| Peyote | |
|---|---|

| |
| Peyote in the wild | |
 Vulnerable | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
L. williamsii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lophophora williamsii | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Echinocactus williamsii Lemaire ex Salm-Dyck
Lophophora lewinii (K. Schumann) Rusby
Lophophora echinata Croizat
Lophophora fricii Habermann
L. williamsii var. fricii (Habermann) Grym
L. diffusa subsp. fricii (Habermann) Halda
Lophophora jourdaniana Haberman
| |
Lophophora williamsii (/loʊˈfɒfərə
Known for its psychoactive properties when ingested, peyote is used worldwide, having a long history of ritualistic and medicinal use by indigenous North Americans. Peyote contains the hallucinogen mescaline.
Description
A group of Lophophora williamsii.
A flowering peyote.
The various species of the genus Lophophora
grow low to the ground and they often form groups with numerous,
crowded shoots. The blue-green, yellow-green or sometimes reddish-green
shoots are mostly flattened spheres with sunken shoot tips. They can
reach heights of from 2 to 7 centimeters (0.79 to 2.76 in) and diameters
of 4 to 12 cm (1.6 to 4.7 in). There are often significant, vertical
ribs consisting of low and rounded or hump-like bumps. From the cusp areoles
arises a tuft of soft, yellowish or whitish woolly hairs. Spines are
absent.
Flowers are pink or white to slightly yellowish, sometimes reddish. They
open during the day, are from 1 to 2.4 cm long, and reach a diameter
from 1 to 2.2 cm.
Lophophora williamsii seedling at roughly 1 1/2 months of age
The cactus produces flowers sporadically; these are followed by small
edible pink fruit. The club-shaped to elongated, fleshy fruits are bare
and more or less rosy colored. At maturity, they are brownish-white and
dry. The fruits do not burst open on their own and they are between 1.5
and 2 cm long. They contain black, pear-shaped seeds that are 1 to
1.5 mm long and 1 mm wide.
The seeds require hot and humid conditions to germinate. Peyote contains
a large spectrum of phenethylamine alkaloids. The principal one is mescaline for which the content of Lophophora williamsii is about 0.4% fresh (undried) and 3–6% dried.
Peyote is extremely slow growing. Cultivated specimens grow
considerably faster, sometimes taking less than three years to go from
seedling to mature flowering adult. More rapid growth can be achieved by
grafting peyote onto mature San Pedro root stock.
The top of the above-ground part of the cactus, the crown, consists of
disc-shaped buttons. These are cut above the roots and sometimes dried.
When done properly, the top of the root forms a callus and the root does
not rot.
When poor harvesting techniques are used, however, the entire plant
dies. Currently in South Texas, peyote grows naturally but has been
over-harvested, to the point that the state has listed it as an endangered species.
The buttons are generally chewed, or boiled in water to produce a
psychoactive tea. Peyote is extremely bitter and most people are nauseated before they feel the onset of the psychoactive effects.
Distribution and habitat
Range of wild peyote
L. williamsii is native to southern North America, mainly distributed in Mexico. In the United States it grows in Southern Texas. In Mexico it grows in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas in the north to San Luis Potosi and Zacatecas. It is primarily found at elevations of 100–1,500 m (330–4,920 ft) and exceptionally up to 1,900 m (6,200 ft) in the Chihuahuan desert,
but is also present in the more mild climate of Tamaulipas. Its habitat
is primarily in desert scrub, particularly thorn scrub in Tamaulipas.
It is common on or near limestone hills.
Uses
Psychoactive and medicinal
Dried Lophophora williamsii slices ("Peyote Buttons") with a US 5 cent coin for scale
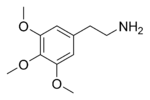
Chemical structure of mescaline, the primary hallucinogen in peyote
When used for its psychoactive
properties, common doses for pure mescaline range from roughly 200 to
400 mg. This translates to a dose of roughly 10 to 20 g of dried peyote
buttons of average potency; however, potency varies considerably between
samples, making it difficult to measure doses accurately without first
extracting the mescaline. The effects last about 10 to 12 hours. Peyote is reported to trigger rich visual or auditory effects.
