| Human immunodeficiency viruses | |
|---|---|

| |
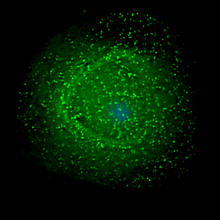
| Scanning electron micrograph of HIV-1 (in green) budding from cultured lymphocyte. Multiple round bumps on cell surface represent sites of assembly and budding of virions. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Pararnavirae |
| Phylum: | Artverviricota |
| Class: | Revtraviricetes |
| Order: | Ortervirales |
| Family: | Retroviridae |
| Subfamily: | Orthoretrovirinae |
| Genus: | Lentivirus |
| Groups included | |
| Other lentiviruses | |
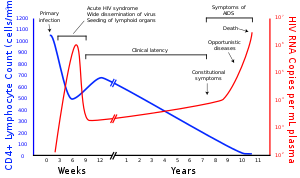
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. In most cases, HIV is a sexually transmitted infection and occurs by contact with or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and vaginal fluids. Research has shown (for both same-sex and opposite-sex couples) that HIV is untransmittable through condomless sexual intercourse if the HIV-positive partner has a consistently undetectable viral load. Non-sexual transmission can occur from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy, during childbirth by exposure to her blood or vaginal fluid, and through breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.
HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system, such as helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells), macrophages, and dendritic cells. HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through a number of mechanisms, including pyroptosis of abortively infected T cells, apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells, direct viral killing of infected cells, and killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells. When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections, leading to the development of AIDS.
Virology
Classification
| Species | Virulence | Infectivity | Prevalence | Inferred origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 | High | High | Global | Common chimpanzee |
| HIV-2 | Lower | Low | West Africa | Sooty mangabey |
HIV is a member of the genus Lentivirus, part of the family Retroviridae. Lentiviruses have many morphologies and biological properties in common. Many species are infected by lentiviruses, which are characteristically responsible for long-duration illnesses with a long incubation period. Lentiviruses are transmitted as single-stranded, positive-sense, enveloped RNA viruses. Upon entry into the target cell, the viral RNA genome is converted (reverse transcribed) into double-stranded DNA by a virally encoded enzyme, reverse transcriptase, that is transported along with the viral genome in the virus particle. The resulting viral DNA is then imported into the cell nucleus and integrated into the cellular DNA by a virally encoded enzyme, integrase, and host co-factors. Once integrated, the virus may become latent, allowing the virus and its host cell to avoid detection by the immune system, for an indeterminate amount of time. The HIV virus can remain dormant in the human body for up to ten years after primary infection; during this period the virus does not cause symptoms. Alternatively, the integrated viral DNA may be transcribed, producing new RNA genomes and viral proteins, using host cell resources, that are packaged and released from the cell as new virus particles that will begin the replication cycle anew.
Two types of HIV have been characterized: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is the virus that was initially discovered and termed both lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) and human T-lymphotropic virus 3 (HTLV-III). HIV-1 is more virulent and more infective than HIV-2, and is the cause of the majority of HIV infections globally. The lower infectivity of HIV-2, compared to HIV-1, implies that fewer of those exposed to HIV-2 will be infected per exposure. Due to its relatively poor capacity for transmission, HIV-2 is largely confined to West Africa.
Structure and genome
HIV is different in structure from other retroviruses. It is roughly spherical with a diameter of about 120 nm, around 60 times smaller than a red blood cell. It is composed of two copies of positive-sense single-stranded RNA that codes for the virus's nine genes enclosed by a conical capsid composed of 2,000 copies of the viral protein p24. The single-stranded RNA is tightly bound to nucleocapsid proteins, p7, and enzymes needed for the development of the virion such as reverse transcriptase, proteases, ribonuclease and integrase. A matrix composed of the viral protein p17 surrounds the capsid ensuring the integrity of the virion particle.
This is, in turn, surrounded by the viral envelope, that is composed of the lipid bilayer taken from the membrane of a human host cell when the newly formed virus particle buds from the cell. The viral envelope contains proteins from the host cell and relatively few copies of the HIV envelope protein, which consists of a cap made of three molecules known as glycoprotein (gp) 120, and a stem consisting of three gp41 molecules that anchor the structure into the viral envelope. The envelope protein, encoded by the HIV env gene, allows the virus to attach to target cells and fuse the viral envelope with the target cell's membrane releasing the viral contents into the cell and initiating the infectious cycle.
