| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Hydrogen sulfide
| |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01206 | ||
| 3535004 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.070 | ||
| EC Number | 231-977-3 | ||
| 303 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Hydrogen+sulfide | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | MX1225000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1053 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| H2S | |||
| Molar mass | 34.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Pungent, like that of rotten eggs | ||
| Density | 1.363 g dm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −82 °C (−116 °F; 191 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −60 °C (−76 °F; 213 K) | ||
| 4 g dm−3 (at 20 °C) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 1740 kPa (at 21 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.0 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Sulfonium | ||
| Conjugate base | Bisulfide | ||
| −25.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.000644 (0 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| C2v | |||
| Bent | |||
| 0.97 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
1.003 J K−1 g−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S |
206 J mol−1 K−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−21 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Flammable and highly toxic | ||
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
|||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R12, R26, R50 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2), S9, S16, S36, S38, S45, S61 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −82.4 °C (−116.3 °F; 190.8 K) [8] | ||
| 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.3–46% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
| ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
C 20 ppm; 50 ppm [10-minute maximum peak] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
C 10 ppm (15 mg/m3) [10-minute] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
100 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related hydrogen chalcogenides
|
|||
Related compounds
|
Phosphine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
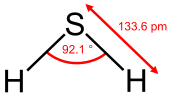
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula H
2S. It is a colorless chalcogen hydride gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It is very poisonous, corrosive, and flammable.
Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion which is done by sulfate-reducing microorganisms. H
2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. The human body produces small amounts of H
2S and uses it as a signaling molecule.
Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of hydrogen sulfide in 1777.
The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, but this spelling is not recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) or the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Properties
Hydrogen sulfide is slightly denser than air; a mixture of H
2S and air can be explosive. Hydrogen sulfide burns in oxygen with a blue flame to form sulfur dioxide (SO
2) and water. In general, hydrogen sulfide acts as a reducing agent, especially in the presence of base, which forms SH−.
2S and air can be explosive. Hydrogen sulfide burns in oxygen with a blue flame to form sulfur dioxide (SO
2) and water. In general, hydrogen sulfide acts as a reducing agent, especially in the presence of base, which forms SH−.
At high temperatures or in the presence of catalysts, sulfur dioxide reacts with hydrogen sulfide to form elemental sulfur and water. This reaction is exploited in the Claus process, an important industrial method to dispose of hydrogen sulfide.
Hydrogen sulfide is slightly soluble in water and acts as a weak acid (pKa = 6.9 in 0.01–0.1 mol/litre solutions at 18 °C), giving the hydrosulfide ion HS− (also written SH−).
Hydrogen sulfide and its solutions are colorless. When exposed to air,
it slowly oxidizes to form elemental sulfur, which is not soluble in
water. The sulfide anion S2− is not formed in aqueous solution.
Hydrogen sulfide reacts with metal ions to form metal sulfides, which are insoluble, often dark colored solids. Lead(II) acetate paper is used to detect hydrogen sulfide because it readily converts to lead(II) sulfide, which is black. Treating metal sulfides with strong acid often liberates hydrogen sulfide.
At pressures above 90 GPa (gigapascal), hydrogen sulfide becomes a metallic conductor of electricity. When cooled below a critical temperature this high-pressure phase exhibits superconductivity. The critical temperature increases with pressure, ranging from 23 K at 100 GPa to 150 K at 200 GPa.
If hydrogen sulfide is pressurized at higher temperatures, then cooled,
the critical temperature reaches 203 K (−70 °C), the highest accepted
superconducting critical temperature as of 2015. By substituting a small
part of sulfur with phosphorus and using even higher pressures, it has
been predicted that it may be possible to raise the critical temperature
to above 0 °C (273 K) and achieve room-temperature superconductivity.
Production
Hydrogen sulfide is most commonly obtained by its separation from sour gas, which is natural gas with a high content of H
2S. It can also be produced by treating hydrogen with molten elemental sulfur at about 450 °C. Hydrocarbons can serve as a source of hydrogen in this process.