In addition to psychoactive use, some Native American tribes use
the plant in the belief it may have curative properties. They employ
peyote to treat such varied ailments as toothache, pain in childbirth, fever, breast pain, skin diseases, rheumatism, diabetes, colds, and blindness. The US Dispensatory lists peyote under the name Anhalonium, and states it can be used in various preparations for neurasthenia, hysteria and asthma. Peyote also contains an alkaloid called peyocactin. It is now called hordenine.[citation needed] Peyote poisoning has been a concern in California.
Chemical structure of hordenine (peyocactin), an antimicrobial compound contained in the peyote cactus
History
In 2005 researchers used radiocarbon dating and alkaloid analysis to study two specimens of peyote buttons found in archaeological digs from a site called Shumla Cave No. 5 on the Rio Grande in Texas. The results dated the specimens to between 3780 and 3660 BCE.
Alkaloid extraction yielded approximately 2% of the alkaloids including
mescaline in both samples. This indicates that native North Americans
were likely to have used peyote since at least five-and-a-half thousand
years ago.
Specimens from a burial cave in west central Coahuila, Mexico have been similarly analyzed and dated to 810 to 1070 CE.
Peyote in Wirikuta, Mexico
From earliest recorded time, peyote has been used by indigenous peoples, such as the Huichol of northern Mexico and by various Native American tribes, native to or relocated to the Southern Plains states of present-day Oklahoma and Texas. Its usage was also recorded among various Southwestern Athabaskan-language tribal groups. The Tonkawa, the Mescalero, and Lipan Apache were the source or first practitioners of peyote religion in the regions north of present-day Mexico. They were also the principal group to introduce peyote to newly arrived migrants, such as the Comanche and Kiowa from the Northern Plains. The religious, ceremonial, and healing uses of peyote may date back over 2,000 years.
Under the auspices of what came to be known as the Native American Church,
in the 19th century, American Indians in more widespread regions to the
north began to use peyote in religious practices, as part of a revival
of native spirituality. Its members refer to peyote as "the sacred
medicine", and use it to combat spiritual, physical, and other social
ills. Concerned about the drug's psychoactive effects, between the 1880s
and 1930s, U.S. authorities attempted to ban Native American religious
rituals involving peyote, including the Ghost Dance.
Today the Native American Church is one among several religious
organizations to use peyote as part of its religious practice. Some
users claim the drug connects them to God.
Traditional Navajo belief or ceremonial practice did not mention the use of peyote before its introduction by the neighboring Utes. The Navajo Nation now has the most members of the Native American Church.
Dr. John Raleigh Briggs (1851–1907) was the first to draw scientific attention of the Western scientific world to peyote. Louis Lewin described Anhalonium lewinii in 1888. Arthur Heffter conducted self experiments on its effects in 1897. Similarly, Norwegian ethnographer Carl Sofus Lumholtz studied and wrote about the use of peyote among the Indians of Mexico. Lumholtz also reported that, lacking other intoxicants, Texas Rangers captured by Union forces during the American Civil War soaked peyote buttons in water and became "intoxicated with the liquid".
Adverse reactions
A study published in 2007 found no evidence of long-term cognitive problems related to peyote use in Native American Church ceremonies, but researchers stressed their results may not apply to those who use peyote in other contexts. A four-year large-scale study of Navajo who regularly ingested peyote found only one case where peyote was associated with a psychotic break
in an otherwise healthy person; other psychotic episodes were
attributed to peyote use in conjunction with pre-existing substance
abuse or mental health problems. Later research found that those with pre-existing mental health issues are more likely to have adverse reactions to peyote. Peyote use does not appear to be associated with hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (a.k.a. "flashbacks") after religious use. Peyote does not seem to be associated with physical dependence, but some users may experience psychological dependence.
