Radon (/ˈreɪdɒn/) is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of radium. It is one of the densest substances that remains a gas under normal conditions, and is considered to be a health hazard due to its radioactivity. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days. Due to its high radioactivity, it has been less well-studied by chemists, but a few compounds are known.
Radon is formed as part of the normal radioactive decay chain of uranium into 206Pb. Uranium has been present since the earth was formed and its most common isotope has a very long half-life (4.5 billion years), which is the time required for one-half of uranium to break down. Thus, uranium and radon, will continue to occur for millions of years at about the same concentrations as they do now.
Radon is responsible for the majority of the mean public exposure to ionizing radiation. It is often the single largest contributor to an individual's background radiation dose, and is the most variable from location to location. Radon gas from natural sources can accumulate in buildings, especially in confined areas such as attics, and basements. It can also be found in some spring waters and hot springs.
According to a 2003 report EPA's Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes from the United States Environmental Protection Agency, epidemiological evidence shows a clear link between lung cancer and high concentrations of radon, with 21,000 radon-induced U.S. lung cancer deaths per year—second only to cigarette smoking. Thus in geographic areas where radon is present in heightened concentrations, radon is considered a significant indoor air contaminant.
Occurrence
Concentration units
Radon concentration is usually measured in the atmosphere in becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m3), which is an SI derived unit. As a frame of reference, typical domestic exposures are about 100 Bq/m3 indoors and 10-20 Bq/m3 outdoors. In the US, radon concentrations are often measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/l), with 1 pCi/l = 37 Bq/m3.
The mining industry traditionally measures exposure using the working level (WL) index, and the cumulative exposure in working level months (WLM): 1 WL equals any combination of short-lived 222Rn progeny (218Po, 214Pb, 214Bi, and 214Po) in 1 liter of air that releases 1.3 × 105 MeV of potential alpha energy; one WL is equivalent to 2.08 × 10−5 joules per cubic meter of air (J/m3).[1] The SI unit of cumulative exposure is expressed in joule-hours per cubic meter (J·h/m3). One WLM is equivalent to 3.6 × 10−3 J·h/m3. An exposure to 1 WL for 1 working month (170 hours) equals 1 WLM cumulative exposure.
A cumulative exposure of 1 WLM is roughly equivalent to living one year in an atmosphere with a radon concentration of 230 Bq/m3.
The radon (222Rn) released into the air decays to 210Pb and other radioisotopes. The levels of 210Pb can be measured. The rate of deposition of this radioisotope is dependent on the weather.
Natural
Radon concentrations found in natural environments are much too low to be detected by chemical means: for example, a 1000 Bq/m3 (relatively high) concentration corresponds to 0.17 pico-gram per cubic meter. The average concentration of radon in the atmosphere is about 6×10−20 atoms of radon for each molecule in the air, or about 150 atoms in each ml of air. The entire radon activity of the Earth's atmosphere at a time is due to some tens of grams of radon, consistently replaced by decay of larger amounts of radium and uranium. Concentrations can vary greatly from place to place. In the open air, it ranges from 1 to 100 Bq/m3, even less (0.1 Bq/m3) above the ocean. In caves, aerated mines, or in poorly ventilated dwellings, its concentration can climb to 20-2,000 Bq/m3.
In mining contexts, radon concentrations can be much higher. Ventilation regulations try to maintain concentrations in uranium mines under the "working level", and under 3 WL (546 pCi 222Rn per liter of air; 20.2 kBq/m3 measured from 1976 to 1985) 95 percent of the time. The concentration in the air at the (unventilated) Gastein Healing Gallery averages 43 kBq/m3 (about 1.2 nCi/L) with maximal value of 160 kBq/m3 (about 4.3 nCi/L).
Radon emanates naturally from the ground and from some building materials all over the world, wherever traces of uranium or thorium can be found, and particularly in regions with soils containing granite or shale, which have a higher concentration of uranium. Every square mile of surface soil, to a depth of 6 inches (2.6 km2 to a depth of 15 cm), contains approximately 1 gram of radium, which releases radon in small amounts to the atmosphere Sand used in making concrete is the major source of radon in buildings.
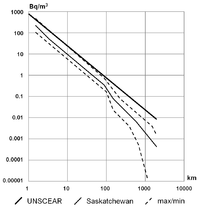
On a global scale, it is estimated that 2,400 million curies (91 TBq) of radon are released from soil annually. Not all granitic regions are prone to high emissions of radon. Being a rare gas, it usually migrates freely through faults and fragmented soils, and may accumulate in caves or water. Due to its very small half-life (four days for 222Rn), its concentration decreases very quickly when the distance from the production area increases.
Its atmospheric concentration varies greatly depending on the season and conditions. For instance, it has been shown to accumulate in the air if there is a meteorological inversion and little wind.
Because atmospheric radon concentrations are very low, radon-rich water exposed to air continually loses radon by volatilization. Hence, ground water generally has higher concentrations of 222Rn than surface water, because the radon is continuously produced by radioactive decay of 226Ra present in rocks. Likewise, the saturated zone of a soil frequently has a higher radon content than the unsaturated zone because of diffusional losses to the atmosphere. As a below-ground source of water, some springs—including hot springs—contain significant amounts of radon. The towns of Boulder, Montana; Misasa; Bad Kreuznach, Germany; and the country of Japan have radium-rich springs which emit radon. To be classified as a radon mineral water, radon concentration must be above a minimum of 2 nCi/L (74 Bq/L). The activity of radon mineral water reaches 2,000 Bq/L in Merano and 4,000 Bq/L in the village of Lurisia (Ligurian Alps, Italy).
