League of Nations Société des Nations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1920–1946 | |||||||
|
Semi-official flag (1939) | |||||||
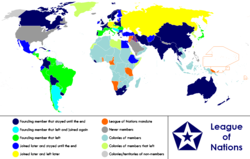 Anachronous world map showing member states of the League during its 26-year history. | |||||||
| Status | Intergovernmental organisation | ||||||
| Headquarters | Geneva | ||||||
| Common languages | French and English | ||||||
| Secretary‑General | |||||||
• 1920–1933 | Sir Eric Drummond | ||||||
• 1933–1940 | Joseph Avenol | ||||||
• 1940–1946 | Seán Lester | ||||||
| Deputy Secretary-General | |||||||
• 1919–1923 | Jean Monnet | ||||||
• 1923–1933 | Joseph Avenol | ||||||
• 1937–1940 | Seán Lester | ||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||
| 10 January 1920 | |||||||
• First meeting | 16 January 1920 | ||||||
| 20 April 1946 | |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
The League of Nations (French: Société des Nations [sɔsjete de nɑsjɔ̃]), was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. Founded on 10 January 1920 following the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War, it ceased operations on 20 April 1946.
The organisation's primary goals, as stated in its Covenant, included preventing wars through collective security and disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Its other concerns included labour conditions, just treatment of native inhabitants, human and drug trafficking, the arms trade, global health, prisoners of war, and protection of minorities in Europe. The Covenant of the League of Nations was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and it became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920. The first meeting of the Council of the League took place on 16 January 1920, and the first meeting of Assembly of the League took place on 15 November 1920. In 1919 U.S. president Woodrow Wilson won the Nobel Peace Prize for his role as the leading architect of the League.
The diplomatic philosophy behind the League represented a fundamental shift from the preceding hundred years. The League lacked its own armed force and depended on the victorious First World War Allies (Britain, France, Italy and Japan were the permanent members of the Executive Council) to enforce its resolutions, keep to its economic sanctions, or provide an army when needed. The Great Powers were often reluctant to do so. Sanctions could hurt League members, so they were reluctant to comply with them. During the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, when the League accused Italian soldiers of targeting International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement medical tents, Benito Mussolini responded that "the League is very well when sparrows shout, but no good at all when eagles fall out."
At its greatest extent from 28 September 1934 to 23 February 1935, it had 58 members. After some notable successes and some early failures in the 1920s, the League ultimately proved incapable of preventing aggression by the Axis powers in the 1930s. The credibility of the organization was weakened by the fact that the United States never joined the League and the Soviet Union joined late and was soon expelled after invading Finland. Germany withdrew from the League, as did Japan, Italy, Spain and others. The onset of the Second World War in 1939 showed that the League had failed its primary purpose; it was inactive until its abolition. The League lasted for 26 years; the United Nations (UN) replaced it in 1946 and inherited several agencies and organisations founded by the League.
Origins
Background
The concept of a peaceful community of nations had been proposed as early as 1795, when Immanuel Kant's Perpetual Peace: A Philosophical Sketch outlined the idea of a league of nations to control conflict and promote peace between states. Kant argued for the establishment of a peaceful world community, not in a sense of a global government, but in the hope that each state would declare itself a free state that respects its citizens and welcomes foreign visitors as fellow rational beings, thus promoting peaceful society worldwide. International co-operation to promote collective security originated in the Concert of Europe that developed after the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century in an attempt to maintain the status quo between European states and so avoid war.
By 1910 international law developed, with the first Geneva Conventions establishing laws dealing with humanitarian relief during wartime, and the international Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 governing rules of war and the peaceful settlement of international disputes. Theodore Roosevelt
at the acceptance for his Nobel Prize in 1910, Roosevelt said: "it
would be a masterstroke if those great powers honestly bent on peace
would form a League of Peace."
One small forerunner of the League of Nations, the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), was formed by the peace activists William Randal Cremer and Frédéric Passy in 1889 (and is currently still in existence as an international body with a focus on the various elected legislative bodies of the world.) The IPU was founded with an international scope, with a third of the members of parliaments (in the 24 countries that had parliaments) serving as members of the IPU by 1914. Its foundational aims were to encourage governments to solve international disputes by peaceful means. Annual conferences were established to help governments refine the process of international arbitration. Its structure was designed as a council headed by a president, which would later be reflected in the structure of the League.
Initial proposals
At the start of the First World War, the first schemes for an international organisation to prevent future wars began to gain considerable public support, particularly in Great Britain and the United States. Goldsworthy Lowes Dickinson, a British political scientist, coined the term "League of Nations" in 1914 and drafted a scheme for its organisation. Together with Lord Bryce, he played a leading role in the founding of the group of internationalist pacifists known as the Bryce Group, later the League of Nations Union. The group became steadily more influential among the public and as a pressure group within the then governing Liberal Party. In Dickinson's 1915 pamphlet After the War he wrote of his "League of Peace" as being essentially an organisation for arbitration and conciliation. He felt that the secret diplomacy of the early twentieth century had brought about war and thus could write that, "the impossibility of war, I believe, would be increased in proportion as the issues of foreign policy should be known to and controlled by public opinion." The ‘Proposals’ of the Bryce Group were circulated widely, both in England and the US, where they had a profound influence on the nascent international movement.
In January 1915, a peace conference directed by Jane Addams was held in the neutral United States. The delegates adopted a platform calling for creation of international bodies with administrative and legislative powers to develop a "permanent league of neutral nations" to work for peace and disarmament. Within months a call was made for an international women's conference to be held in The Hague. Coordinated by Mia Boissevain, Aletta Jacobs and Rosa Manus, the Congress, which opened on 28 April 1915 was attended by 1,136 participants from neutral nations, and resulted in the establishment of an organization which would become the Women's International League for Peace and Freedom (WILPF). At the close of the conference, two delegations of women were dispatched to meet European heads of state over the next several months. They secured agreement from reluctant foreign ministers, who overall felt that such a body would be ineffective, but agreed to participate or not impede creation of a neutral mediating body, if other nations agreed and if President Woodrow Wilson would initiate a body. In the midst of the War, Wilson refused.
In 1915, a similar body to the Bryce group was set up in the United States led by former president William Howard Taft. It was called the League to Enforce Peace. It advocated the use of arbitration in conflict resolution and the imposition of sanctions on aggressive countries. None of these early organisations envisioned a continuously functioning body; with the exception of the Fabian Society in England, they maintained a legalistic approach that would limit the international body to a court of justice. The Fabians were the first to argue for a "Council" of states, necessarily the Great Powers, who would adjudicate world affairs, and for the creation of a permanent secretariat to enhance international co-operation across a range of activities.
