 | |
| Paradigm | Multi-paradigm: functional, procedural, reflective, meta |
|---|---|
| Designed by | John McCarthy |
| Developer | Steve Russell, Timothy P. Hart, Mike Levin |
| First appeared | 1960 |
| Typing discipline | Dynamic, strong |
Lisp (historically LISP, an acronym for list processing) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket and Clojure.
Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the read–eval–print loop.
The name LISP derives from "LISt Processor". Linked lists are one of Lisp's major data structures, and Lisp source code is made of lists. Thus, Lisp programs can manipulate source code as a data structure, giving rise to the macro systems that allow programmers to create new syntax or new domain-specific languages embedded in Lisp.
The interchangeability of code and data gives Lisp its instantly recognizable syntax. All program code is written as s-expressions,
or parenthesized lists. A function call or syntactic form is written as
a list with the function or operator's name first, and the arguments
following; for instance, a function f that takes three arguments would be called as (f arg1 arg2 arg3).
History
John McCarthy began developing Lisp in 1958 while he was at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). McCarthy published its design in a paper in Communications of the ACM in April 1960, entitled "Recursive Functions of Symbolic Expressions and Their Computation by Machine, Part I". He showed that with a few simple operators and a notation for anonymous functions borrowed from Church, one can build a Turing-complete language for algorithms.
Information Processing Language was the first AI language, from 1955 or 1956, and already included many of the concepts, such as list-processing and recursion, which came to be used in Lisp.
McCarthy's original notation used bracketed "M-expressions" that would be translated into S-expressions. As an example, the M-expression car[cons[A,B]] is equivalent to the S-expression (car (cons A B)).
Once Lisp was implemented, programmers rapidly chose to use
S-expressions, and M-expressions were abandoned. M-expressions surfaced
again with short-lived attempts of MLisp by Horace Enea and CGOL by Vaughan Pratt.
Lisp was first implemented by Steve Russell on an IBM 704 computer using punched cards. Russell had read McCarthy's paper and realized (to McCarthy's surprise) that the Lisp eval function could be implemented in machine code.
According to McCarthy:
Steve Russell said, look, why don't I program this eval ... and I said to him, ho, ho, you're confusing theory with practice, this eval is intended for reading, not for computing. But he went ahead and did it. That is, he compiled the eval in my paper into IBM 704 machine code, fixing bugs, and then advertised this as a Lisp interpreter, which it certainly was. So at that point Lisp had essentially the form that it has today ...
The result was a working Lisp interpreter which could be used to run Lisp programs, or more properly, "evaluate Lisp expressions".
Two assembly language macros for the IBM 704 became the primitive operations for decomposing lists: car (Contents of the Address part of Register number) and cdr (Contents of the Decrement part of Register number), where "register" refers to registers of the computer's central processing unit (CPU). Lisp dialects still use car and cdr (/kɑːr/ and /ˈkʊdər/) for the operations that return the first item in a list and the rest of the list, respectively.
The first complete Lisp compiler, written in Lisp, was implemented in 1962 by Tim Hart and Mike Levin at MIT, and could be compiled by simply having an existing LISP interpreter interpret the compiler code, producing machine code output able to be executed at a 40-fold improvement in speed over that of the interpreter. This compiler introduced the Lisp model of incremental compilation, in which compiled and interpreted functions can intermix freely. The language used in Hart and Levin's memo is much closer to modern Lisp style than McCarthy's earlier code.
Garbage collection routines were developed by MIT graduate student Daniel Edwards, prior to 1962.
During the 1980s and 1990s, a great effort was made to unify the work on new Lisp dialects (mostly successors to Maclisp such as ZetaLisp and NIL (New Implementation of Lisp) into a single language. The new language, Common Lisp, was somewhat compatible with the dialects it replaced (the book Common Lisp the Language notes the compatibility of various constructs). In 1994, ANSI published the Common Lisp standard, "ANSI X3.226-1994 Information Technology Programming Language Common Lisp".
Connection to artificial intelligence
Since inception, Lisp was closely connected with the artificial intelligence research community, especially on PDP-10 systems. Lisp was used as the implementation of the language Micro Planner, which was used in the famous AI system SHRDLU. In the 1970s, as AI research spawned commercial offshoots, the performance of existing Lisp systems became a growing issue, as programmers needed to be familiar with the performance ramifications of the various techniques and choices involved in the implementation of Lisp.
Genealogy and variants
Over its sixty-year history, Lisp has spawned many variations on the core theme of an S-expression language. Moreover, each given dialect may have several implementations—for instance, there are more than a dozen implementations of Common Lisp.
Differences between dialects may be quite visible—for instance, Common Lisp uses the keyword defun to name a function, but Scheme uses define.
Within a dialect that is standardized, however, conforming
implementations support the same core language, but with different
extensions and libraries.