Radon is also found in some petroleum. Because radon has a similar pressure and temperature curve as propane, and oil refineries separate petrochemicals based on their boiling points, the piping carrying freshly separated propane in oil refineries can become partially radioactive due to radon decay particles. Residues from the oil and gas industry often contain radium and its daughters. The sulfate scale from an oil well can be radium rich, while the water, oil, and gas from a well often contains radon. The radon decays to form solid radioisotopes which form coatings on the inside of pipework. In an oil processing plant, the area of the plant where propane is processed is often one of the more contaminated areas, because radon has a similar boiling point as propane.
Accumulation in dwellings
Typical domestic exposures are of around 100 Bq/m3 indoors, but specifics of construction and ventilation strongly affect levels of accumulation; a further complications for risk assessment is that concentrations in a single location may differ by a factor of two over an hour, and concentrations can vary greatly even between two adjoining rooms in the same structure.
The distribution of radon concentrations tends to be asymmetrical around the average, the larger concentrations have a disproportionately greater weight. Indoor radon concentration is usually assumed to follow a lognormal distribution on a given territory. Thus, the geometric mean is generally used for estimating the "average" radon concentration in an area. The mean concentration ranges from less than 10 Bq/m3 to over 100 Bq/m3 in some European countries. Typical geometric standard deviations found in studies range between 2 and 3, meaning (given the 68-95-99.7 rule) that the radon concentration is expected to be more than a hundred times the mean concentration for 2 to 3% of the cases.
The so-called "Watras incident" in 1984 (named for American construction engineer Stanley Watras), in which Watras, an employee at a U.S. nuclear power plant, triggered radiation monitors while leaving work over several days — despite the fact that the plant had not yet been fueled, and despite Watras being decontaminated and sent home "clean" each evening — pointed to a source of contamination outside the power plant, which turned out to be radon levels of 100,000 Bq/m3 (2.7 nCi/L) in the basement of his home. He was told that living in the home was the equivalent of smoking 135 packs of cigarettes a day, and he and his family had increased their risk of developing lung cancer by 13 or 14 percent. The incident dramatized the fact that radon levels in particular dwellings can occasionally be orders of magnitude higher than typical. Radon soon became a standard homeowner concern, though typical domestic exposures are two to three orders of magnitude lower (100 Bq/m3, or 2.5 pCi/L), making individual testing essential to assessment of radon risk in any particular dwelling.
Radon exists in every U.S. state, and approximately 6% of all American houses have elevated levels. The highest average radon concentrations in the United States are found in Iowa and in the Appalachian Mountain areas in southeastern Pennsylvania. Some of the highest readings have been recorded in Mallow, County Cork, Ireland. Iowa has the highest average radon concentrations in the United States due to significant glaciation that ground the granitic rocks from the Canadian Shield and deposited it as soils making up the rich Iowa farmland. Many cities within the state, such as Iowa City, have passed requirements for radon-resistant construction in new homes. In a few locations, uranium tailings have been used for landfills and were subsequently built on, resulting in possible increased exposure to radon.
Jewelry contamination
In the early 20th century, 210Pb-contaminated gold, from gold seeds that were used in radiotherapy which had held 222Rn, were melted down and made into a small number of jewelry pieces, such as rings, in the U.S. Wearing such a contaminated ring could lead to a skin exposure of 10 to 100 millirad/day (0.004 to 0.04 mSv/h).
Health effects
Cancer in miners
The health effects of high exposure to radon in mines, where exposures reaching 1,000,000 Bq/m3 can be found, can be recognized in Paracelsus' 1530 description of a wasting disease of miners, the mala metallorum. Though at the time radon itself was not understood to be the cause—indeed, neither it nor radiation had even been discovered—mineralogist Georg Agricola recommended ventilation of mines to avoid this mountain sickness (Bergsucht). In 1879, the "wasting" was identified as lung cancer by Herting and Hesse in their investigation of miners from Schneeberg, Germany.
Beyond mining in general, radon is a particular problem in the mining of uranium; significant excess lung cancer deaths have been identified in epidemiological studies of uranium miners and other hard-rock miners employed in the 1940s and 1950s. Residues from processing of uranium ore can also be a source of radon. Radon resulting from the high radium content in uncovered dumps and tailing ponds can be easily released into the atmosphere.
The first major studies with radon and health occurred in the context of uranium mining, first in the Joachimsthal region of Bohemia and then in the Southwestern United States during the early Cold War. Because radon is a product of the radioactive decay of uranium, underground uranium mines may have high concentrations of radon. Many uranium miners in the Four Corners region contracted lung cancer and other pathologies as a result of high levels of exposure to radon in the mid-1950s. The increased incidence of lung cancer was particularly pronounced among Native American and Mormon miners, because those groups normally have low rates of lung cancer. Safety standards requiring expensive ventilation were not widely implemented or policed during this period.
In studies of uranium miners, workers exposed to radon levels of 50 to 150 picocuries of radon per liter of air (2000–6000 Bq/m3) for about 10 years have shown an increased frequency of lung cancer. Statistically significant excesses in lung cancer deaths were present after cumulative exposures of less than 50 WLM. There is, however, unexplained heterogeneity in these results (whose confidence interval do not always overlap). The size of the radon-related increase in lung cancer risk varied by more than an order of magnitude between the different studies.