In the course of the diplomatic efforts surrounding World War I, both sides had to clarify their long-term war aims. By 1916 in Britain, fighting on the side of the Allies, and in the neutral United States, long-range thinkers had begun to design a unified international organisation to prevent future wars. Historian Peter Yearwood argues that when the new coalition government of David Lloyd George took power in December 1916, there was widespread discussion among intellectuals and diplomats of the desirability of establishing such an organisation. When Lloyd George was challenged by Wilson to state his position with an eye on the postwar situation, he endorsed such an organisation. Wilson himself included in his Fourteen Points in January 1918 a "league of nations to ensure peace and justice." British foreign secretary, Arthur Balfour, argued that, as a condition of durable peace, "behind international law, and behind all treaty arrangements for preventing or limiting hostilities, some form of international sanction should be devised which would give pause to the hardiest aggressor."
The war had had a profound impact, affecting the social, political and economic systems of Europe and inflicting psychological and physical damage. Several empires collapsed: first the Russian Empire in February 1917, followed by the German Empire, Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Anti-war sentiment rose across the world; the First World War was described as "the war to end all wars", and its possible causes were vigorously investigated. The causes identified included arms races, alliances, militaristic nationalism, secret diplomacy, and the freedom of sovereign states to enter into war for their own benefit. One proposed remedy was the creation of an international organisation whose aim was to prevent future war through disarmament, open diplomacy, international co-operation, restrictions on the right to wage war, and penalties that made war unattractive.
In London Balfour commissioned the first official report into the matter in early 1918, under the initiative of Lord Robert Cecil. The British committee was finally appointed in February 1918. It was led by Walter Phillimore (and became known as the Phillimore Committee), but also included Eyre Crowe, William Tyrrell, and Cecil Hurst. The recommendations of the so-called Phillimore Commission included the establishment of a "Conference of Allied States" that would arbitrate disputes and impose sanctions on offending states. The proposals were approved by the British government, and much of the commission's results were later incorporated into the Covenant of the League of Nations.
The French also drafted a much more far-reaching proposal in June 1918; they advocated annual meetings of a council to settle all disputes, as well as an "international army" to enforce its decisions.
American President Woodrow Wilson instructed Edward M. House to draft a US plan which reflected Wilson's own idealistic views (first articulated in the Fourteen Points of January 1918), as well as the work of the Phillimore Commission. The outcome of House's work and Wilson's own first draft proposed the termination of "unethical" state behaviour, including forms of espionage and dishonesty. Methods of compulsion against recalcitrant states would include severe measures, such as "blockading and closing the frontiers of that power to commerce or intercourse with any part of the world and to use any force that may be necessary..."
The two principal drafters and architects of the covenant of the League of Nations were the British politician Lord Robert Cecil and the South African statesman Jan Smuts. Smuts' proposals included the creation of a Council of the great powers as permanent members and a non-permanent selection of the minor states. He also proposed the creation of a Mandate system for captured colonies of the Central Powers during the war. Cecil focused on the administrative side and proposed annual Council meetings and quadrennial meetings for the Assembly of all members. He also argued for a large and permanent secretariat to carry out the League's administrative duties.
The League of Nations was relatively more universal and inclusive in its membership and structure than previous international organisations, but the organisation enshrined racial hierarchy by curtailing the right to self-determination and prevented decolonization.
Establishment
At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Wilson, Cecil and Smuts all put forward their draft proposals. After lengthy negotiations between the delegates, the Hurst–Miller draft was finally produced as a basis for the Covenant. After more negotiation and compromise, the delegates finally approved of the proposal to create the League of Nations (French: Société des Nations, German: Völkerbund) on 25 January 1919. The final Covenant of the League of Nations was drafted by a special commission, and the League was established by Part I of the Treaty of Versailles. On 28 June 1919, 44 states signed the Covenant, including 31 states which had taken part in the war on the side of the Triple Entente or joined it during the conflict.
French women's rights advocates invited international feminists to participate in a parallel conference to the Paris Conference in hopes that they could gain permission to participate in the official conference. The Inter-Allied Women's Conference asked to be allowed to submit suggestions to the peace negotiations and commissions and were granted the right to sit on commissions dealing specifically with women and children. Though they asked for enfranchisement and full legal protection under the law equal with men, those rights were ignored. Women won the right to serve in all capacities, including as staff or delegates in the League of Nations organization. They also won a declaration that member nations should prevent trafficking of women and children and should equally support humane conditions for children, women and men labourers. At the Zürich Peace Conference held between 17 and 19 May 1919, the women of the WILPF condemned the terms of the Treaty of Versailles for both its punitive measures, as well as its failure to provide for condemnation of violence and exclusion of women from civil and political participation. Upon reading the Rules of Procedure for the League of Nations, Catherine Marshall, a British suffragist, discovered that the guidelines were completely undemocratic and they were modified based on her suggestion.
The League would be made up of a General Assembly (representing all member states), an Executive Council (with membership limited to major powers), and a permanent secretariat. Member states were expected to "respect and preserve as against external aggression" the territorial integrity of other members and to disarm "to the lowest point consistent with domestic safety." All states were required to submit complaints for arbitration or judicial inquiry before going to war. The Executive Council would create a Permanent Court of International Justice to make judgements on the disputes.
Despite Wilson's efforts to establish and promote the League, for which he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in October 1919, the United States never joined. Senate Republicans led by Henry Cabot Lodge wanted a League with the reservation that only Congress could take the U.S. into war. Lodge gained a majority of Senators and Wilson refused to allow a compromise. The Senate voted on the ratification on March 19, 1920, and the 49-35 vote fell short of the needed 2/3 majority.
The League held its first council meeting in Paris on 16 January 1920, six days after the Versailles Treaty and the Covenant of the League of Nations came into force. On 1 November 1920, the headquarters of the League was moved from London to Geneva, where the first General Assembly was held on 15 November 1920. The Palais Wilson on Geneva's western lakeshore, named after Woodrow Wilson, was the League's first permanent home.
Languages and symbols
The official languages of the League of Nations were French and English.
In 1939, a semi-official emblem for the League of Nations emerged: two five-pointed stars within a blue pentagon. They symbolised the Earth's five continents and "five races." A bow at the top displayed the English name ("League of Nations"), while another at the bottom showed the French ("Société des Nations").
Principal organs
The main constitutional organs of the League were the Assembly, the council, and the Permanent Secretariat. It also had two essential wings: the Permanent Court of International Justice and the International Labour Organization. In addition, there were several auxiliary agencies and commissions. Each organ's budget was allocated by the Assembly (the League was supported financially by its member states).
The relations between the Assembly and the Council and the competencies of each were for the most part not explicitly defined. Each body could deal with any matter within the sphere of competence of the League or affecting peace in the world. Particular questions or tasks might be referred to either.
Unanimity was required for the decisions of both the Assembly and the Council, except in matters of procedure and some other specific cases such as the admission of new members. This requirement was a reflection of the League's belief in the sovereignty of its component nations; the League sought a solution by consent, not by dictation. In case of a dispute, the consent of the parties to the dispute was not required for unanimity.
