| Great Wall of China | |
|---|---|
萬里長城 / 万里长城 | |
 | |
 Map of all the wall constructions | |
| General information | |
| Type | Fortification |
| Country | China |
| Coordinates | 40.68°N 117.23°ECoordinates: 40.68°N 117.23°E |
| Technical details | |
| Size | 21,196 km (13,171 mi) |
| Official name | The Great Wall |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | i, ii, iii, iv, vi |
| Designated | 1987 (11th session) |
| Reference no. | 438 |
| State Party | China |
| Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Great Wall of China | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 長城 | ||
| Simplified Chinese | 长城 | ||
| Literal meaning | "The Long Wall" | ||
| |||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 萬里長城 | ||
| Simplified Chinese | 万里长城 | ||
| Literal meaning | "The 10,000-li Long Wall" | ||
|
The Great Wall of China (traditional Chinese: 萬里長城; simplified Chinese: 万里长城; pinyin: Wànlǐ Chángchéng) is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe. Several walls were built from as early as the 7th century BC, with selective stretches later joined together by Qin Shi Huang (220–206 BC), the first emperor of China. Little of the Qin wall remains. Later on, many successive dynasties built and maintained multiple stretches of border walls. The most well-known sections of the wall were built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644).
Apart from defense, other purposes of the Great Wall have included border controls, allowing the imposition of duties on goods transported along the Silk Road, regulation or encouragement of trade and the control of immigration and emigration. Furthermore, the defensive characteristics of the Great Wall were enhanced by the construction of watchtowers, troop barracks, garrison stations, signaling capabilities through the means of smoke or fire, and the fact that the path of the Great Wall also served as a transportation corridor.
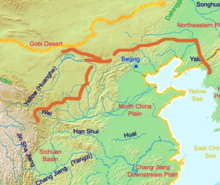
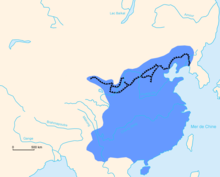
The frontier walls built by different dynasties have multiple courses. Collectively, they stretch from Liaodong in the east to Lop Lake in the west, from the present-day Sino–Russian border in the north to Tao River (Taohe) in the south; along an arc that roughly delineates the edge of the Mongolian steppe; spanning over 20,000 km (12,000 mi) in total. Today, the defensive system of the Great Wall is generally recognized as one of the most impressive architectural feats in history.
Names
The collection of fortifications known as the Great Wall of China has historically had a number of different names in both Chinese and English.
In Chinese histories, the term "Long Wall(s)" (t 長城, s 长城, Chángchéng) appears in Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian, where it referred both to the separate great walls built between and north of the Warring States and to the more unified construction of the First Emperor. The Chinese character 城, meaning city or fortress, is a phono-semantic compound of the "earth" radical 土 and phonetic 成, whose Old Chinese pronunciation has been reconstructed as *deŋ. It originally referred to the rampart which surrounded traditional Chinese cities and was used by extension for these walls around their respective states; today, however, it is much more often the Chinese word for "city".
The longer Chinese name "Ten-Thousand Mile Long Wall" (t 萬里長城, s 万里长城, Wànlǐ Chángchéng) came from Sima Qian's description of it in the Records, though he did not name the walls as such. The AD 493 Book of Song quotes the frontier general Tan Daoji referring to "the long wall of 10,000 miles", closer to the modern name, but the name rarely features in pre-modern times otherwise. The traditional Chinese mile (里, lǐ) was an often irregular distance that was intended to show the length of a standard village and varied with terrain but was usually standardized at distances around a third of an English mile (540 m). Since China's metrication in 1930, it has been exactly equivalent to 500 metres or 1,600 feet, which would make the wall's name describe a distance of 5,000 km (3,100 mi). However, this use of "ten-thousand" (wàn) is figurative in a similar manner to the Greek and English myriad and simply means "innumerable" or "immeasurable".
Because of the wall's association with the First Emperor's supposed tyranny, the Chinese dynasties after Qin usually avoided referring to their own additions to the wall by the name "Long Wall". Instead, various terms were used in medieval records, including "frontier(s)" (塞, Sài),[15] "rampart(s)" (垣, Yuán), "barrier(s)" (障, Zhàng), "the outer fortresses" (外堡, Wàibǎo), and "the border wall(s)" (t 邊牆, s 边墙, Biānqiáng). Poetic and informal names for the wall included "the Purple Frontier" (紫塞, Zǐsài) and "the Earth Dragon" (t 土龍, s 土龙, Tǔlóng). Only during the Qing period did "Long Wall" become the catch-all term to refer to the many border walls regardless of their location or dynastic origin, equivalent to the English "Great Wall".
