Maurya Empire
Jambudvīpa, Pṛthvī
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 322 BCE–185 BCE | |||||||||||||||||||||||
![The maximum extent of the Maurya Empire, as shown in many modern maps. See also this alternative map.[2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2c/Maurya_Empire%2C_c.250_BCE_2.png/250px-Maurya_Empire%2C_c.250_BCE_2.png)
The maximum extent of the Maurya Empire, as shown in many modern maps.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Pataliputra (Present-day Patna, Bihar) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Sanskrit, Magadhi Prakrit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Buddhism Jainism, Ajivika, Hinduism | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy, as described in Chanakya's Arthashastra | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• 322–298 BCE
| Chandragupta | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 298–272 BCE
| Bindusara | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 268–232 BCE
| Ashoka | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 232–224 BCE
| Dasharatha | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 224–215 BCE
| Samprati | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 215–202 BCE
| Shalishuka | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 202–195 BCE
| Devavarman | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 195–187 BCE
| Shatadhanvan | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 187–180 BCE
| Brihadratha | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 322 BCE | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• Assassination of Brihadratha by Pushyamitra Shunga
| 185 BCE | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 261 BCE | 3,400,000 km2 (1,300,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 250 BCE | 5,000,000 km2 (1,900,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• 261 BCE
| 50 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Panas | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
The Maurya Empire was a geographically-extensive Iron Age historical power based in Magadha and founded by Chandragupta Maurya which dominated the Indian subcontinent between 322 and 187 BCE. Comprising the majority of South Asia, the Maurya Empire was centralized by the conquest of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and its capital city was located at Pataliputra (modern Patna). The empire was the largest political entity to have existed in the Indian subcontinent, spanning over 5 million square kilometres (1.9 million square miles) at its zenith under Ashoka.
Chandragupta Maurya raised an army, with the assistance of Chanakya (also known as Kauṭilya), and overthrew the Nanda Empire in c. 322 BCE. Chandragupta rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India by conquering the satraps left by Alexander the Great, and by 317 BCE the empire had fully occupied northwestern India. The Mauryan Empire then defeated Seleucus I, a diadochus and founder of the Seleucid Empire during the Seleucid–Mauryan war, thus acquiring territory west of the Indus River.
At its greatest extent, the empire stretched along the natural boundary of the Himalayas, to the east into Assam, to the west into Balochistan (southwest Pakistan and southeast Iran) and the Hindu Kush mountains of what is now eastern Afghanistan. The dynasty expanded into India's southern regions by the reign of the emperors Pushkar and Bindusara, but it excluded Kalinga (modern Odisha), until it was conquered by Ashoka. It declined for about 50 years after Ashoka's rule, and dissolved in 185 BCE with the foundation of the Shunga dynasty in Magadha.
Under Chandragupta Maurya and his successors, internal and
external trade, agriculture, and economic activities all thrived and
expanded across South Asia due to the creation of a single and efficient
system of finance, administration, and security. The Maurya dynasty
built the Grand Trunk Road, one of Asia's oldest and longest trade networks, connecting the Indian subcontinent with Central Asia. After the Kalinga War, the Empire experienced nearly half a century of centralized rule under Ashoka. Chandragupta Maurya's embrace of Jainism increased socio-religious reform across South Asia, while Ashoka's embrace of Buddhism and sponsorship of Buddhist missionaries allowed for the expansion of that faith into Sri Lanka, northwest India, Central Asia, Southeast Asia, Egypt, and Hellenistic Europe.
The population of the empire has been estimated to be about 50–60
million, making the Mauryan Empire one of the most populous empires of
antiquity. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka are the primary sources of written records of Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath is the national emblem of the modern Republic of India.
Etymology
The name "Maurya" does not occur in Ashoka's inscriptions, or the contemporary Greek accounts such as Megasthenes's Indica, but it is attested by the following sources:
- The Junagadh rock inscription of Rudradaman (c. 150 CE) prefixes "Maurya" to the names Chandragupta and Ashoka.
- The Puranas (c. 4th century CE or earlier) use Maurya as a dynastic appellation.
- The Buddhist texts state that Chandragupta belonged to the "Moriya" clan of the Shakyas, the tribe to which Gautama Buddha belonged.
- The Jain texts state that Chandragupta was the son of a royal superintendent of peacocks (mayura-poshaka).
According to the Buddhist tradition, the ancestors of the Maurya kings had settled in a region where peacocks (mora in Pali)
were abundant. Therefore, they came to be known as "Moriyas",
literally, "belonging to the place of peacocks". According to another
Buddhist account, these ancestors built a city called Moriya-nagara
("Moriya-city"), which was so called, because it was built with the
"bricks coloured like peacocks' necks".
The dynasty's connection to the peacocks, as mentioned in the
Buddhist and Jain traditions, seems to be corroborated by archaeological
evidence. For example, peacock figures are found on the Ashoka pillar at Nandangarh and several sculptures on the Great Stupa of Sanchi. Based on this eviedence, modern scholars theorize that the peacock may have been the dynasty's emblem.
Some later authors, such as Dhundiraja (a commentator on the Mudrarakshasa) and an annotator of the Vishnu Purana,state
that the word "Maurya" is derived from Mura, the name of the wife of a
Nanda king and the mother (or grandmother) of the first Maurya king.