The Permanent Secretariat, established at the seat of the League at Geneva, comprised a body of experts in various spheres under the direction of the general secretary. Its principal sections were Political, Financial and Economics, Transit, Minorities and Administration (administering the Saar and Danzig), Mandates, Disarmament, Health, Social (Opium and Traffic in Women and Children), Intellectual Cooperation and International Bureaux, Legal, and Information. The staff of the Secretariat was responsible for preparing the agenda for the Council and the Assembly and publishing reports of the meetings and other routine matters, effectively acting as the League's civil service. In 1931 the staff numbered 707.
The Assembly consisted of representatives of all members of the League, with each state allowed up to three representatives and one vote. It met in Geneva and, after its initial sessions in 1920, it convened once a year in September. The special functions of the Assembly included the admission of new members, the periodical election of non-permanent members to the Council, the election with the Council of the judges of the Permanent Court, and control of the budget. In practice, the Assembly was the general directing force of League activities.
The League Council acted as a type of executive body directing the Assembly's business. It began with four permanent members – Great Britain, France, Italy, and Japan – and four non-permanent members that were elected by the Assembly for a three-year term. The first non-permanent members were Belgium, Brazil, Greece, and Spain.
The composition of the Council was changed several times. The number of non-permanent members was first increased to six on 22 September 1922 and to nine on 8 September 1926. Werner Dankwort of Germany pushed for his country to join the League; joining in 1926, Germany became the fifth permanent member of the Council. Later, after Germany and Japan both left the League, the number of non-permanent seats was increased from nine to eleven, and the Soviet Union was made a permanent member giving the Council a total of fifteen members. The Council met, on average, five times a year and in extraordinary sessions when required. In total, 107 sessions were held between 1920 and 1939.
Other bodies
The League oversaw the Permanent Court of International Justice and several other agencies and commissions created to deal with pressing international problems. These included the Disarmament Commission, the International Labour Organization (ILO), the Mandates Commission, the International Commission on Intellectual Cooperation (precursor to UNESCO), the Permanent Central Opium Board, the Commission for Refugees, and the Slavery Commission. Three of these institutions were transferred to the United Nations after the Second World War: the International Labour Organization, the Permanent Court of International Justice (as the International Court of Justice), and the Health Organisation (restructured as the World Health Organization).
The Permanent Court of International Justice was provided for by the Covenant, but not established by it. The Council and the Assembly established its constitution. Its judges were elected by the Council and the Assembly, and its budget was provided by the latter. The Court was to hear and decide any international dispute which the parties concerned submitted to it. It might also give an advisory opinion on any dispute or question referred to it by the Council or the Assembly. The Court was open to all the nations of the world under certain broad conditions.
The International Labour Organization was created in 1919 on the basis of Part XIII of the Treaty of Versailles. The ILO, although having the same members as the League and being subject to the budget control of the Assembly, was an autonomous organisation with its own Governing Body, its own General Conference and its own Secretariat. Its constitution differed from that of the League: representation had been accorded not only to governments but also to representatives of employers' and workers' organisations. Albert Thomas was its first director.
The ILO successfully restricted the addition of lead to paint, and convinced several countries to adopt an eight-hour work day and forty-eight-hour working week. It also campaigned to end child labour, increase the rights of women in the workplace, and make shipowners liable for accidents involving seamen. After the demise of the League, the ILO became an agency of the United Nations in 1946.
The League's health organisation had three bodies: the Health Bureau, containing permanent officials of the League; the General Advisory Council or Conference, an executive section consisting of medical experts; and the Health Committee. The committee's purpose was to conduct inquiries, oversee the operation of the League's health work, and prepare work to be presented to the council. This body focused on ending leprosy, malaria, and yellow fever, the latter two by starting an international campaign to exterminate mosquitoes. The Health Organisation also worked successfully with the government of the Soviet Union to prevent typhus epidemics, including organising a large education campaign.
The League of Nations had devoted serious attention to the question of international intellectual co-operation since its creation. The First Assembly in December 1920 recommended that the Council take action aiming at the international organisation of intellectual work, which it did by adopting a report presented by the Fifth Committee of the Second Assembly and inviting a Committee on Intellectual Cooperation to meet in Geneva in August 1922. The French philosopher Henri Bergson became the first chairman of the committee. The work of the committee included: an inquiry into the conditions of intellectual life, assistance to countries where intellectual life was endangered, creation of national committees for intellectual co-operation, co-operation with international intellectual organisations, protection of intellectual property, inter-university co-operation, co-ordination of bibliographical work and international interchange of publications, and international co-operation in archaeological research.
Introduced by the second International Opium Convention, the Permanent Central Opium Board had to supervise the statistical reports on trade in opium, morphine, cocaine and heroin. The board also established a system of import certificates and export authorisations for the legal international trade in narcotics.
The Slavery Commission sought to eradicate slavery and slave trading across the world, and fought forced prostitution. Its main success was through pressing the governments who administered mandated countries to end slavery in those countries. The League secured a commitment from Ethiopia to end slavery as a condition of membership in 1923, and worked with Liberia to abolish forced labour and intertribal slavery. The United Kingdom had not supported Ethiopian membership of the League on the grounds that "Ethiopia had not reached a state of civilisation and internal security sufficient to warrant her admission."
The League also succeeded in reducing the death rate of workers constructing the Tanganyika railway from 55 to 4 percent. Records were kept to control slavery, prostitution, and the trafficking of women and children. Partly as a result of pressure brought by the League of Nations, Afghanistan abolished slavery in 1923, Iraq in 1924, Nepal in 1926, Transjordan and Persia in 1929, Bahrain in 1937, and Ethiopia in 1942.
Led by Fridtjof Nansen, the Commission for Refugees was established on 27 June 1921 to look after the interests of refugees, including overseeing their repatriation and, when necessary, resettlement. At the end of the First World War, there were two to three million ex-prisoners of war from various nations dispersed throughout Russia; within two years of the commission's foundation, it had helped 425,000 of them return home. It established camps in Turkey in 1922 to aid the country with an ongoing refugee crisis, helping to prevent the spread of cholera, smallpox and dysentery as well as feeding the refugees in the camps. It also established the Nansen passport as a means of identification for stateless people.
The Committee for the Study of the Legal Status of Women sought to inquire into the status of women all over the world. It was formed in 1937, and later became part of the United Nations as the Commission on the Status of Women.
The Covenant of the League said little about economics. Nonetheless, in 1920 the Council of the League called for a financial conference. The First Assembly at Geneva provided for the appointment of an Economic and Financial Advisory Committee to provide information to the conference. In 1923, a permanent economic and financial Organization came into being.
Members
Of the League's 42 founding members, 23 (24 counting Free France) remained members until it was dissolved in 1946. In the founding year, six other states joined, only two of which remained members throughout the League's existence. Under the Weimar Republic, Germany was admitted to the League of Nations through a resolution passed on 8 September 1926.
An additional 15 countries joined later. The largest number of member states was 58, between 28 September 1934 (when Ecuador joined) and 23 February 1935 (when Paraguay withdrew).