Heterogeneities are possibly due to systematic errors in exposure ascertainment, unaccounted for differences in the study populations (genetic, lifestyle, etc.), or confounding mine exposures. There are a number of confounding factors to consider, including exposure to other agents, ethnicity, smoking history, and work experience. The cases reported in these miners cannot be attributed solely to radon or radon daughters but may be due to exposure to silica, to other mine pollutants, to smoking, or to other causes. The majority of miners in the studies are smokers and all inhale dust and other pollutants in mines. Because radon and cigarette smoke both cause lung-cancer, and since the effect of smoking is far above that of radon, it is complicated to disentangle the effects of the two kinds of exposure; misinterpreting the smoking habit by a few percent can blur out the radon effect.
Since that time, ventilation and other measures have been used to reduce radon levels in most affected mines that continue to operate. In recent years, the average annual exposure of uranium miners has fallen to levels similar to the concentrations inhaled in some homes. This has reduced the risk of occupationally induced cancer from radon, although it still remains an issue both for those who are currently employed in affected mines and for those who have been employed in the past. The power to detect any excess risks in miners nowadays is likely to be small, exposures being much smaller than in the early years of mining.
A confounding factor with mines is that both radon concentration and carcinogenic dust (such as quartz dust) depend on the amount of ventilation. This makes it very difficult to state that radon causes cancer in miners; the lung cancers could be partially or wholly caused by high dust concentrations from poor ventilation.
Health risks
Radon-222 has been classified by International Agency for Research on Cancer as being carcinogenic to humans. In September 2009, the World Health Organization released a comprehensive global initiative on radon that recommended a reference level of 100 Bq/m3 for radon, urging establishment or strengthening of radon measurement and mitigation programs as well as development building codes requiring radon prevention measures in homes under construction. Elevated lung cancer rates have been reported from a number of cohort and case-control studies of underground miners exposed to radon and its decay products but the main confounding factor in all miners' studies is smoking and dust. Up to the most of regulatory bodies there is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of radon and its decay products in humans for such exposures. However, the discussion about the opposite results is still going on, especially a recent retrospective case-control study of lung cancer risk showed substantial cancer rate reduction between 50 and 123 Bq per cubic meter relative to a group at zero to 25 Bq per cubic meter. Additionally, the meta-analysis of many radon studies, which independently show radon risk increase, gives no confirmation of that conclusion: the joined data show log-normal distribution with the maximal value in zero risk of lung cancer below 800 Bq per cubic meter.
The primary route of exposure to radon and its progeny is inhalation. Radiation exposure from radon is indirect. The health hazard from radon does not come primarily from radon itself, but rather from the radioactive products formed in the decay of radon. The general effects of radon to the human body are caused by its radioactivity and consequent risk of radiation-induced cancer. Lung cancer is the only observed consequence of high concentration radon exposures; both human and animal studies indicate that the lung and respiratory system are the primary targets of radon daughter-induced toxicity.
Radon has a short half-life (3.8 days) and decays into other solid particulate radium-series radioactive nuclides. Two of these decay products, polonium-218 and 214, present a significant radiologic hazard. If the gas is inhaled, the radon atoms decay in the airways or the lungs, resulting in radioactive polonium and ultimately lead atoms attaching to the nearest tissue. If dust or aerosol is inhaled that already carries radon decay products, the deposition pattern of the decay products in the respiratory tract depends on the behaviour of the particles in the lungs. Smaller diameter particles diffuse further into the respiratory system, whereas the larger — tens to hundreds of micron-sized — particles often deposit higher in the airways and are cleared by the body's mucociliary staircase. Deposited radioactive atoms or dust or aerosol particles continue to decay, causing continued exposure by emitting energetic alpha radiation with some associated gamma radiation too, that can damage vital molecules in lung cells, by either creating free radicals or causing DNA breaks or damage, perhaps causing mutations that sometimes turn cancerous. In addition, through ingestion and blood transport, following crossing of the lung membrane by radon, radioactive progeny may also be transported to other parts of the body.
The risk of lung cancer caused by smoking is much higher than the risk of lung cancer caused by indoor radon. Radiation from radon has been attributed to increase of lung cancer among smokers too. It is generally believed that exposure to radon and cigarette smoking are synergistic; that is, that the combined effect exceeds the sum of their independent effects. This is because the daughters of radon often become attached to smoke and dust particles, and are then able to lodge in the lungs.
It is unknown whether radon causes other types of cancer, but recent studies suggest a need for further studies to assess the relationship between radon and leukemia.
The effects of radon, if found in food or drinking water, are unknown. Following ingestion of radon dissolved in water, the biological half-life for removal of radon from the body ranges from 30 to 70 minutes. More than 90% of the absorbed radon is eliminated by exhalation within 100 minutes, By 600 minutes, only 1% of the absorbed amount remains in the body.
Health risks in children
While radon presents the aforementioned risks in adults, exposure in children leads to a unique set of health hazards that are still being researched. The physical composition of children leads to faster rates of exposure through inhalation given that their respiratory rate is higher than that of adults, resulting in more gas exchange and more potential opportunities for radon to be inhaled.
The resulting health effects in children are similar to those of adults, predominantly including lung cancer and respiratory illnesses such as asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia. While there have been numerous studies assessing the link between radon exposure and childhood leukemia, the results are largely varied. Many ecological studies show a positive association between radon exposure and childhood leukemia; however, most case control studies have produced a weak correlation. Genotoxicity has been noted in children exposed to high levels of radon, specifically a significant increase of frequency of aberrant cells was noted, as well as an “increase in the frequencies of single and double fragments, chromosome interchanges, [and] number of aberrations chromatid and chromosome type”.