However, the Puranas themselves make no mention of Mura and do not talk
of any relation between the Nanda and the Maurya dynasties.
Dhundiraja's derivation of the word seems to be his own invention:
according to the Sanskrit rules, the derivative of the feminine name
Mura (IAST: Murā) would be "Maureya"; the term "Maurya" can only be derived from the masculine "Mura".
History
The Maurya dynasty ruled for 137 years.
Chandragupta Maurya and Chanakya
The Maurya Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya, with help from Chanakya, at Takshashila, a noted center of learning. According to several legends, Chanakya travelled to Magadha, a kingdom that was large and militarily powerful and feared by its neighbours, but was insulted by its king Dhana Nanda, of the Nanda dynasty. Chanakya swore revenge and vowed to destroy the Nanda Empire. Meanwhile, the conquering armies of Alexander the Great refused to cross the Beas River and advance further eastward, deterred by the prospect of battling Magadha. Alexander returned to Babylon and re-deployed most of his troops west of the Indus River. Soon after Alexander died in Babylon in 323 BCE, his empire fragmented into independent kingdoms led by his generals.
The Greek generals Eudemus and Peithon
ruled in the Indus Valley until around 317 BCE, when Chandragupta
Maurya (with the help of Chanakya, who was now his advisor) orchestrated
a rebellion to drive out the Greek governors, and subsequently brought
the Indus Valley under the control of his new seat of power in Magadha.
Chandragupta Maurya's rise to power is shrouded in mystery and
controversy. On one hand, a number of ancient Indian accounts, such as
the drama Mudrarakshasa (Signet ring of Rakshasa – Rakshasa was the prime minister of Magadha) by Vishakhadatta, describe his royal ancestry and even link him with the Nanda family. A kshatriya clan known as the Maurya's are referred to in the earliest Buddhist texts, Mahaparinibbana Sutta.
However, any conclusions are hard to make without further historical
evidence. Chandragupta first emerges in Greek accounts as
"Sandrokottos". As a young man he is said to have met Alexander. He is also said to have met the Nanda king, angered him, and made a narrow escape. Chanakya's original intentions were to train army under Chandragupta's command.
Conquest of Magadha
Chanakya encouraged Chandragupta Maurya and his army to take over the
throne of Magadha. Using his intelligence network, Chandragupta
gathered many young men from across Magadha and other provinces, men
upset over the corrupt and oppressive rule of king Dhana Nanda,
plus the resources necessary for his army to fight a long series of
battles. These men included the former general of Taxila, accomplished
students of Chanakya, the representative of King Parvataka, his son Malayaketu, and the rulers of small states. The Macedonians (described as Yona
or Yavana in Indian sources) may then have participated, together with
other groups, in the armed uprising of Chandragupta Maurya against the Nanda dynasty. The Mudrarakshasa of Visakhadutta as well as the Jaina work Parisishtaparvan talk of Chandragupta's alliance with the Himalayan king Parvataka, often identified with Porus, although this identification is not accepted by all historians. This Himalayan alliance gave Chandragupta a composite and powerful army made up of Yavanas (Greeks), Kambojas, Shakas (Scythians), Kiratas (Himalayans), Parasikas (Persians) and Bahlikas (Bactrians) who took Pataliputra (also called Kusumapura, "The City of Flowers"):
- "Kusumapura was besieged from every direction by the forces of Parvata and Chandragupta: Shakas, Yavanas, Kiratas, Kambojas, Parasikas, Bahlikas and others, assembled on the advice of Chanakya" in Mudrarakshasa 2
Preparing to invade Pataliputra, Maurya came up with a strategy. A
battle was announced and the Magadhan army was drawn from the city to a
distant battlefield to engage with Maurya's forces. Maurya's general and
spies meanwhile bribed the corrupt general of Nanda. He also managed to
create an atmosphere of civil war in the kingdom, which culminated in
the death of the heir to the throne. Chanakya managed to win over
popular sentiment. Ultimately Nanda resigned, handing power to
Chandragupta, and went into exile and was never heard of again. Chanakya
contacted the prime minister, Rakshasas, and made him understand that
his loyalty was to Magadha, not to the Nanda dynasty, insisting that he
continue in office. Chanakya also reiterated that choosing to resist
would start a war that would severely affect Magadha and destroy the
city. Rakshasa accepted Chanakya's reasoning, and Chandragupta Maurya
was legitimately installed as the new King of Magadha. Rakshasa became
Chandragupta's chief advisor, and Chanakya assumed the position of an
elder statesman.
Chandragupta Maurya
Pataliputra, capital of the Mauryas. Ruins of pillared hall at Kumrahar site.
The Pataliputra capital, discovered at the Bulandi Bagh site of Pataliputra, 4th-3rd c. BCE.
In 305 BCE, Chandragupta led a series of campaigns to retake the satrapies left behind by Alexander the Great when he returned westwards, while Seleucus I Nicator
fought to defend these territories. The two rulers concluded a peace
treaty in 303 BCE, including a marital alliance. Chandragupta snatched
the satrapies of Paropamisade (Kamboja and Gandhara), Arachosia (Kandhahar) and Gedrosia (Balochistan), and Seleucus I Nicator received 500 war elephants that were to have a decisive role in his victory against western Hellenistic kings at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BCE. Diplomatic relations were established and several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes, Deimakos and Dionysius resided at the Mauryan court. Megasthenes in particular was a notable Greek ambassador in the court of Chandragupta Maurya. According to Arrian, ambassador Megasthenes (c.350–c.290 BCE) lived in Arachosia and travelled to Pataliputra.
