| https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standardization |
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate a normalization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of standardization is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions.
History
Early examples
Standard weights and measures were developed by the Indus Valley civilization. The centralized weight and measure system served the commercial interest of Indus merchants as smaller weight measures were used to measure luxury goods while larger weights were employed for buying bulkier items, such as food grains etc. Weights existed in multiples of a standard weight and in categories. Technical standardisation enabled gauging devices to be effectively used in angular measurement and measurement for construction. Uniform units of length were used in the planning of towns such as Lothal, Surkotada, Kalibangan, Dolavira, Harappa, and Mohenjo-daro. The weights and measures of the Indus civilization also reached Persia and Central Asia, where they were further modified. Shigeo Iwata describes the excavated weights unearthed from the Indus civilization:
A total of 558 weights were excavated from Mohenjodaro, Harappa, and Chanhu-daro, not including defective weights. They did not find statistically significant differences between weights that were excavated from five different layers, each measuring about 1.5 m in depth. This was evidence that strong control existed for at least a 500-year period. The 13.7-g weight seems to be one of the units used in the Indus valley. The notation was based on the binary and decimal systems. 83% of the weights which were excavated from the above three cities were cubic, and 68% were made of chert.
18th century attempts
The implementation of standards in industry and commerce became highly important with the onset of the Industrial Revolution and the need for high-precision machine tools and interchangeable parts.
Henry Maudslay developed the first industrially practical screw-cutting lathe in 1800. This allowed for the standardization of screw thread sizes for the first time and paved the way for the practical application of interchangeability (an idea that was already taking hold) to nuts and bolts.
Before this, screw threads were usually made by chipping and filing (that is, with skilled freehand use of chisels and files). Nuts were rare; metal screws, when made at all, were usually for use in wood. Metal bolts passing through wood framing to a metal fastening on the other side were usually fastened in non-threaded ways (such as clinching or upsetting against a washer). Maudslay standardized the screw threads used in his workshop and produced sets of taps and dies that would make nuts and bolts consistently to those standards, so that any bolt of the appropriate size would fit any nut of the same size. This was a major advance in workshop technology.
National standard
Maudslay's work, as well as the contributions of other engineers, accomplished a modest amount of industry standardization; some companies' in-house standards spread a bit within their industries.
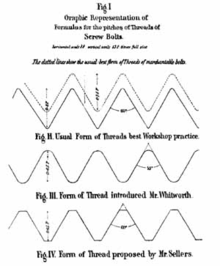
Joseph Whitworth's screw thread measurements were adopted as the first (unofficial) national standard by companies around the country in 1841. It came to be known as the British Standard Whitworth, and was widely adopted in other countries.
This new standard specified a 55° thread angle and a thread depth of 0.640327p and a radius of 0.137329p, where p is the pitch. The thread pitch increased with diameter in steps specified on a chart. An example of the use of the Whitworth thread is the Royal Navy's Crimean War gunboats. These were the first instance of "mass-production" techniques being applied to marine engineering.
With the adoption of BSW by British railway lines, many of which had previously used their own standard both for threads and for bolt head and nut profiles, and improving manufacturing techniques, it came to dominate British manufacturing.
American Unified Coarse was originally based on almost the same imperial fractions. The Unified thread angle is 60° and has flattened crests (Whitworth crests are rounded). Thread pitch is the same in both systems except that the thread pitch for the 1⁄2 in. (inch) bolt is 12 threads per inch (tpi) in BSW versus 13 tpi in the UNC.
National standards body
By the end of the 19th century, differences in standards between companies, was making trade increasingly difficult and strained. For instance, an iron and steel dealer recorded his displeasure in The Times: "Architects and engineers generally specify such unnecessarily diverse types of sectional material or given work that anything like economical and continuous manufacture becomes impossible. In this country no two professional men are agreed upon the size and weight of a girder to employ for given work."
The Engineering Standards Committee was established in London in 1901 as the world's first national standards body. It subsequently extended its standardization work and became the British Engineering Standards Association in 1918, adopting the name British Standards Institution in 1931 after receiving its Royal Charter in 1929. The national standards were adopted universally throughout the country, and enabled the markets to act more rationally and efficiently, with an increased level of cooperation.
After the First World War, similar national bodies were established in other countries. The Deutsches Institut für Normung was set up in Germany in 1917, followed by its counterparts, the American National Standard Institute and the French Commission Permanente de Standardisation, both in 1918.