Historically significant dialects


- LISP 1 – First implementation.
- LISP 1.5 – First widely distributed version, developed by McCarthy and others at MIT. So named because it contained several improvements on the original "LISP 1" interpreter, but was not a major restructuring as the planned LISP 2 would be.
- Stanford LISP 1.6 – This was a successor to LISP 1.5 developed at the Stanford AI Lab, and widely distributed to PDP-10 systems running the TOPS-10 operating system. It was rendered obsolete by Maclisp and InterLisp.
- MACLISP – developed for MIT's Project MAC, MACLISP is a direct descendant of LISP 1.5. It ran on the PDP-10 and Multics systems. MACLISP would later come to be called Maclisp, and is often referred to as MacLisp. The "MAC" in MACLISP is related neither to Apple's Macintosh nor to McCarthy.
- Interlisp – developed at BBN Technologies for PDP-10 systems running the TENEX operating system, later adopted as a "West coast" Lisp for the Xerox Lisp machines as InterLisp-D. A small version called "InterLISP 65" was published for the 6502-based Atari 8-bit family computer line. For quite some time, Maclisp and InterLisp were strong competitors.
- Franz Lisp – originally a University of California, Berkeley project; later developed by Franz Inc. The name is a humorous deformation of the name "Franz Liszt", and does not refer to Allegro Common Lisp, the dialect of Common Lisp sold by Franz Inc., in more recent years.
- XLISP, which AutoLISP was based on.
- Standard Lisp and Portable Standard Lisp were widely used and ported, especially with the Computer Algebra System REDUCE.
- ZetaLisp, also termed Lisp Machine Lisp – used on the Lisp machines, direct descendant of Maclisp. ZetaLisp had a big influence on Common Lisp.
- LeLisp is a French Lisp dialect. One of the first Interface Builders (called SOS Interface) was written in LeLisp.
- Scheme (1975).
- Common Lisp (1984), as described by Common Lisp the Language – a consolidation of several divergent attempts (ZetaLisp, Spice Lisp, NIL, and S-1 Lisp) to create successor dialects to Maclisp, with substantive influences from the Scheme dialect as well. This version of Common Lisp was available for wide-ranging platforms and was accepted by many as a de facto standard until the publication of ANSI Common Lisp (ANSI X3.226-1994). Among the most widespread sub-dialects of Common Lisp are Steel Bank Common Lisp (SBCL), CMU Common Lisp (CMU-CL), Clozure OpenMCL (not to be confused with Clojure!), GNU CLisp, and later versions of Franz Lisp; all of them adhere to the later ANSI CL standard (see below).
- Dylan was in its first version a mix of Scheme with the Common Lisp Object System.
- EuLisp – attempt to develop a new efficient and cleaned-up Lisp.
- ISLISP – attempt to develop a new efficient and cleaned-up Lisp. Standardized as ISO/IEC 13816:1997 and later revised as ISO/IEC 13816:2007: Information technology – Programming languages, their environments and system software interfaces – Programming language ISLISP.
- IEEE Scheme – IEEE standard, 1178–1990 (R1995).
- ANSI Common Lisp – an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard for Common Lisp, created by subcommittee X3J13, chartered to begin with Common Lisp: The Language as a base document and to work through a public consensus process to find solutions to shared issues of portability of programs and compatibility of Common Lisp implementations. Although formally an ANSI standard, the implementation, sale, use, and influence of ANSI Common Lisp has been and continues to be seen worldwide.
- ACL2 or "A Computational Logic for Applicative Common Lisp", an applicative (side-effect free) variant of Common LISP. ACL2 is both a programming language which can model computer systems, and a tool to help proving properties of those models.
- Clojure, a recent dialect of Lisp which compiles to the Java virtual machine and has a particular focus on concurrency.
- Game Oriented Assembly Lisp (or GOAL) is a video game programming language developed by Andy Gavin at Naughty Dog. It was written using Allegro Common Lisp and used in the development of the entire Jak and Daxter series of games developed by Naughty Dog.
2000 to present
After having declined somewhat in the 1990s, Lisp has experienced a resurgence of interest after 2000. Most new activity has been focused around implementations of Common Lisp, Scheme, Emacs Lisp, Clojure, and Racket, and includes development of new portable libraries and applications.
Many new Lisp programmers were inspired by writers such as Paul Graham and Eric S. Raymond to pursue a language others considered antiquated. New Lisp programmers often describe the language as an eye-opening experience and claim to be substantially more productive than in other languages. This increase in awareness may be contrasted to the "AI winter" and Lisp's brief gain in the mid-1990s.
As of 2010, there were eleven actively maintained Common Lisp implementations.