Chandragupta established a strong centralized state with an
administration at Pataliputra, which, according to Megasthenes, was
"surrounded by a wooden wall pierced by 64 gates and 570 towers". Aelian, although not expressly quoting Megasthenes nor mentionning Pataliputra, described Indian palaces as superior in splendor to Persia's Susa or Ectabana. The architecture of the city seems to have had many similarities with Persian cities of the period.
Chandragupta's son Bindusara extended the rule of the Mauryan empire towards southern India. The famous Tamil poet Mamulanar of the Sangam literature described how the Deccan Plateau was invaded by the Maurya army. He also had a Greek ambassador at his court, named Megasthenes.
Megasthenes describes a disciplined multitude under Chandragupta, who live simply, honestly, and do not know writing:
The Indians all live frugally, especially when in camp. They dislike a great undisciplined multitude, and consequently they observe good order. Theft is of very rare occurrence. Megasthenes says that those who were in the camp of Sandrakottos, wherein lay 400,000 men, found that the thefts reported on any one day did not exceed the value of two hundred drachmae, and this among a people who have no written laws, but are ignorant of writing, and must therefore in all the business of life trust to memory. They live, nevertheless, happily enough, being simple in their manners and frugal. They never drink wine except at sacrifices. Their beverage is a liquor composed from rice instead of barley, and their food is principally a rice-pottage.
— Strabo XV. i. 53–56, quoting Megasthenes.
Chandragupta renounced his throne and followed Jain teacher Bhadrabahu. He is said to have lived as an ascetic at Shravanabelagola for several years before fasting to death, as per the Jain practice of sallekhana.
Bindusara
A silver coin of 1 karshapana of the Maurya empire, period of Bindusara Maurya about 297-272 BC, workshop of Pataliputra. Obv: Symbols with a Sun Rev: Symbol Dimensions: 14 x 11 mm Weight: 3.4 g.
Bindusara was born to Chandragupta, the founder of the Mauryan Empire. This is attested by several sources, including the various Puranas and the Mahavamsa. He is attested by the Buddhist texts such as Dipavamsa and Mahavamsa ("Bindusaro"); the Jain texts such as Parishishta-Parvan; as well as the Hindu texts such as Vishnu Purana ("Vindusara"). According to the 12th century Jain writer Hemachandra's Parishishta-Parvan, the name of Bindusara's mother was Durdhara. Some Greek sources also mention him by the name "Amitrochates" or its variations.
Historian Upinder Singh estimates that Bindusara ascended the throne around 297 BCE. Bindusara, just 22 years old, inherited a large empire that consisted of what is now, Northern, Central and Eastern parts of India along with parts of Afghanistan and Baluchistan. Bindusara extended this empire to the southern part of India, as far as what is now known as Karnataka.
He brought sixteen states under the Mauryan Empire and thus conquered
almost all of the Indian peninsula (he is said to have conquered the
'land between the two seas' – the peninsular region between the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea). Bindusara didn't conquer the friendly Tamil kingdoms of the Cholas, ruled by King Ilamcetcenni, the Pandyas, and Cheras. Apart from these southern states, Kalinga (modern Odisha) was the only kingdom in India that didn't form the part of Bindusara's empire. It was later conquered by his son Ashoka, who served as the viceroy of Ujjaini during his father's reign, which highlights the importance of the town.
Bindusara's life has not been documented as well as that of his
father Chandragupta or of his son Ashoka. Chanakya continued to serve as
prime minister during his reign. According to the medieval Tibetan
scholar Taranatha who visited India, Chanakya helped Bindusara "to
destroy the nobles and kings of the sixteen kingdoms and thus to become
absolute master of the territory between the eastern and western
oceans." During his rule, the citizens of Taxila revolted twice. The reason for the first revolt was the maladministration of Susima,
his eldest son. The reason for the second revolt is unknown, but
Bindusara could not suppress it in his lifetime. It was crushed by
Ashoka after Bindusara's death.
Bindusara maintained friendly diplomatic relations with the Hellenic World. Deimachus was the ambassador of Seleucid emperor Antiochus I at Bindusara's court. Diodorus states that the king of Palibothra (Pataliputra, the Mauryan capital) welcomed a Greek author, Iambulus. This king is usually identified as Bindusara. Pliny states that the Egyptian king Philadelphus sent an envoy named Dionysius to India. According to Sailendra Nath Sen, this appears to have happened during Bindusara's reign.
Unlike his father Chandragupta (who at a later stage converted to Jainism), Bindusara believed in the Ajivika sect. Bindusara's guru Pingalavatsa (Janasana) was a Brahmin of the Ajivika sect. Bindusara's wife, Queen Subhadrangi (Queen Aggamahesi) was a Brahmin
also of the Ajivika sect from Champa (present Bhagalpur district).
Bindusara is credited with giving several grants to Brahmin monasteries (Brahmana-bhatto).
Historical evidence suggests that Bindusara died in the 270s BCE. According to Upinder Singh, Bindusara died around 273 BCE. Alain Daniélou believes that he died around 274 BCE.
