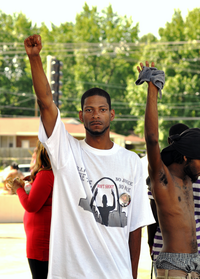Black Power is a political slogan and a name which is given to various associated ideologies which aim to achieve self-determination for people of African descent. It is primarily, but not exclusively, used by African Americans in the United States. The Black Power movement was prominent in the late 1960s and early 1970s, emphasizing racial pride and the creation of black political and cultural institutions to nurture and promote black collective interests and advance black values.
The basis of Black Power is various ideologies that aim at achieving self-determination for black people in the U.S. Black power dictates that blacks create their own identities despite being subjected to pre-existing societal factors.
"Black Power" expresses a range of political goals, from defense against racial oppression, to the establishment of social institutions and a self-sufficient economy, including black-owned bookstores, cooperatives, farms, and media. However, the movement has been criticized for alienating itself from the mainstream civil rights movement, for its apparent support of racial segregation, and for constituting black superiority over other races.
Etymology
The earliest known usage of the term "Black Power" is found in Richard Wright's 1954 book Black Power. New York politician Adam Clayton Powell Jr. used the term on May 29, 1966, during an address at Howard University: "To demand these God-given rights is to seek black power."
The first popular use of the term "Black Power" as a political and racial slogan was by Stokely Carmichael (later known as Kwame Ture) and Willie Ricks (later known as Mukasa Dada), both organizers and spokespersons for the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC). On June 16, 1966, in a speech in Greenwood, Mississippi, after the shooting of James Meredith during the March Against Fear, Stokely Carmichael said:
This is the twenty-seventh time I have been arrested and I ain't going to jail no more! The only way we gonna stop them white men from whuppin' us is to take over. What we gonna start sayin' now is Black Power!
Stokely Carmichael saw the concept of "Black Power" as a means of
solidarity between individuals within the movement. It was a replacement
of the "Freedom Now!" slogan of Carmichael's contemporary, the
non-violent leader Martin Luther King.
With his use of the term, Carmichael felt this movement was not just a
movement for racial desegregation, but rather a movement to help end how
American racism had weakened blacks. He said, "'Black
Power' means black people coming together to form a political force and
either electing representatives or forcing their representatives to
speak their needs."
Variants
Black Power adherents believed in black autonomy, with a variety of tendencies such as black nationalism, black self-determination, and black separatism. Such positions caused friction with leaders of the mainstream Civil Rights Movement,
and thus the two movements have sometimes been viewed as inherently
antagonistic. Civil Rights leaders often proposed passive, non-violent
tactics while the Black Power movement felt that, in the words of Stokely Carmichael and Charles V. Hamilton,
"a 'non-violent' approach to civil rights is an approach black people
cannot afford and a luxury white people do not deserve." "However, many groups and individuals—including Rosa Parks, Robert F. Williams, Maya Angelou, Gloria Richardson, and Fay Bellamy Powell—participated
in both civil rights and black power activism. A growing number of
scholars conceive of the civil rights and black power movements as one
interconnected Black Freedom Movement.
Numerous Black Power advocates were in favor of black self
determination due to the belief that black people must lead and run
their own organizations. Stokely Carmichael
is such an advocate and states that, "only black people can convey the
revolutionary idea—and it is a revolutionary idea—that black people are
able to do things themselves." However, this is not to say that Black Power advocates promoted racial segregation. Stokely Carmichael and Charles V. Hamilton write that "there is a definite, much-needed role that whites can play." They felt that whites could serve the movement by educating other white people.
Not all Black Power advocates were in favor of black separatism. While Stokely Carmichael and SNCC were in favor of separatism for a time in the late 1960s, organizations such as the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense were not. Though the Panthers considered themselves to be at war with the prevailing white supremacist power structure, they were not at war with all whites, but rather with those (mostly white) individuals empowered by the injustices of the structure and responsible for its reproduction.
Bobby Seale,
Chairman and Co-Founder of the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense,
was outspoken about this issue. His stance was that the oppression of black people was more a result of economic exploitation than anything innately racist. In his book Seize the Time, he states that "In our view it is a class struggle between the massive proletarian working class and the small, minority ruling class.
