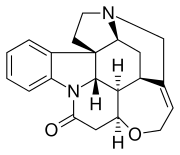
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Strychnidin-10-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.290 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1692 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C21H22N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 334.419 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White or translucent crystal or crystalline powder; Bitter tasting |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.36 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 270 °C; 518 °F; 543 K |
| Boiling point | 284 to 286 °C; 543 to 547 °F; 557 to 559 K |
| 0.02% (20°C)[2] | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.25[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Very toxic |
| GHS piktogrami |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H300, H310, H330, H410 | |
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P284, P301+310 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non flammable. |
| Non flammable. | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
0.5 mg/kg (dog, oral) 0.5 mg/kg (cat, oral) 2 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 16 mg/kg (rat, oral) 2.35 mg/kg (rat, oral)[4] |
LDLo (lowest published)
|
0.6 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.15 mg/m3[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.15 mg/m3[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
3 mg/m3[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Strychnine (/ˈstrɪkniːn/ STRIK-neen or /-nɪn/ -nin; US mainly /ˈstrɪknaɪn/ STRIK-nyne) is a highly toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the eyes or mouth, causes poisoning which results in muscular convulsions and eventually death through asphyxia. While it has no known medicinal effects, in the past the convulsant effect was believed to be beneficial in small doses. The most common source is from the seeds of the Strychnos nux-vomica tree.
Biosynthesis
Strychnine is a terpene indole alkaloid belonging to the Strychnos family of Corynanthe alkaloids, and it is derived from tryptamine and secologanin. The enzyme, strictosidine synthase, catalyzes the condensation of tryptamine and secologanin, followed by a Pictet-Spengler reaction to form strictosidine.
While the enzymes that catalyze the following steps have not been
identified, the steps have been inferred by isolation of intermediates
from Strychnos nux-vomica. The next step is hydrolysis of the acetal, which opens the ring by elimination of glucose (O-Glu) and provides a reactive aldehyde. The nascent aldehyde is then attacked by a secondary amine to afford geissoschizine, a common intermediate of many related compounds in the Strychnos family.
A reverse Pictet-Spengler reaction cleaves the C2–C3 bond, while a subsequent Mannich reaction forms the C3–C7 bond, and a Michael addition forms the C2–C16 bond to provide dehydropreakuammicine. Hydrolysis of the methyl ester and decarboxylation leads to norfluorocurarine. Stereospecific reduction of the endocyclic double bond by NADPH and hydroxylation provides the Wieland-Gumlich aldehyde, which was first isolated by Heimberger and Scott in 1973, although previously synthesized by Wieland and Gumlich in 1932. To elongate the appendage by 2 carbons, acetyl-CoA is added to the aldehyde in an aldol reaction
to afford prestrychnine. Strychnine is then formed by a facile addition
of the amine with the carboxylic acid or its activated CoA thioester, followed by ring-closure via displacement of an activated alcohol.
Chemical synthesis
As early researchers have noted, the strychnine molecular structure,
with its specific array of rings, stereocenters, and nitrogen functional
groups, is a complex synthetic target, and has stimulated interest for
that reason and for interest in the structure-activity relationships underlying its pharmacologic activities. An early synthetic chemist targeting strychnine, R.B. Woodward,
quoted the chemist who determined its structure through chemical
decomposition and related physical studies as saying that "for its
molecular size it is the most complex organic substance known"
(attributed to Sir Robert Robinson).
The first total synthesis of strychnine was reported by the research group of R. B. Woodward in 1954, and is considered a classic in this field. The Woodward account published in 1954 was very brief (3 pp.), but was followed by a 42-page report in 1963.
The molecule has since received continuing wide attention in the years
since for the challenges to synthetic organic strategy and tactics
presented by its complexity; its synthesis has been targeted and its
stereocontrolled preparation independently achieved by more than a
dozen research groups since the first success (see main strychnine total synthesis article).
Mechanism of action
Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of glycine and acetylcholine receptors.