As the sole viral protein on the surface of the virus, the envelope protein is a major target for HIV vaccine efforts. Over half of the mass of the trimeric envelope spike is N-linked glycans. The density is high as the glycans shield the underlying viral protein from neutralisation by antibodies. This is one of the most densely glycosylated molecules known and the density is sufficiently high to prevent the normal maturation process of glycans during biogenesis in the endoplasmic and Golgi apparatus. The majority of the glycans are therefore stalled as immature 'high-mannose' glycans not normally present on human glycoproteins that are secreted or present on a cell surface. The unusual processing and high density means that almost all broadly neutralising antibodies that have so far been identified (from a subset of patients that have been infected for many months to years) bind to, or are adapted to cope with, these envelope glycans.
The molecular structure of the viral spike has now been determined by X-ray crystallography and cryogenic electron microscopy. These advances in structural biology were made possible due to the development of stable recombinant forms of the viral spike by the introduction of an intersubunit disulphide bond and an isoleucine to proline mutation (radical replacement of an amino acid) in gp41. The so-called SOSIP trimers not only reproduce the antigenic properties of the native viral spike, but also display the same degree of immature glycans as presented on the native virus. Recombinant trimeric viral spikes are promising vaccine candidates as they display less non-neutralising epitopes than recombinant monomeric gp120, which act to suppress the immune response to target epitopes.
The RNA genome consists of at least seven structural landmarks (LTR, TAR, RRE, PE, SLIP, CRS, and INS), and nine genes (gag, pol, and env, tat, rev, nef, vif, vpr, vpu, and sometimes a tenth tev, which is a fusion of tat, env and rev), encoding 19 proteins. Three of these genes, gag, pol, and env, contain information needed to make the structural proteins for new virus particles. For example, env codes for a protein called gp160 that is cut in two by a cellular protease to form gp120 and gp41. The six remaining genes, tat, rev, nef, vif, vpr, and vpu (or vpx in the case of HIV-2), are regulatory genes for proteins that control the ability of HIV to infect cells, produce new copies of virus (replicate), or cause disease.
The two tat proteins (p16 and p14) are transcriptional transactivators for the LTR promoter acting by binding the TAR RNA element. The TAR may also be processed into microRNAs that regulate the apoptosis genes ERCC1 and IER3. The rev protein (p19) is involved in shuttling RNAs from the nucleus and the cytoplasm by binding to the RRE RNA element. The vif protein (p23) prevents the action of APOBEC3G (a cellular protein that deaminates cytidine to uridine in the single-stranded viral DNA and/or interferes with reverse transcription). The vpr protein (p14) arrests cell division at G2/M. The nef protein (p27) down-regulates CD4 (the major viral receptor), as well as the MHC class I and class II molecules.
Nef also interacts with SH3 domains. The vpu protein (p16) influences the release of new virus particles from infected cells. The ends of each strand of HIV RNA contain an RNA sequence called a long terminal repeat (LTR). Regions in the LTR act as switches to control production of new viruses and can be triggered by proteins from either HIV or the host cell. The Psi element is involved in viral genome packaging and recognized by gag and rev proteins. The SLIP element (TTTTTT) is involved in the frameshift in the gag-pol reading frame required to make functional pol.
Tropism
The term viral tropism refers to the cell types a virus infects. HIV can infect a variety of immune cells such as CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and microglial cells. HIV-1 entry to macrophages and CD4+ T cells is mediated through interaction of the virion envelope glycoproteins (gp120) with the CD4 molecule on the target cells' membrane and also with chemokine co-receptors.
Macrophage-tropic (M-tropic) strains of HIV-1, or non-syncytia-inducing strains (NSI; now called R5 viruses) use the β-chemokine receptor, CCR5, for entry and are thus able to replicate in both macrophages and CD4+ T cells. This CCR5 co-receptor is used by almost all primary HIV-1 isolates regardless of viral genetic subtype. Indeed, macrophages play a key role in several critical aspects of HIV infection. They appear to be the first cells infected by HIV and perhaps the source of HIV production when CD4+ cells become depleted in the patient. Macrophages and microglial cells are the cells infected by HIV in the central nervous system. In the tonsils and adenoids of HIV-infected patients, macrophages fuse into multinucleated giant cells that produce huge amounts of virus.
T-tropic strains of HIV-1, or syncytia-inducing strains (SI; now called X4 viruses) replicate in primary CD4+ T cells as well as in macrophages and use the α-chemokine receptor, CXCR4, for entry.
Dual-tropic HIV-1 strains are thought to be transitional strains of HIV-1 and thus are able to use both CCR5 and CXCR4 as co-receptors for viral entry.
The α-chemokine SDF-1, a ligand for CXCR4, suppresses replication of T-tropic HIV-1 isolates. It does this by down-regulating the expression of CXCR4 on the surface of HIV target cells. M-tropic HIV-1 isolates that use only the CCR5 receptor are termed R5; those that use only CXCR4 are termed X4, and those that use both, X4R5. However, the use of co-receptors alone does not explain viral tropism, as not all R5 viruses are able to use CCR5 on macrophages for a productive infection and HIV can also infect a subtype of myeloid dendritic cells, which probably constitute a reservoir that maintains infection when CD4+ T cell numbers have declined to extremely low levels.