Working-class people of all colors must unite against the exploitative,
oppressive ruling class. So let me emphasize again—we believe our fight
is a class struggle and not a race struggle."
Internationalist offshoots of black power include African Internationalism, pan-Africanism, black nationalism, and black supremacy.
History
The term "Black Power" was used in a different sense in the 1850s by black leader Frederick Douglass as an alternative name for the Slave Power—that is the disproportionate political power at the national level held by slave owners in the South.
Douglass predicted: "The days of Black Power are numbered. Its course,
indeed is onward. But with the swiftness of an arrow, it rushes to the
tomb. While crushing its millions, it is also crushing itself. The sword
of Retribution, suspended by a single hair, hangs over it. That sword
must fall. Liberty must triumph."
In Apartheid Era South Africa, Nelson Mandela's African National Congress used the call-and-response chant "Amandla! (Power!)", "Ngawethu! (The power is ours!)" from the late 1950s onward.
The modern American concept emerged from the Civil Rights Movement in the early 1960s. Beginning in 1959, Robert F. Willams, president of the Monroe, North Carolina chapter of the NAACP, openly questioned the ideology of nonviolence and its domination of the movement's strategy. Williams was supported by prominent leaders such as Ella Baker and James Forman, and opposed by others, such as Roy Wilkins (the national NAACP chairman) and Martin Luther King Jr. In 1961, Maya Angelou, Leroi Jones, and Mae Mallory led a riotous (and widely covered) demonstration at the United Nations in order to protest against the assassination of Patrice Lumumba. Malcolm X, national representative of the Nation of Islam,
also launched an extended critique of nonviolence and integrationism at
this time. After seeing the increasing militancy of blacks in the wake
of the 16th Street Baptist Church bombing, and wearying of Elijah Muhammad's domination of the Nation of Islam,
Malcolm left that organization and engaged with the mainstream of the
Civil Rights Movement. Malcolm was now open to voluntary racial integration as a long-term goal, but he still supported armed self-defense, self-reliance, and black nationalism;
he became a simultaneous spokesman for the militant wing of the Civil
Rights Movement and the non-separatist wing of the Black Power movement.
An early manifestation of Black Power in popular culture was the performances given by Nina Simone at Carnegie Hall in March 1964, and the album In Concert
which resulted from them. Nina Simone mocked liberal nonviolence ("Go
Limp"), and took a vengeful position toward white racists ("Mississippi Goddamn" and her adaptation of "Pirate Jenny"). Historian Ruth Feldstein
writes that, "Contrary to the neat historical trajectories which
suggest that black power came late in the decade and only after the
'successes' of earlier efforts, Simone's album makes clear that black
power perspectives were already taking shape and circulating widely...in
the early 1960s."
By 1966, most of SNCC's field staff, among them Stokely
Carmichael (later Kwame Ture), were becoming critical of the nonviolent
approach to confronting racism and inequality—articulated and promoted
by Martin Luther King, Jr., Roy Wilkins, and other moderates—and they rejected desegregation
as a primary objective. King was critical of the black power movement,
stating in an August 1967 speech to the SCLC: "Let us be dissatisfied
until that day when nobody will shout 'White Power!' — when nobody will
shout 'Black Power!' — but everybody will talk about God's power and
human power." In his 1967 book, Where Do We Go from Here: Chaos or Community?, King stated:
In the final analysis the weakness of Black Power is its failure to see that the black man needs the white man and the white man needs the black man. However much we may try to romanticize the slogan, there is no separate black path to power and fulfillment that does not intersect white paths, and there is no separate white path to power and fulfillment, short of social disaster, that does not share that power with black aspirations for freedom and human dignity. We are bound together in a single garment of destiny. The language, the cultural patterns, the music, the material prosperity, and even the food of America are an amalgam of black and white.
SNCC's base of support was generally younger and more working-class than that of the other "Big Five"
civil rights organizations and became increasingly more militant and
outspoken over time. As a result, as the Civil Rights Movement
progressed, increasingly radical, more militant voices came to the fore
to aggressively challenge white hegemony. Increasing numbers of black
youth, particularly, rejected their elders' moderate path of
cooperation, racial integration
and assimilation. They rejected the notion of appealing to the
public's conscience and religious creeds and took the tack articulated
by another black activist more than a century before, abolitionist Frederick Douglass, who wrote:
Those who profess to favor freedom, and yet depreciate agitation, are men who want crops without plowing up the ground. They want rain without thunder and lightning. They want the ocean without the awful roar of its many waters. ... Power concedes nothing without demand. It never did and it never will.
