| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Pronunciation | /ˈdɛnɛb/, /ˈdɛnəb/ |
| Right ascension | 20h 41m 25.9s |
| Declination | +45° 16′ 49″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 1.25 (1.21 - 1.29) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A2 Ia |
| U−B color index | −0.23 |
| B−V color index | +0.09 |
| Variable type | Alpha Cygni |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −4.5 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1.99 mas/yr Dec.: 1.95 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.29 ± 0.32 mas |
| Distance | 2615 ± 215 ly (802 ± 66 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −8.38 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 19 ± 4 M☉ |
| Radius | 203 ± 17 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 196,000 ± 32,000 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.10 ± 0.05 cgs |
| Temperature | 8,525 ± 75 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | -0.25 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 20 ± 2 km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Deneb /ˈdɛnɛb/ is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky, with an average apparent magnitude of +1.25. A blue-white supergiant, Deneb rivals Rigel as the most luminous first magnitude star. However its distance, and hence luminosity, is poorly known; its luminosity is somewhere between 55,000 and 196,000 times that of the Sun. Its Bayer designation is α Cygni which is Latinised to Alpha Cygni, abbreviated to Alpha Cyg or α Cyg.
Nomenclature
α Cygni (Latinised to Alpha Cygni) is the star's designation given by Johann Bayer in 1603. The traditional name Deneb is derived from the Arabic word for "tail", from the phrase ذنب الدجاجة Dhanab al-Dajājah, or "tail of the hen". The IAU Working Group on Star Names has recognised the name Deneb for this star, and it is entered in their Catalog of Star Names.
An older traditional name is Arided /ˈærɪdɛd/, from the Arabic ar-ridf
'the one sitting behind the rider' (or just 'the follower'), perhaps
referring to the other major stars of Cygnus, which were called al-fawāris 'the riders'.
Observation
The Summer Triangle
The 19th brightest star in the night sky, Deneb culminates each year on October 23 at 6 PM and September 7 at 9 PM, corresponding to summer evenings in the northern hemisphere.
It never dips below the horizon at or above 45° north latitude, just
grazing the northern horizon at its lowest point at such locations as Minneapolis, Montréal and Turin. In the southern hemisphere, Deneb is not visible south of 45° parallel south, so it just barely rises above the horizon in South Africa, southern Australia, and northern New Zealand during the southern winter.
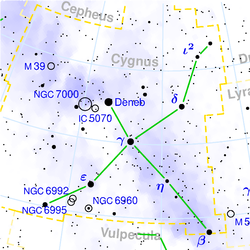
Deneb is located at the tip of the Northern Cross asterism made up of the brightest stars in Cygnus, the others being Albireo (Beta Cygni), Gamma Cygni, Delta Cygni, and Epsilon Cygni. It also lies at one vertex of the prominent and widely spaced asterism called the Summer Triangle, shared with the first-magnitude stars Vega in the constellation Lyra and Altair in Aquila. This outline of stars is the approximate shape of a right triangle, with Deneb located at one of the acute angles.
In 1984, the 90 cm (36-inch) reflecting Yapp telescope at Herstmonceux was tested with an echelle spectrograph from Queen's University Belfast and a CCD camera. Observations of the stars Deneb and Arcturus (Alpha Boötis) were conducted in the summer of 1984.
Pole star
Due to the Earth's axial precession, Deneb will be an approximate pole star (7° off of the north celestial pole) at around 9800 AD.
| Preceded by | Pole Star | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| Alderamin | 8700 AD to 11000 AD | Delta Cygni |
Physical characteristics
Deneb's place at the top-centre part of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
Deneb's adopted distance from the Earth is around 802 parsecs (2,620 ly).
This is derived by a variety of different methods, including spectral
luminosity classes, atmospheric modelling, stellar evolution models,
assumed membership of the Cygnus OB7
association, and direct measurement of angular diameter, but these
methods give different distances and all have significant margins of
error. The original derivation of a parallax using measurements from the astrometric satellite Hipparcos gave an uncertain result of 1.01 ± 0.57 mas that was consistent with this distance. However, a more recent
reanalysis gives the much larger parallax whose distance is barely half
the current accepted value.
One 2008 calculation using the Hipparcos data puts the most likely
distance at 475 parsecs (1,550 ly), with an uncertainty of around 15%.
The controversy over whether the direct Hipparcos measurements can be
ignored in favour of a wide range of indirect stellar models and
interstellar distance scales is similar to the better known situation
with the Pleiades.
Deneb's absolute magnitude
is currently estimated as −8.4, placing it among the visually brightest
stars known, with an estimated luminosity nearly 200,000 L☉. This is towards the upper end of values published over the past few decades, which vary between 55,000 L☉ and 196,000 L☉.
Deneb is the most luminous first magnitude star, that is, stars
with a brighter apparent magnitude than 1.5. Deneb is also the most
distant of the 30 brightest stars by a factor of almost 2. Based on its temperature and luminosity, and also on direct measurements of its tiny angular diameter (a mere 0.002 seconds of arc), Deneb appears to have a diameter of about over 200 times that of the Sun; if placed at the center of the Solar System, Deneb would extend out to the orbit of the Earth. It is one of the largest white 'A' spectral type stars known.