Sailendra Nath Sen believes that he died around 273-272 BCE, and that
his death was followed by a four-year struggle of succession, after
which his son Ashoka became the emperor in 269-268 BCE. According to the Mahavamsa, Bindusara reigned for 28 years. The Vayu Purana, which names Chandragupta's successor as "Bhadrasara", states that he ruled for 25 years.
Ashoka
Aśoka pillar at Sarnath. ca. 250 BCE.
Ashoka pillar at Vaishali.
Fragment of the 6th Pillar Edict of Ashoka (238 BCE), in Brahmi, sandstone, British Museum.
As a young prince, Ashoka (r. 272–232 BCE)
was a brilliant commander who crushed revolts in Ujjain and
Takshashila. As monarch he was ambitious and aggressive, re-asserting
the Empire's superiority in southern and western India. But it was his
conquest of Kalinga
(262–261 BCE) which proved to be the pivotal event of his life. Ashoka
used Kalinga to project power over a large region by building a
fortification there and securing it as a possession.
Although Ashoka's army succeeded in overwhelming Kalinga forces of
royal soldiers and civilian units, an estimated 100,000 soldiers and
civilians were killed in the furious warfare, including over 10,000 of
Ashoka's own men. Hundreds of thousands of people were adversely
affected by the destruction and fallout of war. When he personally
witnessed the devastation, Ashoka began feeling remorse. Although the
annexation of Kalinga was completed, Ashoka embraced the teachings of Buddhism, and renounced war and violence. He sent out missionaries to travel around Asia and spread Buddhism to other countries.
Ashoka implemented principles of ahimsa
by banning hunting and violent sports activity and ending indentured
and forced labor (many thousands of people in war-ravaged Kalinga had
been forced into hard labour and servitude). While he maintained a large
and powerful army, to keep the peace and maintain authority, Ashoka
expanded friendly relations with states across Asia and Europe, and he
sponsored Buddhist missions. He undertook a massive public works
building campaign across the country. Over 40 years of peace, harmony
and prosperity made Ashoka one of the most successful and famous
monarchs in Indian history. He remains an idealized figure of
inspiration in modern India.
The Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, are found throughout the Subcontinent. Ranging from as far west as Afghanistan and as far south as Andhra (Nellore District),
Ashoka's edicts state his policies and accomplishments. Although
predominantly written in Prakrit, two of them were written in Greek, and one in both Greek and Aramaic. Ashoka's edicts refer to the Greeks, Kambojas, and Gandharas
as peoples forming a frontier region of his empire. They also attest to
Ashoka's having sent envoys to the Greek rulers in the West as far as
the Mediterranean. The edicts precisely name each of the rulers of the Hellenic world at the time such as Amtiyoko (Antiochus), Tulamaya (Ptolemy), Amtikini (Antigonos), Maka (Magas) and Alikasudaro (Alexander) as recipients of Ashoka's proselytism.
The Edicts also accurately locate their territory "600 yojanas away" (a
yojanas being about 7 miles), corresponding to the distance between the
center of India and Greece (roughly 4,000 miles).
Decline
Ashoka was followed for 50 years by a succession of weaker kings. Brihadratha, the last ruler of the Mauryan dynasty, held territories that had shrunk considerably from the time of emperor Ashoka. Brihadratha was assassinated in 185 BCE during a military parade by the Brahmin general Pushyamitra Shunga, commander-in-chief of his guard, who then took over the throne and established the Shunga dynasty.
Shunga coup (185 BCE)
Buddhist records such as the Ashokavadana write that the assassination of Brihadratha and the rise of the Shunga empire led to a wave of religious persecution for Buddhists, and a resurgence of Hinduism. According to Sir John Marshall,
Pushyamitra may have been the main author of the persecutions, although
later Shunga kings seem to have been more supportive of Buddhism. Other
historians, such as Etienne Lamotte and Romila Thapar,
among others, have argued that archaeological evidence in favour of the
allegations of persecution of Buddhists are lacking, and that the
extent and magnitude of the atrocities have been exaggerated.
Establishment of the Indo-Greek Kingdom (180 BCE)
The fall of the Mauryas left the Khyber Pass unguarded, and a wave of foreign invasion followed. The Greco-Bactrian king, Demetrius,
capitalized on the break-up, and he conquered southern Afghanistan and
parts of northwestern India around 180 BCE, forming the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
The Indo-Greeks would maintain holdings on the trans-Indus region, and
make forays into central India, for about a century. Under them,
Buddhism flourished, and one of their kings, Menander, became a famous figure of Buddhism; he was to establish a new capital of Sagala, the modern city of Sialkot.
However, the extent of their domains and the lengths of their rule are
subject to much debate. Numismatic evidence indicates that they retained
holdings in the subcontinent right up to the birth of Christ. Although
the extent of their successes against indigenous powers such as the Shungas, Satavahanas, and Kalingas are unclear, what is clear is that Scythian tribes, renamed Indo-Scythians, brought about the demise of the Indo-Greeks from around 70 BCE and retained lands in the trans-Indus, the region of Mathura, and Gujarat.
Administration
Statuettes of the Mauryan era
The Empire was divided into four provinces, with the imperial capital at Pataliputra. From Ashokan edicts, the names of the four provincial capitals are Tosali (in the east), Ujjain (in the west), Suvarnagiri (in the south), and Taxila (in the north). The head of the provincial administration was the Kumara (royal prince), who governed the provinces as king's representative. The kumara
was assisted by Mahamatyas and council of ministers. This
organizational structure was reflected at the imperial level with the
Emperor and his Mantriparishad (Council of Ministers).