Most early 1960s civil rights leaders did not believe in physically
violent retaliation. However, much of the African-American
rank-and-file, especially those leaders with strong working-class ties,
tended to complement nonviolent action with armed self-defense. For
instance, prominent nonviolent activist Fred Shuttlesworth
of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (and a leader of the
1963 Birmingham campaign), had worked closely with an armed defense
group that was led by Colonel Stone Johnson. As Alabama historian Frye Gaillard writes,
-
- ...these were the kind of men Fred Shuttlesworth admired, a mirror of the toughness he aspired to himself…They went armed [during the Freedom Rides], for it was one of the realities of the civil rights movement that however nonviolent it may have been at its heart, there was always a current of 'any means necessary,' as the black power advocates would say later on.
During the March Against Fear, there was a division between those aligned with Martin Luther King, Jr. and those aligned with Carmichael, marked by their respective slogans, "Freedom Now" and "Black Power."
While King never endorsed the slogan, and in fact opposed the
Black Power movement, his rhetoric sometimes came close to it. In his
1967 book Where Do We Go From Here?, King wrote that "power is
not the white man's birthright; it will not be legislated for us and
delivered in neat government packages."
"Crisis and Commitment Statement"
The "Crisis and Commitment Statement" was a full-page ad taken out in the New York Times on October 14, 1966.
The ad was written and signed onto by Civil Rights leaders, condemning
the "extreme" measures used by groups such as the Black Power movement,
while reaffirming the basic tenets of the Civil Rights Movement. The statement was signed by Dorothy Height, A. Philip Randolph, Bayard Rustin, Roy Wilkins, Whitney Young, and Hobson R. Reynolds.
Impact
Although
the concept remained imprecise and contested and the people who used the
slogan ranged from business people who used it to push black capitalism
to revolutionaries who sought an end to capitalism, the idea of Black
Power exerted a significant influence. It helped organize scores of
community self-help groups and institutions that did not depend on
Whites, encouraged colleges and universities to start black studies programs, mobilized black voters, and improved racial pride and self-esteem.
One of the most spectacular and unexpected demonstrations for Black Power occurred at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City. At the conclusion of the 200m race, at the medal ceremony, United States gold medalist Tommie Smith and bronze medalist John Carlos wore Olympic Project for Human Rights badges and showed the raised fist (see 1968 Olympics Black Power salute) as the anthem played. Accompanying them was silver medalist Peter Norman, a white Australian sprinter, who also wore an OPHR badge to show his support for the two African Americans.
Black politics
Tommie Smith and John Carlos showing the raised fist on the podium after the 200 m race at the 1968 Summer Olympics.
Though the Black Power movement did not remedy the political problems
faced by African Americans in the 1960s and 1970s, the movement did
contribute to the development of black politics both directly and
indirectly. As a contemporary of and successor to the Civil Rights
Movement, the Black Power movement created, what sociologist Herbert H.
Haines refers to as a "positive radical flank effect"
on political affairs of the 1960s. Though the nature of the
relationship between the Civil Rights Movement and the Black Power
movement is contested, Haines' study of the relationship between black
radicals and the mainstream civil rights movement indicates that Black
Power generated a "crisis in American institutions which made the
legislative agenda of 'polite, realistic, and businesslike' mainstream
organizations" more appealing to politicians. In this way, it can be
argued that the more strident and oppositional messages of the Black
Power movement indirectly enhanced the bargaining position of more
moderate activists.
Black Power activists approached politics with vitality, variety, wit,
and creativity that shaped the way future generations approached dealing
with America's societal problems (McCartney 188). These activists
capitalized on the nation's recent awareness of the political nature of
oppression, a primary focus of the Civil Rights Movement, developing
numerous political action caucuses and grass roots community associations to remedy the situation.
The National Black Political Convention, held March 10–12, 1972,
was a significant milestone in black politics of the Black Power era.