The open source community has created new supporting infrastructure: CLiki is a wiki that collects Common Lisp related information, the Common Lisp directory lists resources, #lisp is a popular IRC channel and allows the sharing and commenting of code snippets (with support by lisppaste, an IRC bot written in Lisp), Planet Lisp collects the contents of various Lisp-related blogs, on LispForum users discuss Lisp topics, Lispjobs is a service for announcing job offers and there is a weekly news service, Weekly Lisp News. Common-lisp.net is a hosting site for open source Common Lisp projects. Quicklisp is a library manager for Common Lisp.
Fifty years of Lisp (1958–2008) was celebrated at LISP50@OOPSLA. There are regular local user meetings in Boston, Vancouver, and Hamburg. Other events include the European Common Lisp Meeting, the European Lisp Symposium and an International Lisp Conference.
The Scheme community actively maintains over twenty implementations. Several significant new implementations (Chicken, Gambit, Gauche, Ikarus, Larceny, Ypsilon) have been developed in the 2000s (decade). The Revised5 Report on the Algorithmic Language Scheme standard of Scheme was widely accepted in the Scheme community. The Scheme Requests for Implementation process has created a lot of quasi standard libraries and extensions for Scheme. User communities of individual Scheme implementations continue to grow. A new language standardization process was started in 2003 and led to the R6RS Scheme standard in 2007. Academic use of Scheme for teaching computer science seems to have declined somewhat. Some universities are no longer using Scheme in their computer science introductory courses; MIT now uses Python instead of Scheme for its undergraduate computer science program and MITx massive open online course.
There are several new dialects of Lisp: Arc, Hy, Nu, Liskell, and LFE (Lisp Flavored Erlang). The parser for Julia is implemented in Femtolisp, a dialect of Scheme (Julia is inspired by Scheme, which in turn is a Lisp dialect).
In October 2019, Paul Graham released a specification for Bel, "a new dialect of Lisp."
Major dialects
Common Lisp and Scheme represent two major streams of Lisp development. These languages embody significantly different design choices.
Common Lisp is a successor to Maclisp. The primary influences were Lisp Machine Lisp, Maclisp, NIL, S-1 Lisp, Spice Lisp, and Scheme.[45] It has many of the features of Lisp Machine Lisp (a large Lisp dialect used to program Lisp Machines), but was designed to be efficiently implementable on any personal computer or workstation. Common Lisp is a general-purpose programming language and thus has a large language standard including many built-in data types, functions, macros and other language elements, and an object system (Common Lisp Object System). Common Lisp also borrowed certain features from Scheme such as lexical scoping and lexical closures. Common Lisp implementations are available for targeting different platforms such as the LLVM, the Java virtual machine, x86-64, PowerPC, Alpha, ARM, Motorola 68000, and MIPS, and operating systems such as Windows, macOS, Linux, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Dragonfly BSD, and Heroku.
Scheme is a statically scoped and properly tail-recursive dialect of the Lisp programming language invented by Guy L. Steele, Jr. and Gerald Jay Sussman. It was designed to have exceptionally clear and simple semantics and few different ways to form expressions. Designed about a decade earlier than Common Lisp, Scheme is a more minimalist design. It has a much smaller set of standard features but with certain implementation features (such as tail-call optimization and full continuations) not specified in Common Lisp. A wide variety of programming paradigms, including imperative, functional, and message passing styles, find convenient expression in Scheme. Scheme continues to evolve with a series of standards (Revised Report on the Algorithmic Language Scheme) and a series of Scheme Requests for Implementation.
Clojure is a dialect of Lisp that targets mainly the Java virtual machine, and the Common Language Runtime (CLR), the Python VM, the Ruby VM YARV, and compiling to JavaScript. It is designed to be a pragmatic general-purpose language. Clojure draws considerable influences from Haskell and places a very strong emphasis on immutability. Clojure provides access to Java frameworks and libraries, with optional type hints and type inference, so that calls to Java can avoid reflection and enable fast primitive operations. Clojure is not designed to be backwards compatible with other Lisp dialects.
Further, Lisp dialects are used as scripting languages in many applications, with the best-known being Emacs Lisp in the Emacs editor, AutoLISP and later Visual Lisp in AutoCAD, Nyquist in Audacity, and Scheme in LilyPond. The potential small size of a useful Scheme interpreter makes it particularly popular for embedded scripting. Examples include SIOD and TinyScheme, both of which have been successfully embedded in the GIMP image processor under the generic name "Script-fu". LIBREP, a Lisp interpreter by John Harper originally based on the Emacs Lisp language, has been embedded in the Sawfish window manager.
Standardized dialects
Lisp has officially standardized dialects: R6RS Scheme, R7RS Scheme, IEEE Scheme, ANSI Common Lisp and ISO ISLISP.