Peyote can have strong emetic effects, and one death has been attributed to esophageal bleeding caused by vomiting after peyote ingestion in a Native American patient with a history of alcohol abuse. Peyote is also known to cause potentially serious variations in heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and pupillary dilation.
Research into the huichol natives of central-western Mexico, who have taken peyote regularly for an estimated 1,500 years or more, found no evidence of chromosome damage in either men or women.
Cultural significance
A Native American Peyote Drummer (circa 1927)
Huichol culture
The Huichol religion consists of four principal deities:
Corn, Blue Deer, Peyote, and the Eagle, all descended from their Sun
God, "Tao Jreeku". Schaefer has interpreted this to mean that peyote is
the soul of their religious culture and a visionary sacrament that opens a pathway to the other deities.
- Huichol art
Legality
United Nations
Article 32 of the Convention on Psychotropic Substances allows nations to exempt certain traditional uses of substances from prohibition:
A State on whose territory there are plants growing wild which contain psychotropic substances from among those in Schedule I and which are traditionally used by certain small, clearly determined groups in magical or religious rites, may, at the time of signature, ratification or accession, make reservations concerning these plants, in respect of the provisions of article 7, except for the provisions relating to international trade.
However, this exemption would apply only if the peyote cactus were
ever explicitly added to the Schedules of the Psychotropic Convention.
Currently the Convention applies only to chemicals. Peyote and other
psychedelic plants are neither listed nor regulated by the Convention.
Canada
Mescaline is listed as a Schedule III controlled substance under the Canadian Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, but peyote is specifically exempt. Possession and use of peyote plants is legal.
United States
Non-drug uses of peyote in religious ceremonies by the Native American Church and its members are exempt from registration. This law has been codified as a statute in the American Indian Religious Freedom Act of 1978, and made part of the common law in Peyote Way Church of God, Inc. v. Thornburgh, (5th Cir. 1991); it is also in administrative law at the 21 C.F.R. 1307.31 which states for "Special Exempt Persons":
Section 1307.31 Native American Church. The listing of peyote as a controlled substance in Schedule I does not apply to the nondrug use of peyote in bona fide religious ceremonies of the Native American Church, and members of the Native American Church so using peyote are exempt from registration. Any person who manufactures peyote for or distributes peyote to the Native American Church, however, is required to obtain registration annually and to comply with all other requirements of law.
U.S. v. Boyll, 774 F.Supp. 1333 (D.N.M. 1991) addresses this racial issue specifically and concludes:
For the reasons set out in this Memorandum Opinion and Order, the Court holds that, pursuant to 21 C.F.R. § 1307.31 (1990), the classification of peyote as a Schedule I controlled substance, see 21 U.S.C. § 812(c), Schedule I(c)(12), does not apply to the importation, possession or use of peyote for 'bona fide' ceremonial use by members of the Native American Church, regardless of race.
Following the passage of the American Indian Religious Freedom Act Amendments of 1994, United States federal law (and many state laws) protects the harvest, possession, consumption and cultivation of peyote as part of "bona fide religious ceremonies" (the federal statute is the American Indian Religious Freedom Act, codified at 42 U.S.C. § 1996a,
"Traditional Indian religious use of the peyote sacrament", exempting
only use by Native American persons. US v. Boyll expanded permitted use
to all persons engaged in traditional Indian use, regardless of race.
All US states with the exception of Idaho and Texas allow usage by
non-native, non-enrolled persons in the context of ceremonies of the Native American Church.
Some states such as Arizona additionally exempt any general bona fide
religious activity or spiritual intent. US jurisdictions enacted these
specific statutory exemptions in reaction to the US Supreme Court's decision in Employment Division v. Smith, 494 U.S. 872
(1990), which held that laws prohibiting the use of peyote that do not
specifically exempt religious use nevertheless do not violate the Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment. Peyote is listed by the United States DEA as a Schedule I controlled substance.