea–United States relations.
Malaysian refining plans
In early 2011, Australian mining company, Lynas, was reported to be "hurrying to finish" a 230 million USD rare-earth refinery on the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia's industrial port of Kuantan. The plant would refine ore — lanthanides concentrate from the Mount Weld mine in Australia. The ore would be trucked to Fremantle and transported by container ship to Kuantan. Within two years, Lynas was said to expect the refinery to be able to meet nearly a third of the world's demand for rare-earth materials, not counting China. The Kuantan development brought renewed attention to the Malaysian town of Bukit Merah in Perak, where a rare-earth mine operated by a Mitsubishi Chemical subsidiary, Asian Rare Earth, closed in 1992 and left continuing environmental and health concerns. In mid-2011, after protests, Malaysian government restrictions on the Lynas plant were announced. At that time, citing subscription-only Dow Jones Newswire reports, a Barrons report said the Lynas investment was $730 million, and the projected share of the global market it would fill put at "about a sixth." An independent review initiated by the Malaysian Government, and conducted by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in 2011 to address concerns of radioactive hazards, found no non-compliance with international radiation safety standards.However, the Malaysian authorities confirmed that as of October 2011, Lynas was not given any permit to import any rare-earth ore into Malaysia. On February 2, 2012, the Malaysian AELB (Atomic Energy Licensing Board) recommended that Lynas be issued a Temporary Operating License (TOL) subject to completion of a number of conditions. On April 3, 2012, Lynas announced to the Malaysian media that these conditions had been met, and was now waiting on the issuance of the licence. On 2 September 2014, Lynas was issued a 2-year Full Operating Stage License (FOSL) by the Malaysian Atomic Energy Licensing Board (AELB).
Other sources
Significant quantities of rare-earth oxides are found in tailings accumulated from 50 years of uranium ore, shale and loparite mining at Sillamäe, Estonia. Due to the rising prices of rare earths, extraction of these oxides has become economically viable. The country currently exports around 3,000 tonnes per year, representing around 2% of world production. Similar resources are suspected in the western United States, where gold rush-era mines are believed to have discarded large amounts of rare earths, because they had no value at the time.In May 2012, researchers from two universities in Japan announced that they had discovered rare earths in Ehime Prefecture, Japan.
In January 2013 a Japanese deep-sea research vessel obtained seven deep-sea mud core samples from the Pacific Ocean seafloor at 5,600 to 5,800 meters depth, approximately 250 kilometres (160 mi) south of the island of Minami-Tori-Shima. The research team found a mud layer 2 to 4 meters beneath the seabed with concentrations of up to 0.66% rare-earth oxides. A potential deposit might compare in grade with the ion-absorption-type deposits in southern China that provide the bulk of Chinese REO mine production, which grade in the range of 0.05% to 0.5% REO.
Recycling
Another recently developed source of rare earths is electronic waste and other wastes that have significant rare-earth components. New advances in recycling technology have made extraction of rare earths from these materials more feasible, and recycling plants are currently operating in Japan, where there is an estimated 300,000 tons of rare earths stored in unused electronics. In France, the Rhodia group is setting up two factories, in La Rochelle and Saint-Fons, that will produce 200 tons of rare earths a year from used fluorescent lamps, magnets and batteries. Coal and coal by-products are a potential source of critical elements including rare earth elements (REE) with estimated amounts in the range of 50 million metric tons.Uses
The uses, applications, and demand for rare-earth elements has expanded over the years. This is particularly due to the uses of rare-earth elements in low-carbon technologies. Some important uses of rare-earth elements are applicable to the production of high-performance magnets, catalysts, alloys, glasses, and electronics. Nd is important in magnet production. Rare-earth elements in this category are used in the electric motors of hybrid vehicles, wind turbines, hard disc drives, portable electronics, microphones, speakers. Ce and La are important as catalysts, and are used for petroleum refining and as diesel additives. Ce, La and Nd are important in alloy making, and in the production of fuel cells and Nickel-metal hydride batteries. Ce, Ga and Nd are important in electronics and are used in the production of LCD and plasma screens, fiber optics, lasers, as well as in medical imaging. Additional uses for earth elements are as tracers in medical applications, fertilizers, and in water treatment.REEs have been used in agriculture to increase plant growth, productivity, and stress resistance seemingly without negative effects for human and animal consumption. REEs are used in agriculture through REE-enriched fertilizers which is a widely used practice in China. In addition, REEs are feed additives for livestock which has resulted in increased production such as larger animals and a higher production of eggs and dairy products. However, this practice has resulted in REE bio-accumulation within livestock and has impacted vegetation and algae growth in these agricultural areas. Additionally while no ill effects have been observed at current low concentrations the effects over the long term and with accumulation over time are unknown prompting some calls for more research into their possible effects.