Childhood exposure
Because radon is generally associated with diseases that are not detected until many years after elevated exposure, the public may not consider the amount of radon that children are currently being exposed to. Aside from the exposure in the home, one of the major contributors to radon exposure in children are the schools in which they attend almost every day. A survey was conducted in schools across the United States to detect radon levels, and it was estimated that about one in five schools has at least one room (more than 70,000 schoolrooms) with short-term levels above 4pCi/L.
Many states have active radon testing and mitigation programs in place, which require testing in buildings such as public schools. However, these are not standardized nationwide, and the rules and regulations on reducing high radon levels are even less common. The School Health Policies and Practices Study (SHPPS), conducted by the CDC in 2012, found that of schools located in counties with high predicted indoor radon levels, only 42.4% had radon testing policies, and a mere 37.5% had policy for radon-resistant new construction practices. Only about 20% of all schools nationwide have done testing, even though the EPA recommends that every school be tested. These numbers are arguably not high enough to ensure protection of the majority of children from elevated radon exposures. For exposure standards to be effective, they should be set for those most susceptible.
Effective dose and cancer risks estimations
UNSCEAR recommends a reference value of 9 nSv (Bq·h/m3)−1. For example, a person living (7000 h/year) in a concentration of 40 Bq/m3 receives an effective dose of 1 mSv/year.
Studies of miners exposed to radon and its decay products provide a direct basis for assessing their lung cancer risk. The BEIR VI report, entitled Health Effects of Exposure to Radon, reported an excess relative risk from exposure to radon that was equivalent to 1.8% per megabecquerel hours per cubic meter (MBq·h/m3) (95% confidence interval: 0.3, 35) for miners with cumulative exposures below 30 MBq·h/m3. Estimates of risk per unit exposure are 5.38×10−4 per WLM; 9.68×10−4/WLM for ever smokers; and 1.67×10−4 per WLM for never smokers.
According to the UNSCEAR modeling, based on these miner's studies, the excess relative risk from long-term residential exposure to radon at 100 Bq/m3 is considered to be about 0.16 (after correction for uncertainties in exposure assessment), with about a threefold factor of uncertainty higher or lower than that value. In other words, the absence of ill effects (or even positive hormesis effects) at 100 Bq/m3 are compatible with the known data.
The ICPR 65 model follows the same approach, and estimates the relative lifelong risk probability of radon-induced cancer death to 1.23 × 10−6 per Bq/(m3·year). This relative risk is a global indicator; the risk estimation is independent of sex, age, or smoking habit. Thus, if a smoker's chances of dying of lung cancer are 10 times that of a nonsmoker's, the relative risks for a given radon exposure will be the same according to that model, meaning that the absolute risk of a radon-generated cancer for a smoker is (implicitly) tenfold that of a nonsmoker. The risk estimates correspond to a unit risk of approximately 3–6 × 10−5 per Bq/m3, assuming a lifetime risk of lung cancer of 3%. This means that a person living in an average European dwelling with 50 Bq/m3 has a lifetime excess lung cancer risk of 1.5–3 × 10−3. Similarly, a person living in a dwelling with a high radon concentration of 1000 Bq/m3 has a lifetime excess lung cancer risk of 3–6%, implying a doubling of background lung cancer risk.
The BEIR VI model proposed by the National Academy of Sciences of the USA is more complex. It is a multiplicative model that estimates an excess risk per exposure unit. It takes into account age, elapsed time since exposure, and duration and length of exposure, and its parameters allow for taking smoking habits into account. In the absence of other causes of death, the absolute risks of lung cancer by age 75 at usual radon concentrations of 0, 100, and 400 Bq/m3 would be about 0.4%, 0.5%, and 0.7%, respectively, for lifelong nonsmokers, and about 25 times greater (10%, 12%, and 16%) for cigarette smokers.
There is great uncertainty in applying risk estimates derived from studies in miners to the effects of residential radon, and direct estimates of the risks of residential radon are needed.
As with the miner data, the same confounding factor of other carcinogens such as dust applies. Radon concentration is high in poorly ventilated homes and buildings and such buildings tend to have poor air quality, larger concentrations of dust etc. BEIR VI did not consider that other carcinogens such as dust might be the cause of some or all of the lung cancers, thus omitting a possible spurious relationship.
Studies on domestic exposure
The largest natural contributor to public radiation dose is radon, a naturally occurring, radioactive gas found in soil and rock, which comprises approximately 55% of the annual background dose. Radon gas levels vary by locality and the composition of the underlying soil and rocks.
Radon (at concentrations encountered in mines) was recognized as carcinogenic in the 1980s, in view of the lung cancer statistics for miners' cohorts. Although radon may present significant risks, thousands of persons annually go to radon-contaminated mines for deliberate exposure to help with the symptoms of arthritis without any serious health effects.
Radon as a terrestrial source of background radiation is of particular concern because, although overall very rare, where it does occur it often does so in high concentrations. Some of these areas, including parts of Cornwall and Aberdeenshire have high enough natural radiation levels that nuclear licensed sites cannot be built there—the sites would already exceed legal limits before they opened, and the natural topsoil and rock would all have to be disposed of as low-level nuclear waste. People in affected localities can receive up to 10 mSv per year background radiation.