2S. It can also be produced by treating hydrogen with molten elemental sulfur at about 450 °C. Hydrocarbons can serve as a source of hydrogen in this process.
Sulfate-reducing (resp. sulfur-reducing) bacteria generate usable energy under low-oxygen conditions by using sulfates (resp. elemental sulfur) to oxidize organic compounds or hydrogen; this produces hydrogen sulfide as a waste product.
A standard lab preparation is to treat ferrous sulfide with a strong acid in a Kipp generator:
- FeS + 2 HCl → FeCl2 + H2S
- CH3C(S)NH2 + H2O → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2S
Many metal and nonmetal sulfides, e.g. aluminium sulfide, phosphorus pentasulfide, silicon disulfide liberate hydrogen sulfide upon exposure to water:
- 6 H2O + Al2S3 → 3 H2S + 2 Al(OH)3
This gas is also produced by heating sulfur with solid organic
compounds and by reducing sulfurated organic compounds with hydrogen.
Water heaters can aid the conversion of sulfate in water to hydrogen sulfide gas. This is due to providing a warm environment sustainable for sulfur bacteria
and maintaining the reaction which interacts between sulfate in the
water and the water heater anode, which is usually made from magnesium metal.
Biosynthesis in the body
Hydrogen sulfide can be generated in cells via enzymatic or non enzymatic pathway. H
2S in the body acts as a gaseous signaling molecule which is known to inhibit Complex IV of the mitochondrial electron transport chain which effectively reduces ATP generation and biochemical activity within cells. Three enzymes are known to synthesize H
2S: cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), cystathionine β-synthetase (CBS) and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST). These enzymes have been identified in a breadth of biological cells and tissues, and their activity has been observed to be induced by a number of disease states. It is becoming increasingly clear that H
2S is an important mediator of a wide range of cell functions in health and in disease. CBS and CSE are the main proponents of H
2S biogenesis, which follows the trans-sulfuration pathway. These enzymes are characterized by the transfer of a sulfur atom from methionine to serine to form a cysteine molecule. 3-MST also contributes to hydrogen sulfide production by way of the cysteine catabolic pathway. Dietary amino acids, such as methionine and cysteine serve as the primary substrates for the transulfuration pathways and in the production of hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide can also be synthesized by non-enzymatic pathway, which is derived from proteins such as ferredoxins and Rieske proteins.
2S in the body acts as a gaseous signaling molecule which is known to inhibit Complex IV of the mitochondrial electron transport chain which effectively reduces ATP generation and biochemical activity within cells. Three enzymes are known to synthesize H
2S: cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), cystathionine β-synthetase (CBS) and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST). These enzymes have been identified in a breadth of biological cells and tissues, and their activity has been observed to be induced by a number of disease states. It is becoming increasingly clear that H
2S is an important mediator of a wide range of cell functions in health and in disease. CBS and CSE are the main proponents of H
2S biogenesis, which follows the trans-sulfuration pathway. These enzymes are characterized by the transfer of a sulfur atom from methionine to serine to form a cysteine molecule. 3-MST also contributes to hydrogen sulfide production by way of the cysteine catabolic pathway. Dietary amino acids, such as methionine and cysteine serve as the primary substrates for the transulfuration pathways and in the production of hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide can also be synthesized by non-enzymatic pathway, which is derived from proteins such as ferredoxins and Rieske proteins.
H
2S has been shown to be involved in physiological processes like vasoconstriction in animals, increasing seed germination and stress responses in plants. Hydrogen sulfide signaling is also innately intertwined with physiological processes that are known to be moderated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). H
2S has been shown to interact with NO resulting in several different cellular effects, as well as the formation of a new signal called nitrosothiol. Hydrogen Sulfide is also known to increase the levels of glutathione which acts to reduce or disrupt ROS levels in cells. In these early days in the field of H
2S biochemistry and signaling there are more questions than answers.