Environmental considerations
REEs are naturally found in very low concentration in the environment. Near mining and industrial sites the concentrations can rise to many times the normal background levels. Once in the environment REEs can leech into the soil where their transport is determined by numerous factors such as erosion, weathering, pH, precipitation, ground water, etc. Acting much like metals they can speciate depending on the soil condition being either motile or adsorbed to soil particles depending on conditions. Depending on their bio-availability REEs can be absorbed into plants and later consumed by humans and animals. Including the mining of REEs and REE-enriched fertilizers, the production of phosphorus fertilizers also contribute to REE contamination due to their production and deposition around the phosphorus fertilizer production plants. Furthermore, strong acids are used during the extraction process of REEs, which can then leach out in to the environment and be transported through water bodies and result in the acidification of aquatic environments. Another additive of REE mining that contributes to REE environmental contamination is cerium oxide (CeO2) which is produced during the combustion of diesel and is released as an exhaust particulate matter and contributes heavily to soil and water contamination.
False-color satellite image of the Bayan Obo Mining District, 2006
Consequences and remediation
The Bukit Merah mine in Malaysia has been the focus of a US$100 million cleanup that is proceeding in 2011. After having accomplished the hilltop entombment of 11,000 truckloads of radioactively contaminated material, the project is expected to entail in summer, 2011, the removal of "more than 80,000 steel barrels of radioactive waste to the hilltop repository."In May 2011, after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, widespread protests took place in Kuantan over the Lynas refinery and radioactive waste from it. The ore to be processed has very low levels of thorium, and Lynas founder and chief executive Nicholas Curtis said "There is absolutely no risk to public health." T. Jayabalan, a doctor who says he has been monitoring and treating patients affected by the Mitsubishi plant, "is wary of Lynas's assurances. The argument that low levels of thorium in the ore make it safer doesn't make sense, he says, because radiation exposure is cumulative." Construction of the facility has been halted until an independent United Nations IAEA panel investigation is completed, which is expected by the end of June 2011. New restrictions were announced by the Malaysian government in late June.
IAEA panel investigation is completed and no construction has been halted. Lynas is on budget and on schedule to start producing 2011. The IAEA report has concluded in a report issued on Thursday June 2011 said it did not find any instance of "any non-compliance with international radiation safety standards" in the project.
If the proper safety standards are followed, REE mining is relatively low impact. Molycorp (before going bankrupt) often exceeded environmental regulations to improve public image.
Environmental pollution
Pollution of REEs are mainly caused during the mining process because during the extraction of the ores from rocks, a significant amount of water usage and wastewater production. Also, acidic substances are used during the extraction process, which can leach in to the soil and surrounding environment. In addition, due to the low abundance and varying spatial distribution of REEs, the mining process uses a significant amount of energy, which will have a negative impact on the environment. The sources of pollution from REEs consist of; dust and particulates, soil, ground water, rain, radioactivity and bio-accumulation due to high concentrations in terrestrial environments. The pollution in the US versus the pollution in China is variable due to the fact that REE mining in the US is subject to regulations, which indicates that there is more pollution mitigation strategies in place. Where as in China there have been numerous studies that show that areas surrounding mines/industrial sites are heavily contaminated with REEs, which may be due to the lack of protocol on REE mining.Literature published in 2004 suggests that along with previously established pollution mitigation, a more circular supply chain would help mitigate some of the pollution that the extraction point. This means recycling and reusing REEs that are already in use or reaching the end of their life cycle.