This led to a health policy problem: what is the health impact of exposure to radon concentrations (100 Bq/m3) typically found in some buildings?
Detection methods
When exposure to a carcinogenic substance is suspected, the cause/effect relationship on any given case can never be ascertained. Lung cancer occurs spontaneously, and there is no difference between a "natural" cancer and another one caused by radon (or smoking). Furthermore, it takes years for a cancer to develop, so that determining the past exposure of a case is usually very approximative. The health effect of radon can only be demonstrated through theory and statistical observation.
The study design for epidemiological methods may be of three kinds:
- The best proofs come from observations of cohorts (predetermined populations with known exposures and exhaustive follow-up), such as those on miners, or on Hiroshima and Nagasaki survivors. Such studies are efficient, but very costly when the population needs to be a large one. Such studies can only be used when the effect is strong enough, hence, for high exposures.
- Alternate proofs are case-control studies (the environment factors of a "case" population is individually determined, and compared to that of a "control″ population, to see what the difference might have been, and which factors may be significant), like the ones that have been used to demonstrate the link between lung cancer and smoking. Such studies can identify key factors when the signal/noise ratio is strong enough, but are very sensitive to selection bias, and prone to the existence of confounding factors.
- Lastly, ecological studies may be used (where the global environment variables and their global effect on two different populations are compared). Such studies are "cheap and dirty": they can be easily conducted on very large populations (the whole USA, in Dr Cohen's study), but are prone to the existence of confounding factors, and exposed to the ecological fallacy problem.
Furthermore, theory and observation must confirm each other for a relationship to be accepted as fully proven. Even when a statistical link between factor and effect appears significant, it must be backed by a theoretical explanation; and a theory is not accepted as factual unless confirmed by observations.
Epidemiology studies of domestic exposures
Cohort studies are impractical for the study of domestic radon exposure. With the expected effect of small exposures being very small, the direct observation of this effect would require huge cohorts: the populations of whole countries.
Several ecological studies have been performed to assess possible relationships between selected cancers and estimated radon levels within particular geographic regions where environmental radon levels appear to be higher than other geographic regions. Results of such ecological studies are mixed; both positive and negative associations, as well as no significant associations, have been suggested.
The most direct way to assess the risks posed by radon in homes is through case-control studies.
The studies have not produced a definitive answer, primarily because the risk is likely to be very small at the low exposure encountered from most homes and because it is difficult to estimate radon exposures that people have received over their lifetimes. In addition, it is clear that far more lung cancers are caused by smoking than are caused by radon.
Epidemiologic radon studies have found trends to increased lung cancer risk from radon with a no evidence of a threshold, and evidence against a threshold above high as 150 Bq/m3 (almost exactly the EPA's action level of 4 pCi/L). Another study similarly found that there is no evidence of a threshold but lacked the statistical power to clearly identify the threshold at this low level. Notably, the latter deviance from zero at low level convinced the World Health Organization that, "The dose-response relation seems to be linear without evidence of a threshold, meaning that the lung cancer risk increases proportionally with increasing radon exposure."
The most elaborate case-control epidemiologic radon study performed by R. William Field and colleagues identified a 50% increased lung cancer risk with prolonged radon exposure at the EPA's action level of 4 pCi/L. Iowa has the highest average radon concentrations in the United States and a very stable population which added to the strength of the study. For that study, the odds ratio was found to be increased slightly above the confidence interval (95% CI) for cumulative radon exposures above 17 WLM (6.2 pC/L=230 Bq/m3 and above).
The results of a methodical ten-year-long, case-controlled study of residential radon exposure in Worcester County, Massachusetts, found an apparent 60% reduction in lung cancer risk amongst people exposed to low levels (0–150 Bq/m3) of radon gas; levels typically encountered in 90% of American homes—an apparent support for the idea of radiation hormesis. In that study, a significant result (95% CI) was obtained for the 75-150 Bq/m3 category. The study paid close attention to the cohort's levels of smoking, occupational exposure to carcinogens and education attainment. However, unlike the majority of the residential radon studies, the study was not population-based. Errors in retrospective exposure assessment could not be ruled out in the finding at low levels. Other studies into the effects of domestic radon exposure have not reported a hormetic effect; including for example the respected "Iowa Radon Lung Cancer Study" of Field et al. (2000), which also used sophisticated radon exposure dosimetry.
Intentional exposure
"Radon therapy" is an intentional exposure to radon via inhalation or ingestion. Nevertheless, epidemiological evidence shows a clear link between breathing high concentrations of radon and incidence of lung cancer.
Arthritis
In the late 20th century and early 21st century, some "health mines" were established in Basin, Montana, which attracted people seeking relief from health problems such as arthritis through limited exposure to radioactive mine water and radon. The practice is controversial because of the "well-documented ill effects of high-dose radiation on the body." Radon has nevertheless been found to induce beneficial long-term effects.
Bathing
Radioactive water baths have been applied since 1906 in Jáchymov, Czech Republic, but even before radon discovery they were used in Bad Gastein, Austria. Radium-rich springs are also used in traditional Japanese onsen in Misasa, Tottori Prefecture. Drinking therapy is applied in Bad Brambach, Germany. Inhalation therapy is carried out in Gasteiner-Heilstollen, Austria, in Kowary, Poland and in Boulder, Montana, United States. In the United States and Europe there are several "radon spas", where people sit for minutes or hours in a high-radon atmosphere in the belief that low doses of radiation will invigorate or energize them.