Deneb is a bluish-white star of spectral type A2Ia, with a surface temperature of 8,500 Kelvin. Since 1943, its spectrum has served as one of the stable references by which other stars are classified. Its mass is estimated at 19 M☉. Stellar winds causes matter to be lost at an average rate of 8±3×10−7 M☉ per year, 100,000 times the Sun's rate of mass loss or equivalent to about one Earth mass per 500 years.
Evolutionary state
Deneb spent much of its early life as a 23 M☉ O-type main-sequence star but it has now exhausted the hydrogen in its core and begun to cool and expand. Stars in the mass range of Deneb eventually expand to become the most luminous red supergiants, and within a few million years their cores will collapse producing a supernova explosion. It is now known that red supergiants up to a certain mass explode as the commonly seen type II-P supernovae,
but more massive ones lose their outer layers to become hotter again.
Depending on their initial masses and the rate of mass loss, they may
explode as yellow hypergiants or luminous blue variables, or they may become Wolf-Rayet stars before exploding in a type Ib or Ic supernova.
Identifying whether Deneb is currently evolving towards a red
supergiant or is currently evolving bluewards again would place valuable
constraints on the classes of stars that explode as red supergiants and
those that explode as hotter stars.
Stars evolving red-wards for the first time are most likely fusing hydrogen in a shell around a helium core that has not yet grown hot enough to start fusion to carbon and oxygen. Convection has begun dredging
up fusion products but these do not reach the surface. Post-red
supergiant stars are expected to show those fusion products at the
surface due to stronger convection during the red supergiant phase and
due to loss of the obscuring outer layers of the star. Deneb is thought
to be increasing its temperature after a period as a red supergiant,
although current models do not exactly reproduce the surface elements
showing in its spectrum.
Variable star
Deneb is the brightest example of the Alpha Cygni type(ACYG) variable stars, whose small irregular amplitudes and rapid pulsations can cause its magnitude to vary anywhere between 1.21 to 1.29.
Its variability was discovered by Lee in 1910,
but was not formally placed as a unique class of variable stars until
the 1985 4th edition of the General Catalogue of Variable Stars. The cause of the pulsations of Alpha Cygni variable stars are not fully understood, but their irregular nature seems to be due to beating
of multiple pulsation periods. Analysis of radial velocities determined
16 different harmonic pulsation modes with periods ranging between 6.9
to 100.8 days. A longer period of about 800 days probably also exists. Deneb is considered by astronomers to be prototype of ACYG variables.
Possible spectroscopic companion
Deneb has been reported as a possible single line spectroscopic binary with a period of about 850 days, where the spectral lines from the star suggest cyclical radial velocity changes. Later investigations have found no evidence supporting the existence of a companion.
Etymology and cultural significance
Wide-field view of the Summer Triangle and the Milky Way. Deneb is at the left-centre of the picture.
Names similar to Deneb have been given to at least seven different stars, most notably Deneb Kaitos, the brightest star in the constellation of Cetus; Deneb Algedi, the brightest star in Capricornus; and Denebola, the second brightest star in Leo. All these stars are referring to the tail of the animals that their respective constellations represent.
Denebadigege was used in the Alfonsine Tables, other variants include Deneb Adige, Denebedigege and Arided. This latter name was derived from Al Ridhādh, a name for the constellation. Johann Bayer called it Arrioph, derived from Aridf and Al Ridf, 'the hindmost' or Gallina. German poet and author Philippus Caesius termed it Os rosae, or Rosemund in German, or Uropygium – the parson's nose. The names Arided and Aridif have fallen out of use.
In Chinese, 天津 (Tiān Jīn), meaning Celestial Ford, refers to an asterism consisting of Deneb, Gamma Cygni, Delta Cygni, 30 Cygni, Nu Cygni, Tau Cygni, Upsilon Cygni, Zeta Cygni and Epsilon Cygni. Consequently, the Chinese name for Deneb itself is 天津四 (Tiān Jīn sì, English: the Fourth Star of the Celestial Ford).
In the Chinese love story of Qi Xi, Deneb marks the magpie bridge across the Milky Way, which allows the separated lovers Niu Lang (Altair) and Zhi Nü (Vega)
to be reunited on one special night of the year in late summer. In
other versions of the story, Deneb is a fairy who acts as chaperone when
the lovers meet.
Namesakes
USS Arided was a United States Navy Crater-class cargo ship named after the star. The SS Deneb was an Italian merchant vessel that bore this name from 1951 until she was scrapped in 1966.
In fiction
The star Deneb, and hypothetical planets orbiting it, have been used many times in literature, film, electronic games, and music. Examples include several episodes of the Star Trek TV series, the Silver Surfer comic book, the Rush albums A Farewell to Kings and Hemispheres, the Descent: FreeSpace – The Great War computer game, Stellaris, science fiction novel Hyperion, and Andy Weir, in his novel The Martian.