Language innovations
Paul Graham identifies nine important aspects of Lisp that distinguished it from existing languages like Fortran:
- Conditionals not limited to goto
- First-class functions
- Recursion
- Treating variables uniformly as pointers, leaving types to values
- Garbage collection
- Programs made entirely of expressions with no statements
- The symbol data type, distinct from the string data type
- Notation for code made of trees of symbols (using many parentheses)
- Full language available at load time, compile time, and run time
Lisp was the first language where the structure of program code is represented faithfully and directly in a standard data structure—a quality much later dubbed "homoiconicity". Thus, Lisp functions can be manipulated, altered or even created within a Lisp program without lower-level manipulations. This is generally considered one of the main advantages of the language with regard to its expressive power, and makes the language suitable for syntactic macros and meta-circular evaluation.
A conditional using an if–then–else syntax was invented by McCarthy for a chess program written in Fortran. He proposed its inclusion in ALGOL, but it was not made part of the Algol 58 specification. For Lisp, McCarthy used the more general cond-structure. Algol 60 took up if–then–else and popularized it.
Lisp deeply influenced Alan Kay, the leader of the research team that developed Smalltalk at Xerox PARC; and in turn Lisp was influenced by Smalltalk, with later dialects adopting object-oriented programming features (inheritance classes, encapsulating instances, message passing, etc.) in the 1970s. The Flavors object system introduced the concept of multiple inheritance and the mixin. The Common Lisp Object System provides multiple inheritance, multimethods with multiple dispatch, and first-class generic functions, yielding a flexible and powerful form of dynamic dispatch. It has served as the template for many subsequent Lisp (including Scheme) object systems, which are often implemented via a metaobject protocol, a reflective meta-circular design in which the object system is defined in terms of itself: Lisp was only the second language after Smalltalk (and is still one of the very few languages) to possess such a metaobject system. Many years later, Alan Kay suggested that as a result of the confluence of these features, only Smalltalk and Lisp could be regarded as properly conceived object-oriented programming systems.
Lisp introduced the concept of automatic garbage collection, in which the system walks the heap looking for unused memory. Progress in modern sophisticated garbage collection algorithms such as generational garbage collection was stimulated by its use in Lisp.
Edsger W. Dijkstra in his 1972 Turing Award lecture said,
With a few very basic principles at its foundation, it [LISP] has shown a remarkable stability. Besides that, LISP has been the carrier for a considerable number of in a sense our most sophisticated computer applications. LISP has jokingly been described as "the most intelligent way to misuse a computer". I think that description a great compliment because it transmits the full flavour of liberation: it has assisted a number of our most gifted fellow humans in thinking previously impossible thoughts.
Largely because of its resource requirements with respect to early computing hardware (including early microprocessors), Lisp did not become as popular outside of the AI community as Fortran and the ALGOL-descended C language. Because of its suitability to complex and dynamic applications, Lisp enjoyed some resurgence of popular interest in the 2010s.
Syntax and semantics
- Note: This article's examples are written in Common Lisp (though most are also valid in Scheme).
Symbolic expressions (S-expressions)
Lisp is an expression oriented language. Unlike most other languages, no distinction is made between "expressions" and "statements"; all code and data are written as expressions. When an expression is evaluated, it produces a value (possibly multiple values), which can then be embedded into other expressions. Each value can be any data type.
McCarthy's 1958 paper introduced two types of syntax: Symbolic expressions (S-expressions, sexps), which mirror the internal representation of code and data; and Meta expressions (M-expressions), which express functions of S-expressions. M-expressions never found favor, and almost all Lisps today use S-expressions to manipulate both code and data.
The use of parentheses is Lisp's most immediately obvious difference from other programming language families. As a result, students have long given Lisp nicknames such as Lost In Stupid Parentheses, or Lots of Irritating Superfluous Parentheses. However, the S-expression syntax is also responsible for much of Lisp's power: the syntax is simple and consistent, which facilitates manipulation by computer. However, the syntax of Lisp is not limited to traditional parentheses notation. It can be extended to include alternative notations. For example, XMLisp is a Common Lisp extension that employs the metaobject protocol to integrate S-expressions with the Extensible Markup Language (XML).
The reliance on expressions gives the language great flexibility. Because Lisp functions are written as lists, they can be processed exactly like data. This allows easy writing of programs which manipulate other programs (metaprogramming). Many Lisp dialects exploit this feature using macro systems, which enables extension of the language almost without limit.
Lists
A Lisp list is written with its elements separated by whitespace, and surrounded by parentheses. For example, (1 2 foo) is a list whose elements are the three atoms 1, 2, and foo.
These values are implicitly typed: they are respectively two integers
and a Lisp-specific data type called a "symbol", and do not have to be
declared as such.
The empty list () is also represented as the special atom nil. This is the only entity in Lisp which is both an atom and a list.
Expressions are written as lists, using prefix notation.