Held in Gary, Indiana,
a majorly black city, the convention included a diverse group of black
activists, although it completely excluded whites. The convention was
criticized for its racial exclusivity by Roy Wilkins of the NAACP, a
group that supported integration.
The delegates created a National Black Political Agenda with stated
goals including the election of a proportionate number of black
representatives to Congress, community control of schools, national
health insurance, etc. Though the convention did not result in any
direct policy, the convention advanced goals of the Black Power movement
and left participants buoyed by a spirit of possibility and themes of
unity and self-determination. A concluding note to the convention,
addressing its supposed idealism, read: "At every critical moment of our
struggle in America we have had to press relentlessly against the
limits of the 'realistic' to create new realities for the life of our
people. This is our challenge at Gary and beyond, for a new Black
politics demands new vision, new hope and new definitions of the
possible. Our time has come. These things are necessary. All things are
possible."
Though such political activism may not have resulted in direct policy,
they provided political models for later movements, advanced a pro-black
political agenda, and brought sensitive issues to the forefront of
American politics. In its confrontational and often oppositional nature,
the Black Power movement started a debate within the black community
and America as a nation over issues of racial progress, citizenship, and
democracy, namely "the nature of American society and the place of the
African American in it."
The continued intensity of debate over these same social and political
issues is a tribute to the impact of the Black Power movement in
arousing the political awareness and passions of citizens.
Other minorities
Though
the aims of the Black Power movement were racially specific, much of
the movement's impact has been its influence on the development and
strategies of later political and social movements. By igniting and
sustaining debate on the nature of American society, the Black Power
movement created what other multiracial and minority groups interpreted
to be a viable template for the overall restructuring of society.
By opening up discussion on issues of democracy and equality, the Black
Power movement paved the way for a diverse plurality of social justice
movements, including black feminism, environmental movements, affirmative action, and gay and lesbian rights. Central to these movements were the issues of identity politics and structural inequality, features emerging from the Black Power movement.
Because the Black Power movement emphasized and explored a black
identity, movement activists were forced to confront issues of gender
and class as well. Many activists in the Black Power movement became
active in related movements. This is seen in the case of the "second
wave" of women's rights
activism, a movement supported and orchestrated to a certain degree by
women working from within the coalition ranks of the Black Power
movement.
The boundaries between social movements became increasingly unclear at
the end of the 1960s and into the 1970s; where the Black Power movement
ends and where these other social movements begin is often unclear. "It
is pertinent to note that as the movement expanded the variables of
gender, class, and only compounded issues of strategy and methodology in
black protest thought."
African-American identity
Protester raises his hand in black power salute, Ferguson, Missouri, 15 August 2014
Due to the negative and militant reputation of such auxiliaries as that of the Black Panther Party,
many people felt that this movement of "insurrection" would soon serve
to cause discord and disharmony through the entire U.S. Even Stokely
Carmichael stated, "When you talk of Black Power, you talk of building a
movement that will smash everything Western civilization has created."
Though Black Power at the most basic level refers to a political
movement, the psychological and cultural messages of the Black Power
movement, though less tangible, have had perhaps a longer-lasting impact
on American society than concrete political changes. Indeed, "fixation
on the 'political' hinders appreciation of the movement's cultural
manifestations and unnecessarily obscures black culture's role in
promoting the psychological well being of the Afro-American people," states William L. Van Deburg,
author of A New Day in Babylon, "movement leaders never were as
successful in winning power for the people as they were in convincing
people that they had sufficient power within themselves to escape 'the
prison of self-deprecation'"
Primarily, the liberation and empowerment experienced by African
Americans occurred in the psychological realm. The movement uplifted the
black community as a whole by cultivating feelings of racial solidarity
and positive self-identity, often in opposition to the world of white
Americans, a world that had physically and psychologically oppressed
Blacks for generations. Stokely Carmichael stated that "the goal of
black self-determination and black self-identity—Black Power—is
recognition of the virtues in themselves as black people."
Through the movement, blacks came to understand themselves and their
culture by exploring and debating the question, "who are we?" in order
to establish a unified and viable identity. And "if black people are to know themselves as a vibrant, valiant people, they must know their roots."