Radiotherapy
Radon has been produced commercially for use in radiation therapy, but for the most part has been replaced by radionuclides made in accelerators and nuclear reactors. Radon has been used in implantable seeds, made of gold or glass, primarily used to treat cancers. The gold seeds were produced by filling a long tube with radon pumped from a radium source, the tube being then divided into short sections by crimping and cutting. The gold layer keeps the radon within, and filters out the alpha and beta radiations, while allowing the gamma rays to escape (which kill the diseased tissue). The activities might range from 0.05 to 5 millicuries per seed (2 to 200 MBq). The gamma rays are produced by radon and the first short-lived elements of its decay chain (218Po, 214Pb, 214Bi, 214Po).
Radon and its first decay products being very short-lived, the seed is left in place. After 11 half-lives (42 days), radon radioactivity is at 1/2000 of its original level. At this stage, the predominant residual activity is due to the radon decay product 210Pb, whose half-life (22.3 year) is 2000 times that of radon, and its descendants 210Bi and 210Po, totaling 0.03% of the initial seed activity.
Health policies
Current policy in the U.S.A.
Federal Radon Action Plan
The Federal Radon Action Plan, also known as FRAP, was created in 2010 and launched in 2011. It was piloted by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in conjunction with the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services, Agriculture, Defense, Energy, Housing and Urban Development, the Interior, Veterans Affairs, and the General Services Administration. The goal set forth by FRAP was to eliminate radon induced cancer that can be prevented by expanding radon testing, mitigating high levels of radon exposure, and developing radon resistant construction, and to meet Healthy People 2020 radon objectives. They identified the barriers to change as limited public knowledge of the dangers of radon exposure, the perceived high costs of mitigation, and the availability of radon testing. As a result, they also identified major ways to create change: demonstrate the importance of testing and the ease of mitigation, provide incentives for testing and mitigation, and build the radon services industry. To complete these goals, representatives from each organization and department established specific commitments and timelines to complete tasks and continued to meet periodically. However, FRAP was concluded in 2016 as The National Radon Action Plan took over. In the final report on commitments, it was found that FRAP completed 88% of their commitments. They reported achieving the highest rates of radon mitigation and new construction mitigation in the United States as of 2014. FRAP concluded that because of their efforts, at least 1.6 million homes, schools, and childcare facilities received direct and immediate positive effects.
National Radon Action Plan
The National Radon Action Plan, also known as NRAP, was created in 2014 and launched in 2015. It is led by The American Lung Association with collaborative efforts from the American Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists, American Society of Home Inspectors, Cancer Survivors Against Radon, Children’s Environmental Health Network, Citizens for Radioactive Radon Reduction, Conference of Radiation Control Program Directors, Environmental Law Institute, National Center for Healthy Housing, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, and U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. The goals of NRAP are to continue efforts set forth by FRAP to eliminate radon induced cancer that can be prevented by expanding radon testing, mitigating high levels of radon exposure, and developing radon resistant construction. NRAP also aims to reduce radon risk in 5 million homes, and save 3,200 lives by 2020. To complete these goals, representatives from each organization have established the following action plans: embed radon risk reduction as a standard practice across housing sectors, provide incentives and support to test and mitigate radon, promote the use of certified radon services and build the industry, and increase public attention to radon risk and the importance of reduction. The NRAP is currently in action, implementing programs, identifying approaches, and collaborating across organizations to achieve these goals.
= Policies and scientific modelling worldwide
Dose-effect model retained
The only dose-effect relationship available are those of miners cohorts (for much higher exposures), exposed to radon. Studies of Hiroshima and Nagasaki survivors are less informative (the exposure to radon is chronic, localized, and the ionizing radiations are alpha rays). Although low-exposed miners experienced exposures comparable to long-term residence in high-radon dwellings, the mean cumulative exposure among miners is approximately 30-fold higher than that associated with long-term residency in a typical home. Moreover, the smoking is a significant confounding factor in all miners' studies. It can be concluded from miner studies that when the radon exposure in dwellings compares to that in mines (above 1000 Bq/m3), radon is a proven health hazard; but in the 1980s very little was known on the dose-effect relationship, both theoretically and statistical.
Studies have been made since the 1980s, both on epidemiological studies and in the radiobiology field. In the radiobiology and carcinogenesis studies, progress has been made in understanding the first steps of cancer development, but not to the point of validating a reference dose-effect model. The only certainty gained is that the process is very complex, the resulting dose-effect response being complex, and most probably not a linear one. Biologically based models have also been proposed that could project substantially reduced carcinogenicity at low doses. In the epidemiological field, no definite conclusion has been reached. However, from the evidence now available, a threshold exposure, that is, a level of exposure below which there is no effect of radon, cannot be excluded.
Given the radon distribution observed in dwellings, and the dose-effect relationship proposed by a given model, a theoretical number of victims can be calculated, and serve as a basis for public health policies.
With the BEIR VI model, the main health effect (nearly 75% of the death toll) is to be found at low radon concentration exposures, because most of the population (about 90%) lives in the 0-200 Bq/m3 range. Under this modeling, the best policy is obviously to reduce the radon levels of all homes where the radon level is above average, because this leads to a significant decrease of radon exposure on a significant fraction of the population; but this effect is predicted in the 0-200 Bq/m3 range, where the linear model has its maximum uncertainty. From the statistical evidence available, a threshold exposure cannot be excluded; if such a threshold exists, the real radon health effect would in fact be limited to those homes where the radon concentrations reaches that observed in mines — at most a few percent. If a radiation hormesis effect exists after all, the situation would be even worse: under that hypothesis, suppressing the natural low exposure to radon (in the 0-200 Bq/m3 range) would actually lead to an increase of cancer incidence, due to the suppression of this (hypothetical) protecting effect. As the low-dose response is unclear, the choice of a model is very controversial.