On 26 May 1937, Egypt became the last state to join the League. The first member to withdraw permanently from the League was Costa Rica on 22 January 1925; having joined on 16 December 1920, this also makes it the member to have most quickly withdrawn. Brazil was the first founding member to withdraw (14 June 1926), and Haiti the last (April 1942). Iraq, which joined in 1932, was the first member that had previously been a League of Nations mandate.
The Soviet Union became a member on 18 September 1934, and was expelled on 14 December 1939 for invading Finland. In expelling the Soviet Union, the League broke its own rule: only 7 of 15 members of the Council voted for expulsion (United Kingdom, France, Belgium, Bolivia, Egypt, South Africa, and the Dominican Republic), short of the majority required by the Covenant. Three of these members had been made Council members the day before the vote (South Africa, Bolivia, and Egypt). This was one of the League's final acts before it practically ceased functioning due to the Second World War.
Mandates
At the end of the First World War, the Allied powers were confronted with the question of the disposal of the former German colonies in Africa and the Pacific, and the several Arabic-speaking provinces of the Ottoman Empire. The Peace Conference adopted the principle that these territories should be administered by different governments on behalf of the League – a system of national responsibility subject to international supervision. This plan, defined as the mandate system, was adopted by the "Council of Ten" (the heads of government and foreign ministers of the main Allied powers: Britain, France, the United States, Italy, and Japan) on 30 January 1919 and transmitted to the League of Nations.
League of Nations mandates were established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations. The Permanent Mandates Commission supervised League of Nations mandates, and also organised plebiscites in disputed territories so that residents could decide which country they would join. There were three mandate classifications: A, B and C.
The A mandates (applied to parts of the old Ottoman Empire) were "certain communities" that had
...reached a stage of development where their existence as independent nations can be provisionally recognised subject to the rendering of administrative advice and assistance by a Mandatory until such time as they are able to stand alone. The wishes of these communities must be a principal consideration in the selection of the Mandatory.
— Article 22, The Covenant of the League of Nations
The B mandates were applied to the former German colonies that the League took responsibility for after the First World War. These were described as "peoples" that the League said were
...at such a stage that the Mandatory must be responsible for the administration of the territory under conditions which will guarantee freedom of conscience and religion, subject only to the maintenance of public order and morals, the prohibition of abuses such as the slave trade, the arms traffic and the liquor traffic, and the prevention of the establishment of fortifications or military and naval bases and of military training of the natives for other than police purposes and the defence of territory, and will also secure equal opportunities for the trade and commerce of other Members of the League.
— Article 22, The Covenant of the League of Nations
South West Africa and certain South Pacific Islands were administered by League members under C mandates. These were classified as "territories"
...which, owing to the sparseness of their population, or their small size, or their remoteness from the centres of civilisation, or their geographical contiguity to the territory of the Mandatory, and other circumstances, can be best administered under the laws of the Mandatory as integral portions of its territory, subject to the safeguards above mentioned in the interests of the indigenous population."
— Article 22, The Covenant of the League of Nations
Mandatory powers
The territories were governed by mandatory powers, such as the United Kingdom in the case of the Mandate of Palestine, and the Union of South Africa in the case of South-West Africa, until the territories were deemed capable of self-government. Fourteen mandate territories were divided up among seven mandatory powers: the United Kingdom, the Union of South Africa, France, Belgium, New Zealand, Australia and Japan. With the exception of the Kingdom of Iraq, which joined the League on 3 October 1932, these territories did not begin to gain their independence until after the Second World War, in a process that did not end until 1990. Following the demise of the League, most of the remaining mandates became United Nations Trust Territories.
In addition to the mandates, the League itself governed the Territory of the Saar Basin for 15 years, before it was returned to Germany following a plebiscite, and the Free City of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland) from 15 November 1920 to 1 September 1939.
Resolving territorial disputes
The aftermath of the First World War left many issues to be settled, including the exact position of national boundaries and which country particular regions would join. Most of these questions were handled by the victorious Allied powers in bodies such as the Allied Supreme Council. The Allies tended to refer only particularly difficult matters to the League. This meant that, during the early interwar period, the League played little part in resolving the turmoil resulting from the war. The questions the League considered in its early years included those designated by the Paris Peace treaties.
As the League developed, its role expanded, and by the middle of the 1920s it had become the centre of international activity. This change can be seen in the relationship between the League and non-members. The United States and Russia, for example, increasingly worked with the League. During the second half of the 1920s, France, Britain and Germany were all using the League of Nations as the focus of their diplomatic activity, and each of their foreign secretaries attended League meetings at Geneva during this period. They also used the League's machinery to try to improve relations and settle their differences.
Åland Islands
Åland is a collection of around 6,500 islands in the Baltic Sea, midway between Sweden and Finland. The islands are almost exclusively Swedish-speaking, but in 1809, the Åland Islands, along with Finland, were taken by Imperial Russia. In December 1917, during the turmoil of the Russian October Revolution, Finland declared its independence, but most of the Ålanders wished to rejoin Sweden. The Finnish government considered the islands to be a part of their new nation, as the Russians had included Åland in the Grand Duchy of Finland, formed in 1809. By 1920, the dispute had escalated to the point that there was danger of war. The British government referred the problem to the League's Council, but Finland would not let the League intervene, as they considered it an internal matter. The League created a small panel to decide if it should investigate the matter and, with an affirmative response, a neutral commission was created. In June 1921, the League announced its decision: the islands were to remain a part of Finland, but with guaranteed protection of the islanders, including demilitarisation. With Sweden's reluctant agreement, this became the first European international agreement concluded directly through the League.
Upper Silesia
The Allied powers referred the problem of Upper Silesia to the League after they had been unable to resolve the territorial dispute between Poland and Germany. In 1919 Poland voiced a claim to Upper Silesia, which had been part of Prussia. The Treaty of Versailles had recommended a plebiscite in Upper Silesia to determine whether the territory should become part of Germany or Poland. Complaints about the attitude of the German authorities led to rioting and eventually to the first two Silesian Uprisings (1919 and 1920). A plebiscite took place on 20 March 1921, with 59.6 per cent (around 500,000) of the votes cast in favour of joining Germany, but Poland claimed the conditions surrounding it had been unfair. This result led to the Third Silesian Uprising in 1921.
On 12 August 1921, the League was asked to settle the matter; the Council created a commission with representatives from Belgium, Brazil, China and Spain to study the situation. The committee recommended that Upper Silesia be divided between Poland and Germany according to the preferences shown in the plebiscite and that the two sides should decide the details of the interaction between the two areas – for example, whether goods should pass freely over the border due to the economic and industrial interdependence of the two areas. In November 1921, a conference was held in Geneva to negotiate a convention between Germany and Poland. A final settlement was reached, after five meetings, in which most of the area was given to Germany, but with the Polish section containing the majority of the region's mineral resources and much of its industry. When this agreement became public in May 1922, bitter resentment was expressed in Germany, but the treaty was still ratified by both countries. The settlement produced peace in the area until the beginning of the Second World War.