It primarily affects the motor nerve fibers in the spinal cord which
control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one end of a
nerve cell by the binding of neurotransmitters to the receptors. In the presence of an inhibitory neurotransmitter, such as glycine,
a greater quantity of excitatory neurotransmitters must bind to
receptors before there will be an action potential generated. Glycine
acts primarily as an agonist of the glycine receptor, which is a
ligand-gated chloride channel in neurons located in the spinal cord and
in the brain. This chloride channel will allow the negatively charged
chloride ions into the neuron, causing a hyperpolarization which pushes
the membrane potential further from threshold. Strychnine is an antagonist
of glycine; it binds noncovalently to the same receptor, preventing the
inhibitory effects of glycine on the postsynaptic neuron. Therefore, action potentials
are triggered with lower levels of excitatory neurotransmitters. When
the inhibitory signals are prevented, the motor neurons are more easily
activated and the victim will have spastic muscle contractions,
resulting in death by asphyxiation. Strychnine binds the Aplysia californica acetylcholine binding protein (a homolog of nicotinic receptors) with high affinity but low specificity, and does so in multiple conformations.
Toxicity
In high doses, strychnine is very toxic to humans (minimum lethal
oral dose in adults is 30–120 mg) and many other animals (oral LD50 = 16 mg/kg in rats, 2 mg/kg in mice), and poisoning by inhalation, swallowing, or absorption through eyes or mouth can be fatal. S. nux-vomica seeds are generally effective as a poison only when they are crushed or chewed before swallowing because the pericarp is quite hard and indigestible; poisoning symptoms may therefore not appear if the seeds are ingested whole.
Animal toxicity
Strychnine
poisoning in animals usually occurs from ingestion of baits designed
for use against gophers, moles, and coyotes. Strychnine is also used as a
rodenticide, but is not specific to such unwanted pests and may kill other small animals. In the United States, most baits containing strychnine have been replaced with zinc phosphide baits since 1990. In the Netherlands, rodenticides with strychnine are forbidden. Some animals are immune to strychnine, usually these are species such as fruit bats that have evolved resistance to poisonous alkaloids in the fruit they eat. The drugstore beetle has a symbiotic gut yeast that allows it to digest pure strychnine.
Strychnine toxicity in rats is dependent on sex. It is more toxic to females than to males when administered via subcutaneous injection or intraperitoneal injection.
Differences are due to higher rates of metabolism by male rat liver
microsomes. Dogs and cats are more susceptible among domestic animals,
pigs are believed to be as susceptible as dogs, and horses are able to
tolerate relatively large amounts of strychnine. Birds affected by
strychnine poisoning exhibit wing droop, salivation, tremors, muscle tenseness, and convulsions. Death occurs as a result of respiratory arrest. The clinical signs of strychnine poisoning relate to its effects on the central nervous system.
The first clinical signs of poisoning include nervousness,
restlessness, twitching of the muscles, and stiffness of the neck. As
the poisoning progresses, the muscular twitching becomes more pronounced
and convulsions suddenly appear in all the skeletal muscles. The limbs
are extended and the neck is curved to opisthotonus.
The pupils are widely dilated. As death approaches, the convulsions
follow one another with increased rapidity, severity, and duration.
Death results from asphyxia due to prolonged paralysis of the
respiratory muscles. Following the ingestion of strychnine, symptoms of
poisoning usually appear within 15 to 60 min. The LD50-values for strychnine in animals are listed below in table 1.
| The LD50 values for strychnine in animals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Organism | Route | LD50 (mg/kg) |
| Bird-wild | Oral | 16 |
| Cat | Intravenous | 0.33 |
| Cat | Oral | 0.5 |
| Dog | Intravenous | 0.8 |
| Dog | Subcutaneous | 0.35 |
| Dog | Oral | 0.5 |
| Duck | Oral | 3.0 |
| Mouse | Intraperitoneal | 0.98 |
| Mouse | Intravenous | 0.41 |
| Mouse | Oral | 2.0 |
| Mouse | Parenteral | 1.06 |
| Mouse | Subcutaneous | 0.47 |
| Pigeon | Oral | 21.0 |
| Quail | Oral | 23.0 |
| Rabbit | Intravenous | 0.4 |
| Rabbit | Oral | 0.6 |
| Rat | Oral | 16.0 |
| Rat | Intravenous | 2.35 |
Human toxicity
An 1809 painting depicting opisthotonus
The symptoms of poisoning in humans are generally similar to those as
in other animals, because the mechanism of action is apparently similar
across species. The toxicity of strychnine in humans is not ethically
studied, so most information known comes from cases of strychnine
poisoning, both unintentional and deliberate.
After injection, inhalation, or ingestion, the first symptoms to appear are generalized muscle spasms.