Some people are resistant to certain strains of HIV. For example, people with the CCR5-Δ32 mutation are resistant to infection by the R5 virus, as the mutation leaves HIV unable to bind to this co-receptor, reducing its ability to infect target cells.
Sexual intercourse is the major mode of HIV transmission. Both X4 and R5 HIV are present in the seminal fluid, which enables the virus to be transmitted from a male to his sexual partner. The virions can then infect numerous cellular targets and disseminate into the whole organism. However, a selection process leads to a predominant transmission of the R5 virus through this pathway. In patients infected with subtype B HIV-1, there is often a co-receptor switch in late-stage disease and T-tropic variants that can infect a variety of T cells through CXCR4. These variants then replicate more aggressively with heightened virulence that causes rapid T cell depletion, immune system collapse, and opportunistic infections that mark the advent of AIDS. HIV-positive patients acquire an enormously broad spectrum of opportunistic infections, which was particularly problematic prior to the onset of HAART therapies; however, the same infections are reported among HIV-infected patients examined post-mortem following the onset of antiretroviral therapies. Thus, during the course of infection, viral adaptation to the use of CXCR4 instead of CCR5 may be a key step in the progression to AIDS. A number of studies with subtype B-infected individuals have determined that between 40 and 50 percent of AIDS patients can harbour viruses of the SI and, it is presumed, the X4 phenotypes.
HIV-2 is much less pathogenic than HIV-1 and is restricted in its worldwide distribution to West Africa. The adoption of "accessory genes" by HIV-2 and its more promiscuous pattern of co-receptor usage (including CD4-independence) may assist the virus in its adaptation to avoid innate restriction factors present in host cells. Adaptation to use normal cellular machinery to enable transmission and productive infection has also aided the establishment of HIV-2 replication in humans. A survival strategy for any infectious agent is not to kill its host, but ultimately become a commensal organism. Having achieved a low pathogenicity, over time, variants that are more successful at transmission will be selected.
Replication cycle
Entry to the cell
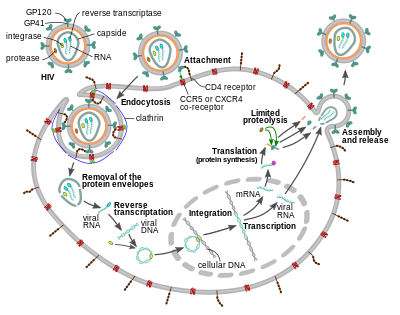
The HIV virion enters macrophages and CD4+ T cells by the adsorption of glycoproteins on its surface to receptors on the target cell followed by fusion of the viral envelope with the target cell membrane and the release of the HIV capsid into the cell.
Entry to the cell begins through interaction of the trimeric envelope complex (gp160 spike) on the HIV viral envelope and both CD4 and a chemokine co-receptor (generally either CCR5 or CXCR4, but others are known to interact) on the target cell surface. Gp120 binds to integrin α4β7 activating LFA-1, the central integrin involved in the establishment of virological synapses, which facilitate efficient cell-to-cell spreading of HIV-1. The gp160 spike contains binding domains for both CD4 and chemokine receptors.
The first step in fusion involves the high-affinity attachment of the CD4 binding domains of gp120 to CD4. Once gp120 is bound with the CD4 protein, the envelope complex undergoes a structural change, exposing the chemokine receptor binding domains of gp120 and allowing them to interact with the target chemokine receptor. This allows for a more stable two-pronged attachment, which allows the N-terminal fusion peptide gp41 to penetrate the cell membrane. Repeat sequences in gp41, HR1, and HR2 then interact, causing the collapse of the extracellular portion of gp41 into a hairpin shape. This loop structure brings the virus and cell membranes close together, allowing fusion of the membranes and subsequent entry of the viral capsid.
After HIV has bound to the target cell, the HIV RNA and various enzymes, including reverse transcriptase, integrase, ribonuclease, and protease, are injected into the cell. During the microtubule-based transport to the nucleus, the viral single-strand RNA genome is transcribed into double-strand DNA, which is then integrated into a host chromosome.
HIV can infect dendritic cells (DCs) by this CD4-CCR5 route, but another route using mannose-specific C-type lectin receptors such as DC-SIGN can also be used. DCs are one of the first cells encountered by the virus during sexual transmission. They are currently thought to play an important role by transmitting HIV to T cells when the virus is captured in the mucosa by DCs. The presence of FEZ-1, which occurs naturally in neurons, is believed to prevent the infection of cells by HIV.