Albania
The frontiers of the Principality of Albania had not been set during the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, as they were left for the League to decide. They had not yet been determined by September 1921, creating an unstable situation. Greek troops conducted military operations in the south of Albania. Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslav) forces became engaged, after clashes with Albanian tribesmen, in the northern part of the country. The League sent a commission of representatives from various powers to the region. In November 1921, the League decided that the frontiers of Albania should be the same as they had been in 1913, with three minor changes that favoured Yugoslavia. Yugoslav forces withdrew a few weeks later, albeit under protest.
The borders of Albania again became the cause of international conflict when Italian General Enrico Tellini and four of his assistants were ambushed and killed on 24 August 1923 while marking out the newly decided border between Greece and Albania. Italian leader Benito Mussolini was incensed and demanded that a commission investigate the incident within five days. Whatever the results of the investigation, Mussolini insisted that the Greek government pay Italy fifty million lire in reparations. The Greeks said they would not pay unless it was proved that the crime was committed by Greeks.
Mussolini sent a warship to shell the Greek island of Corfu, and Italian forces occupied the island on 31 August 1923. This contravened the League's covenant, so Greece appealed to the League to deal with the situation. The Allies agreed (at Mussolini's insistence) that the Conference of Ambassadors should be responsible for resolving the dispute because it was the conference that had appointed General Tellini. The League Council examined the dispute, but then passed on their findings to the Conference of Ambassadors to make the final decision. The conference accepted most of the League's recommendations, forcing Greece to pay fifty million lire to Italy, even though those who committed the crime were never discovered. Italian forces then withdrew from Corfu.
Memel
The port city of Memel (now Klaipėda) and the surrounding area, with a predominantly German population, was under provisional Entente control according to Article 99 of the Treaty of Versailles. The French and Polish governments favoured turning Memel into an international city, while Lithuania wanted to annex the area. By 1923, the fate of the area had still not been decided, prompting Lithuanian forces to invade in January 1923 and seize the port. After the Allies failed to reach an agreement with Lithuania, they referred the matter to the League of Nations. In December 1923, the League Council appointed a Commission of Inquiry. The commission chose to cede Memel to Lithuania and give the area autonomous rights. The Klaipėda Convention was approved by the League Council on 14 March 1924, and then by the Allied powers and Lithuania. In 1939 Germany retook the region following the rise of the Nazis and an ultimatum to Lithuania, demanding the return of the region under threat of war. The League of Nations failed to prevent the secession of the Memel region to Germany.
Hatay
With League oversight, the Sanjak of Alexandretta in the French Mandate of Syria was given autonomy in 1937. Renamed Hatay, its parliament declared independence as the Republic of Hatay in September 1938, after elections the previous month. It was annexed by Turkey with French consent in mid-1939.
Mosul
The League resolved a dispute between the Kingdom of Iraq and the Republic of Turkey over control of the former Ottoman province of Mosul in 1926. According to the British, who had been awarded a League of Nations mandate over Iraq in 1920 and therefore represented Iraq in its foreign affairs, Mosul belonged to Iraq; on the other hand, the new Turkish republic claimed the province as part of its historic heartland. A League of Nations Commission of Inquiry, with Belgian, Hungarian and Swedish members, was sent to the region in 1924; it found that the people of Mosul did not want to be part of either Turkey or Iraq, but if they had to choose, they would pick Iraq. In 1925, the commission recommended that the region stay part of Iraq, under the condition that the British hold the mandate over Iraq for another 25 years, to ensure the autonomous rights of the Kurdish population. The League Council adopted the recommendation and decided on 16 December 1925 to award Mosul to Iraq. Although Turkey had accepted the League of Nations' arbitration in the Treaty of Lausanne (1923), it rejected the decision, questioning the Council's authority. The matter was referred to the Permanent Court of International Justice, which ruled that, when the Council made a unanimous decision, it must be accepted. Nonetheless, Britain, Iraq and Turkey ratified a separate treaty on 5 June 1926 that mostly followed the decision of the League Council and also assigned Mosul to Iraq. It was agreed that Iraq could still apply for League membership within 25 years and that the mandate would end upon its admission.
Vilnius
After the First World War, Poland and Lithuania both regained their independence but soon became immersed in territorial disputes. During the Polish–Soviet War, Lithuania signed the Moscow Peace Treaty with the Soviet Union that laid out Lithuania's frontiers. This agreement gave Lithuanians control of the city of Vilnius (Lithuanian: Vilnius, Polish: Wilno), the old Lithuanian capital, but a city with a majority Polish population. This heightened tension between Lithuania and Poland and led to fears that they would resume the Polish–Lithuanian War, and on 7 October 1920, the League negotiated the Suwałki Agreement establishing a cease-fire and a demarcation line between the two nations. On 9 October 1920, General Lucjan Żeligowski, commanding a Polish military force in contravention of the Suwałki Agreement, took the city and established the Republic of Central Lithuania.
After a request for assistance from Lithuania, the League Council called for Poland's withdrawal from the area. The Polish government indicated they would comply, but instead reinforced the city with more Polish troops. This prompted the League to decide that the future of Vilnius should be determined by its residents in a plebiscite and that the Polish forces should withdraw and be replaced by an international force organised by the League. The plan was met with resistance in Poland, Lithuania, and the Soviet Union, which opposed any international force in Lithuania. In March 1921, the League abandoned plans for the plebiscite. After unsuccessful proposals by Paul Hymans to create a federation between Poland and Lithuania, which was intended as a reincarnation of the former union which both Poland and Lithuania had once shared before losing its independence, Vilnius and the surrounding area was formally annexed by Poland in March 1922. After Lithuania took over the Klaipėda Region, the Allied Conference set the frontier between Lithuania and Poland, leaving Vilnius within Poland, on 14 March 1923. Lithuanian authorities refused to accept the decision, and officially remained in a state of war with Poland until 1927. It was not until the 1938 Polish ultimatum that Lithuania restored diplomatic relations with Poland and thus de facto accepted the borders.
Colombia and Peru
There were several border conflicts between Colombia and Peru in the early part of the 20th century, and in 1922, their governments signed the Salomón-Lozano Treaty in an attempt to resolve them. As part of this treaty, the border town of Leticia and its surrounding area was ceded from Peru to Colombia, giving Colombia access to the Amazon River. On 1 September 1932, business leaders from Peruvian rubber and sugar industries who had lost land, as a result, organised an armed takeover of Leticia. At first, the Peruvian government did not recognise the military takeover, but President of Peru Luis Sánchez Cerro decided to resist a Colombian re-occupation. The Peruvian Army occupied Leticia, leading to an armed conflict between the two nations. After months of diplomatic negotiations, the governments accepted mediation by the League of Nations, and their representatives presented their cases before the Council. A provisional peace agreement, signed by both parties in May 1933, provided for the League to assume control of the disputed territory while bilateral negotiations proceeded. In May 1934, a final peace agreement was signed, resulting in the return of Leticia to Colombia, a formal apology from Peru for the 1932 invasion, demilitarisation of the area around Leticia, free navigation on the Amazon and Putumayo Rivers, and a pledge of non-aggression.