They appear very quickly after inhalation or injection — within as few
as five minutes — and take somewhat longer to manifest after ingestion,
typically approximately 15 minutes. With a very high dose, the onset of respiratory failure and brain death can occur in 15 to 30 minutes. If a lower dose is ingested, other symptoms begin to develop, including seizures, cramping, stiffness, hypervigilance, and agitation.
Seizures caused by strychnine poisoning can start as early as 15
minutes after exposure and last 12 – 24 hours. They are often triggered
by sights, sounds, or touch and can cause other adverse symptoms,
including hyperthermia, rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuric kidney failure, metabolic acidosis, and respiratory acidosis. During seizures, mydriasis (abnormal dilation), exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyes), and nystagmus (involuntary eye movements) may occur.
As strychnine poisoning progresses, tachycardia (rapid heart beat), hypertension (high blood pressure), tachypnea (rapid breathing), cyanosis (blue discoloration), diaphoresis (sweating), water-electrolyte imbalance, leukocytosis (high number of white blood cells), trismus (lockjaw), risus sardonicus (spasm of the facial muscles), and opisthotonus
(dramatic spasm of the back muscles, causing arching of the back and
neck) can occur. In rare cases, the affected person may experience nausea or vomiting.
The proximate cause of death in strychnine poisoning can be cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, multiple organ failure, or brain damage.
The minimum lethal dose values estimated from different cases of strychnine poisoning are listed below in table 2.
| Minimum lethal dose estimates for strychnine in humans | ||
|---|---|---|
| Route | Dose (mg) | |
| Human | Oral | 100–120 |
| Human | Oral | 30–60 |
| Human (child) | Oral | 15 |
| Human (adult) | Oral | 50–100 |
| Human (adult) | Oral | 30–100 |
| Human | Intravenously | 5–10 (approximate) |
For occupational exposures to strychnine, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set exposure limits at 0.15 mg/m3 over an 8-hour work day.
Because strychnine produces some of the most dramatic and painful
symptoms of any known toxic reaction, strychnine poisoning is often
portrayed in literature and film including authors Agatha Christie and Arthur Conan Doyle.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Strychnine
may be introduced into the body orally, by inhalation, or by injection.
It is a potently bitter substance, and in humans has been shown to
activate bitter taste receptors TAS2R10 and TAS2R46. Strychnine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Distribution
Strychnine is transported by plasma and erythrocytes.
Due to slight protein binding, strychnine leaves the bloodstream
quickly and distributes to the tissues. Approximately 50% of the
ingested dose can enter the tissues in 5 minutes. Also within a few
minutes of ingestion, strychnine can be detected in the urine. Little
difference was noted between oral and intramuscular administration of
strychnine in a 4 mg dose.
In persons killed by strychnine, the highest concentrations are found
in the blood, liver, kidney and stomach wall. The usual fatal dose is
60–100 mg strychnine and is fatal after a period of 1–2 hours, though
lethal doses vary depending on the individual.
Metabolism
Strychnine is rapidly metabolized by the liver microsomal enzyme system requiring NADPH and O2. Strychnine competes with the inhibitory neurotransmitter glycine resulting in an excitatory state. However, the toxicokinetics
after overdose have not been well described. In most severe cases of
strychnine poisoning, the patient dies before reaching the hospital. The
biological half-life
of strychnine is about 10 hours. This half-life suggests that normal
hepatic function can efficiently degrade strychnine even when the
quantity ingested is high enough to cause severe poisoning.
Excretion
A
few minutes after ingestion, strychnine is excreted unchanged in the
urine, and accounts for about 5 to 15% of a sublethal dose given over 6
hours. Approximately 10 to 20% of the dose will be excreted unchanged in
the urine in the first 24 hours. The percentage excreted decreases with
the increasing dose. Of the amount excreted by the kidneys, about 70%
is excreted in the first 6 hours, and almost 90% in the first 24 hours.
Excretion is virtually complete in 48 to 72 hours.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote
for strychnine but recovery from exposure is possible with early
supportive medical treatment. Strychnine poisoning demands aggressive
management with early control of muscle spasms, intubation if loss of
airway control, toxin removal (decontamination),
intravenous hydration and potentially active cooling efforts in the
context of hyperthermia as well as hemodialysis in kidney failure (to
note, strychnine has not been shown to be removed by hemodialysis). Strychnine poisoning in today's age generally results from herbal remedies and strychnine-containing rodenticides.