Black Lives Matter protest in September 2016
Throughout the Civil Rights Movement and black history, there has
been tension between those wishing to minimize and maximize racial
difference. W.E.B. Du Bois
and Martin Luther King Jr. often attempted to deemphasize race in their
quest for equality, while those advocating for separatism and
colonization emphasized an extreme and irreconcilable difference between
races. The Black Power movement largely achieved an equilibrium of
"balanced and humane ethnocentrism."
The impact of the Black Power movement in generating discussion about
ethnic identity and black consciousness supported the appearance and
expansion of academic fields of American studies, Black Studies, and African studies, and the founding of several museums devoted to African-American history and culture in this period.
In these ways the Black Power movement led to greater respect for and
attention accorded to African Americans' history and culture.
Britain
Black Power got a foothold in Britain when Carmichael came to London in July 1967 to attend the Dialectics of Liberation Congress. As well as his address at the Congress, he also made a speech at Speakers' Corner. At that time, there was no Black Power organization in Britain, although there was Michael X's Racial Adjustment Action Society (RAAS). However, this was more influenced by the Malcolm X's visit to Britain in 1964. Malcolm X also adopted Islam at this stage, whereas Black Power was not organized around any religious institution.
The Black Power Manifesto was launched on 10 November 1967, published by the Universal Coloured People's Association. Obi Egbuna, the spokesperson for the group, claimed they had recruited 778 members in London during the previous seven weeks. In 1968 Egbuna published Black Power or Death. He was also active with CLR James, Calvin Hernton and others in the Antiuniversity of London, set up following the Dialectics of Liberation Congress.
Black people in Britain
who identified themselves as the British Black Power Movement (BBMP)
formed in the 1960s. They worked with the U.S. Black Panther Party in
1967–68, and 1968–72.[54]
The On March 2, 1970, roughly one hundred people protested outside the
U.S. embassy in Grosvenor Square, London, in support of the U.S. Black
Panther founder Bobby Seale, who was on trial for murder in New Haven,
Connecticut.
They chanted "Free Bobby!" and carried posters proclaiming "Free, Free
bobby Seale" and "You can kill a revolutionary but not a revolution."
London police arrested sixteen of the protestors that day, three women
and thirteen men with threatening and assaulting police officers,
distributing a flier entitled "the Definition of Black Power", intending
to incite a breach of the peace, and willful damage to a police
raincoat. The raincoat charge was dropped by the judge, but the judge
found five of the accused guilty of the remaining charges.
Jamaica
A Black Power movement arose in Jamaica in the late 1960s. Though Jamaica had gained independence from the British Empire in 1962, and Prime Minister Hugh Shearer was black, many cabinet ministers (such as Edward Seaga)
and business elites were white. Large segments of the black majority
population were unemployed or did not earn a living wage. The Jamaica Labour Party government of Hugh Shearer banned Black Power literature such as The Autobiography of Malcolm X and the works of Eldridge Cleaver and Stokely Carmichael.
Guyanese academic Walter Rodney was appointed as a lecturer at the University of the West Indies
in January 1968, and became one of the main exponents of Black Power in
Jamaica. When the Shearer government banned Rodney from re-entering the
country, the Rodney Riots broke out. As a result of the Rodney affair, radical groups and publications such as Abeng began to emerge, and the opposition People's National Party gained support. In the 1972 election, the Jamaica Labour Party was defeated by the People's National Party, and Michael Manley, who had expressed support for Black Power, became Prime Minister.
Beauty
The cultivation of pride in the African-American race was often summarized in the phrase "Black is Beautiful."
The phrase is rooted in its historical context, yet the relationship to
it has changed in contemporary times. "I don't think it's 'Black is
beautiful' anymore. It's 'I am beautiful and I'm black.' It's not the
symbolic thing, the afro,
power sign… That phase is over and it succeeded. My children feel
better about themselves and they know that they're black," stated a
respondent in Bob Blauner's longitudinal oral history of U.S. race
relations in 1986.
The outward manifestations of an appreciation and celebration of
blackness abound: black dolls, natural hair, black Santas, models and
celebrities that were once rare and symbolic have become commonplace.
The "Black is beautiful" cultural movement aimed to dispel the notion that black people's natural features such as skin color, facial features and hair are inherently ugly. John Sweat Rock was the first to coin the phrase "Black is Beautiful", in the slavery era. The movement asked that men and women stop straightening their hair and attempting to lighten or bleach their skin. The prevailing idea in American culture was that black features are less attractive or desirable than white features.
