 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌdɛkstroʊæmˈfɛtəmiːn/ |
| Trade names | Dexedrine, Metamina, Attentin, Zenzedi, Procentra, Amfexa |
| Synonyms | D-Amphetamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605027 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Dependence liability | Moderate |
| Addiction liability | High |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 75–100% |
| Protein binding | 15–40% |
| Metabolism | CYP2D6, DBH, FMO3 |
| Onset of action | IR dosing: 0.5–1.5 hours XR dosing: 1.5–2 hours |
| Elimination half-life | 9–11 hourspH-dependent: 7–34 hours |
| Duration of action | IR dosing: 3–6 hoursXR dosing: 8–12 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (45%); urinary pH-dependent |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.103 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13N |
| Molar mass | 135.210 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 0.913 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 201.5 °C (394.7 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 20 mg/mL (20 °C) |
Dextroamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and an amphetamine enantiomer that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine was also used by military air, tank and special forces as a 'go-pill' during fatigue-inducing missions such as night-time bombing missions or extended combat operations.
The amphetamine molecule exists as two enantiomers, levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Dextroamphetamine is the dextrorotatory, or 'right-handed', enantiomer and exhibits more pronounced effects on the central nervous system than levoamphetamine. Pharmaceutical dextroamphetamine sulfate is available as both a brand name and generic drug in a variety of dosage forms. Dextroamphetamine is sometimes prescribed as the inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine dimesylate, which is converted into dextroamphetamine after absorption.
Dextroamphetamine, like other amphetamines, elicits its stimulating effects via several distinct actions: it inhibits or reverses the transporter proteins for the monoamine neurotransmitters (namely the serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine transporters) either via trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) or in a TAAR1 independent fashion when there are high cytosolic concentrations of the monoamine neurotransmitters and it releases these neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles via vesicular monoamine transporter 2. It also shares many chemical and pharmacological properties with human trace amines, particularly phenethylamine and N-methylphenethylamine, the latter being an isomer of amphetamine produced within the human body.
Uses
Medical
Dexedrine IR tablets
Dexedrine Spansule 5, 10 and 15 mg capsules
Dextroamphetamine is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy (a sleep disorder), and is sometimes prescribed off-label for its past medical indications, such as depression and obesity.
Long-term amphetamine exposure at sufficiently high doses in some animal species is known to produce abnormal dopamine system development or nerve damage, but, in humans with ADHD, pharmaceutical amphetamines appear to improve brain development and nerve growth. Reviews of magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) studies suggest that long-term treatment with amphetamine
decreases abnormalities in brain structure and function found in
subjects with ADHD, and improves function in several parts of the brain,
such as the right caudate nucleus of the basal ganglia.
Reviews of clinical stimulant research have established the
safety and effectiveness of long-term continuous amphetamine use for the
treatment of ADHD. Randomized controlled trials
of continuous stimulant therapy for the treatment of ADHD spanning
2 years have demonstrated treatment effectiveness and safety.
Two reviews have indicated that long-term continuous stimulant therapy
for ADHD is effective for reducing the core symptoms of ADHD (i.e.,
hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity), enhancing quality of life and academic achievement, and producing improvements in a large number of functional outcomes
across 9 categories of outcomes related to academics, antisocial
behavior, driving, non-medicinal drug use, obesity, occupation,
self-esteem, service use (i.e., academic, occupational, health,
financial, and legal services), and social function.
One review highlighted a nine-month randomized controlled trial of
amphetamine treatment for ADHD in children that found an average
increase of 4.5 IQ points, continued increases in attention, and continued decreases in disruptive behaviors and hyperactivity. Another review indicated that, based upon the longest follow-up studies
conducted to date, lifetime stimulant therapy that begins during
childhood is continuously effective for controlling ADHD symptoms and
reduces the risk of developing a substance use disorder as an adult.