Historians theorise that the organisation of the Empire was in line with the extensive bureaucracy described by Kautilya in the Arthashastra:
a sophisticated civil service governed everything from municipal
hygiene to international trade. The expansion and defense of the empire
was made possible by what appears to have been one of the largest armies
in the world during the Iron Age.
According to Megasthenes, the empire wielded a military of 600,000
infantry, 30,000 cavalry, 8,000 chariots and 9,000 war elephants besides
followers and attendants. A vast espionage
system collected intelligence for both internal and external security
purposes. Having renounced offensive warfare and expansionism, Ashoka
nevertheless continued to maintain this large army, to protect the
Empire and instil stability and peace across West and South Asia.
Economy
Maurya statuette, 2nd century BCE.
For the first time in South Asia,
political unity and military security allowed for a common economic
system and enhanced trade and commerce, with increased agricultural
productivity. The previous situation involving hundreds of kingdoms,
many small armies, powerful regional chieftains, and internecine
warfare, gave way to a disciplined central authority. Farmers were freed
of tax and crop collection burdens from regional kings, paying instead
to a nationally administered and strict-but-fair system of taxation as
advised by the principles in the Arthashastra. Chandragupta
Maurya established a single currency across India, and a network of
regional governors and administrators and a civil service provided
justice and security for merchants, farmers and traders. The Mauryan
army wiped out many gangs of bandits, regional private armies, and
powerful chieftains who sought to impose their own supremacy in small
areas. Although regimental in revenue collection, Maurya also sponsored
many public works and waterways to enhance productivity, while internal
trade in India expanded greatly due to new-found political unity and
internal peace.
Under the Indo-Greek friendship treaty, and during Ashoka's reign, an international network of trade expanded. The Khyber Pass, on the modern boundary of Pakistan and Afghanistan,
became a strategically important port of trade and intercourse with the
outside world. Greek states and Hellenic kingdoms in West Asia became
important trade partners of India. Trade also extended through the Malay peninsula
into Southeast Asia. India's exports included silk goods and textiles,
spices and exotic foods. The external world came across new scientific
knowledge and technology with expanding trade with the Mauryan Empire.
Ashoka also sponsored the construction of thousands of roads, waterways,
canals, hospitals, rest-houses and other public works. The easing of
many over-rigorous administrative practices, including those regarding
taxation and crop collection, helped increase productivity and economic
activity across the Empire.
In many ways, the economic situation in the Mauryan Empire is
analogous to the Roman Empire of several centuries later. Both had
extensive trade connections and both had organizations similar to corporations.
While Rome had organizational entities which were largely used for
public state-driven projects, Mauryan India had numerous private
commercial entities. These existed purely for private commerce and
developed before the Mauryan Empire itself.
Religion
Jainism
Bhadrabahu Cave, Shravanabelagola where Chandragupta is said to have died
Chandragupta Maurya embraced Jainism
after retiring, when he renounced his throne and material possessions
to join a wandering group of Jain monks. Chandragupta was a disciple of
the Jain monk Acharya Bhadrabahu. It is said that in his last days, he observed the rigorous but self-purifying Jain ritual of santhara (fast unto death), at Shravana Belgola in Karnataka. Samprati, the grandson of Ashoka,
also patronized Jainism. Samprati was influenced by the teachings of
Jain monks like Suhastin and he is said to have built 125,000 derasars across India. Some of them are still found in the towns of Ahmedabad, Viramgam, Ujjain, and Palitana. It is also said that just like Ashoka, Samprati sent messengers and preachers to Greece, Persia and the Middle East for the spread of Jainism, but, to date, no research has been done in this area.
Thus, Jainism became a vital force under the Mauryan Rule. Chandragupta and Samprati are credited for the spread of Jainism in South India. Hundreds of thousands of temples and stupas are said to have been erected during their reigns.
Buddhism
The stupa, which contained the relics of Buddha, at the center of the Sanchi complex was originally built by the Maurya Empire, but the balustrade around it is Sunga, and the decorative gateways are from the later Satavahana period.
The Dharmarajika stupa in Taxila, modern Pakistan, is also thought to have been established by Emperor Asoka.
Magadha, the centre of the empire, was also the birthplace of Buddhism. Ashoka initially practised Hinduism but later embraced Buddhism; following the Kalinga War, he renounced expansionism and aggression, and the harsher injunctions of the Arthashastra
on the use of force, intensive policing, and ruthless measures for tax
collection and against rebels. Ashoka sent a mission led by his son Mahinda and daughter Sanghamitta to Sri Lanka, whose king Tissa
was so charmed with Buddhist ideals that he adopted them himself and
made Buddhism the state religion. Ashoka sent many Buddhist missions to West Asia, Greece and South East Asia,
and commissioned the construction of monasteries and schools, as well
as the publication of Buddhist literature across the empire. He is
believed to have built as many as 84,000 stupas across India, such as Sanchi and Mahabodhi Temple, and he increased the popularity of Buddhism in Afghanistan, Thailand and North Asia including Siberia. Ashoka helped convene the Third Buddhist Council
of India's and South Asia's Buddhist orders near his capital, a council
that undertook much work of reform and expansion of the Buddhist
religion. Indian merchants embraced Buddhism and played a large role in
spreading the religion across the Mauryan Empire.