Arts and culture
The
Black Power movement produced artistic and cultural products that both
embodied and generated pride in "blackness" and further defined an
African-American identity that remains contemporary. Black Power is
often seen as a cultural revolution as much as a political revolution,
with the goal of celebrating and emphasizing the distinctive group
culture of African Americans to an American society that had previously
been dominated by white artistic and cultural expressions. Black power
utilized all available forms of folk, literary, and dramatic expression
based in a common ancestral past to promote a message of
self-actualization and cultural self-definition.
The emphasis on a distinctive black culture during the Black Power
movement publicized and legitimized a culture gap between Blacks and
Whites that had previously been ignored and denigrated. More generally,
in recognizing the legitimacy of another culture and challenging the
idea of white cultural superiority, the Black Power movement paved the
way for the celebration of multiculturalism in America today.
The cultural concept of "soul" was fundamental to the image of
African-American culture embodied by the Black Power movement. Soul, a
type of "in-group cultural cachet," was closely tied to black America's
need for individual and group self-identification.
A central expression of the "soulfulness" of the Black Power
generation was a cultivation of aloofness and detachment, the creation
of an "aura or emotional invulnerability," a persona that challenged
their position of relative powerlessness in greater society. The
nonverbal expressions of this attitude, including everything from
posture to handshakes, were developed as a counterpoint to the rigid,
"up-tight" mannerisms of white people. Though the iconic symbol of black
power, the arms raised with biceps flexed and clenched fists, is
temporally specific, variants of the multitude of handshakes, or "giving
and getting skin," in the 1960s and 1970s as a mark of communal
solidarity continue to exist as a part of black culture.
Clothing style also became an expression of Black Power in the 1960s
and 1970s. Though many of the popular trends of the movement remained
confined to the decade, the movement redefined standards of beauty that
were historically influenced by Whites and instead celebrated a natural
"blackness." As Stokely Carmichael said in 1966, "We have to stop being ashamed of being black. A broad nose, thick lip and nappy hair is us and we are going to call that beautiful whether they like it or not."
"Natural" hair styles, such as the Afro, became a socially acceptable
tribute to group unity and a highly visible celebration of black
heritage. Though the same social messages may no longer consciously
influence individual hair or clothing styles in today's society, the
Black Power movement was influential in diversifying standards of beauty
and aesthetic choices. The Black Power movement raised the idea of a
black aesthetic that revealed the worth and beauty of all black people.
In developing a powerful identity from the most elemental aspects
of African-American folk life, the Black Power movement generated
attention to the concept of "soul food,"
a fresh, authentic, and natural style of cooking that originated in
Africa. The flavor and solid nourishment of the food was credited with
sustaining African Americans through centuries of oppression in America
and became an important aid in nurturing contemporary racial pride.
Black Power advocates used the concept of "soul food" to further
distinguish between white and black culture; though the basic elements
of soul food were not specific to African-American food, Blacks believed
in the distinctive quality, if not superiority, of foods prepared by
Blacks. No longer racially specific, traditional "soul foods" such as yams, collard greens, and deep-fried chicken continue to hold a place in contemporary culinary life.
Black Arts Movement
The Black Arts Movement or BAM, founded in Harlem by writer and activist Amiri Baraka (born Everett LeRoy Jones), can be seen as the artistic branch of the Black Power movement.
This movement inspired black people to establish ownership of
publishing houses, magazines, journals and art institutions. Other
well-known writers who were involved with this movement included Nikki Giovanni; Don L. Lee, later known as Haki Madhubuti; Sonia Sanchez; Maya Angelou; Dudley Randall; Sterling Plumpp; Larry Neal; Ted Joans; Ahmos Zu-Bolton; and Etheridge Knight. Several black-owned publishing houses and publications sprang from the BAM, including Madhubuti's Third World Press, Broadside Press, Zu-Bolton's Energy Black South Press, and the periodicals Callaloo and Yardbird Reader. Although not strictly involved with the Movement, other notable African-American writers such as novelists Ishmael Reed and Toni Morrison and poet Gwendolyn Brooks can be considered to share some of its artistic and thematic concerns.