As of 2009, models of ADHD suggest that it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain's neurotransmitter systems; these functional impairments involve impaired dopamine neurotransmission in the mesocorticolimbic projection and norepinephrine neurotransmission in the noradrenergic projections from the locus coeruleus to the prefrontal cortex. Psychostimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamine are effective in treating ADHD because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems. Approximately 80% of those who use these stimulants see improvements in ADHD symptoms.
Children with ADHD who use stimulant medications generally have better
relationships with peers and family members, perform better in school,
are less distractible and impulsive, and have longer attention spans. The Cochrane reviews
on the treatment of ADHD in children, adolescents, and adults with
pharmaceutical amphetamines stated that short-term studies have
demonstrated that these drugs decrease the severity of symptoms, but
they have higher discontinuation rates than non-stimulant medications
due to their adverse side effects. A Cochrane review on the treatment of ADHD in children with tic disorders such as Tourette syndrome indicated that stimulants in general do not make tics worse, but high doses of dextroamphetamine could exacerbate tics in some individuals.
Enhancing performance
Cognitive performance
In 2015, a systematic review and a meta-analysis of high quality clinical trials
found that, when used at low (therapeutic) doses, amphetamine produces
modest yet unambiguous improvements in cognition, including working memory, long-term episodic memory, inhibitory control, and some aspects of attention, in normal healthy adults; these cognition-enhancing effects of amphetamine are known to be partially mediated through the indirect activation of both dopamine receptor D1 and adrenoceptor α2 in the prefrontal cortex. A systematic review from 2014 found that low doses of amphetamine also improve memory consolidation, in turn leading to improved recall of information.
Therapeutic doses of amphetamine also enhance cortical network
efficiency, an effect which mediates improvements in working memory in
all individuals. Amphetamine and other ADHD stimulants also improve task saliency (motivation to perform a task) and increase arousal (wakefulness), in turn promoting goal-directed behavior.
Stimulants such as amphetamine can improve performance on difficult and
boring tasks and are used by some students as a study and test-taking
aid. Based upon studies of self-reported illicit stimulant use, 5–35% of college students use diverted ADHD stimulants, which are primarily used for enhancement of academic performance rather than as recreational drugs.
However, high amphetamine doses that are above the therapeutic range
can interfere with working memory and other aspects of cognitive
control.
Physical performance
Amphetamine is used by some athletes for its psychological and athletic performance-enhancing effects, such as increased endurance and alertness;
however, non-medical amphetamine use is prohibited at sporting events
that are regulated by collegiate, national, and international
anti-doping agencies. In healthy people at oral therapeutic doses, amphetamine has been shown to increase muscle strength, acceleration, athletic performance in anaerobic conditions, and endurance (i.e., it delays the onset of fatigue), while improving reaction time. Amphetamine improves endurance and reaction time primarily through reuptake inhibition and release of dopamine in the central nervous system. Amphetamine and other dopaminergic drugs also increase power output at fixed levels of perceived exertion by overriding a "safety switch", allowing the core temperature limit to increase in order to access a reserve capacity that is normally off-limits. At therapeutic doses, the adverse effects of amphetamine do not impede athletic performance; however, at much higher doses, amphetamine can induce effects that severely impair performance, such as rapid muscle breakdown and elevated body temperature.
Recreational
Dextroamphetamine is also used recreationally as a euphoriant and aphrodisiac, and like other amphetamines is used as a club drug for its energetic and euphoric high. Dextroamphetamine is considered to have a high potential for misuse in a recreational manner since individuals typically report feeling euphoric, more alert, and more energetic after taking the drug. Large recreational doses of dextroamphetamine may produce symptoms of dextroamphetamine overdose.
Recreational users sometimes open dexedrine capsules and crush the
contents in order to snort it or subsequently dissolve it in water and
inject it. Injection into the bloodstream can be dangerous because insoluble fillers within the tablets can block small blood vessels. Chronic overuse of dextroamphetamine can lead to severe drug dependence, resulting in withdrawal symptoms when drug use stops.