Saar
Saar was a province formed from parts of Prussia and the Rhenish Palatinate and placed under League control by the Treaty of Versailles. A plebiscite was to be held after fifteen years of League rule to determine whether the province should belong to Germany or France. When the referendum was held in 1935, 90.3 per cent of voters supported becoming part of Germany, which was quickly approved by the League Council.
Other conflicts
In addition to territorial disputes, the League also tried to intervene in other conflicts between and within nations. Among its successes were its fight against the international trade in opium and sexual slavery, and its work to alleviate the plight of refugees, particularly in Turkey in the period up to 1926. One of its innovations in this latter area was the 1922 introduction of the Nansen passport, which was the first internationally recognised identity card for stateless refugees.
Greece and Bulgaria
After an incident involving sentries on the Greek-Bulgarian border in October 1925, fighting began between the two countries. Three days after the initial incident, Greek troops invaded Bulgaria. The Bulgarian government ordered its troops to make only token resistance, and evacuated between ten thousand and fifteen thousand people from the border region, trusting the League to settle the dispute. The League condemned the Greek invasion, and called for both Greek withdrawal and compensation to Bulgaria.
Liberia
Following accusations of forced labour on the large American-owned Firestone rubber plantation and American accusations of slave trading, the Liberian government asked the League to launch an investigation. The resulting commission was jointly appointed by the League, the United States, and Liberia. In 1930, a League report confirmed the presence of slavery and forced labour. The report implicated many government officials in the selling of contract labour and recommended that they be replaced by Europeans or Americans, which generated anger within Liberia and led to the resignation of President Charles D. B. King and his vice-president. The Liberian government outlawed forced labour and slavery and asked for American help in social reforms.
Mukden Incident: Japan attacks China
The Mukden Incident, also known as the "Manchurian Incident" was a decisive setback that weakened The League because its major members refused to tackle Japanese aggression. Japan itself withdrew.
Under the agreed terms of the Twenty-One Demands with China, the Japanese government had the right to station its troops in the area around the South Manchurian Railway, a major trade route between the two countries, in the Chinese region of Manchuria. In September 1931, a section of the railway was lightly damaged by the Japanese Kwantung Army as a pretext for an invasion of Manchuria. The Japanese army claimed that Chinese soldiers had sabotaged the railway and in apparent retaliation (acting contrary to orders from Tokyo) occupied all of Manchuria. They renamed the area Manchukuo, and on 9 March 1932 set up a puppet government, with Pu Yi, the former emperor of China, as its executive head. This new entity was recognised only by the governments of Italy, Spain and Nazi Germany; the rest of the world still considered Manchuria legally part of China.
The League of Nations sent observers. The Lytton Report appeared a year later (October 1932). It declared Japan to be the aggressor and demanded Manchuria be returned to China. The report passed 42–1 in the Assembly in 1933 (only Japan voting against), but instead of removing its troops from China, Japan withdrew from the League. In the end, as British historian Charles Mowat argued, collective security was dead:
- The League and the ideas of collective security and the rule of law were defeated; partly because of indifference and of sympathy with the aggressor, but partly because the League powers were unprepared, preoccupied with other matters, and too slow to perceive the scale of Japanese ambitions.
Chaco War
The League failed to prevent the 1932 war between Bolivia and Paraguay over the arid Gran Chaco region. Although the region was sparsely populated, it contained the Paraguay River, which would have given either landlocked country access to the Atlantic Ocean, and there was also speculation, later proved incorrect, that the Chaco would be a rich source of petroleum. Border skirmishes throughout the late 1920s culminated in an all-out war in 1932 when the Bolivian army attacked the Paraguayans at Fort Carlos Antonio López at Lake Pitiantuta. Paraguay appealed to the League of Nations, but the League did not take action when the Pan-American Conference offered to mediate instead. The war was a disaster for both sides, causing 57,000 casualties for Bolivia, whose population was around three million, and 36,000 dead for Paraguay, whose population was approximately one million. It also brought both countries to the brink of economic disaster. By the time a ceasefire was negotiated on 12 June 1935, Paraguay had seized control of most of the region, as was later recognised by the 1938 truce.
Italian invasion of Abyssinia
In October 1935, Italian dictator Benito Mussolini sent 400,000 troops to invade Abyssinia (Ethiopia). Marshal Pietro Badoglio led the campaign from November 1935, ordering bombing, the use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas, and the poisoning of water supplies, against targets which included undefended villages and medical facilities. The modern Italian Army defeated the poorly armed Abyssinians and captured Addis Ababa in May 1936, forcing Emperor of Ethiopia Haile Selassie to flee.
The League of Nations condemned Italy's aggression and imposed economic sanctions in November 1935, but the sanctions were largely ineffective since they did not ban the sale of oil or close the Suez Canal (controlled by Britain). As Stanley Baldwin, the British Prime Minister, later observed, this was ultimately because no one had the military forces on hand to withstand an Italian attack. In October 1935, the US president, Franklin D. Roosevelt, invoked the recently passed Neutrality Acts and placed an embargo on arms and munitions to both sides, but extended a further "moral embargo" to the belligerent Italians, including other trade items. On 5 October and later on 29 February 1936, the United States endeavoured, with limited success, to limit its exports of oil and other materials to normal peacetime levels. The League sanctions were lifted on 4 July 1936, but by that point, Italy had already gained control of the urban areas of Abyssinia.
The Hoare–Laval Pact of December 1935 was an attempt by the British Foreign Secretary Samuel Hoare and the French Prime Minister Pierre Laval to end the conflict in Abyssinia by proposing to partition the country into an Italian sector and an Abyssinian sector. Mussolini was prepared to agree to the pact, but news of the deal leaked out. Both the British and French public vehemently protested against it, describing it as a sell-out of Abyssinia. Hoare and Laval were forced to resign, and the British and French governments dissociated themselves from the two men. In June 1936, although there was no precedent for a head of state addressing the Assembly of the League of Nations in person, Haile Selassie spoke to the Assembly, appealing for its help in protecting his country.
The Abyssinian crisis showed how the League could be influenced by the self-interest of its members; one of the reasons why the sanctions were not very harsh was that both Britain and France feared the prospect of driving Mussolini and Adolf Hitler into an alliance.
Spanish Civil War
On 17 July 1936, the Spanish Army launched a coup d'état, leading to a prolonged armed conflict between Spanish Republicans (the elected leftist national government) and the Nationalists (conservative, anti-communist rebels who included most officers of the Spanish Army). Julio Álvarez del Vayo, the Spanish Minister of Foreign Affairs, appealed to the League in September 1936 for arms to defend Spain's territorial integrity and political independence. The League members would not intervene in the Spanish Civil War nor prevent foreign intervention in the conflict. Adolf Hitler and Mussolini continued to aid General Francisco Franco's Nationalists, while the Soviet Union, to a much lesser extent, helped the Spanish Republic. In February 1937, the League did ban foreign volunteers, but this was in practice a symbolic move.