HIV-1 entry, as well as entry of many other retroviruses, has long been believed to occur exclusively at the plasma membrane. More recently, however, productive infection by pH-independent, clathrin-mediated endocytosis of HIV-1 has also been reported and was recently suggested to constitute the only route of productive entry.
Replication and transcription
Shortly after the viral capsid enters the cell, an enzyme called reverse transcriptase liberates the positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome from the attached viral proteins and copies it into a complementary DNA (cDNA) molecule. The process of reverse transcription is extremely error-prone, and the resulting mutations may cause drug resistance or allow the virus to evade the body's immune system. The reverse transcriptase also has ribonuclease activity that degrades the viral RNA during the synthesis of cDNA, as well as DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity that creates a sense DNA from the antisense cDNA. Together, the cDNA and its complement form a double-stranded viral DNA that is then transported into the cell nucleus. The integration of the viral DNA into the host cell's genome is carried out by another viral enzyme called integrase.
The integrated viral DNA may then lie dormant, in the latent stage of HIV infection. To actively produce the virus, certain cellular transcription factors need to be present, the most important of which is NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B), which is upregulated when T cells become activated. This means that those cells most likely to be targeted, entered and subsequently killed by HIV are those actively fighting infection.
During viral replication, the integrated DNA provirus is transcribed into RNA. The full-length genomic RNAs (gRNA) can be packaged into new viral particles in a pseudodiploid form. The selectivity in the packaging is explained by the structural properties of the dimeric conformer of the gRNA. The gRNA dimer is characterized by a tandem three-way junction within the gRNA monomer, in which the SD and AUG hairpins, responsible for splicing and translation respectively, are sequestered and the DIS (dimerization initiation signal) hairpin is exposed.The formation of the gRNA dimer is mediated by a ‘kissing’ interaction between the DIS hairpin loops of the gRNA monomers. At the same time, certain guanosine residues in the gRNA are made available for binding of the nucleocapsid (NC) protein leading to the subsequent virion assembly. The labile gRNA dimer has been also reported to achieve a more stable conformation following the NC binding, in which both the DIS and the U5:AUG regions of the gRNA participate in extensive base pairing.
RNA can also be processed to produce mature messenger RNAs (mRNAs). In most cases, this processing involves RNA splicing to produce mRNAs that are shorter than the full-length genome. Which part of the RNA is removed during RNA splicing determines which of the HIV protein-coding sequences is translated.
Mature HIV mRNAs are exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where they are translated to produce HIV proteins, including Rev. As the newly produced Rev protein is produced it moves to the nucleus, where it binds to full-length, unspliced copies of virus RNAs and allows them to leave the nucleus. Some of these full-length RNAs function as mRNAs that are translated to produce the structural proteins Gag and Env. Gag proteins bind to copies of the virus RNA genome to package them into new virus particles. HIV-1 and HIV-2 appear to package their RNA differently. HIV-1 will bind to any appropriate RNA. HIV-2 will preferentially bind to the mRNA that was used to create the Gag protein itself.
Recombination
Two RNA genomes are encapsidated in each HIV-1 particle (see Structure and genome of HIV). Upon infection and replication catalyzed by reverse transcriptase, recombination between the two genomes can occur. Recombination occurs as the single-strand, positive-sense RNA genomes are reverse transcribed to form DNA. During reverse transcription, the nascent DNA can switch multiple times between the two copies of the viral RNA. This form of recombination is known as copy-choice. Recombination events may occur throughout the genome. Anywhere from two to 20 recombination events per genome may occur at each replication cycle, and these events can rapidly shuffle the genetic information that is transmitted from parental to progeny genomes.
Viral recombination produces genetic variation that likely contributes to the evolution of resistance to anti-retroviral therapy. Recombination may also contribute, in principle, to overcoming the immune defenses of the host. Yet, for the adaptive advantages of genetic variation to be realized, the two viral genomes packaged in individual infecting virus particles need to have arisen from separate progenitor parental viruses of differing genetic constitution. It is unknown how often such mixed packaging occurs under natural conditions.
Bonhoeffer et al. suggested that template switching by reverse transcriptase acts as a repair process to deal with breaks in the single-stranded RNA genome. In addition, Hu and Temin suggested that recombination is an adaptation for repair of damage in the RNA genomes. Strand switching (copy-choice recombination) by reverse transcriptase could generate an undamaged copy of genomic DNA from two damaged single-stranded RNA genome copies. This view of the adaptive benefit of recombination in HIV could explain why each HIV particle contains two complete genomes, rather than one. Furthermore, the view that recombination is a repair process implies that the benefit of repair can occur at each replication cycle, and that this benefit can be realized whether or not the two genomes differ genetically. On the view that recombination in HIV is a repair process, the generation of recombinational variation would be a consequence, but not the cause of, the evolution of template switching.