2S has been shown to be involved in physiological processes like vasoconstriction in animals, increasing seed germination and stress responses in plants. Hydrogen sulfide signaling is also innately intertwined with physiological processes that are known to be moderated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). H
2S has been shown to interact with NO resulting in several different cellular effects, as well as the formation of a new signal called nitrosothiol. Hydrogen Sulfide is also known to increase the levels of glutathione which acts to reduce or disrupt ROS levels in cells. In these early days in the field of H
2S biochemistry and signaling there are more questions than answers.
Uses
Production of sulfur, thioorganic compounds, and alkali metal sulfides
The main use of hydrogen sulfide is as a precursor to elemental sulfur. Several organosulfur compounds are produced using hydrogen sulfide. These include methanethiol, ethanethiol, and thioglycolic acid.
Upon combining with alkali metal bases, hydrogen sulfide converts to alkali hydrosulfides such as sodium hydrosulfide and sodium sulfide:
- H2S + NaOH → NaSH + H2O
- NaSH + NaOH → Na2S + H2O
These compounds are used in the paper making. Specifically, salts of SH− break bonds between lignin and cellulose components of pulp in the Kraft process.
Reversibly sodium sulfide in the presence of acids turns into
hydrosulfides and hydrogen sulfide; this supplies hydrosulfides in
organic solutions and is utilized in the production of thiophenol.
Analytical chemistry
For well over a century, hydrogen sulfide was important in analytical chemistry, in the qualitative inorganic analysis of metal ions. In these analyses, heavy metal (and nonmetal) ions (e.g., Pb(II), Cu(II), Hg(II), As(III)) are precipitated from solution upon exposure to H
2S. The components of the resulting precipitate redissolve with some selectivity, and are thus identified.
2S. The components of the resulting precipitate redissolve with some selectivity, and are thus identified.
Precursor to metal sulfides
As
indicated above, many metal ions react with hydrogen sulfide to give
the corresponding metal sulfides. This conversion is widely exploited.
For example, gases or waters contaminated by hydrogen sulfide can be
cleaned with metals, by forming metal sulfides. In the purification of
metal ores by flotation,
mineral powders are often treated with hydrogen sulfide to enhance the
separation. Metal parts are sometimes passivated with hydrogen sulfide.
Catalysts used in hydrodesulfurization are routinely activated with hydrogen sulfide, and the behavior of metallic catalysts used in other parts of a refinery is also modified using hydrogen sulfide.
Miscellaneous applications
Hydrogen sulfide is used to separate deuterium oxide, or heavy water, from normal water via the Girdler sulfide process.
Scientists from the University of Exeter discovered that cell exposure to small amounts of hydrogen sulfide gas can prevent mitochondrial
damage. When the cell is stressed with disease, enzymes are drawn into
the cell to produce small amounts of hydrogen sulfide. This study could
have further implications on preventing strokes, heart disease and arthritis.
A suspended animation-like state has been induced in rodents with the use of hydrogen sulfide, resulting in hypothermia with a concomitant reduction in metabolic rate. Also oxygen demand was reduced, thereby protecting against hypoxia. In addition, hydrogen sulfide has been shown to reduce inflammation in various situations.
Occurrence
Deposit of sulfur on a rock, caused by volcanic gas
Small amounts of hydrogen sulfide occur in crude petroleum, but natural gas can contain up to 90%. Volcanoes and some hot springs (as well as cold springs) emit some H
2S, where it probably arises via the hydrolysis of sulfide minerals, i.e. MS + H
2O → MO + H
2S.[citation needed] Hydrogen sulfide can be present naturally in well water, often as a result of the action of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Hydrogen sulfide is created by the human body in small doses through bacterial breakdown of proteins containing sulfur in the intestinal tract. It is also produced in the mouth (halitosis).
2S, where it probably arises via the hydrolysis of sulfide minerals, i.e. MS + H
2O → MO + H
2S.[citation needed] Hydrogen sulfide can be present naturally in well water, often as a result of the action of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Hydrogen sulfide is created by the human body in small doses through bacterial breakdown of proteins containing sulfur in the intestinal tract. It is also produced in the mouth (halitosis).