Architectural remains
Mauryan architecture in the Barabar Caves. Lomas Rishi Cave. 3rd century BCE.
The greatest monument of this period, executed in the reign of Chandragupta Maurya, was the old palace at the site of Kumhrar. Excavations at the site of Kumhrar
nearby have unearthed the remains of the palace. The palace is thought
to have been an aggregate of buildings, the most important of which was
an immense pillared hall supported on a high substratum of timbers. The
pillars were set in regular rows, thus dividing the hall into a number
of smaller square bays. The number of columns is 80, each about 7 meters
high. According to the eyewitness account of Megasthenes,
the palace was chiefly constructed of timber, and was considered to
exceed in splendour and magnificence the palaces of Susa and Ecbatana,
its gilded pillars being adorned with golden vines and silver birds. The
buildings stood in an extensive park studded with fish ponds and
furnished with a great variety of ornamental trees and shrubs. Kauṭilya's Arthashastra
also gives the method of palace construction from this period. Later
fragments of stone pillars, including one nearly complete, with their
round tapering shafts and smooth polish, indicate that Ashoka was
responsible for the construction of the stone columns which replaced the
earlier wooden ones.
During the Ashokan period, stonework was of a highly diversified order and comprised lofty free-standing pillars, railings of stupas,
lion thrones and other colossal figures. The use of stone had reached
such great perfection during this time that even small fragments of
stone art were given a high lustrous polish resembling fine enamel. This
period marked the beginning of the Buddhist school of architecture.
Ashoka was responsible for the construction of several stupas, which were large domes and bearing symbols of Buddha. The most important ones are located at Sanchi, Bharhut, Amaravati, Bodhgaya and Nagarjunakonda. The most widespread examples of Mauryan architecture are the Ashoka pillars and carved edicts of Ashoka, often exquisitely decorated, with more than 40 spread throughout the Indian subcontinent.
The peacock was a dynastic symbol of Mauryans, as depicted by Ashoka's pillars at Nandangarh and Sanchi Stupa.
Natural history
The two Yakshas, possibly 3rd century BCE, found in Pataliputra.
The protection of animals in India became serious business by the
time of the Maurya dynasty; being the first empire to provide a unified
political entity in India, the attitude of the Mauryas towards forests,
their denizens, and fauna in general is of interest.
The Mauryas firstly looked at forests as resources. For them, the
most important forest product was the elephant. Military might in those
times depended not only upon horses and men but also battle-elephants; these played a role in the defeat of Seleucus, one of Alexander's
former generals. The Mauryas sought to preserve supplies of elephants
since it was cheaper and took less time to catch, tame and train wild
elephants than to raise them. Kautilya's Arthashastra contains not only maxims on ancient statecraft, but also unambiguously specifies the responsibilities of officials such as the Protector of the Elephant Forests.
On the border of the forest, he should establish a forest for elephants guarded by foresters. The Office of the Chief Elephant Forester should with the help of guards protect the elephants in any terrain. The slaying of an elephant is punishable by death.
The Mauryas also designated separate forests to protect supplies of
timber, as well as lions and tigers for skins. Elsewhere the Protector of Animals also worked to eliminate thieves, tigers and other predators to render the woods safe for grazing cattle.
The Mauryas valued certain forest tracts in strategic or economic
terms and instituted curbs and control measures over them. They
regarded all forest tribes with distrust and controlled them with
bribery and political subjugation. They employed some of them, the
food-gatherers or aranyaca to guard borders and trap animals. The
sometimes tense and conflict-ridden relationship nevertheless enabled
the Mauryas to guard their vast empire.
When Ashoka embraced Buddhism
in the latter part of his reign, he brought about significant changes
in his style of governance, which included providing protection to
fauna, and even relinquished the royal hunt. He was the first ruler in
history to advocate conservation
measures for wildlife and even had rules inscribed in stone edicts. The
edicts proclaim that many followed the king's example in giving up the
slaughter of animals; one of them proudly states:
Our king killed very few animals.
However, the edicts of Ashoka reflect more the desire of rulers than
actual events; the mention of a 100 'panas' (coins) fine for poaching
deer in royal hunting preserves shows that rule-breakers did exist. The
legal restrictions conflicted with the practices freely exercised by the
common people in hunting, felling, fishing and setting fires in
forests.
Contacts with the Hellenistic world
Mauryan ringstone, with standing goddess. Northwest Pakistan. 3rd Century BCE
Foundation of the Empire
Relations with the Hellenistic world may have started from the very beginning of the Maurya Empire. Plutarch reports that Chandragupta Maurya met with Alexander the Great, probably around Taxila in the northwest:
- "Sandrocottus, when he was a stripling, saw Alexander himself, and we are told that he often said in later times that Alexander narrowly missed making himself master of the country, since its king was hated and despised on account of his baseness and low birth". Plutarch 62-4
Reconquest of the Northwest (c. 317–316 BCE)
Chandragupta
ultimately occupied Northwestern India, in the territories formerly
ruled by the Greeks, where he fought the satraps (described as
"Prefects" in Western sources) left in place after Alexander (Justin),
among whom may have been Eudemus, ruler in the western Punjab until his departure in 317 BCE or Peithon, son of Agenor, ruler of the Greek colonies along the Indus until his departure for Babylon in 316 BCE.