HIV-1 infection causes chronic inflammation and production of reactive oxygen species. Thus, the HIV genome may be vulnerable to oxidative damage, including breaks in the single-stranded RNA. For HIV, as well as for viruses in general, successful infection depends on overcoming host defense strategies that often include production of genome-damaging reactive oxygen species. Thus, Michod et al. suggested that recombination by viruses is an adaptation for repair of genome damage, and that recombinational variation is a byproduct that may provide a separate benefit.
Assembly and release
The final step of the viral cycle, assembly of new HIV-1 virions, begins at the plasma membrane of the host cell. The Env polyprotein (gp160) goes through the endoplasmic reticulum and is transported to the Golgi apparatus where it is cleaved by furin resulting in the two HIV envelope glycoproteins, gp41 and gp120. These are transported to the plasma membrane of the host cell where gp41 anchors gp120 to the membrane of the infected cell. The Gag (p55) and Gag-Pol (p160) polyproteins also associate with the inner surface of the plasma membrane along with the HIV genomic RNA as the forming virion begins to bud from the host cell. The budded virion is still immature as the gag polyproteins still need to be cleaved into the actual matrix, capsid and nucleocapsid proteins. This cleavage is mediated by the packaged viral protease and can be inhibited by antiretroviral drugs of the protease inhibitor class. The various structural components then assemble to produce a mature HIV virion. Only mature virions are then able to infect another cell.
Spread within the body
The classical process of infection of a cell by a virion can be called "cell-free spread" to distinguish it from a more recently recognized process called "cell-to-cell spread". In cell-free spread (see figure), virus particles bud from an infected T cell, enter the blood or extracellular fluid and then infect another T cell following a chance encounter. HIV can also disseminate by direct transmission from one cell to another by a process of cell-to-cell spread, for which two pathways have been described. Firstly, an infected T cell can transmit virus directly to a target T cell via a virological synapse. Secondly, an antigen-presenting cell (APC), such as a macrophage or dendritic cell, can transmit HIV to T cells by a process that either involves productive infection (in the case of macrophages) or capture and transfer of virions in trans (in the case of dendritic cells). Whichever pathway is used, infection by cell-to-cell transfer is reported to be much more efficient than cell-free virus spread. A number of factors contribute to this increased efficiency, including polarised virus budding towards the site of cell-to-cell contact, close apposition of cells, which minimizes fluid-phase diffusion of virions, and clustering of HIV entry receptors on the target cell towards the contact zone. Cell-to-cell spread is thought to be particularly important in lymphoid tissues, where CD4+ T cells are densely packed and likely to interact frequently. Intravital imaging studies have supported the concept of the HIV virological synapse in vivo. The many dissemination mechanisms available to HIV contribute to the virus's ongoing replication in spite of anti-retroviral therapies.
Genetic variability
HIV differs from many viruses in that it has very high genetic variability. This diversity is a result of its fast replication cycle, with the generation of about 1010 virions every day, coupled with a high mutation rate of approximately 3 x 10−5 per nucleotide base per cycle of replication and recombinogenic properties of reverse transcriptase.
This complex scenario leads to the generation of many variants of HIV in a single infected patient in the course of one day. This variability is compounded when a single cell is simultaneously infected by two or more different strains of HIV. When simultaneous infection occurs, the genome of progeny virions may be composed of RNA strands from two different strains. This hybrid virion then infects a new cell where it undergoes replication. As this happens, the reverse transcriptase, by jumping back and forth between the two different RNA templates, will generate a newly synthesized retroviral DNA sequence that is a recombinant between the two parental genomes. This recombination is most obvious when it occurs between subtypes.
The closely related simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) has evolved into many strains, classified by the natural host species. SIV strains of the African green monkey (SIVagm) and sooty mangabey (SIVsmm) are thought to have a long evolutionary history with their hosts. These hosts have adapted to the presence of the virus, which is present at high levels in the host's blood, but evokes only a mild immune response, does not cause the development of simian AIDS, and does not undergo the extensive mutation and recombination typical of HIV infection in humans.