The first element in the list is the name of a function, the name of a
macro, a lambda expression or the name of a "special operator" (see
below). The remainder of the list are the arguments. For example, the
function list returns its arguments as a list, so the expression
(list 1 2 (quote foo))
evaluates to the list (1 2 foo). The "quote" before the foo
in the preceding example is a "special operator" which returns its
argument without evaluating it. Any unquoted expressions are recursively
evaluated before the enclosing expression is evaluated. For example,
(list 1 2 (list 3 4))
evaluates to the list (1 2 (3 4)). Note that the third argument is a list; lists can be nested.
Operators
Arithmetic operators are treated similarly. The expression
(+ 1 2 3 4)
evaluates to 10. The equivalent under infix notation would be "1 + 2 + 3 + 4".
Lisp has no notion of operators as implemented in Algol-derived languages. Arithmetic operators in Lisp are variadic functions (or n-ary), able to take any number of arguments. A C-style '++' increment operator is sometimes implemented under the name incf giving syntax
(incf x)
equivalent to (setq x (+ x 1)), returning the new value of x.
"Special operators" (sometimes called "special forms") provide Lisp's control structure. For example, the special operator if
takes three arguments. If the first argument is non-nil, it evaluates
to the second argument; otherwise, it evaluates to the third argument.
Thus, the expression
(if nil
(list 1 2 "foo")
(list 3 4 "bar"))
evaluates to (3 4 "bar"). Of course, this would be more useful if a non-trivial expression had been substituted in place of nil.
Lisp also provides logical operators and, or and not. The and and or operators do short-circuit evaluation and will return their first nil and non-nil argument respectively.
(or (and "zero" nil "never") "James" 'task 'time)
will evaluate to "James".
Lambda expressions and function definition
Another special operator, lambda,
is used to bind variables to values which are then evaluated within an
expression. This operator is also used to create functions: the
arguments to lambda
are a list of arguments, and the expression or expressions to which the
function evaluates (the returned value is the value of the last
expression that is evaluated). The expression
(lambda (arg) (+ arg 1))
evaluates to a function that, when applied, takes one argument, binds it to arg
and returns the number one greater than that argument. Lambda
expressions are treated no differently from named functions; they are
invoked the same way. Therefore, the expression
((lambda (arg) (+ arg 1)) 5)
evaluates to 6. Here, we're doing a function application: we execute the anonymous function by passing to it the value 5.
Named functions are created by storing a lambda expression in a symbol using the defun macro.
(defun foo (a b c d) (+ a b c d))
(defun f (a) b...) defines a new function named f in the global environment. It is conceptually similar to the expression:
(setf (fdefinition 'f) #'(lambda (a) (block f b...)))
where setf is a macro used to set the value of the first argument fdefinition 'f to a new function object. fdefinition is a global function definition for the function named f. #' is an abbreviation for function special operator, returning a function object.
Atoms
In the original LISP there were two fundamental data types:
atoms and lists. A list was a finite ordered sequence of elements,
where each element is either an atom or a list, and an atom was a number or a symbol. A symbol was essentially a unique named item, written as an alphanumeric string in source code, and used either as a variable name or as a data item in symbolic processing. For example, the list (FOO (BAR 1) 2) contains three elements: the symbol FOO, the list (BAR 1), and the number 2.
The essential difference between atoms and lists was that atoms were immutable and unique. Two atoms that appeared in different places in source code but were written in exactly the same way represented the same object, whereas each list was a separate object that could be altered independently of other lists and could be distinguished from other lists by comparison operators.
As more data types were introduced in later Lisp dialects, and programming styles evolved, the concept of an atom lost importance. Many dialects still retained the predicate atom for legacy compatibility, defining it true for any object which is not a cons.
Conses and lists
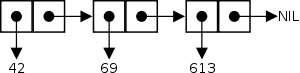
A Lisp list is implemented as a singly linked list. Each cell of this list is called a cons (in Scheme, a pair) and is composed of two pointers, called the car and cdr. These are respectively equivalent to the data and next fields discussed in the article linked list.
Of the many data structures that can be built out of cons cells, one of the most basic is called a proper list. A proper list is either the special nil (empty list) symbol, or a cons in which the car points to a datum (which may be another cons structure, such as a list), and the cdr points to another proper list.
If a given cons is taken to be the head of a linked list, then
its car points to the first element of the list, and its cdr points to
the rest of the list. For this reason, the car and cdr functions are also called first and rest when referring to conses which are part of a linked list (rather than, say, a tree).
Thus, a Lisp list is not an atomic object, as an instance of a container class in C++ or Java would be. A list is nothing more than an aggregate of linked conses. A variable that refers to a given list is simply a pointer to the first cons in the list. Traversal of a list can be done by cdring down the list; that is, taking successive cdrs to visit each cons of the list; or by using any of several higher-order functions to map a function over a list.
Because conses and lists are so universal in Lisp systems, it is a common misconception that they are Lisp's only data structures. In fact, all but the most simplistic Lisps have other data structures, such as vectors (arrays), hash tables, structures, and so forth.