Sections of the wall in south Gobi Desert and Mongolian steppe are sometimes referred to as "Wall of Genghis Khan", even though Genghis Khan did not construct any walls or permanent defense lines himself.
The current English name evolved from accounts of "the Chinese wall" from early modern European travelers. By the nineteenth century, "The Great Wall of China" had become standard in English and French, although other European languages such as German continue to refer to it as "the Chinese wall".
History
Early walls
The Chinese were already familiar with the techniques of wall-building by the time of the Spring and Autumn period between the 8th and 5th centuries BC. During this time and the subsequent Warring States period, the states of Qin, Wei, Zhao, Qi, Han, Yan, and Zhongshan all constructed extensive fortifications to defend their own borders. Built to withstand the attack of small arms such as swords and spears, these walls were made mostly of stone or by stamping earth and gravel between board frames.
King Zheng of Qin conquered the last of his opponents and unified China as the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty ("Qin Shi Huang") in 221 BC. Intending to impose centralized rule and prevent the resurgence of feudal lords, he ordered the destruction of the sections of the walls that divided his empire among the former states. To position the empire against the Xiongnu people from the north, however, he ordered the building of new walls to connect the remaining fortifications along the empire's northern frontier. "Build and move on" was a central guiding principle in constructing the wall, implying that the Chinese were not erecting a permanently fixed border. Transporting the large quantity of materials required for construction was difficult, so builders always tried to use local resources. Stones from the mountains were used over mountain ranges, while rammed earth was used for construction in the plains. There are no surviving historical records indicating the exact length and course of the Qin walls. Most of the ancient walls have eroded away over the centuries, and very few sections remain today. The human cost of the construction is unknown, but it has been estimated by some authors that hundreds of thousands workers died building the Qin wall. Later, the Han, the Northern Dynasties and the Sui all repaired, rebuilt, or expanded sections of the Great Wall at great cost to defend themselves against northern invaders. The Tang and Song dynasties did not undertake any significant effort in the region. Non-Han dynasties also built their border walls: the Xianbei-ruled Northern Wei, the Khitan-ruled Liao, Jurchen Jin and the Tangut-established Western Xia, who ruled vast territories over Northern China throughout centuries, all constructed defensive walls but those were located much to the north of the other Great Walls as we know it, within China's province of Inner Mongolia and in Mongolia itself.
Ming era
The Great Wall concept was revived again under the Ming in the 14th century, and following the Ming army's defeat by the Oirats in the Battle of Tumu. The Ming had failed to gain a clear upper hand over the Mongolian tribes after successive battles, and the long-drawn conflict was taking a toll on the empire. The Ming adopted a new strategy to keep the nomadic tribes out by constructing walls along the northern border of China. Acknowledging the Mongol control established in the Ordos Desert, the wall followed the desert's southern edge instead of incorporating the bend of the Yellow River.
Unlike the earlier fortifications, the Ming construction was stronger and more elaborate due to the use of bricks and stone instead of rammed earth. Up to 25,000 watchtowers are estimated to have been constructed on the wall. As Mongol raids continued periodically over the years, the Ming devoted considerable resources to repair and reinforce the walls. Sections near the Ming capital of Beijing were especially strong. Qi Jiguang between 1567 and 1570 also repaired and reinforced the wall, faced sections of the ram-earth wall with bricks and constructed 1,200 watchtowers from Shanhaiguan Pass to Changping to warn of approaching Mongol raiders. During the 1440s–1460s, the Ming also built a so-called "Liaodong Wall". Similar in function to the Great Wall (whose extension, in a sense, it was), but more basic in construction, the Liaodong Wall enclosed the agricultural heartland of the Liaodong province, protecting it against potential incursions by Jurched-Mongol Oriyanghan from the northwest and the Jianzhou Jurchens from the north. While stones and tiles were used in some parts of the Liaodong Wall, most of it was in fact simply an earth dike with moats on both sides.