Second Sino-Japanese War
Following a long record of instigating localised conflicts throughout the 1930s, Japan began a full-scale invasion of China on 7 July 1937. On 12 September, the Chinese representative, Wellington Koo, appealed to the League for international intervention. Western countries were sympathetic to the Chinese in their struggle, particularly in their stubborn defence of Shanghai, a city with a substantial number of foreigners. The League was unable to provide any practical measures; on 4 October, it turned the case over to the Nine Power Treaty Conference.
Soviet invasion of Finland
The Nazi-Soviet Pact of 23 August 1939, contained secret protocols outlining spheres of interest. Finland and the Baltic states, as well as eastern Poland, fell into the Soviet sphere. After invading Poland on 17 September 1939, on 30 November the Soviets invaded Finland. Then "the League of Nations for the first time expelled a member who had violated the Covenant." The League action of 14 December 1939, stung. "The Soviet Union was the only League member ever to suffer such an indignity."
Failure of disarmament
Article 8 of the Covenant gave the League the task of reducing "armaments to the lowest point consistent with national safety and the enforcement by common action of international obligations". In the 1920s little of the League's time and energy was devoted to this goal, as many members doubted that serious disarmament could be achieved or was even desirable.
The League scored some successes, including the 1925 Conference for the Supervision of the International Trade in Arms and Ammunition and in Implements of War. It started to collect international arms data. Most important was the passage in 1925 of the Geneva protocol banning poison gas in war. It reflected strong worldwide public opinion, although the United States did not ratify it until 1975.
The League had numerous failures and shortfalls. In 1921 it set up the Temporary Mixed Commission on Armaments to explore possibilities for disarmament. It was made up not of government representatives but of famous individuals. They rarely agreed. Proposals ranged from abolishing chemical warfare and strategic bombing to the limitation of more conventional weapons, such as tanks. A draft treaty was assembled in 1923 that made aggressive war illegal and bound the member states to defend victims of aggression by force. Since the onus of responsibility would, in practice, be on the great powers of the League, it was vetoed by Great Britain, who feared that this pledge would strain its own commitment to police its British Empire.
The Allied powers were also under obligation by the Treaty of Versailles to attempt to disarm, and the armament restrictions imposed on the defeated countries had been described as the first step toward worldwide disarmament. The League Covenant assigned the League the task of creating a disarmament plan for each state, but the Council devolved this responsibility to a special commission set up in 1926 to prepare for the 1932–1934 World Disarmament Conference. Members of the League held different views towards the issue. The French were reluctant to reduce their armaments without a guarantee of military help if they were attacked; Poland and Czechoslovakia felt vulnerable to attack from the west and wanted the League's response to aggression against its members to be strengthened before they disarmed. Without this guarantee, they would not reduce armaments because they felt the risk of attack from Germany was too great. Fear of attack increased as Germany regained its strength after the First World War, especially after Adolf Hitler gained power and became German Chancellor in 1933. In particular, Germany's attempts to overturn the Treaty of Versailles and the reconstruction of the German military made France increasingly unwilling to disarm.
The World Disarmament Conference was convened by the League of Nations in Geneva in 1932, with representatives from 60 states. It was a failure. A one-year moratorium on the expansion of armaments, later extended by a few months, was proposed at the start of the conference. The Disarmament Commission obtained initial agreement from France, Italy, Spain, Japan, and Britain to limit the size of their navies but no final agreement was reached. Ultimately, the Commission failed to halt the military build-up by Germany, Italy, Spain and Japan during the 1930s.
The League was mostly silent in the face of major events leading to the Second World War, such as Hitler's remilitarisation of the Rhineland, occupation of the Sudetenland and Anschluss of Austria, which had been forbidden by the Treaty of Versailles. In fact, League members themselves re-armed. In 1933, Japan simply withdrew from the League rather than submit to its judgement, as did Germany the same year (using the failure of the World Disarmament Conference to agree to arms parity between France and Germany as a pretext), Italy and Spain in 1937. The final significant act of the League was to expel the Soviet Union in December 1939 after it invaded Finland.
General weaknesses
The onset of the Second World War demonstrated that the League had failed in its primary purpose, the prevention of another world war. There were a variety of reasons for this failure, many connected to general weaknesses within the organisation. Additionally, the power of the League was limited by the United States' refusal to join.
Origins and structure
The origins of the League as an organisation created by the Allied powers as part of the peace settlement to end the First World War led to it being viewed as a "League of Victors". The League's neutrality tended to manifest itself as indecision. It required a unanimous vote of nine, later fifteen, Council members to enact a resolution; hence, conclusive and effective action was difficult, if not impossible. It was also slow in coming to its decisions, as certain ones required the unanimous consent of the entire Assembly. This problem mainly stemmed from the fact that the primary members of the League of Nations were not willing to accept the possibility of their fate being decided by other countries, and by enforcing unanimous voting had effectively given themselves veto power.
Global representation
Representation at the League was often a problem. Though it was intended to encompass all nations, many never joined, or their period of membership was short. The most conspicuous absentee was the United States. President Woodrow Wilson had been a driving force behind the League's formation and strongly influenced the form it took, but the US Senate voted not to join on 19 November 1919. Ruth Henig has suggested that, had the United States become a member, it would have also provided support to France and Britain, possibly making France feel more secure, and so encouraging France and Britain to co-operate more fully regarding Germany, thus making the rise to power of the Nazi Party less likely. Conversely, Henig acknowledges that if the US had been a member, its reluctance to engage in war with European states or to enact economic sanctions might have hampered the ability of the League to deal with international incidents. The structure of the US federal government might also have made its membership problematic, as its representatives at the League could not have made decisions on behalf of the executive branch without having the prior approval of the legislative branch.
In January 1920, when the League was born, Germany was not permitted to join because it was seen as having been the aggressor in the First World War. Soviet Russia was also initially excluded because Communist regimes were not welcomed and membership would have been initially dubious due to the Russian Civil War in which both sides claimed to be the legitimate government of the country. The League was further weakened when major powers left in the 1930s. Japan began as a permanent member of the Council since the country was an Allied Power in the First World War, but withdrew in 1933 after the League voiced opposition to its occupation of Manchuria. Italy began as a permanent member of the Council but withdrew in 1937 after roughly a year following the end of the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. Spain also began as a permanent member of the Council, but withdrew in 1939 after the Spanish Civil War ended in a victory for the Nationalists. The League had accepted Germany, also as a permanent member of the Council, in 1926, deeming it a "peace-loving country", but Adolf Hitler pulled Germany out when he came to power in 1933.
Collective security
Another important weakness grew from the contradiction between the idea of collective security that formed the basis of the League and international relations between individual states. The League's collective security system required nations to act, if necessary, against states they considered friendly, and in a way that might endanger their national interests, to support states for which they had no normal affinity. This weakness was exposed during the Abyssinia Crisis, when Britain and France had to balance maintaining the security they had attempted to create for themselves in Europe "to defend against the enemies of internal order", in which Italy's support played a pivotal role, with their obligations to Abyssinia as a member of the League.