S-expressions represent lists
Parenthesized
S-expressions represent linked list structures. There are several ways
to represent the same list as an S-expression. A cons can be written in dotted-pair notation as (a . b), where a is the car and b the cdr. A longer proper list might be written (a . (b . (c . (d . nil)))) in dotted-pair notation. This is conventionally abbreviated as (a b c d) in list notation. An improper list may be written in a combination of the two – as (a b c . d) for the list of three conses whose last cdr is d (i.e., the list (a . (b . (c . d))) in fully specified form).
List-processing procedures
Lisp provides many built-in procedures for accessing and controlling lists. Lists can be created directly with the list procedure, which takes any number of arguments, and returns the list of these arguments.
(list 1 2 'a 3)
;Output: (1 2 a 3)
(list 1 '(2 3) 4)
;Output: (1 (2 3) 4)
Because of the way that lists are constructed from cons pairs, the cons procedure can be used to add an element to the front of a list. Note that the cons procedure is asymmetric in how it handles list arguments, because of how lists are constructed.
(cons 1 '(2 3))
;Output: (1 2 3)
(cons '(1 2) '(3 4))
;Output: ((1 2) 3 4)
The append procedure appends two (or more) lists to one another. Because Lisp lists are linked lists, appending two lists has asymptotic time complexity
(append '(1 2) '(3 4))
;Output: (1 2 3 4)
(append '(1 2 3) '() '(a) '(5 6))
;Output: (1 2 3 a 5 6)
Lisp lists, being simple linked lists, can share structure with one another. That is to say, two lists can have the same tail, or final sequence of conses. For instance, after the execution of the following Common Lisp code:
(setf foo (list 'a 'b 'c))
(setf bar (cons 'x (cdr foo)))
the lists foo and bar are (a b c) and (x b c) respectively. However, the tail (b c) is the same structure in both lists. It is not a copy; the cons cells pointing to b and c are in the same memory locations for both lists.
Sharing structure rather than copying can give a dramatic
performance improvement. However, this technique can interact in
undesired ways with functions that alter lists passed to them as
arguments. Altering one list, such as by replacing the c with a goose, will affect the other:
(setf (third foo) 'goose)
This changes foo to (a b goose), but thereby also changes bar to (x b goose) – a possibly unexpected result. This can be a source of bugs, and functions which alter their arguments are documented as destructive for this very reason.
Aficionados of functional programming
avoid destructive functions. In the Scheme dialect, which favors the
functional style, the names of destructive functions are marked with a
cautionary exclamation point, or "bang"—such as set-car! (read set car bang), which replaces the car of a cons. In the Common Lisp dialect, destructive functions are commonplace; the equivalent of set-car! is named rplaca for "replace car". This function is rarely seen, however, as Common Lisp includes a special facility, setf,
to make it easier to define and use destructive functions. A frequent
style in Common Lisp is to write code functionally (without destructive
calls) when prototyping, then to add destructive calls as an
optimization where it is safe to do so.
Self-evaluating forms and quoting
Lisp
evaluates expressions which are entered by the user. Symbols and lists
evaluate to some other (usually, simpler) expression – for instance, a
symbol evaluates to the value of the variable it names; (+ 2 3) evaluates to 5. However, most other forms evaluate to themselves: if entering 5 into Lisp, it returns 5.
Any expression can also be marked to prevent it from being
evaluated (as is necessary for symbols and lists). This is the role of
the quote special operator, or its abbreviation ' (one quotation mark). For instance, usually if entering the symbol foo,
it returns the value of the corresponding variable (or an error, if
there is no such variable). To refer to the literal symbol, enter (quote foo) or, usually, 'foo.
Both Common Lisp and Scheme also support the backquote operator (termed quasiquote in Scheme), entered with the ` character (grave accent).
This is almost the same as the plain quote, except it allows
expressions to be evaluated and their values interpolated into a quoted
list with the comma , unquote and comma-at ,@ splice operators. If the variable snue has the value (bar baz) then `(foo ,snue) evaluates to (foo (bar baz)), while `(foo ,@snue) evaluates to (foo bar baz). The backquote is most often used in defining macro expansions.
Self-evaluating forms and quoted forms are Lisp's equivalent of literals. It may be possible to modify the values of (mutable) literals in program code. For instance, if a function returns a quoted form, and the code that calls the function modifies the form, this may alter the behavior of the function on subsequent invocations.
(defun should-be-constant ()
'(one two three))
(let ((stuff (should-be-constant)))
(setf (third stuff) 'bizarre)) ; bad!
(should-be-constant) ; returns (one two bizarre)
Modifying a quoted form like this is generally considered bad style, and is defined by ANSI Common Lisp as erroneous (resulting in "undefined" behavior in compiled files, because the file-compiler can coalesce similar constants, put them in write-protected memory, etc.).