Contraindications
According to the International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA), amphetamine is contraindicated in people with a history of drug abuse, cardiovascular disease, severe agitation, or severe anxiety. It is also contraindicated in people experiencing advanced arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), glaucoma (increased eye pressure), hyperthyroidism (excessive production of thyroid hormone), or moderate to severe hypertension. These agencies indicate that people who have experienced allergic reactions to other stimulants or who are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should not take amphetamine, although safe concurrent use of amphetamine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors has been documented. These agencies also state that anyone with anorexia nervosa, bipolar disorder, depression, hypertension, liver or kidney problems, mania, psychosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, seizures, thyroid problems, tics, or Tourette syndrome should monitor their symptoms while taking amphetamine.
Evidence from human studies indicates that therapeutic amphetamine use
does not cause developmental abnormalities in the fetus or newborns
(i.e., it is not a human teratogen), but amphetamine abuse does pose risks to the fetus.
Amphetamine has also been shown to pass into breast milk, so the IPCS
and the USFDA advise mothers to avoid breastfeeding when using it. Due to the potential for reversible growth impairments, the USFDA advises monitoring the height and weight of children and adolescents prescribed an amphetamine pharmaceutical.
Adverse effects
Physical
At normal therapeutic doses, the physical side effects of amphetamine vary widely by age and from person to person. Cardiovascular side effects can include hypertension or hypotension from a vasovagal response, Raynaud's phenomenon (reduced blood flow to the hands and feet), and tachycardia (increased heart rate). Sexual side effects in males may include erectile dysfunction, frequent erections, or prolonged erections. Gastrointestinal side effects may include abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, and nausea. Other potential physical side effects include appetite loss, blurred vision, dry mouth, excessive grinding of the teeth, nosebleed, profuse sweating, rhinitis medicamentosa (drug-induced nasal congestion), reduced seizure threshold, tics (a type of movement disorder), and weight loss. Dangerous physical side effects are rare at typical pharmaceutical doses.
Amphetamine stimulates the medullary respiratory centers, producing faster and deeper breaths.
In a normal person at therapeutic doses, this effect is usually not
noticeable, but when respiration is already compromised, it may be
evident. Amphetamine also induces contraction in the urinary bladder sphincter, the muscle which controls urination, which can result in difficulty urinating. This effect can be useful in treating bed wetting and loss of bladder control. The effects of amphetamine on the gastrointestinal tract are unpredictable. If intestinal activity is high, amphetamine may reduce gastrointestinal motility (the rate at which content moves through the digestive system); however, amphetamine may increase motility when the smooth muscle of the tract is relaxed. Amphetamine also has a slight analgesic effect and can enhance the pain relieving effects of opioids.
USFDA-commissioned studies from 2011, indicate that in children,
young adults, and adults there is no association between serious adverse
cardiovascular events (sudden death, heart attack, and stroke) and the medical use of amphetamine or other ADHD stimulants. However, amphetamine pharmaceuticals are contraindicated in individuals with cardiovascular disease.
Psychological
At normal therapeutic doses, the most common psychological side effects of amphetamine include increased alertness, apprehension, concentration, initiative, self-confidence and sociability, mood swings (elated mood followed by mildly depressed mood), insomnia or wakefulness, and decreased sense of fatigue. Less common side effects include anxiety, change in libido, grandiosity, irritability, repetitive or obsessive behaviors, and restlessness; these effects depend on the user's personality and current mental state. Amphetamine psychosis (e.g., delusions and paranoia) can occur in heavy users. Although very rare, this psychosis can also occur at therapeutic doses during long-term therapy. According to the USFDA, "there is no systematic evidence" that stimulants produce aggressive behavior or hostility.
Amphetamine has also been shown to produce a conditioned place preference in humans taking therapeutic doses, meaning that individuals acquire a preference for spending time in places where they have previously used amphetamine.