Towards the end of the Ming, the Great Wall helped defend the empire against the Manchu invasions that began around 1600. Even after the loss of all of Liaodong, the Ming army held the heavily fortified Shanhai Pass, preventing the Manchus from conquering the Chinese heartland. The Manchus were finally able to cross the Great Wall in 1644, after Beijing had already fallen to Li Zicheng's rebels. Before this time, the Manchus had crossed the Great Wall multiple times to raid, but this time it was for conquest. The gates at Shanhai Pass were opened on May 25 by the commanding Ming general, Wu Sangui, who formed an alliance with the Manchus, hoping to use the Manchus to expel the rebels from Beijing. The Manchus quickly seized Beijing, and eventually defeated both the rebel-founded Shun dynasty and the remaining Ming resistance, establishing the Qing dynasty rule over all of China.
Under Qing rule, China's borders extended beyond the walls and Mongolia was annexed into the empire, so constructions on the Great Wall were discontinued. On the other hand, the so-called Willow Palisade, following a line similar to that of the Ming Liaodong Wall, was constructed by the Qing rulers in Manchuria. Its purpose, however, was not defense but rather to prevent Han Chinese migration into Manchuria.
Foreign accounts
None of the Europeans who visited China or Mongolia in the 13th and 14th centuries, such as Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, William of Rubruck, Marco Polo, Odoric of Pordenone and Giovanni de' Marignolli, mentioned the Great Wall.
The North African traveler Ibn Battuta, who also visited China during the Yuan dynasty c. 1346, had heard about China's Great Wall, possibly before he had arrived in China. He wrote that the wall is "sixty days' travel" from Zeitun (modern Quanzhou) in his travelogue Gift to Those Who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling. He associated it with the legend of the wall mentioned in the Qur'an, which Dhul-Qarnayn (commonly associated with Alexander the Great) was said to have erected to protect people near the land of the rising sun from the savages of Gog and Magog. However, Ibn Battuta could find no one who had either seen it or knew of anyone who had seen it, suggesting that although there were remnants of the wall at that time, they were not significant.
Soon after Europeans reached Ming China by ship in the early 16th century, accounts of the Great Wall started to circulate in Europe, even though no European was to see it for another century. Possibly one of the earliest European descriptions of the wall and of its significance for the defense of the country against the "Tartars" (i.e. Mongols) may be the one contained in João de Barros's 1563 Asia. Other early accounts in Western sources include those of Gaspar da Cruz, Bento de Goes, Matteo Ricci, and Bishop Juan González de Mendoza, the latter in 1585 describing it as a "superbious and mightie work" of architecture, though he had not seen it. In 1559, in his work "A Treatise of China and the Adjoyning Regions", Gaspar da Cruz offers an early discussion of the Great Wall. Perhaps the first recorded instance of a European actually entering China via the Great Wall came in 1605, when the Portuguese Jesuit brother Bento de Góis reached the northwestern Jiayu Pass from India. Early European accounts were mostly modest and empirical, closely mirroring contemporary Chinese understanding of the Wall, although later they slid into hyperbole, including the erroneous but ubiquitous claim that the Ming walls were the same ones that were built by the first emperor in the 3rd century BC.
When China opened its borders to foreign merchants and visitors after its defeat in the First and Second Opium Wars, the Great Wall became a main attraction for tourists. The travelogues of the later 19th century further enhanced the reputation and the mythology of the Great Wall.
Course
A formal definition of what constitutes a "Great Wall" has not been agreed upon, making the full course of the Great Wall difficult to describe in its entirety. The defensive lines contain multiple stretches of ramparts, trenches and ditches, as well as individual fortresses.
In 2012, based on existing research and the results of a comprehensive mapping survey, the National Cultural Heritage Administration of China concluded that the remaining Great Wall associated sites include 10,051 wall sections, 1,764 ramparts or trenches, 29,510 individual buildings, and 2,211 fortifications or passes, with the walls and trenches spanning a total length of 21,196 km (13,171 mi). Incorporating advanced technologies, the study has concluded that the Ming Great Wall measure 8,850 km (5,500 mi). This consists of 6,259 km (3,889 mi) of wall sections, 359 km (223 mi) of trenches and 2,232 km (1,387 mi) of natural defensive barriers such as hills and rivers. In addition, Qin, Han and earlier Great Wall sites are 3,080 km (1,914 mi) long in total; Jin dynasty (1115–1234) border fortifications are 4,010 km (2,492 mi) in length; the remainder date back to Northern Wei, Northern Qi, Sui, Tang, the Five Dynasties, Song, Liao and Xixia. About half of the sites are located in Inner Mongolia (31%) and Hebei (19%).