Lisp's formalization of quotation has been noted by Douglas Hofstadter (in Gödel, Escher, Bach) and others as an example of the philosophical idea of self-reference.
Scope and closure
The Lisp family splits over the use of dynamic or static (a.k.a. lexical) scope. Clojure, Common Lisp and Scheme make use of static scoping by default, while newLISP, Picolisp and the embedded languages in Emacs and AutoCAD use dynamic scoping. Since version 24.1, Emacs uses both dynamic and lexical scoping.
List structure of program code; exploitation by macros and compilers
A fundamental distinction between Lisp and other languages is that in Lisp, the textual representation of a program is simply a human-readable description of the same internal data structures (linked lists, symbols, number, characters, etc.) as would be used by the underlying Lisp system.
Lisp uses this to implement a very powerful macro system. Like other macro languages such as the one defined by the C preprocessor (the macro preprocessor for the C, Objective-C and C++ programming languages), a macro returns code that can then be compiled. However, unlike C preprocessor macros, the macros are Lisp functions and so can exploit the full power of Lisp.
Further, because Lisp code has the same structure as lists, macros can be built with any of the list-processing functions in the language. In short, anything that Lisp can do to a data structure, Lisp macros can do to code. In contrast, in most other languages, the parser's output is purely internal to the language implementation and cannot be manipulated by the programmer.
This feature makes it easy to develop efficient languages within languages. For example, the Common Lisp Object System can be implemented cleanly as a language extension using macros. This means that if an application needs a different inheritance mechanism, it can use a different object system. This is in stark contrast to most other languages; for example, Java does not support multiple inheritance and there is no reasonable way to add it.
In simplistic Lisp implementations, this list structure is directly interpreted to run the program; a function is literally a piece of list structure which is traversed by the interpreter in executing it. However, most substantial Lisp systems also include a compiler. The compiler translates list structure into machine code or bytecode for execution. This code can run as fast as code compiled in conventional languages such as C.
Macros expand before the compilation step, and thus offer some
interesting options. If a program needs a precomputed table, then a
macro might create the table at compile time, so the compiler need only
output the table and need not call code to create the table at run time.
Some Lisp implementations even have a mechanism, eval-when, that allows code to be present during compile time (when a macro would need it), but not present in the emitted module.
Evaluation and the read–eval–print loop
Lisp languages are often used with an interactive command line, which may be combined with an integrated development environment (IDE). The user types in expressions at the command line, or directs the IDE to transmit them to the Lisp system. Lisp reads the entered expressions, evaluates them, and prints the result. For this reason, the Lisp command line is called a read–eval–print loop (REPL).
The basic operation of the REPL is as follows. This is a simplistic description which omits many elements of a real Lisp, such as quoting and macros.
The read
function accepts textual S-expressions as input, and parses them into
an internal data structure. For instance, if you type the text (+ 1 2) at the prompt, read translates this into a linked list with three elements: the symbol +,
the number 1, and the number 2. It so happens that this list is also a
valid piece of Lisp code; that is, it can be evaluated. This is because
the car of the list names a function—the addition operation.
Note that a foo will be read as a single symbol. 123 will be read as the number one hundred and twenty-three. "123" will be read as the string "123".
The eval
function evaluates the data, returning zero or more other Lisp data as a
result. Evaluation does not have to mean interpretation; some Lisp
systems compile every expression to native machine code. It is simple,
however, to describe evaluation as interpretation: To evaluate a list
whose car names a function, eval
first evaluates each of the arguments given in its cdr, then applies
the function to the arguments. In this case, the function is addition,
and applying it to the argument list (1 2) yields the answer 3. This is the result of the evaluation.
The symbol foo evaluates to the value of the symbol foo. Data like the string "123" evaluates to the same string. The list (quote (1 2 3)) evaluates to the list (1 2 3).
It is the job of the print function to represent output to the user. For a simple result such as 3 this is trivial. An expression which evaluated to a piece of list structure would require that print traverse the list and print it out as an S-expression.
To implement a Lisp REPL, it is necessary only to implement these
three functions and an infinite-loop function. (Naturally, the
implementation of eval will be complex, since it must also implement all special operators like if or lambda.) This done, a basic REPL is one line of code: (loop (print (eval (read)))).
The Lisp REPL typically also provides input editing, an input history, error handling and an interface to the debugger.
Lisp is usually evaluated eagerly. In Common Lisp, arguments are evaluated in applicative order ('leftmost innermost'), while in Scheme order of arguments is undefined, leaving room for optimization by a compiler.
Control structures
Lisp
originally had very few control structures, but many more were added
during the language's evolution. (Lisp's original conditional operator, cond, is the precursor to later if-then-else structures.)
Programmers in the Scheme dialect often express loops using tail recursion.