Reinforcement disorders
Addiction
Addiction
is a serious risk with heavy recreational amphetamine use, but is
unlikely to occur from long-term medical use at therapeutic doses; in fact, lifetime stimulant therapy for ADHD that begins during childhood reduces the risk of developing substance use disorders as an adult. Pathological overactivation of the mesolimbic pathway, a dopamine pathway that connects the ventral tegmental area to the nucleus accumbens, plays a central role in amphetamine addiction. Individuals who frequently self-administer
high doses of amphetamine have a high risk of developing an amphetamine
addiction, since chronic use at high doses gradually increase the level
of accumbal ΔFosB, a "molecular switch" and "master control protein" for addiction.
Once nucleus accumbens ΔFosB is sufficiently overexpressed, it begins
to increase the severity of addictive behavior (i.e., compulsive
drug-seeking) with further increases in its expression. While there are no effective drugs for treating amphetamine addiction as of 2015, regularly engaging in sustained aerobic exercise appears to reduce the risk of developing such an addiction. Sustained aerobic exercise on a regular basis also appears to be an effective treatment for amphetamine addiction; exercise therapy improves clinical treatment outcomes and may be used as a combination therapy with cognitive behavioral therapy, which is the best clinical treatment available as of 2015.
Biomolecular mechanisms
Chronic use of amphetamine at excessive doses causes alterations in gene expression in the mesocorticolimbic projection, which arise through transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms. The most important transcription factors that produce these alterations are Delta FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (ΔFosB), cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). ΔFosB is the most significant biomolecular mechanism in addiction because ΔFosB overexpression (i.e., an abnormally high level of gene expression which produces a pronounced gene-related phenotype) in the D1-type medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens is necessary and sufficient for many of the neural adaptations and regulates multiple behavioral effects (e.g., reward sensitization and escalating drug self-administration) involved in addiction.
Once ΔFosB is sufficiently overexpressed, it induces an addictive state
that becomes increasingly more severe with further increases in ΔFosB
expression. It has been implicated in addictions to alcohol, cannabinoids, cocaine, methylphenidate, nicotine, opioids, phencyclidine, propofol, and substituted amphetamines, among others.
ΔJunD, a transcription factor, and G9a, a histone methyltransferase enzyme, both oppose the function of ΔFosB and inhibit increases in its expression. Sufficiently overexpressing ΔJunD in the nucleus accumbens with viral vectors
can completely block many of the neural and behavioral alterations seen
in chronic drug abuse (i.e., the alterations mediated by ΔFosB). ΔFosB also plays an important role in regulating behavioral responses to natural rewards, such as palatable food, sex, and exercise. Since both natural rewards and addictive drugs induce the expression
of ΔFosB (i.e., they cause the brain to produce more of it), chronic
acquisition of these rewards can result in a similar pathological state
of addiction. Consequently, ΔFosB is the most significant factor involved in both amphetamine addiction and amphetamine-induced sexual addictions, which are compulsive sexual behaviors that result from excessive sexual activity and amphetamine use. These sexual addictions are associated with a dopamine dysregulation syndrome which occurs in some patients taking dopaminergic drugs.
The effects of amphetamine on gene regulation are both dose- and route-dependent.
Most of the research on gene regulation and addiction is based upon
animal studies with intravenous amphetamine administration at very high
doses.
The few studies that have used equivalent (weight-adjusted) human
therapeutic doses and oral administration show that these changes, if
they occur, are relatively minor. This suggests that medical use of amphetamine does not significantly affect gene regulation.
Pharmacological treatments
As of 2015, there is no effective pharmacotherapy for amphetamine addiction. Reviews from 2015 and 2016 indicated that TAAR1-selective agonists have significant therapeutic potential as a treatment for psychostimulant addictions; however, as of February 2016, the only compounds which are known to function as TAAR1-selective agonists are experimental drugs. Amphetamine addiction is largely mediated through increased activation of dopamine receptors and co-localized NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens; magnesium ions inhibit NMDA receptors by blocking the receptor calcium channel.