Impact on vegetation
The mining of REEs have caused the contamination of surrounding soil and water of these production areas, which has impacted vegetation in these area by decreasing chlorophyll production which affects photosynthesis and inhibits the growth of the plants. However, the impact of REE contamination on vegetation is dependent on the plants present in the contaminated environments because there are some plants that do retain and absorb REEs and there are some that don't. Also, the ability for the vegetation to intake the REE in dependent on the type of REE present in the soil, hence there are a multitude of factors that influence this process. Agricultural plants are the main type of vegetation affected by REE contamination in the environment. Also, the main two plants that have a higher chance of absorbing and storing REEs are apples and beets. Furthermore, there is a possibility that the REE that can leach out in to aquatic environments can be absorbed by aquatic vegetation, which can then bio-accumulate and potentially enter the human food-chain if livestock or humans choose to eat the vegetation. An example of this situation was the case of the water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in China, where the water was contaminated due to a REE-enriched fertilizer being used in an agricultural area of close proximity. This led to the nearby aquatic environment becoming contaminated with Cerium and resulted in the water hyacinth becoming three times more concentrated in Cerium than its surrounding water.Impact on human health
REEs are a large group with many different properties and levels in the environment, because of this, and limited research it has been difficult to determine safe levels of exposure for humans. A number of studies have focused on risk assessment based on routes of exposure and divergence from back ground levels related to nearby agriculture,mining, and industry. It has been demonstrated that numerous REEs have toxic properties and are present in the environment or in work places. Exposure to these can lead to a wide range of negative health outcomes such as cancer, respiratory issues, dental loss including death. However these elements are numerous and present in many different forms and at different levels of toxicity, as such it has been difficult to give blanket warnings on cancer risk and toxicity as some of these are harmless while others pose a risk.What toxicity is shown appears to be at very high levels of exposure through ingestion of contaminated food and water, through inhalation of dust/smoke particles either as an occupational hazard or due to proximity to contaminated sites such as mines and cities. Therefore, the main issues that these residents would face is bioaccumulation of REEs and the impact on their respiratory system but overall, there can be other possible short term and long term health effects. It was found that people living near mines in China had many times the levels of REEs in their blood, urine, bone and hair compared to controls far from mining sites. This higher level was related to the high levels of REEs present in the vegetables they cultivated, the soil, and the water from the wells indicating that the high levels were caused by the nearby mine. While REE levels varied between men and women the group most at risk were children because REEs can impacted the neurological development of children. Hence, it can impact their IQ and can cause memory loss.
Residents blamed a rare-earth refinery at Bukit Merah for birth defects and eight leukemia cases within five years in a community of 11,000 — after many years with no leukemia cases. Seven of the leukemia victims died. Osamu Shimizu, a director of Asian Rare Earth, said "the company might have sold a few bags of calcium phosphate fertilizer on a trial basis as it sought to market byproducts; calcium phosphate is not radioactive or dangerous" in reply to a former resident of Bukit Merah who said that "The cows that ate the grass [grown with the fertilizer] all died." Malaysia's Supreme Court ruled on 23 December 1993 that there was no evidence that the local chemical joint venture Asian Rare Earth was contaminating the local environment.