Scheme's commonality in academic computer science has led some students
to believe that tail recursion is the only, or the most common, way to
write iterations in Lisp, but this is incorrect. All oft-seen Lisp
dialects have imperative-style iteration constructs, from Scheme's do loop to Common Lisp's complex loop
expressions. Moreover, the key issue that makes this an objective
rather than subjective matter is that Scheme makes specific requirements
for the handling of tail calls,
and thus the reason that the use of tail recursion is generally
encouraged for Scheme is that the practice is expressly supported by the
language definition. By contrast, ANSI Common Lisp does not require
the optimization commonly termed a tail call elimination. Thus, the
fact that tail recursive style as a casual replacement for the use of
more traditional iteration constructs (such as do, dolist or loop) is discouraged
in Common Lisp is not just a matter of stylistic preference, but
potentially one of efficiency (since an apparent tail call in Common
Lisp may not compile as a simple jump) and program correctness (since tail recursion may increase stack use in Common Lisp, risking stack overflow).
Some Lisp control structures are special operators, equivalent to other languages' syntactic keywords. Expressions using these operators have the same surface appearance as function calls, but differ in that the arguments are not necessarily evaluated—or, in the case of an iteration expression, may be evaluated more than once.
In contrast to most other major programming languages, Lisp allows implementing control structures using the language. Several control structures are implemented as Lisp macros, and can even be macro-expanded by the programmer who wants to know how they work.
Both Common Lisp and Scheme have operators for non-local control
flow. The differences in these operators are some of the deepest
differences between the two dialects. Scheme supports re-entrant continuations using the call/cc
procedure, which allows a program to save (and later restore) a
particular place in execution. Common Lisp does not support re-entrant
continuations, but does support several ways of handling escape
continuations.
Often, the same algorithm can be expressed in Lisp in either an imperative or a functional style. As noted above, Scheme tends to favor the functional style, using tail recursion and continuations to express control flow. However, imperative style is still quite possible. The style preferred by many Common Lisp programmers may seem more familiar to programmers used to structured languages such as C, while that preferred by Schemers more closely resembles pure-functional languages such as Haskell.
Because of Lisp's early heritage in list processing, it has a
wide array of higher-order functions relating to iteration over
sequences. In many cases where an explicit loop would be needed in other
languages (like a for
loop in C) in Lisp the same task can be accomplished with a
higher-order function. (The same is true of many functional programming
languages.)
A good example is a function which in Scheme is called map and in Common Lisp is called mapcar. Given a function and one or more lists, mapcar applies the function successively to the lists' elements in order, collecting the results in a new list:
(mapcar #'+ '(1 2 3 4 5) '(10 20 30 40 50))
This applies the + function to each corresponding pair of list elements, yielding the result (11 22 33 44 55).
Examples
Here are examples of Common Lisp code.
The basic "Hello, World!" program:
(print "Hello, World!")
Lisp syntax lends itself naturally to recursion. Mathematical problems such as the enumeration of recursively defined sets are simple to express in this notation. For example, to evaluate a number's factorial:
(defun factorial (n)
(if (zerop n) 1
(* n (factorial (1- n)))))
An alternative implementation takes less stack space than the previous version if the underlying Lisp system optimizes tail recursion:
(defun factorial (n &optional (acc 1))
(if (zerop n) acc
(factorial (1- n) (* acc n))))
Contrast the examples above with an iterative version which uses Common Lisp's loop macro:
(defun factorial (n)
(loop for i from 1 to n
for fac = 1 then (* fac i)
finally (return fac)))
The following function reverses a list. (Lisp's built-in reverse function does the same thing.)
(defun -reverse (list)
(let ((return-value))
(dolist (e list) (push e return-value))
return-value))
Object systems
Various object systems and models have been built on top of, alongside, or into Lisp, including:
- The Common Lisp Object System, CLOS, is an integral part of ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS descended from New Flavors and CommonLOOPS. ANSI Common Lisp was the first standardized object-oriented programming language (1994, ANSI X3J13).
- ObjectLisp or Object Lisp, used by Lisp Machines Incorporated and early versions of Macintosh Common Lisp
- LOOPS (Lisp Object-Oriented Programming System) and the later CommonLoops
- Flavors, built at MIT, and its descendant New Flavors (developed by Symbolics).
- KR (short for Knowledge Representation), a constraints-based object system developed to aid the writing of Garnet, a GUI library for Common Lisp.
- Knowledge Engineering Environment (KEE) used an object system named UNITS and integrated it with an inference engine and a truth maintenance system (ATMS).
Operating systems
Several operating systems, including language-based systems, are based on Lisp (use Lisp features, conventions, methods, data structures, etc.), or are written in Lisp, including:
Genera, renamed Open Genera, by Symbolics; Medley, written in Interlisp, originally a family of graphical operating systems that ran on Xerox's later Star workstations; Mezzano; Interim;ChrysaLisp, by developers of Tao Systems' TAOS.