BAM sought "to link, in a highly conscious manner, art and
politics in order to assist in the liberation of black people", and
produced an increase in the quantity and visibility of African-American
artistic production.
Though many elements of the Black Arts movement are separate from the
Black Power movement, many goals, themes, and activists overlapped.
Literature, drama, and music of Blacks "served as an oppositional and
defensive mechanism through which creative artists could confirm their
identity while articulating their own unique impressions of social
reality."
In addition to acting as highly visible and unifying representations of
"blackness," the artistic products of the Black Power movement also
utilized themes of black empowerment and liberation.
For instance, black recording artists not only transmitted messages of
racial unity through their music, they also became significant role
models for a younger generation of African Americans.
Updated protest songs not only bemoaned oppression and societal wrongs,
but utilized adversity as a reference point and tool to lead others to
activism. Some Black Power era artists conducted brief mini-courses in
the techniques of empowerment. In the tradition of cultural
nationalists, these artists taught that in order to alter social
conditions, Blacks first had to change the way they viewed themselves;
they had to break free of white norms and strive to be more natural, a
common theme of African-American art and music. Musicians such as the Temptations
sang lyrics such as "I have one single desire, just like you / So move
over, son, 'cause I'm comin' through" in their song "Message From a
Black Man," they expressed the revolutionary sentiments of the Black
Power movement.
Ishmael Reed, who is considered neither a movement apologist nor
advocate, said: "I wasn't invited to participate because I was
considered an integrationist" but he went on to explain the positive
aspects of the Black Arts Movement and the Black Power movement:
I think what Black Arts did was inspire a whole lot of Black people to write. Moreover, there would be no multiculturalism movement without Black Arts. Latinos, Asian Americans, and others all say they began writing as a result of the example of the 1960s. Blacks gave the example that you don't have to assimilate. You could do your own thing, get into your own background, your own history, your own tradition and your own culture. I think the challenge is for cultural sovereignty and Black Arts struck a blow for that.
By breaking into a field typically reserved for white Americans,
artists of the Black Power era expanded opportunities for current
African Americans. "Today's writers and performers," writes William L.
Van Deburg, "recognize that they owe a great deal to Black Power's
explosion of cultural orthodoxy."
Criticism
Bayard Rustin,
an elder statesman of the Civil Rights Movement, was a harsh critic of
Black Power in its earliest days. Writing in 1966, shortly after the
March Against Fear, Rustin said that Black Power "not only lacks any
real value for the civil rights movement, but [...] its propagation is
positively harmful. It diverts the movement from a meaningful debate
over strategy and tactics, it isolates the Negro community, and it
encourages the growth of anti-Negro forces." He particularly criticized
the Congress of Racial Equality
(CORE) and SNCC for their turn toward Black Power, arguing that these
two organizations once "awakened the country, but now they emerge
isolated and demoralized, shouting a slogan that may afford a momentary
satisfaction but that is calculated to destroy them and their movement."
The Black Power slogan was also criticized by Martin Luther King Jr.,
who stated that the black power movement "connotates black supremacy
and an anti-white feeling that does not or should not prevail." The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
(NAACP) also disapproved of Black Power, particularly Roy Wilkins, then
the NAACP's executive director, who stated that Black Power was "a
reverse Hitler, a reverse Ku Klux Klan...the father of hate and mother
of violence." The Black Power slogan was also met with opposition from the leadership of SCLC and the Urban League.
Politicians in high office also spoke out against Black Power: in 1966, President Lyndon Johnson
criticized extremists on both sides of the racial divide, stating "we
are not interested in Black Power, and we're not interested in white
power, but we are interested in American democratic power with a small
'd'". At a NAACP rally the next day, Vice President Hubert Humphrey
argued "Racism is racism and we must reject calls for racism whether
they come from a throat that is white or one that is black."
Responses
Kwame Ture, formerly known as Stokely Carmichael, and Charles V. Hamilton, both activists with the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee and authors of the book, Black Power: The Politics of Liberation
highlight that some observers and critics of the Black Power movement
conflated "Black Power" with "Black Supremacy." They countered that
Black Power advocates were not proposing a mirror-image of white
supremacy and domination, instead they were working towards "an
effective share in the total power of society."