Great Wall of Han dynasty near Yumenguan.
Ming dynasty Great Wall at Jinshanling
Han Great Wall
Han fortifications starts from Yumen Pass and Yang Pass, southwest of Dunhuang, in Gansu province. Ruins of the remotest Han border posts are found in Mamitu (t 馬迷途, s 马迷途, Mǎmítú, l "horses losing their way") near Yumen Pass.
Ming Great Wall
The Jiayu Pass, located in Gansu province, is the western terminus of the Ming Great Wall. From Jiayu Pass the wall travels discontinuously down the Hexi Corridor and into the deserts of Ningxia, where it enters the western edge of the Yellow River loop at Yinchuan. Here the first major walls erected during the Ming dynasty cut through the Ordos Desert to the eastern edge of the Yellow River loop. There at Piantou Pass (t 偏頭關, s 偏头关, Piāntóuguān) in Xinzhou, Shanxi province, the Great Wall splits in two with the "Outer Great Wall" (t 外長城, s 外长城, Wài Chǎngchéng) extending along the Inner Mongolia border with Shanxi into Hebei province, and the "Inner Great Wall" (t 內長城, s 內长城, Nèi Chǎngchéng) running southeast from Piantou Pass for some 400 km (250 mi), passing through important passes like the Pingxing Pass and Yanmen Pass before joining the Outer Great Wall at Sihaiye (四海冶, Sìhǎiyě), in Beijing's Yanqing County.
The sections of the Great Wall around Beijing municipality are especially famous: they were frequently renovated and are regularly visited by tourists today. The Badaling Great Wall near Zhangjiakou is the most famous stretch of the wall, for this was the first section to be opened to the public in the People's Republic of China, as well as the showpiece stretch for foreign dignitaries. The Badaling Great Wall saw nearly 10 million visitors in 2018, and in 2019, a daily limit of 65,000 visitors was instated. South of Badaling is the Juyong Pass; when it was used by the Chinese to protect their land, this section of the wall had many guards to defend the capital Beijing. Made of stone and bricks from the hills, this portion of the Great Wall is 7.8 m (25 ft 7 in) high and 5 m (16 ft 5 in) wide.
One of the most striking sections of the Ming Great Wall is where it climbs extremely steep slopes in Jinshanling. There it runs 11 km (7 mi) long, ranges from 5 to 8 m (16 ft 5 in to 26 ft 3 in) in height, and 6 m (19 ft 8 in) across the bottom, narrowing up to 5 m (16 ft 5 in) across the top. Wangjing Lou (t 望京樓, s 望京楼, Wàngjīng Lóu) is one of Jinshanling's 67 watchtowers, 980 m (3,220 ft) above sea level. Southeast of Jinshanling is the Mutianyu Great Wall which winds along lofty, cragged mountains from the southeast to the northwest for 2.25 km (1.40 mi). It is connected with Juyongguan Pass to the west and Gubeikou to the east. This section was one of the first to be renovated following the turmoil of the Cultural Revolution.
At the edge of the Bohai Gulf is Shanhai Pass, considered the traditional end of the Great Wall and the "First Pass Under Heaven". The part of the wall inside Shanhai Pass that meets the sea is named the "Old Dragon Head". 3 km (2 mi) north of Shanhai Pass is Jiaoshan Great Wall (t 焦山長城, s 焦山长城, Jiāoshān Chángchéng), the site of the first mountain of the Great Wall. 15 km (9 mi) northeast from Shanhaiguan is Jiumenkou (t 九門口, s 九门口, Jiǔménkǒu), which is the only portion of the wall that was built as a bridge.
In 2009, 180 km of previously unknown sections of the Ming wall concealed by hills, trenches and rivers were discovered with the help of infrared range finders and GPS devices. In March and April 2015, nine sections with a total length of more than 10 km (6 mi), believed to be part of the Great Wall, were discovered along the border of Ningxia autonomous region and Gansu province.