A portion of global H
2S emissions are due to human activity. By far the largest industrial source of H
2S is petroleum refineries: The hydrodesulfurization process liberates sulfur from petroleum by the action of hydrogen. The resulting H
2S is converted to elemental sulfur by partial combustion via the Claus process, which is a major source of elemental sulfur. Other anthropogenic sources of hydrogen sulfide include coke ovens, paper mills (using the Kraft process), tanneries and sewerage. H
2S arises from virtually anywhere where elemental sulfur comes in contact with organic material, especially at high temperatures. Depending on environmental conditions, it is responsible for deterioration of material through the action of some sulfur oxidizing microorganisms. It is called biogenic sulfide corrosion.
2S emissions are due to human activity. By far the largest industrial source of H
2S is petroleum refineries: The hydrodesulfurization process liberates sulfur from petroleum by the action of hydrogen. The resulting H
2S is converted to elemental sulfur by partial combustion via the Claus process, which is a major source of elemental sulfur. Other anthropogenic sources of hydrogen sulfide include coke ovens, paper mills (using the Kraft process), tanneries and sewerage. H
2S arises from virtually anywhere where elemental sulfur comes in contact with organic material, especially at high temperatures. Depending on environmental conditions, it is responsible for deterioration of material through the action of some sulfur oxidizing microorganisms. It is called biogenic sulfide corrosion.
In 2011 it was reported that increased concentration of H
2S, possibly due to oil field practices, was observed in the Bakken formation crude and presented challenges such as "health and environmental risks, corrosion of wellbore, added expense with regard to materials handling and pipeline equipment, and additional refinement requirements".
2S, possibly due to oil field practices, was observed in the Bakken formation crude and presented challenges such as "health and environmental risks, corrosion of wellbore, added expense with regard to materials handling and pipeline equipment, and additional refinement requirements".
Besides living near a gas and oil drilling operations, ordinary citizens can be exposed to hydrogen sulfide by being near waste water treatment facilities, landfills and farms with manure storage. Exposure occurs through breathing contaminated air or drinking contaminated water.
In municipal waste landfill sites, the burial of organic material rapidly leads to the production of anaerobic digestion within the waste mass and, with the humid atmosphere and relatively high temperature that accompanies biodegradation, biogas
is produced as soon as the air within the waste mass has been reduced.
If there is a source of sulfate bearing material, such as plasterboard
or natural gypsum (calcium sulphate dihydrate), under anaerobic conditions sulfate reducing bacteria
converts this to hydrogen sulfide. These bacteria cannot survive in air
but the moist, warm, anaerobic conditions of buried waste that contains
a high source of carbon – in inert landfills, paper and glue used in
the fabrication of products such as plasterboard can provide a rich source of carbon – is an excellent environment for the formation of hydrogen sulfide.
In industrial anaerobic digestion processes, such as waste water treatment or the digestion of organic waste from agriculture,
hydrogen sulfide can be formed from the reduction of sulfate and the
degradation of amino acids and proteins within organic compounds. Sulfates are relatively non-inhibitory to methane forming bacteria but can be reduced to H2S by sulfate reducing bacteria, of which there are several genera.
Removal from water
A number of processes designed to remove hydrogen sulfide from drinking water.
- Continuous chlorination
- For levels up to 75 mg/L chlorine is used in the purification process as an oxidizing chemical to react with hydrogen sulfide. This reaction yields insoluble solid sulfur. Usually the chlorine used is in the form of sodium hypochlorite.
- Aeration
- For concentrations of hydrogen sulfide less than 2 mg/L aeration is an ideal treatment process. Oxygen is added to water and a reaction between oxygen and hydrogen sulfide react to produce odorless sulfate
- Nitrate addition
- Calcium nitrate can be used to prevent hydrogen sulfide formation in wastewater streams.
Removal from fuel gases
Hydrogen sulfide is commonly found in raw natural gas and biogas. It is typically removed by amine gas treating
technologies. In such processes, the hydrogen sulfide is first
converted to an ammonium salt, whereas the natural gas is unaffected.