Moreover, management should be tailored to the patient's history of
chief complaint and workup to rule out other causes. If a poisoned
person is able to survive for 6 to 12 hours subsequent to initial dose,
they have a good prognosis.
The patient should be kept in a quiet and darkened room, because
excessive manipulation and loud noises may cause convulsions. Because
these convulsions are extremely painful, appropriate analgesics should
be administered. Treatment of strychnine poisoning involves oral
administration of activated charcoal which adsorbs strychnine within the digestive tract; unabsorbed strychnine is removed from the stomach by gastric lavage, along with tannic acid
or potassium permanganate solutions to oxidize strychnine. Activated
charcoal may be beneficial, but its benefit remains unproven, to note
its use should be avoided in any patient with a tenuous airway or
altered mental status. Seizures are controlled by anticonvulsants, such as phenobarbital or diazepam, along with muscle relaxants such as dantrolene to combat muscle rigidity. Historically chloroform or heavy doses of chloral, bromide, urethane or amyl nitrite were used to restrain the convulsions.[citation needed] Because medications such as diazepam are not effective to relieve convulsions in all cases, concurrent use of barbiturates and/or propofol can be utilized.
The sine qua non
of strychnine toxicity is the "awake" seizure, in which tonic-clonic
activity occurs but the patient is alert and oriented throughout and
afterwards. Accordingly, George Harley (1829–1896) showed in 1850 that curare (wourali) was effective
for the treatment of tetanus and strychnine poisoning. It is important
to note that if seizure activity is present, the use of muscle paralysis
will only mask the signs of ongoing seizure activity despite otherwise
ongoing present brain damage.
History
Strychnine was the first alkaloid to be identified in plants of the genus Strychnos, family Loganiaceae. Strychnos, named by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, is a genus of trees and climbing shrubs of the Gentianales
order. The genus contains 196 various species and is distributed
throughout the warm regions of Asia (58 species), America (64 species),
and Africa (75 species). The seeds and bark of many plants in this genus
contain strychnine.
The toxic and medicinal effects of Strychnos nux-vomica
have been well known from the times of ancient India, although the
chemical compound itself was not identified and characterized until the
19th century. The inhabitants of these countries had historical
knowledge of the species Strychnos nux-vomica and Saint-Ignatius' bean (Strychnos ignatii). Strychnos nux-vomica is a tree native to the tropical forests on the Malabar Coast
in Southern India, Sri Lanka and Indonesia, which attains a height of
about 12 metres (39 ft). The tree has a crooked, short, thick trunk and
the wood is close grained and very durable. The fruit has an orange
color and is about the size of a large apple with a hard rind
and contains five seeds, which are covered with a soft wool-like
substance. The ripe seeds look like flattened disks, which are very
hard. These seeds are the chief commercial source of strychnine and were
first imported to and marketed in Europe as a poison to kill rodents
and small predators. Strychnos ignatii
is a woody climbing shrub of the Philippines. The fruit of the plant,
known as Saint Ignatius' bean, contains as many as 25 seeds embedded in
the pulp. The seeds contain more strychnine than other commercial
alkaloids. The properties of S. nux-vomica and S. ignatii are substantially those of the alkaloid strychnine.
Strychnine was first discovered by French chemists Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre-Joseph Pelletier in 1818 in the Saint-Ignatius' bean. In some Strychnos plants a 9,10-dimethoxy derivative of strychnine, the alkaloid brucine, is also present. Brucine
is not as poisonous as strychnine. Historic records indicate that
preparations containing strychnine (presumably) had been used to kill
dogs, cats, and birds in Europe as far back as 1640. The structure of strychnine was first determined in 1946 by Sir Robert Robinson and in 1954 this alkaloid was synthesized in a laboratory by Robert B. Woodward. This is one of the most famous syntheses in the history of organic chemistry. Both chemists won the Nobel prize (Robinson in 1947 and Woodward in 1965).
Strychnine has been used as a plot device in the author Agatha Christie's murder mysteries.
Performance enhancer
Strychnine was popularly used as an athletic performance enhancer and recreational stimulant in the late 19th century and early 20th century, due to its convulsant effects. It was thought to be similar to coffee. Its effects are well-described in H. G. Wells' novella The Invisible Man:
the title character states "Strychnine is a grand tonic ... to take the
flabbiness out of a man." The protagonist replies: "It's the devil, ...
It's the palaeolithic in a bottle."