In contrast, when these strains infect species that have not adapted to SIV ("heterologous" or similar hosts such as rhesus or cynomologus macaques), the animals develop AIDS and the virus generates genetic diversity similar to what is seen in human HIV infection. Chimpanzee SIV (SIVcpz), the closest genetic relative of HIV-1, is associated with increased mortality and AIDS-like symptoms in its natural host. SIVcpz appears to have been transmitted relatively recently to chimpanzee and human populations, so their hosts have not yet adapted to the virus. This virus has also lost a function of the nef gene that is present in most SIVs. For non-pathogenic SIV variants, nef suppresses T cell activation through the CD3 marker. Nef's function in non-pathogenic forms of SIV is to downregulate expression of inflammatory cytokines, MHC-1, and signals that affect T cell trafficking. In HIV-1 and SIVcpz, nef does not inhibit T-cell activation and it has lost this function. Without this function, T cell depletion is more likely, leading to immunodeficiency.
Three groups of HIV-1 have been identified on the basis of differences in the envelope (env) region: M, N, and O. Group M is the most prevalent and is subdivided into eight subtypes (or clades), based on the whole genome, which are geographically distinct. The most prevalent are subtypes B (found mainly in North America and Europe), A and D (found mainly in Africa), and C (found mainly in Africa and Asia); these subtypes form branches in the phylogenetic tree representing the lineage of the M group of HIV-1. Co-infection with distinct subtypes gives rise to circulating recombinant forms (CRFs). In 2000, the last year in which an analysis of global subtype prevalence was made, 47.2% of infections worldwide were of subtype C, 26.7% were of subtype A/CRF02_AG, 12.3% were of subtype B, 5.3% were of subtype D, 3.2% were of CRF_AE, and the remaining 5.3% were composed of other subtypes and CRFs. Most HIV-1 research is focused on subtype B; few laboratories focus on the other subtypes. The existence of a fourth group, "P", has been hypothesised based on a virus isolated in 2009. The strain is apparently derived from gorilla SIV (SIVgor), first isolated from western lowland gorillas in 2006.
HIV-2's closest relative is SIVsm, a strain of SIV found in sooty mangabees. Since HIV-1 is derived from SIVcpz, and HIV-2 from SIVsm, the genetic sequence of HIV-2 is only partially homologous to HIV-1 and more closely resembles that of SIVsm.
Diagnosis
Many HIV-positive people are unaware that they are infected with the virus. For example, in 2001 less than 1% of the sexually active urban population in Africa had been tested, and this proportion is even lower in rural populations. Furthermore, in 2001 only 0.5% of pregnant women attending urban health facilities were counselled, tested or receive their test results. Again, this proportion is even lower in rural health facilities. Since donors may therefore be unaware of their infection, donor blood and blood products used in medicine and medical research are routinely screened for HIV.
HIV-1 testing is initially done using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antibodies to HIV-1. Specimens with a non-reactive result from the initial ELISA are considered HIV-negative, unless new exposure to an infected partner or partner of unknown HIV status has occurred. Specimens with a reactive ELISA result are retested in duplicate. If the result of either duplicate test is reactive, the specimen is reported as repeatedly reactive and undergoes confirmatory testing with a more specific supplemental test (e.g., a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), western blot or, less commonly, an immunofluorescence assay (IFA)). Only specimens that are repeatedly reactive by ELISA and positive by IFA or PCR or reactive by western blot are considered HIV-positive and indicative of HIV infection. Specimens that are repeatedly ELISA-reactive occasionally provide an indeterminate western blot result, which may be either an incomplete antibody response to HIV in an infected person or nonspecific reactions in an uninfected person.
Although IFA can be used to confirm infection in these ambiguous cases, this assay is not widely used. In general, a second specimen should be collected more than a month later and retested for persons with indeterminate western blot results. Although much less commonly available, nucleic acid testing (e.g., viral RNA or proviral DNA amplification method) can also help diagnosis in certain situations. In addition, a few tested specimens might provide inconclusive results because of a low quantity specimen. In these situations, a second specimen is collected and tested for HIV infection.
Modern HIV testing is extremely accurate, when the window period is taken into consideration. A single screening test is correct more than 99% of the time. The chance of a false-positive result in a standard two-step testing protocol is estimated to be about 1 in 250,000 in a low risk population. Testing post-exposure is recommended immediately and then at six weeks, three months, and six months.
The latest recommendations of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that HIV testing must start with an immunoassay combination test for HIV-1 and HIV-2 antibodies and p24 antigen. A negative result rules out HIV exposure, while a positive one must be followed by an HIV-1/2 antibody differentiation immunoassay to detect which antibodies are present. This gives rise to four possible scenarios:
- 1. HIV-1 (+) & HIV-2 (−): HIV-1 antibodies detected
- 2. HIV-1 (−) & HIV-2 (+): HIV-2 antibodies detected
- 3. HIV-1 (+) & HIV-2 (+): both HIV-1 and HIV-2 antibodies detected
- 4. HIV-1 (−) or indeterminate & HIV-2 (−): Nucleic acid test must be carried out to detect the acute infection of HIV-1 or its absence.