Impact on animal health
Experiments exposing rats to various cerium compounds have found accumulation primarily in the lungs and liver. This resulted in various negative health outcomes associated with those organs. REEs have been added to feed in livestock to increase their body mass and increase milk production. They are most-commonly used to increase the body mass of pigs and it was discovered that REEs increase the digestibility and nutrient use of pigs digestive system. Studies point to a dose response when considering toxicity versus positive effects. While small doses in the environment and properly administered seem to have no ill effects. Larger doses have been shown to have negative effects specifically in the organs where they accumulate. The process mining of REEs in China has resulted in soil and water contamination in certain areas, which has then transported through these systems and in these aquatic bodies, it could potentially bio-accumulate within aquatic biota. Furthermore, in some cases animals that live in the REE contaminated areas have been diagnosed with organ or system problems. Furthermore, REEs have been used in freshwater fish farming by allowing the fish to consume the REE because it protects the fish from possible diseases. One main reason why they have been avidly used in animal livestock feeding is that they have had better results than inorganic livestock feed enhancers.Geo-political considerations
China has officially cited resource depletion and environmental concerns as the reasons for a nationwide crackdown on its rare-earth mineral production sector. However, non-environmental motives have also been imputed to China's rare-earth policy. According to The Economist, "Slashing their exports of rare-earth metals… is all about moving Chinese manufacturers up the supply chain, so they can sell valuable finished goods to the world rather than lowly raw materials." Furthermore, China currently has an effective monopoly on the world's REE Value Chain. (all the refineries and processing plants that transform the raw ore into valuable elements). In the words of Deng Xiaoping, a Chinese politician from the late 1970s to the late 1980s, "The Middle East has oil; we have rare earths ... it is of extremely important strategic significance; we must be sure to handle the rare earth issue properly and make the fullest use of our country's advantage in rare earth resources."One possible example of market control is the division of General Motors that deals with miniaturized magnet research, which shut down its US office and moved its entire staff to China in 2006 (it should be noted that China's export quota only applies to the metal but not products made from these metals such as magnets).
It was reported, but officially denied, that China instituted an export ban on shipments of rare-earth oxides (but not alloys) to Japan on 22 September 2010, in response to the detainment of a Chinese fishing boat captain by the Japanese Coast Guard. On September 2, 2010, a few days before the fishing boat incident, The Economist reported that "China...in July announced the latest in a series of annual export reductions, this time by 40% to precisely 30,258 tonnes."
The United States Department of Energy in its 2010 Critical Materials Strategy report identified dysprosium as the element that was most critical in terms of import reliance.
A 2011 report "China's Rare-Earth Industry", issued by the US Geological Survey and US Department of the Interior, outlines industry trends within China and examines national policies that may guide the future of the country's production. The report notes that China's lead in the production of rare-earth minerals has accelerated over the past two decades. In 1990, China accounted for only 27% of such minerals. In 2009, world production was 132,000 metric tons; China produced 129,000 of those tons. According to the report, recent patterns suggest that China will slow the export of such materials to the world: "Owing to the increase in domestic demand, the Government has gradually reduced the export quota during the past several years." In 2006, China allowed 47 domestic rare-earth producers and traders and 12 Sino-foreign rare-earth producers to export. Controls have since tightened annually; by 2011, only 22 domestic rare-earth producers and traders and 9 Sino-foreign rare-earth producers were authorized. The government's future policies will likely keep in place strict controls: "According to China's draft rare-earth development plan, annual rare-earth production may be limited to between 130,000 and 140,000 [metric tons] during the period from 2009 to 2015. The export quota for rare-earth products may be about 35,000 [metric tons] and the Government may allow 20 domestic rare-earth producers and traders to export rare earths."
The United States Geological Survey is actively surveying southern Afghanistan for rare-earth deposits under the protection of United States military forces. Since 2009 the USGS has conducted remote sensing surveys as well as fieldwork to verify Soviet claims that volcanic rocks containing rare-earth metals exist in Helmand province near the village of Khanneshin. The USGS study team has located a sizable area of rocks in the center of an extinct volcano containing light rare-earth elements including cerium and neodymium. It has mapped 1.3 million metric tons of desirable rock, or about 10 years of supply at current demand levels. The Pentagon has estimated its value at about $7.4 billion.