No conclusive statistics being available for the levels of exposure usually found in homes, the risks posed by domestic exposures is usually estimated on the basis of observed lung-cancer deaths caused by higher exposures in mines, under the assumption that the risk of developing lung-cancer increases linearly as the exposure increases. This was the basis for the model proposed by BEIR IV in the 1980s. The linear no-threshold model has since been kept in a conservative approach by the UNSCEAR report and the BEIR VI and BEIR VII publications, essentially for lack of a better choice:
Until the [...] uncertainties on low-dose response are resolved, the Committee believes that [the linear no-threshold model] is consistent with developing knowledge and that it remains, accordingly, the most scientifically defensible approximation of low-dose response. However, a strictly linear dose response should not be expected in all circumstances.
The BEIR VI committee adopted the linear no-threshold assumption based on its understanding of the mechanisms of radon-induced lung cancer, but recognized that this understanding is incomplete and that therefore the evidence for this assumption is not conclusive.
Death toll attributed to radon
In discussing these figures, it should be kept in mind that both the radon distribution in dwelling and its effect at low exposures are not precisely known, and the radon health effect has to be computed (deaths caused by radon domestic exposure cannot be observed as such). These estimations are strongly dependent on the model retained.
According to these models, radon exposure is thought to be the second major cause of lung cancer after smoking. Iowa has the highest average radon concentration in the United States; studies performed there have demonstrated a 50% increased lung cancer risk with prolonged radon exposure above the EPA's action level of 4 pCi/L.
Based on studies carried out by the National Academy of Sciences in the United States, radon would thus be the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, and accounts for 15,000 to 22,000 cancer deaths per year in the US alone. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says that radon is the number one cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. The general population is exposed to small amounts of polonium as a radon daughter in indoor air; the isotopes 214Po and 218Po are thought to cause the majority of the estimated 15,000–22,000 lung cancer deaths in the US every year that have been attributed to indoor radon. The Surgeon General of the United States has reported that over 20,000 Americans die each year of radon-related lung cancer.
In the United Kingdom, residential radon would be, after cigarette smoking, the second most frequent cause of lung cancer deaths: according to models, 83.9% of deaths are attributed to smoking only, 1.0% to radon only, and 5.5% to a combination of radon and smoking.
The World Health Organization has recommended a radon reference concentration of 100 Bq/m3 (2.7 pCi/L). The European Union recommends that action should be taken starting from concentrations of 400 Bq/m3 (11 pCi/L) for older dwellings and 200 Bq/m3 (5 pCi/L) for newer ones. After publication of the North American and European Pooling Studies, Health Canada proposed a new guideline that lowers their action level from 800 to 200 Bq/m3 (22 to 5 pCi/L). The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) strongly recommends action for any dwelling with a concentration higher than 148 Bq/m3 (4 pCi/L), and encourages action starting at 74 Bq/m3 (2 pCi/L).
EPA recommends that all homes should be monitored for radon. If testing shows levels less than 4 picocuries radon per liter of air (160 Bq/m3), then no action is necessary. For levels of 20 picocuries radon per liter of air (800 Bq/m3) or higher, the home owner should consider some type of procedure to decrease indoor radon levels. For instance, as radon has a half-life of four days, opening the windows once a day can cut the mean radon concentration to one fourth of its level.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends homes be fixed if an occupant's long-term exposure will average 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) that is 148 Bq/m3. EPA estimates that one in 15 homes in the United States has radon levels above the recommended guideline of 4 pCi/L. EPA radon risk level tables including comparisons to other risks encountered in life are available in their citizen's guide. The EPA estimates that nationally, 8% to 12% of all dwellings are above their maximum "safe levels" (four picocuries per liter—the equivalent to roughly 200 chest x-rays). The United States Surgeon General and the EPA both recommend that all homes be tested for radon.
The limits retained do not correspond to a known threshold in the biological effect, but are determined by a cost-efficiency analysis. EPA believes that a 150 Bq/m3 level (4 pCi/L) is achievable in the majority of homes for a reasonable cost, the average cost per life saved by using this action level is about $700,000.
For radon concentration in drinkable water, the World Health Organization issued as guidelines (1988) that remedial action should be considered when the radon activity exceeded 100 kBq/m3 in a building, and remedial action should be considered without long delay if exceeding 400 kBq/m3.
Radon testing
There are relatively simple tests for radon gas. Radon test kits are commercially available. The short-term radon test kits used for screening purposes are inexpensive, in many cases free. In the United States, discounted test kits can be purchased online through The National Radon Program Services at Kansas State University or through state radon offices. Information about local radon zones and specific state contact information can be accessed through the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Map. The kit includes a collector that the user hangs in the lowest livable floor of the dwelling for 2 to 7 days. Charcoal canisters are another type of short-term radon test, and are designed to be used for 2 to 4 days. The user then sends the collector to a laboratory for analysis. Both devices are passive, meaning that they do not need power to function.
The accuracy of the residential radon test depends upon the lack of ventilation in the house when the sample is being obtained. Thus, the occupants will be instructed not to open windows, etc., for ventilation during the pendency of test, usually two days or more.