Research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Many governments and research institutions participate in HIV/AIDS research. This research includes behavioral health interventions, such as research into sex education, and drug development, such as research into microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases, HIV vaccines, and anti-retroviral drugs. Other medical research areas include the topics of pre-exposure prophylaxis, post-exposure prophylaxis, circumcision and HIV, and accelerated aging effects.
Treatment and transmission
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs. In many parts of the world, HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS is increasingly rare.
HIV latency, and the consequent viral reservoir in CD4+ T cells, dendritic cells, as well as macrophages, is the main barrier to eradication of the virus.
It is important to note that although HIV is highly virulent, transmission does not occur through sex when an HIV-positive person has a consistently undetectable viral load (<50 copies/ml) due to anti-retroviral treatment. This was first argued by the Swiss Federal Commission for AIDS/HIV in 2008 in the Swiss Statement, though the statement was controversial at the time. However, following multiple studies, it became clear that the chance of passing on HIV through sex is effectively zero where the HIV-positive person has a consistently undetectable viral load; this is known as U=U, "Undetectable=Untransmittable", also phrased as "can't pass it on". The studies demonstrating U=U are: Opposites Attract, PARTNER 1, PARTNER 2, (for male-male couples) and HPTN052 (for heterosexual couples) when "the partner living with HIV had a durably suppressed viral load." In these studies, couples where one partner was HIV positive and one partner was HIV negative were enrolled and regular HIV testing completed. In total from the four studies, 4097 couples were enrolled over four continents and 151,880 acts of condomless sex were reported; there were zero phylogenetically linked transmissions of HIV where the positive partner had an undetectable viral load. Following this, the U=U consensus statement advocating the use of "zero risk" was signed by hundreds of individuals and organisations, including the US CDC, British HIV Association and The Lancet medical journal. The importance of the final results of the PARTNER 2 study were described by the medical director of the Terrence Higgins Trust as "impossible to overstate", while lead author Alison Rodger declared that the message that "undetectable viral load makes HIV untransmittable ... can help end the HIV pandemic by preventing HIV transmission. The authors summarised their findings in The Lancet as follows:
Our results provide a similar level of evidence on viral suppression and HIV transmission risk for gay men to that previously generated for heterosexual couples and suggest that the risk of HIV transmission in gay couples through condomless sex when HIV viral load is suppressed is effectively zero. Our findings support the message of the U=U (undetectable equals untransmittable) campaign, and the benefits of early testing and treatment for HIV.
This result is consistent with the conclusion presented by Anthony S. Fauci, the Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases for the U.S. National Institutes of Health, and his team in a viewpoint published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, that U=U is an effective HIV prevention method when an undetectable viral load is maintained.
Genital herpes (HSV-2) reactivation in those infected with the virus have an associated increase in CCR-5 enriched CD4+ T cells as well as inflammatory dendritic cells in the submucosa of the genital skin. Tropism of HIV for CCR-5 positive cells explains the two to threefold increase in HIV acquisition among persons with genital herpes. Daily antiviral (e.g. acyclovir) medication do not reduce the sub-clinical post reactivation inflammation and therefore does not confer reduced risk of HIV acquisition.
History
Discovery
The first news story on "an exotic new disease" appeared May 18, 1981 in the gay newspaper New York Native.
AIDS was first clinically observed in 1981 in the United States. The initial cases were a cluster of injection drug users and gay men with no known cause of impaired immunity who showed symptoms of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP or PJP, the latter term recognizing that the causative agent is now called Pneumocystis jirovecii), a rare opportunistic infection that was known to occur in people with very compromised immune systems. Soon thereafter, researchers at the NYU School of Medicine studied gay men developing a previously rare skin cancer called Kaposi's sarcoma (KS). Many more cases of PJP and KS emerged, alerting U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and a CDC task force was formed to monitor the outbreak. The earliest retrospectively described case of AIDS is believed to have been in Norway beginning in 1966.
In the beginning, the CDC did not have an official name for the disease, often referring to it by way of the diseases that were associated with it, for example, lymphadenopathy, the disease after which the discoverers of HIV originally named the virus. They also used Kaposi's Sarcoma and Opportunistic Infections, the name by which a task force had been set up in 1981. In the general press, the term GRID, which stood for gay-related immune deficiency, had been coined. The CDC, in search of a name and looking at the infected communities, coined "the 4H disease", as it seemed to single out homosexuals, heroin users, hemophiliacs, and Haitians. However, after determining that AIDS was not isolated to the gay community, it was realized that the term GRID was misleading and AIDS was introduced at a meeting in July 1982. By September 1982 the CDC started using the name AIDS.