- "India, after the death of Alexander, had assassinated his prefects, as if shaking the burden of servitude. The author of this liberation was Sandracottos, but he had transformed liberation in servitude after victory, since, after taking the throne, he himself oppressed the very people he has liberated from foreign domination" Justin XV.4.12–13
- "Later, as he was preparing war against the prefects of Alexander, a huge wild elephant went to him and took him on his back as if tame, and he became a remarkable fighter and war leader. Having thus acquired royal power, Sandracottos possessed India at the time Seleucos was preparing future glory." Justin XV.4.19
Conflict and alliance with Seleucus (305 BCE)
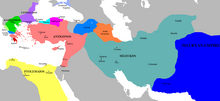
A map showing the north western border of Maurya Empire, including its various neighboring states.
Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of the Asian
portion of Alexander's former empire, conquered and put under his own
authority eastern territories as far as Bactria and the Indus (Appian, History of Rome, The Syrian Wars 55), until in 305 BCE he entered into a confrontation with Emperor Chandragupta:
"Always lying in wait for the neighbouring nations, strong in arms and persuasive in council, he [Seleucus] acquired Mesopotamia, Armenia, 'Seleucid' Cappadocia, Persis, Parthia, Bactria, Arabia, Tapouria, Sogdia, Arachosia, Hyrcania, and other adjacent peoples that had been subdued by Alexander, as far as the river Indus, so that the boundaries of his empire were the most extensive in Asia after that of Alexander. The whole region from Phrygia to the Indus was subject to Seleucus". Appian, History of Rome, The Syrian Wars 55
Though no accounts of the conflict remain, it is clear that Seleucus
fared poorly against the Indian Emperor as he failed to conquer any
territory, and in fact was forced to surrender much that was already
his. Regardless, Seleucus and Chandragupta ultimately reached a
settlement and through a treaty sealed in 305 BCE, Seleucus, according
to Strabo, ceded a number of territories to Chandragupta, including
eastern Afghanistan and Balochistan.
Marital alliance
Chandragupta and Seleucus
concluded a peace treaty and a marital alliance in 303 BCE.
Chandragupta received vast territories and in a return gave Seleucus 500
war elephants, a military asset which would play a decisive role at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BCE. In addition to this treaty, Seleucus dispatched an ambassador, Megasthenes, to Chandragupta, and later Deimakos to his son Bindusara, at the Mauryan court at Pataliputra (modern Patna in Bihar). Later, Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the ruler of Ptolemaic Egypt and contemporary of Ashoka, is also recorded by Pliny the Elder as having sent an ambassador named Dionysius to the Mauryan court.
Mainstream scholarship asserts that Chandragupta received vast territory west of the Indus, including the Hindu Kush, modern-day Afghanistan, and the Balochistan province of Pakistan. Archaeologically, concrete indications of Mauryan rule, such as the inscriptions of the Edicts of Ashoka, are known as far as Kandahar in southern Afghanistan.
| “ | He (Seleucus) crossed the Indus and waged war with Sandrocottus [Maurya], king of the Indians, who dwelt on the banks of that stream, until they came to an understanding with each other and contracted a marriage relationship. | ” |
| “ | After having made a treaty with him (Sandrakotos) and put in order the Orient situation, Seleucos went to war against Antigonus. | ” |
| — Junianus Justinus, Historiarum Philippicarum, libri XLIV, XV.4.15 | ||
The treaty on "Epigamia"
implies lawful marriage between Greeks and Indians was recognized at
the State level, although it is unclear whether it occurred among
dynastic rulers or common people, or both.
Exchange of presents
Classical
sources have also recorded that following their treaty, Chandragupta
and Seleucus exchanged presents, such as when Chandragupta sent various aphrodisiacs to Seleucus:
- "And Theophrastus says that some contrivances are of wondrous efficacy in such matters [as to make people more amorous]. And Phylarchus confirms him, by reference to some of the presents which Sandrakottus, the king of the Indians, sent to Seleucus; which were to act like charms in producing a wonderful degree of affection, while some, on the contrary, were to banish love." Athenaeus of Naucratis, "The deipnosophists" Book I, chapter 32
His son Bindusara 'Amitraghata' (Slayer of Enemies) also is recorded in Classical sources as having exchanged presents with Antiochus I:
- "But dried figs were so very much sought after by all men (for really, as Aristophanes says, "There's really nothing nicer than dried figs"), that even Amitrochates, the king of the Indians, wrote to Antiochus, entreating him (it is Hegesander who tells this story) to buy and send him some sweet wine, and some dried figs, and a sophist; and that Antiochus wrote to him in answer, "The dry figs and the sweet wine we will send you; but it is not lawful for a sophist to be sold in Greece." Athenaeus, "Deipnosophistae" XIV.67
Greek population in India
An
influential and large Greek population was present in the northwest of
the Indian subcontinent under Ashoka's rule, possibly remnants of
Alexander's conquests in the Indus Valley region. In the Rock Edicts of Ashoka, some of them inscribed in Greek, Ashoka states that the Greeks within his dominion were converted to Buddhism:
"Here in the king's dominion among the Greeks, the Kambojas, the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions in Dharma." (Rock Edict Number 13)
- An Edict of Ashoka in Shahbazbarhi, KPK, Pakistan.