One review suggested that, based upon animal testing, pathological
(addiction-inducing) psychostimulant use significantly reduces the level
of intracellular magnesium throughout the brain. Supplemental magnesium treatment has been shown to reduce amphetamine self-administration (i.e., doses given to oneself) in humans, but it is not an effective monotherapy for amphetamine addiction.
Behavioral treatments
Cognitive behavioral therapy is the most effective clinical treatment for psychostimulant addictions as of 2009. Additionally, research on the neurobiological effects of physical exercise suggests that daily aerobic exercise, especially endurance exercise (e.g., marathon running), prevents the development of drug addiction and is an effective adjunct therapy (i.e., a supplemental treatment) for amphetamine addiction. Exercise leads to better treatment outcomes when used as an adjunct treatment, particularly for psychostimulant addictions. In particular, aerobic exercise decreases psychostimulant self-administration, reduces the reinstatement (i.e., relapse) of drug-seeking, and induces increased dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) density in the striatum. This is the opposite of pathological stimulant use, which induces decreased striatal DRD2 density. One review noted that exercise may also prevent the development of a drug addiction by altering ΔFosB or c-Fos immunoreactivity in the striatum or other parts of the reward system.
Dependence and withdrawal
Drug tolerance
develops rapidly in amphetamine abuse (i.e., recreational amphetamine
use), so periods of extended abuse require increasingly larger doses of
the drug in order to achieve the same effect.
According to a Cochrane review on withdrawal
in individuals who compulsively use amphetamine and methamphetamine,
"when chronic heavy users abruptly discontinue amphetamine use, many
report a time-limited withdrawal syndrome that occurs within 24 hours of
their last dose."
This review noted that withdrawal symptoms in chronic, high-dose users
are frequent, occurring in roughly 88% of cases, and persist for 3–4 weeks with a marked "crash" phase occurring during the first week. Amphetamine withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, drug craving, depressed mood, fatigue, increased appetite, increased movement or decreased movement, lack of motivation, sleeplessness or sleepiness, and lucid dreams.
The review indicated that the severity of withdrawal symptoms is
positively correlated with the age of the individual and the extent of
their dependence.
Mild withdrawal symptoms from the discontinuation of amphetamine
treatment at therapeutic doses can be avoided by tapering the dose.
Overdose
An amphetamine overdose can lead to many different symptoms, but is rarely fatal with appropriate care. The severity of overdose symptoms increases with dosage and decreases with drug tolerance to amphetamine.
Tolerant individuals have been known to take as much as 5 grams of
amphetamine in a day, which is roughly 100 times the maximum daily
therapeutic dose.
Symptoms of a moderate and extremely large overdose are listed below;
fatal amphetamine poisoning usually also involves convulsions and coma. In 2013, overdose on amphetamine, methamphetamine, and other compounds implicated in an "amphetamine use disorder" resulted in an estimated 3,788 deaths worldwide (3,425–4,145 deaths, 95% confidence).
Toxicity
In rodents and primates, sufficiently high doses of amphetamine cause dopaminergic neurotoxicity, or damage to dopamine neurons, which is characterized by dopamine terminal degeneration and reduced transporter and receptor function. There is no evidence that amphetamine is directly neurotoxic in humans. However, large doses of amphetamine may indirectly cause dopaminergic neurotoxicity as a result of hyperpyrexia, the excessive formation of reactive oxygen species, and increased autoxidation of dopamine. Animal models of neurotoxicity from high-dose amphetamine exposure indicate that the occurrence of hyperpyrexia (i.e., core body temperature ≥ 40 °C) is necessary for the development of amphetamine-induced neurotoxicity.
Prolonged elevations of brain temperature above 40 °C likely promote
the development of amphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in laboratory
animals by facilitating the production of reactive oxygen species,
disrupting cellular protein function, and transiently increasing blood–brain barrier permeability.
Psychosis
An amphetamine overdose can result in a stimulant psychosis that may
involve a variety of symptoms, such as delusions and paranoia. A Cochrane review on treatment for amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, and methamphetamine psychosis states that about 5–15% of users fail to recover completely. According to the same review, there is at least one trial that shows antipsychotic medications effectively resolve the symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis. Psychosis rarely arises from therapeutic use.