On 23 June 1936, in the wake of the collapse of League efforts to restrain Italy's war against Abyssinia, the British Prime Minister, Stanley Baldwin, told the House of Commons that collective security had
failed ultimately because of the reluctance of nearly all the nations in Europe to proceed to what I might call military sanctions ... The real reason, or the main reason, was that we discovered in the process of weeks that there was no country except the aggressor country which was ready for war ... [I]f collective action is to be a reality and not merely a thing to be talked about, it means not only that every country is to be ready for war; but must be ready to go to war at once. That is a terrible thing, but it is an essential part of collective security.
Ultimately, Britain and France both abandoned the concept of collective security in favour of appeasement in the face of growing German militarism under Hitler. In this context, the League of Nations was also the institution where the first international debate on terrorism took place following the 1934 assassination of King Alexander I of Yugoslavia in Marseille, France, showing its conspiratorial features, many of which are detectable in the discourse of terrorism among states after 9/11.
American diplomatic historian Samuel Flagg Bemis originally supported the League, but after two decades changed his mind:
- The League of Nations has been a disappointing failure.... It has been a failure, not because the United States did not join it; but because the great powers have been unwilling to apply sanctions except where it suited their individual national interests to do so, and because Democracy, on which the original concepts of the League rested for support, has collapsed over half the world.
Pacifism and disarmament
The League of Nations lacked an armed force of its own and depended on the Great Powers to enforce its resolutions, which they were very unwilling to do. Its two most important members, Britain and France, were reluctant to use sanctions and even more reluctant to resort to military action on behalf of the League. Immediately after the First World War, pacifism became a strong force among both the people and governments of the two countries. The British Conservatives were especially tepid to the League and preferred, when in government, to negotiate treaties without the involvement of that organisation. Moreover, the League's advocacy of disarmament for Britain, France, and its other members, while at the same time advocating collective security, meant that the League was depriving itself of the only forceful means by which it could uphold its authority.
When the British cabinet discussed the concept of the League during the First World War, Maurice Hankey, the Cabinet Secretary, circulated a memorandum on the subject. He started by saying, "Generally it appears to me that any such scheme is dangerous to us because it will create a sense of security which is wholly fictitious". He attacked the British pre-war faith in the sanctity of treaties as delusional and concluded by claiming:
It [a League of Nations] will only result in failure and the longer that failure is postponed the more certain it is that this country will have been lulled to sleep. It will put a very strong lever into the hands of the well-meaning idealists who are to be found in almost every Government, who deprecate expenditure on armaments, and, in the course of time, it will almost certainly result in this country being caught at a disadvantage.
The Foreign Office civil servant Sir Eyre Crowe also wrote a memorandum to the British cabinet claiming that "a solemn league and covenant" would just be "a treaty, like other treaties". "What is there to ensure that it will not, like other treaties, be broken?" Crowe went on to express scepticism of the planned "pledge of common action" against aggressors because he believed the actions of individual states would still be determined by national interests and the balance of power. He also criticised the proposal for League economic sanctions because it would be ineffectual and that "It is all a question of real military preponderance". Universal disarmament was a practical impossibility, Crowe warned.
Demise and legacy
As the situation in Europe escalated into war, the Assembly transferred enough power to the Secretary General on 30 September 1938 and 14 December 1939 to allow the League to continue to exist legally and carry on reduced operations. The headquarters of the League, the Palace of Nations, remained unoccupied for nearly six years until the Second World War ended.
At the 1943 Tehran Conference, the Allied powers agreed to create a new body to replace the League: the United Nations. Many League bodies, such as the International Labour Organization, continued to function and eventually became affiliated with the UN. The designers of the structures of the United Nations intended to make it more effective than the League.
The final meeting of the League of Nations took place on 18 April 1946 in Geneva. Delegates from 34 nations attended the assembly. This session concerned itself with liquidating the League: it transferred assets worth approximately $22,000,000 (U.S.) in 1946 (including the Palace of Nations and the League's archives) to the UN, returned reserve funds to the nations that had supplied them, and settled the debts of the League. Robert Cecil, addressing the final session, said:
Let us boldly state that aggression wherever it occurs and however it may be defended, is an international crime, that it is the duty of every peace-loving state to resent it and employ whatever force is necessary to crush it, that the machinery of the Charter, no less than the machinery of the Covenant, is sufficient for this purpose if properly used, and that every well-disposed citizen of every state should be ready to undergo any sacrifice in order to maintain peace ... I venture to impress upon my hearers that the great work of peace is resting not only on the narrow interests of our own nations, but even more on those great principles of right and wrong which nations, like individuals, depend.
The Assembly passed a resolution that "With effect from the day following the close of the present session of the Assembly [i.e., April 19], the League of Nations shall cease to exist except for the sole purpose of the liquidation of its affairs as provided in the present resolution." A Board of Liquidation consisting of nine persons from different countries spent the next 15 months overseeing the transfer of the League's assets and functions to the United Nations or specialised bodies, finally dissolving itself on 31 July 1947.
The archive of the League of Nations was transferred to the United Nations Office at Geneva and is now an entry in the UNESCO Memory of the World Register.
In the past few decades, by research using the League Archives at Geneva, historians have reviewed the legacy of the League of Nations as the United Nations has faced similar troubles to those of the interwar period. Current consensus views that, even though the League failed to achieve its ultimate goal of world peace, it did manage to build new roads towards expanding the rule of law across the globe; strengthened the concept of collective security, giving a voice to smaller nations; helped to raise awareness to problems like epidemics, slavery, child labour, colonial tyranny, refugee crises and general working conditions through its numerous commissions and committees; and paved the way for new forms of statehood, as the mandate system put the colonial powers under international observation.
Professor David Kennedy portrays the League as a unique moment when international affairs were "institutionalised", as opposed to the pre–First World War methods of law and politics.
The principal Allies in the Second World War (the UK, the USSR, France, the U.S., and the Republic of China) became permanent members of the United Nations Security Council in 1946; in 1971, the People's Republic of China replaced the Republic of China (then only in control of Taiwan) as a permanent member of the UN Security Council, and in 1991 the Russian Federation assumed the seat of the dissolved USSR.
Decisions of the Security Council are binding on all members of the UN, and unanimous decisions are not required, unlike in the League Council. Only the five permanent members of the Security Council can wield a veto to protect their vital interests.
League of Nations archives
The League of Nations archives is a collection of the League's records and documents. It consists of approximately 15 million pages of content dating from the inception of the League of Nations in 1919 extending through its dissolution, which commenced in 1946. It is located at the United Nations Office at Geneva.
Total Digital Access to the League of Nations Archives Project (LONTAD)
In 2017, the UN Library & Archives Geneva launched the Total Digital Access to the League of Nations Archives Project (LONTAD), with the intention of preserving, digitizing, and providing online access to the League of Nations archives. It is scheduled for completion in 2022.




