"Now, in times past (officers) called Mahamatras of morality did not exist before. Mahdmatras of morality were appointed by me (when I had been) anointed thirteen years. These are occupied with all sects in establishing morality, in promoting morality, and for the welfare and happiness of those who are devoted to morality (even) among the Greeks, Kambojas and Gandharas, and whatever other western borderers (of mine there are)." (Rock Edict Number 5)
The Kandahar Edict of Ashoka, a bilingual edict (Greek and Aramaic) by king Ashoka, from Kandahar. Kabul Museum. (Click image for translation).
Fragments of Edict 13 have been found in Greek, and a full Edict, written in both Greek and Aramaic, has been discovered in Kandahar.
It is said to be written in excellent Classical Greek, using
sophisticated philosophical terms. In this Edict, Ashoka uses the word Eusebeia ("Piety") as the Greek translation for the ubiquitous "Dharma" of his other Edicts written in Prakrit:
- "Ten years (of reign) having been completed, King Piodasses (Ashoka) made known (the doctrine of) Piety (εὐσέβεια, Eusebeia) to men; and from this moment he has made men more pious, and everything thrives throughout the whole world. And the king abstains from (killing) living beings, and other men and those who (are) huntsmen and fishermen of the king have desisted from hunting. And if some (were) intemperate, they have ceased from their intemperance as was in their power; and obedient to their father and mother and to the elders, in opposition to the past also in the future, by so acting on every occasion, they will live better and more happily". (Trans. by G.P. Carratelli)
Buddhist missions to the West (c. 250 BCE)
- The distribution of the Edicts of Ashoka.
- Map of the Buddhist missions during the reign of Ashoka.
- Territories "conquered by the Dharma" according to Major Rock Edict No.13 of Ashoka (260–218 BCE).
Also, in the Edicts of Ashoka, Ashoka mentions the Hellenistic kings of the period as recipients of his Buddhist proselytism, although no Western historical record of this event remains:
- "The conquest by Dharma has been won here, on the borders, and even six hundred yojanas (5,400–9,600 km) away, where the Greek king Antiochos rules, beyond there where the four kings named Ptolemy, Antigonos, Magas and Alexander rule, likewise in the south among the Cholas, the Pandyas, and as far as Tamraparni (Sri Lanka)." (Edicts of Ashoka, 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika).
Ashoka also encouraged the development of herbal medicine, for men and animals, in their territories:
- "Everywhere within Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi's [Ashoka's] domain, and among the people beyond the borders, the Cholas, the Pandyas, the Satiyaputras, the Keralaputras, as far as Tamraparni and where the Greek king Antiochos rules, and among the kings who are neighbors of Antiochos, everywhere has Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi, made provision for two types of medical treatment: medical treatment for humans and medical treatment for animals. Wherever medical herbs suitable for humans or animals are not available, I have had them imported and grown. Wherever medical roots or fruits are not available I have had them imported and grown. Along roads I have had wells dug and trees planted for the benefit of humans and animals". 2nd Rock Edict
The Greeks in India even seem to have played an active role in the
propagation of Buddhism, as some of the emissaries of Ashoka, such as Dharmaraksita, are described in Pali sources as leading Greek ("Yona") Buddhist monks, active in Buddhist proselytism (the Mahavamsa, XII).
Subhagasena and Antiochos III (206 BCE)
Sophagasenus was an Indian Mauryan ruler of the 3rd century BCE, described in ancient Greek sources, and named Subhagasena or Subhashasena in Prakrit. His name is mentioned in the list of Mauryan princes, and also in the list of the Yadava dynasty, as a descendant of Pradyumna. He may have been a grandson of Ashoka, or Kunala, the son of Ashoka. He ruled an area south of the Hindu Kush, possibly in Gandhara. Antiochos III, the Seleucid king, after having made peace with Euthydemus in Bactria, went to India in 206 BCE and is said to have renewed his friendship with the Indian king there:
"He (Antiochus) crossed the Caucasus and descended into India;
renewed his friendship with Sophagasenus the king of the Indians;
received more elephants, until he had a hundred and fifty altogether;
and having once more provisioned his troops, set out again personally
with his army: leaving Androsthenes of Cyzicus the duty of taking home
the treasure which this king had agreed to hand over to him". Polybius 11.39
Timeline
- 322 BCE: Chandragupta Maurya founded the Mauryan Empire by overthrowing the Nanda Dynasty.
- 317–316 BCE: Chandragupta Maurya conquers the Northwest of the Indian subcontinent.
- 305–303 BCE: Chandragupta Maurya gains territory from the Seleucid Empire.
- 298–269 BCE: Reign of Bindusara, Chandragupta's son. He conquers parts of Deccan, southern India.
- 269–232 BCE: The Mauryan Empire reaches its height under Ashoka, Chandragupta's grandson.
- 261 BCE: Ashoka conquers the kingdom of Kalinga.
- 250 BCE: Ashoka builds Buddhist stupas and erects pillars bearing inscriptions.
- 184 BCE: The empire collapses when Brihadnatha, the last emperor, is killed by Pushyamitra Shunga, a Mauryan general and the founder of the Shunga Empire.
In literature
According to Vicarasreni of Merutunga, Mauryans rose to power in 312 BC.