- RNH2 + H2S ⇌ RNH+
3 + SH−
The bisulfide anion is subsequently regenerated by heating of the
amine sulfide solution. Hydrogen sulfide generated in this process is
typically converted to elemental sulfur using the Claus Process.
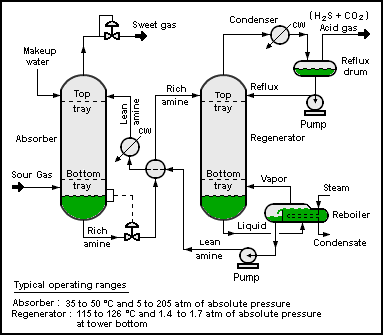
Process flow diagram
of a typical amine treating process used in petroleum refineries,
natural gas processing plants and other industrial facilities.
Safety
Hydrogen sulfide is a highly toxic and flammable gas (flammable range:
4.3–46%). Being heavier than air, it tends to accumulate at the bottom
of poorly ventilated spaces. Although very pungent at first, it quickly
deadens the sense of smell, so victims may be unaware of its presence
until it is too late. For safe handling procedures, a hydrogen sulfide safety data sheet (SDS) should be consulted.
Toxicity
Hydrogen sulfide is a broad-spectrum poison, meaning that it can poison several different systems in the body, although the nervous system is most affected. The toxicity of H
2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration.
2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration.
Since hydrogen sulfide occurs naturally in the body, the
environment, and the gut, enzymes exist to detoxify it. At some
threshold level, believed to average around 300–350 ppm, the oxidative
enzymes become overwhelmed. Many personal safety gas detectors, such as
those used by utility, sewage and petrochemical workers, are set to
alarm at as low as 5 to 10 ppm and to go into high alarm at 15 ppm.
Detoxification is effected by oxidation to sulfate, which is harmless. Hence, low levels of hydrogen sulfide may be tolerated indefinitely.
Diagnostic of extreme poisoning by H
2S is the discolouration of copper coins in the pockets of the victim. Treatment involves immediate inhalation of amyl nitrite, injections of sodium nitrite, or administration of 4-dimethylaminophenol in combination with inhalation of pure oxygen, administration of bronchodilators to overcome eventual bronchospasm, and in some cases hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). HBOT has clinical and anecdotal support.
2S is the discolouration of copper coins in the pockets of the victim. Treatment involves immediate inhalation of amyl nitrite, injections of sodium nitrite, or administration of 4-dimethylaminophenol in combination with inhalation of pure oxygen, administration of bronchodilators to overcome eventual bronchospasm, and in some cases hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). HBOT has clinical and anecdotal support.
Exposure to lower concentrations can result in eye irritation, a sore throat and cough, nausea, shortness of breath, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). These effects are believed to be due to the fact that hydrogen sulfide combines with alkali present in moist surface tissues to form sodium sulfide, a caustic. These symptoms usually go away in a few weeks.
Long-term, low-level exposure may result in fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, poor memory, and dizziness. Chronic exposure to low level H
2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
Short-term, high-level exposure can induce immediate collapse,
with loss of breathing and a high probability of death. If death does
not occur, high exposure to hydrogen sulfide can lead to cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, degeneration of the basal ganglia and cerebral edema. Although respiratory paralysis may be immediate, it can also be delayed up to 72 hours.
- 0.00047 ppm or 0.47 ppb is the odor threshold, the point at which 50% of a human panel can detect the presence of an odor without being able to identify it.
- 10 ppm is the OSHA permissible exposure limit (PEL) (8 hour time-weighted average).
- 10–20 ppm is the borderline concentration for eye irritation.
- 20 ppm is the acceptable ceiling concentration established by OSHA.
- 50 ppm is the acceptable maximum peak above the ceiling concentration for an 8-hour shift, with a maximum duration of 10 minutes.
- 50–100 ppm leads to eye damage.