Long-term kits, taking collections for 3 months up to one year, are also available. An open-land test kit can test radon emissions from the land before construction begins. A Lucas cell is one type of long-term device. A Lucas cell is also an active device, or one that requires power to function. Active devices provide continuous monitoring, and some can report on the variation of radon and interference within the testing period. These tests usually require operation by trained testers and are often more expensive than passive testing. The National Radon Proficiency Program (NRPP) provides a list of radon measurement professionals.
Radon levels fluctuate naturally. An initial test might not be an accurate assessment of a home's average radon level. Transient weather can affect short term measurements. Therefore, a high result (over 4 pCi/L) justifies repeating the test before undertaking more expensive abatement projects. Measurements between 4 and 10 pCi/L warrant a long-term radon test. Measurements over 10 pCi/L warrant only another short-term test so that abatement measures are not unduly delayed. Purchasers of real estate are advised to delay or decline a purchase if the seller has not successfully abated radon to 4 pCi/L or less.
Since radon concentrations vary substantially from day to day, single grab-type measurements are generally not very useful, except as a means of identifying a potential problem area, and indicating a need for more sophisticated testing. The EPA recommends that an initial short-term test be performed in a closed building. An initial short-term test of 2 to 90 days allows residents to be informed quickly in case a home contains high levels of radon. Long-term tests provide a better estimate of the average annual radon level.
Mitigation
Transport of radon in indoor air is almost entirely controlled by the ventilation rate in the enclosure. Since air pressure is usually lower inside houses than it is outside, the home acts like a vacuum, drawing radon gas in through cracks in the foundation or other openings such as ventilation systems. Generally, the indoor radon concentrations increase as ventilation rates decrease. In a well ventilated place, the radon concentration tends to align with outdoor values (typically 10 Bq/m3, ranging from 1 to 100 Bq/m3).
Radon levels in indoor air can be lowered in several ways, from sealing cracks in floors and walls to increasing the ventilation rate of the building. Listed here are some of the accepted ways of reducing the amount of radon accumulating in a dwelling:
- Improving the ventilation of the dwelling and avoiding the transport of radon from the basement, or ground, into living areas;
- Installing crawlspace or basement ventilation systems;
- Installing sub-slab depressurization radon mitigation systems, which vacuum radon from under slab-on-grade foundations;
- Installing sub-membrane depressurization radon mitigation systems, which vacuum radon from under a membrane that covers the ground used in crawlspace foundations;
- Installing a radon sump system in the basement;
- Sealing floors and walls (not a stand-alone solution); and
- Installing a positive pressurization or positive supply ventilation system.
The half-life for radon is 3.8 days, indicating that once the source is removed, the hazard will be greatly reduced within approximately one month (seven half-lives).
Positive-pressure ventilation systems can be combined with a heat exchanger to recover energy in the process of exchanging air with the outside, and simply exhausting basement air to the outside is not necessarily a viable solution as this can draw radon gas into a dwelling. Homes built on a crawl space may benefit from a radon collector installed under a "radon barrier, or membrane" (a sheet of plastic or laminated polyethylene film that covers the crawl space floor).
ASTM E-2121 is a standard for reducing radon in homes as far as practicable below 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) in indoor air.
In the US, approximately 14 states have a state radon programs which train and license radon mitigation contractors and radon measurement professionals. To determine if your state licenses radon professionals contact your state health department. The National Environmental Health Association and the National Radon Safety Board administer voluntary National Radon Proficiency Programs for radon professionals consisting of individuals and companies wanting to take training courses and examinations to demonstrate their competency. Without the proper equipment or technical knowledge, radon levels can actually increase or create other potential hazards and additional costs. A list of certified mitigation service providers is available through state radon offices, which are listed on the EPA website. Indoor radon can be mitigated by sealing basement foundations, water drainage, or by sub-slab, or sub-membrane depressurization. In many cases, mitigators can use PVC piping and specialized radon suction fans to exhaust sub-slab, or sub-membrane radon and other soil gases to the outside atmosphere. Most of these solutions for radon mitigation require maintenance, and it is important to continually replace any fans or filters as needed to continue proper functioning.
Since radon gas is found in most soil and rocks, it is not only able to move into the air, but also into underground water sources. Radon may be present in well water and can be released into the air in homes when water is used for showering and other household uses. If it is suspected that a private well or drinking water may be affected by radon, the National Radon Program Services Hotline at 1-800-SOS-RADON can be contacted for information regarding state radon office phone numbers. State radon offices can provide additional resources, such as local laboratories that can test water for radon.
If it is determined that radon is present in a private well, installing either a point-of-use or point-of-entry solution may be necessary. Point-of-use treatments are installed at the tap, and are only helpful in removing radon from drinking water. To address the more common problem of breathing in radon released from water used during showers and other household activities, a point-of-entry solution may be more reliable. Point-of-entry systems usually involve a granular activated carbon filter, or an aeration system; both methods can help to remove radon before it enters the home’s water distribution system. Aeration systems and granular activation carbon filters both have advantages and disadvantages, so it is recommended to contact state radon departments or a water treatment professional for specific recommendations.
Detractors
The high cost of radon remediation in the 1980s led to detractors arguing that the issue is a financial boondoggle reminiscent of the swine flu scare of 1976. They further argued that the results of mitigation are inconsistent with lowered cancer risk, especially when indoor radon levels are in the lower range of the actionable exposure level.
See also
- International Radon Project
- Lucas cell
- Radon mitigation
- Radon removal
- Radiation Exposure Compensation Act
- Radiohalo