Interactions
Many types of substances are known to interact with amphetamine, resulting in altered drug action or metabolism of amphetamine, the interacting substance, or both. Inhibitors of the enzymes that metabolize amphetamine (e.g., CYP2D6 and FMO3) will prolong its elimination half-life, meaning that its effects will last longer. Amphetamine also interacts with MAOIs, particularly monoamine oxidase A inhibitors, since both MAOIs and amphetamine increase plasma catecholamines (i.e., norepinephrine and dopamine); therefore, concurrent use of both is dangerous. Amphetamine modulates the activity of most psychoactive drugs. In particular, amphetamine may decrease the effects of sedatives and depressants and increase the effects of stimulants and antidepressants. Amphetamine may also decrease the effects of antihypertensives and antipsychotics due to its effects on blood pressure and dopamine respectively. Zinc supplementation may reduce the minimum effective dose of amphetamine when it is used for the treatment of ADHD.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Amphetamine and its enantiomers have been identified as potent full agonists of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1), a GPCR, discovered in 2001, that is important for regulation of monoaminergic systems in the brain. Activation of TAAR1 increases cAMP production via adenylyl cyclase activation and inhibits the function of the dopamine transporter, norepinephrine transporter, and serotonin transporter, as well as inducing the release of these monoamine neurotransmitters (effluxion). Amphetamine enantiomers are also substrates for a specific neuronal synaptic vesicle uptake transporter called VMAT2. When amphetamine is taken up by VMAT2, the vesicle releases (effluxes) dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, among other monoamines, into the cytosol in exchange.
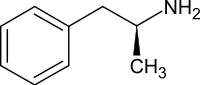
Dextroamphetamine (the dextrorotary enantiomer) and levoamphetamine (the levorotary enantiomer) have identical pharmacodynamics, but their binding affinities to their biomolecular targets vary. Dextroamphetamine is a more potent agonist of TAAR1 than levoamphetamine. Consequently, dextroamphetamine produces roughly three to four times more central nervous system (CNS) stimulation than levoamphetamine; however, levoamphetamine has slightly greater cardiovascular and peripheral effects.
Related endogenous compounds
Amphetamine has a very similar structure and function to the endogenous trace amines, which are naturally occurring neuromodulator molecules produced in the human body and brain. Among this group, the most closely related compounds are phenethylamine, the parent compound of amphetamine, and N-methylphenethylamine, an isomer of amphetamine (i.e., it has an identical molecular formula). In humans, phenethylamine is produced directly from L-phenylalanine by the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) enzyme, which converts L-DOPA into dopamine as well. In turn, N-methylphenethylamine is metabolized from phenethylamine by phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, the same enzyme that metabolizes norepinephrine into epinephrine. Like amphetamine, both phenethylamine and N-methylphenethylamine regulate monoamine neurotransmission via TAAR1; unlike amphetamine, both of these substances are broken down by monoamine oxidase B, and therefore have a shorter half-life than amphetamine.
Pharmacokinetics
The oral bioavailability of amphetamine varies with gastrointestinal pH; it is well absorbed from the gut, and bioavailability is typically over 75% for dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine is a weak base with a pKa of 9.9; consequently, when the pH is basic, more of the drug is in its lipid soluble free base form, and more is absorbed through the lipid-rich cell membranes of the gut epithelium. Conversely, an acidic pH means the drug is predominantly in a water-soluble cationic (salt) form, and less is absorbed. Approximately 15–40% of amphetamine circulating in the bloodstream is bound to plasma proteins. Following absorption, amphetamine readily distributes into most tissues in the body, with high concentrations occurring in cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue.