Characteristics
Before the use of bricks, the Great Wall was mainly built from rammed earth, stones, and wood. During the Ming, however, bricks were heavily used in many areas of the wall, as were materials such as tiles, lime, and stone. The size and weight of the bricks made them easier to work with than earth and stone, so construction quickened. Additionally, bricks could bear more weight and endure better than rammed earth. Stone can hold under its own weight better than brick, but is more difficult to use. Consequently, stones cut in rectangular shapes were used for the foundation, inner and outer brims, and gateways of the wall. Battlements line the uppermost portion of the vast majority of the wall, with defensive gaps a little over 30 cm (12 in) tall, and about 23 cm (9.1 in) wide. From the parapets, guards could survey the surrounding land. Communication between the army units along the length of the Great Wall, including the ability to call reinforcements and warn garrisons of enemy movements, was of high importance. Signal towers were built upon hill tops or other high points along the wall for their visibility. Wooden gates could be used as a trap against those going through. Barracks, stables, and armories were built near the wall's inner surface.
Condition
While portions north of Beijing and near tourist centers have been preserved and even extensively renovated, in many other locations the wall is in disrepair. The wall sometimes provided a source of stones to build houses and roads. Sections of the wall are also prone to graffiti and vandalism, while inscribed bricks were pilfered and sold on the market for up to 50 renminbi. Parts have been destroyed to make way for construction or mining. A 2012 report by the National Cultural Heritage Administration states that 22% of the Ming Great Wall has disappeared, while 1,961 km (1,219 mi) of wall have vanished. More than 60 km (37 mi) of the wall in Gansu province may disappear in the next 20 years, due to erosion from sandstorms. In some places, the height of the wall has been reduced from more than 5 m (16 ft 5 in) to less than 2 m (6 ft 7 in). Various square lookout towers that characterize the most famous images of the wall have disappeared. Many western sections of the wall are constructed from mud, rather than brick and stone, and thus are more susceptible to erosion. In 2014 a portion of the wall near the border of Liaoning and Hebei province was repaired with concrete. The work has been much criticized.
Visibility from space
From the Moon
The notion that the wall can be seen from the moon (with an average orbital radius of 385,000 km (239,000 miles)) is a well-known but untrue myth.
One of the earliest known references to the myth that the Great Wall can be seen from the moon appears in a letter written in 1754 by the English antiquary William Stukeley. Stukeley wrote that, "This mighty wall [Hadrian's wall] of four score miles [130 km] in length is only exceeded by the Chinese Wall, which makes a considerable figure upon the terrestrial globe, and may be discerned at the Moon." The claim was also mentioned by Henry Norman in 1895 where he states "besides its age it enjoys the reputation of being the only work of human hands on the globe visible from the Moon." The issue of "canals" on Mars was prominent in the late 19th century and may have led to the belief that long, thin objects were visible from space. The claim that the Great Wall is visible from the moon also appears in 1932's Ripley's Believe It or Not! strip.
The claim that the Great Wall is visible from the moon has been debunked many times (the apparent width of the Great Wall from the Moon would be the same as that of a human hair viewed from 3 km (2 mi) away) but is still ingrained in popular culture.
From low Earth orbit
A more controversial question is whether the wall is visible from low Earth orbit (an altitude of as little as 160 km (100 mi)). NASA claims that it is barely visible, and only under nearly perfect conditions; it is no more conspicuous than many other man-made objects.
Veteran US astronaut Gene Cernan has stated: "At Earth orbit of 100 to 200 miles [160 to 320 km] high, the Great Wall of China is, indeed, visible to the naked eye." Ed Lu, Expedition 7 Science Officer aboard the International Space Station, adds that, "It's less visible than a lot of other objects. And you have to know where to look."
In October 2003, Chinese astronaut Yang Liwei stated that he had not been able to see the Great Wall of China. In response, the European Space Agency (ESA) issued a press release reporting that from an orbit between 160 and 320 km (100 and 200 mi), the Great Wall is visible to the naked eye.
Leroy Chiao, a Chinese-American astronaut, took a photograph from the International Space Station that shows the wall. It was so indistinct that the photographer was not certain he had actually captured it. Based on the photograph, the China Daily later reported that the Great Wall can be seen from 'space' with the naked eye, under favorable viewing conditions, if one knows exactly where to look.