- At 100–150 ppm the olfactory nerve is paralyzed after a few inhalations, and the sense of smell disappears, often together with awareness of danger.
- 320–530 ppm leads to pulmonary edema with the possibility of death.
- 530–1000 ppm causes strong stimulation of the central nervous system and rapid breathing, leading to loss of breathing.
- 800 ppm is the lethal concentration for 50% of humans for 5 minutes' exposure (LC50).
- Concentrations over 1000 ppm cause immediate collapse with loss of breathing, even after inhalation of a single breath.
Incidents
Hydrogen sulfide was used by the British Army as a chemical weapon during World War I.
It was not considered to be an ideal war gas, but, while other gases
were in short supply, it was used on two occasions in 1916.
In 1975, a hydrogen sulfide release from an oil drilling operation in Denver City, Texas, killed nine people and caused the state legislature to focus on the deadly hazards of the gas. State Representative E L Short took the lead in endorsing an investigation by the Texas Railroad Commission
and urged that residents be warned "by knocking on doors if necessary"
of the imminent danger stemming from the gas. One may die from the
second inhalation of the gas, and a warning itself may be too late.
On September 2, 2005, a leak in the propeller room of a Royal
Caribbean Cruise Liner docked in Los Angeles resulted in the deaths of 3
crewmen due to a sewage line leak. As a result, all such compartments
are now required to have a ventilation system.
A dump of toxic waste containing hydrogen sulfide is believed to have caused 17 deaths and thousands of illnesses in Abidjan, on the West African coast, in the 2006 Côte d'Ivoire toxic waste dump.
In 2014, levels of hydrogen sulfide as high as 83 ppm have been
detected at a recently built mall in Thailand called Siam Square One at
the Siam Square
area. Shop tenants at the mall reported health complications such as
sinus inflammation, breathing difficulties and eye irritation. After
investigation it was determined that the large amount of gas originated
from imperfect treatment and disposal of waste water in the building.
In November 2014, a substantial amount of hydrogen sulfide gas shrouded the central, eastern and southeastern parts of Moscow.
Residents living in the area were urged to stay indoors by the
emergencies ministry. Although the exact source of the gas was not
known, blame had been placed on a Moscow oil refinery.
In June 2016, a mother and her daughter were found deceased in their still-running Porsche Cayenne SUV against a guardrail on Florida's Turnpike, initially thought to be victims of carbon monoxide poisoning. Their deaths remained unexplained as the medical examiner waited for results of toxicology tests on the victims, until urine tests revealed that hydrogen sulfide was the cause of death.
A report from the Orange-Osceola Medical Examiner’s Office indicated
that toxic fumes came from the Porsche’s battery, located under the
front passenger seat.
In January 2017, three utility workers in Key Largo, Florida,
died one by one within seconds of descending into a narrow space beneath
a manhole cover to check a section of paved street, the hole was filled with hydrogen sulfide and methane gas created from years of rotted vegetation.
In an attempt to save the men, a firefighter who entered the hole
without his air tank (because he could not fit through the hole with it)
collapsed within seconds and had to be rescued by a colleague. The firefighter was airlifted to Jackson Memorial Hospital and later recovered.
Suicides
The gas, produced by mixing certain household ingredients, was used in a suicide wave in 2008 in Japan. The wave prompted staff at Tokyo's suicide prevention center to set up a special hot line during "Golden Week", as they received an increase in calls from people wanting to kill themselves during the annual May holiday.
As of 2010, this phenomenon has occurred in a number of US
cities, prompting warnings to those arriving at the site of the suicide.
These first responders, such as emergency services workers or family
members are at risk of death from inhaling lethal quantities of the gas,
or by fire. Local governments have also initiated campaigns to prevent such suicides.
Hydrogen sulfide in the natural environment
Microbial: The sulfur cycle
Sludge from a pond; the black color is due to metal sulfides
Hydrogen sulfide is a central participant in the sulfur cycle, the biogeochemical cycle of sulfur on Earth.