The half-lives of amphetamine enantiomers differ and vary with urine pH. At normal urine pH, the half-lives of dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine are 9–11 hours and 11–14 hours, respectively. Highly acidic urine will reduce the enantiomer half-lives to 7 hours; highly alkaline urine will increase the half-lives up to 34 hours. The immediate-release and extended release variants of salts of both isomers reach peak plasma concentrations at 3 hours and 7 hours post-dose respectively. Amphetamine is eliminated via the kidneys, with 30–40% of the drug being excreted unchanged at normal urinary pH. When the urinary pH is basic, amphetamine is in its free base form, so less is excreted.
When urine pH is abnormal, the urinary recovery of amphetamine may
range from a low of 1% to a high of 75%, depending mostly upon whether
urine is too basic or acidic, respectively. Following oral administration, amphetamine appears in urine within 3 hours. Roughly 90% of ingested amphetamine is eliminated 3 days after the last oral dose.
CYP2D6, dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH), flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), butyrate-CoA ligase (XM-ligase), and glycine N-acyltransferase (GLYAT) are the enzymes known to metabolize amphetamine or its metabolites in humans. Amphetamine has a variety of excreted metabolic products, including 4-hydroxyamphetamine, 4-hydroxynorephedrine, 4-hydroxyphenylacetone, benzoic acid, hippuric acid, norephedrine, and phenylacetone. Among these metabolites, the active sympathomimetics are 4-hydroxyamphetamine, 4-hydroxynorephedrine, and norephedrine. The main metabolic pathways involve aromatic para-hydroxylation, aliphatic alpha- and beta-hydroxylation, N-oxidation, N-dealkylation, and deamination.
The primary active metabolites of amphetamine are 4-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine; at normal urine pH, about 30–40% of amphetamine is excreted unchanged and roughly 50% is excreted as the inactive metabolites (bottom row). The remaining 10–20% is excreted as the active metabolites. Benzoic acid is metabolized by XM-ligase into an intermediate product, benzoyl-CoA, which is then metabolized by GLYAT into hippuric acid.
|
History, society, and culture
Racemic amphetamine was first synthesized under the chemical name "phenylisopropylamine" in Berlin, 1887 by the Romanian chemist Lazar Edeleanu. It was not widely marketed until 1932, when the pharmaceutical company Smith, Kline & French (now known as GlaxoSmithKline) introduced it in the form of the Benzedrine inhaler for use as a bronchodilator. Notably, the amphetamine contained in the Benzedrine inhaler was the liquid free-base, not a chloride or sulfate salt.
Three years later, in 1935, the medical community became aware of
the stimulant properties of amphetamine, specifically
dextroamphetamine, and in 1937 Smith, Kline, and French introduced
tablets under the tradename Dexedrine. In the United States, Dexedrine was approved to treat narcolepsy, attention disorders, and obesity. In Canada indications once included epilepsy and parkinsonism.
Dextroamphetamine was marketed in various other forms in the following
decades, primarily by Smith, Kline, and French, such as several
combination medications including a mixture of dextroamphetamine and amobarbital (a barbiturate) sold under the tradename Dexamyl and, in the 1950s, an extended release capsule (the "Spansule"). Preparations containing dextroamphetamine were also used in World War II as a treatment against fatigue.
It quickly became apparent that dextroamphetamine and other amphetamines had a high potential for misuse, although they were not heavily controlled until 1970, when the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act
was passed by the United States Congress. Dextroamphetamine, along with
other sympathomimetics, was eventually classified as Schedule II, the
most restrictive category possible for a drug with a
government-sanctioned, recognized medical use.
Internationally, it has been available under the names AmfeDyn (Italy),
Curban (US), Obetrol (Switzerland), Simpamina (Italy), Dexedrine/GSK
(US & Canada), Dexedrine/UCB (United Kingdom), Dextropa (Portugal),
and Stild (Spain).
In October 2010, GlaxoSmithKline sold the rights for Dexedrine Spansule to Amedra Pharmaceuticals (a subsidiary of CorePharma).