In 1983, two separate research groups led by American Robert Gallo and French investigators Françoise Barré-Sinoussi and Luc Montagnier independently declared that a novel retrovirus may have been infecting AIDS patients, and published their findings in the same issue of the journal Science. Gallo claimed that a virus his group had isolated from a person with AIDS was strikingly similar in shape to other human T-lymphotropic viruses (HTLVs) his group had been the first to isolate. Gallo admitted in 1987 that the virus he claimed to have discovered in 1984 was in reality a virus sent to him from France the year before. Gallo's group called their newly isolated virus HTLV-III. Montagnier's group isolated a virus from a patient presenting with swelling of the lymph nodes of the neck and physical weakness, two classic symptoms of primary HIV infection. Contradicting the report from Gallo's group, Montagnier and his colleagues showed that core proteins of this virus were immunologically different from those of HTLV-I. Montagnier's group named their isolated virus lymphadenopathy-associated virus (LAV). As these two viruses turned out to be the same, in 1986 LAV and HTLV-III were renamed HIV.
Another group working contemporaneously with the Montagnier and Gallo groups was that of Dr. Jay A. Levy at the University of California, San Francisco. He independently discovered the AIDS virus in 1983 and named it the AIDS associated retrovirus (ARV). This virus was very different from the virus reported by the Montagnier and Gallo groups. The ARV strains indicated, for the first time, the heterogeneity of HIV isolates and several of these remain classic examples of the AIDS virus found in the United States.
Origins
Both HIV-1 and HIV-2 are believed to have originated in non-human primates in West-central Africa, and are believed to have transferred to humans (a process known as zoonosis) in the early 20th century.
HIV-1 appears to have originated in southern Cameroon through the evolution of SIVcpz, a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) that infects wild chimpanzees (HIV-1 descends from the SIVcpz endemic in the chimpanzee subspecies Pan troglodytes troglodytes). The closest relative of HIV-2 is SIVsmm, a virus of the sooty mangabey (Cercocebus atys atys), an Old World monkey living in littoral West Africa (from southern Senegal to western Côte d'Ivoire). New World monkeys such as the owl monkey are resistant to HIV-1 infection, possibly because of a genomic fusion of two viral resistance genes.
HIV-1 is thought to have jumped the species barrier on at least three separate occasions, giving rise to the three groups of the virus, M, N, and O.
There is evidence that humans who participate in bushmeat activities, either as hunters or as bushmeat vendors, commonly acquire SIV. However, SIV is a weak virus, and it is typically suppressed by the human immune system within weeks of infection. It is thought that several transmissions of the virus from individual to individual in quick succession are necessary to allow it enough time to mutate into HIV. Furthermore, due to its relatively low person-to-person transmission rate, it can only spread throughout the population in the presence of one or more high-risk transmission channels, which are thought to have been absent in Africa prior to the 20th century.
Specific proposed high-risk transmission channels, allowing the virus to adapt to humans and spread throughout the society, depend on the proposed timing of the animal-to-human crossing. Genetic studies of the virus suggest that the most recent common ancestor of the HIV-1 M group dates back to circa 1910. Proponents of this dating link the HIV epidemic with the emergence of colonialism and growth of large colonial African cities, leading to social changes, including different patterns of sexual contact (especially multiple, concurrent partnerships), the spread of prostitution, and the concomitant high frequency of genital ulcer diseases (such as syphilis) in nascent colonial cities. While transmission rates of HIV during vaginal intercourse are typically low, they are increased manyfold if one of the partners suffers from a sexually transmitted infection resulting in genital ulcers. Early 1900s colonial cities were notable for their high prevalence of prostitution and genital ulcers to the degree that as of 1928 as many as 45% of female residents of eastern Leopoldville (currently Kinshasa) were thought to have been prostitutes and as of 1933 around 15% of all residents of the same city were infected by one of the forms of syphilis.
The earliest, well-documented case of HIV in a human dates back to 1959 in the Belgian Congo. The virus may have been present in the United States as early as the mid- to late 1960s, as a sixteen-year-old male named Robert Rayford presented with symptoms in 1966 and died in 1969.
An alternative and likely complementary hypothesis points to the widespread use of unsafe medical practices in Africa during years following World War II, such as unsterile reuse of single-use syringes during mass vaccination, antibiotic, and anti-malaria treatment campaigns. Research on the timing of most recent common ancestor for HIV-1 groups M and O, as well as on HIV-2 groups A and B, indicates that SIV has given rise to transmissible HIV lineages throughout the twentieth century. The dispersed timing of these transmissions to humans implies that no single external factor is needed to explain the cross-species transmission of HIV. This observation is consistent with both of the two prevailing views of the origin of the HIV epidemics, namely SIV transmission to humans during the slaughter or butchering of infected primates, and the colonial expansion of sub-Saharan African cities.