In the absence of oxygen, sulfur-reducing and sulfate-reducing bacteria derive energy from oxidizing hydrogen or organic molecules by reducing elemental sulfur or sulfate to hydrogen sulfide. Other bacteria liberate hydrogen sulfide from sulfur-containing amino acids; this gives rise to the odor of rotten eggs and contributes to the odor of flatulence.
As organic matter decays under low-oxygen (or hypoxic) conditions (such as in swamps, eutrophic lakes or dead zones
of oceans), sulfate-reducing bacteria will use the sulfates present in
the water to oxidize the organic matter, producing hydrogen sulfide as
waste. Some of the hydrogen sulfide will react with metal ions in the
water to produce metal sulfides, which are not water-soluble. These
metal sulfides, such as ferrous sulfide FeS, are often black or brown, leading to the dark color of sludge.
Several groups of bacteria can use hydrogen sulfide as fuel,
oxidizing it to elemental sulfur or to sulfate by using dissolved
oxygen, metal oxides (e.g., Fe oxyhydroxides and Mn oxides), or nitrate
as electron acceptors.
The purple sulfur bacteria and the green sulfur bacteria use hydrogen sulfide as an electron donor in photosynthesis, thereby producing elemental sulfur. (In fact, this mode of photosynthesis is older than the mode of cyanobacteria, algae, and plants, which uses water as electron donor and liberates oxygen.)
The biochemistry of hydrogen sulfide is a key part of the chemistry of the iron-sulfur world. In this model of the origin of life on Earth, geologically produced hydrogen sulfide is postulated as an electron donor driving the reduction of carbon dioxide.
Animals
Hydrogen sulfide is lethal to most animals, but a few highly specialized species (extremophiles) do thrive in habitats that are rich in this compound.
In the deep sea, hydrothermal vents and cold seeps with high levels of hydrogen sulfide are home to a number of extremely specialized lifeforms, ranging from bacteria to fish. Because of the absence of light at these depths, these ecosystems rely on chemosynthesis rather than photosynthesis.
Freshwater springs rich in hydrogen sulfide are mainly home to invertebrates, but also include a small number of fish: Cyprinodon bobmilleri (a pupfish from Mexico), Limia sulphurophila (a poeciliid from the Dominican Republic), Gambusia eurystoma (a poeciliid from Mexico), and a few Poecilia (poeciliids from Mexico). Invertebrates and microorganisms in some cave systems, such as Movile Cave, are adapted to high levels of hydrogen sulfide.
Interstellar and planetary occurrence
Hydrogen sulfide has often been detected in the interstellar medium. It also occurs in the clouds of planets in our solar system.
Mass extinctions
A
hydrogen sulfide bloom (green) stretching for about 150km along the
coast of Namibia. As oxygen-poor water reaches the coast, bacteria in
the organic-matter rich sediment produce hydrogen sulfide which is toxic
to fish.
Hydrogen sulfide has been implicated in several mass extinctions that have occurred in the Earth's past. In particular, a buildup of hydrogen sulfide in the atmosphere may have caused the Permian-Triassic extinction event 252 million years ago.
Organic residues from these extinction boundaries indicate that
the oceans were anoxic (oxygen-depleted) and had species of shallow
plankton that metabolized H
2S. The formation of H
2S may have been initiated by massive volcanic eruptions, which emitted carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, which warmed the oceans, lowering their capacity to absorb oxygen that would otherwise oxidize H
2S. The increased levels of hydrogen sulfide could have killed oxygen-generating plants as well as depleted the ozone layer, causing further stress. Small H
2S blooms have been detected in modern times in the Dead Sea and in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Namibia.
2S. The formation of H
2S may have been initiated by massive volcanic eruptions, which emitted carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, which warmed the oceans, lowering their capacity to absorb oxygen that would otherwise oxidize H
2S. The increased levels of hydrogen sulfide could have killed oxygen-generating plants as well as depleted the ozone layer, causing further stress. Small H
2S blooms have been detected in modern times in the Dead Sea and in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Namibia.