The U.S. Air Force uses dextroamphetamine as one of its "go
pills", given to pilots on long missions to help them remain focused and
alert. Conversely, "no-go pills" are used after the mission is
completed, to combat the effects of the mission and "go-pills". The Tarnak Farm incident
was linked by media reports to the use of this drug on long term
fatigued pilots. The military did not accept this explanation, citing
the lack of similar incidents. Newer stimulant medications or awakeness promoting agents with different side effect profiles, such as modafinil, are being investigated and sometimes issued for this reason.
Formulations
Dextroamphetamine sulfate
Dexamphetamine 5 mg generic name tablets
In the United States, immediate release (IR) formulations of dextroamphetamine sulfate are available generically as 5 mg and 10 mg tablets, marketed by Barr (Teva Pharmaceutical Industries), Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Wilshire Pharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharmaceutical USA
and CorePharma. Previous IR tablets sold by the brand names of
Dexedrine and Dextrostat have been discontinued but in 2015 IR tablets
became available by the brand name Zenzedi, offered as 2.5 mg, 5 mg,
7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg and 30 mg tablets. Dextroamphetamine sulfate is also available as a controlled-release
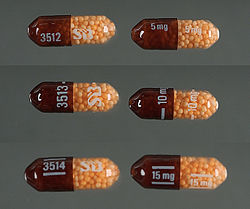
(CR) capsule preparation in strengths of 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg under
the brand name Dexedrine Spansule, with generic versions marketed by
Barr and Mallinckrodt. A bubblegum flavored oral solution is available
under the brand name ProCentra, manufactured by FSC Pediatrics, which is
designed to be an easier method of administration in children who have
difficulty swallowing tablets, each 5 mL contains 5 mg
dextroamphetamine. The conversion rate between dextroamphetamine sulfate to amphetamine free base is .728.
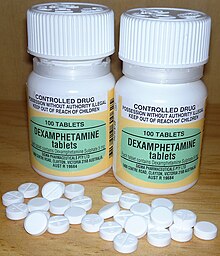
In Australia, dexamphetamine is available in bottles of 100 instant release 5 mg tablets as a generic drug. or slow release dextroamphetamine preparations may be compounded by individual chemists.
Similarly, in the United Kingdom it is only available in 5 mg instant
release sulfate tablets under the generic name dextroamphetamine
sulphate having had been available under the brand name Dexedrine prior
to UCB Pharma disinvesting the product to another pharmaceutical company (Auden Mckenzie).
Lisdexamfetamine
Dextroamphetamine is the active metabolite of the prodrug lisdexamfetamine (L-lysine-dextroamphetamine), available by the brand name Vyvanse (Elvanse in the European market) (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate).
Dextroamphetamine is liberated from lisdexamfetamine enzymatically
following contact with red blood cells. The conversion is rate-limited
by the enzyme, which prevents high blood concentrations of
dextroamphetamine and reduces lisdexamfetamine's drug liking and abuse potential at clinical doses.
Vyvanse is marketed as once-a-day dosing as it provides a slow release
of dextroamphetamine into the body. Vyvanse is available as capsules,
and chewable tablets, and in seven strengths; 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg,
40 mg, 50 mg, 60 mg, and 70 mg. The conversion rate between
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (Vyvanse) to dextroamphetamine base is
29.5%.
Adderall
Adderall 20 mg tablets, some broken in half, with a lengthwise-folded US dollar bill along the bottom
Another pharmaceutical that contains dextroamphetamine is commonly
known by the brand name Adderall. It is available as immediate release
(IR) tablets and extended release (XR) capsules. Adderall contains equal
amounts of four amphetamine salts:
-
- One-quarter racemic (d,l-)amphetamine aspartate monohydrate
- One-quarter dextroamphetamine saccharate
- One-quarter dextroamphetamine sulfate
- One-quarter racemic (d,l-)amphetamine sulfate
Adderall has a total amphetamine base equivalence of 63%.
While the enantiomer ratio by dextroamphetamine salts to
levoamphetamine salts is 3:1, the amphetamine base content is 75.9%
dextroamphetamine, 24.1% levoamphetamine.