Regional standards organization
At a regional level (e.g. Europa, the Americas, Africa, etc) or at subregional level (e.g. Mercosur, Andean Community, South East Asia, South East Africa, etc), several Regional Standardization Organizations exist (see also Standards Organization).
The three regional standards organizations in Europe - or European Standardization Organizations (ESOs) recognised by the EU Regulation on Standardization [Regulation (EU) 1025/2012] are CEN, CENELEC and ETSI. CEN develops standards for numerous kinds of products, materials, services and processes. Some sectors covered by CEN include transport equipment and services, chemicals, construction, consumer products, defence and security, energy, food and feed, health and safety, healthcare, digital sector, machinery or services. The European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) is the European Standardization organization developing standards in the electrotechnical area and corresponding to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in Europe.
International standards
The first modern International Organization (Intergovernmental Organization) the International Telegraph Union (now International Telecommunication Union) was created in 1865 to set international standards in order to connect national telegraph networks, as a merger of two predecessor organizations (Bern and Paris treaties) that had similar objectives, but in more limited territories. With the advent of radiocommunication soon after the creation, the work of the ITU quickly expanded from the standardization of Telegraph communications, to developing standards for telecommunications in general.
International Standards Associations
By the mid to late 19th century, efforts were being made to standardize electrical measurement. Lord Kelvin was an important figure in this process, introducing accurate methods and apparatus for measuring electricity. In 1857, he introduced a series of effective instruments, including the quadrant electrometer, which cover the entire field of electrostatic measurement. He invented the current balance, also known as the Kelvin balance or Ampere balance (SiC), for the precise specification of the ampere, the standard unit of electric current.
R. E. B. Crompton became concerned by the large range of different standards and systems used by electrical engineering companies and scientists in the early 20th century. Many companies had entered the market in the 1890s and all chose their own settings for voltage, frequency, current and even the symbols used on circuit diagrams. Adjacent buildings would have totally incompatible electrical systems simply because they had been fitted out by different companies. Crompton could see the lack of efficiency in this system and began to consider proposals for an international standard for electric engineering.
In 1904, Crompton represented Britain at the International Electrical Congress, held in connection with Louisiana Purchase Exposition in Saint Louis as part of a delegation by the Institute of Electrical Engineers. He presented a paper on standardisation, which was so well received that he was asked to look into the formation of a commission to oversee the process. By 1906 his work was complete and he drew up a permanent constitution for the International Electrotechnical Commission. The body held its first meeting that year in London, with representatives from 14 countries. In honour of his contribution to electrical standardisation, Lord Kelvin was elected as the body's first President.
The International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA) was founded in 1926 with a broader remit to enhance international cooperation for all technical standards and specifications. The body was suspended in 1942 during World War II.
After the war, ISA was approached by the recently formed United Nations Standards Coordinating Committee (UNSCC) with a proposal to form a new global standards body. In October 1946, ISA and UNSCC delegates from 25 countries met in London and agreed to join forces to create the new International Organization for Standardization (ISO); the new organization officially began operations in February 1947.
In general, each country or economy has a single recognized National Standards Body (NSB). Examples include ABNT, AENOR (now called UNE, Spanish Association for Standardization), AFNOR, ANSI, BSI, DGN, DIN, IRAM, JISC, KATS, SABS, SAC, SCC, SIS. An NSB is likely the sole member from that economy in ISO.
NSBs may be either public or private sector organizations, or combinations of the two. For example, the three NSBs of Canada, Mexico and the United States are respectively the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), the General Bureau of Standards (Dirección General de Normas, DGN), and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). SCC is a Canadian Crown Corporation, DGN is a governmental agency within the Mexican Ministry of Economy, and ANSI and AENOR are a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization with members from both the private and public sectors. The determinants of whether an NSB for a particular economy is a public or private sector body may include the historical and traditional roles that the private sector fills in public affairs in that economy or the development stage of that economy.
Usage
Standards can be:
- de facto standards which means they are followed by informal convention or dominant usage.
- de jure standards which are part of legally binding contracts, laws or regulations.
- Voluntary standards which are published and available for people to consider for use.
The existence of a published standard does not necessarily imply that it is useful or correct. Just because an item is stamped with a standard number does not, by itself, indicate that the item is fit for any particular use. The people who use the item or service (engineers, trade unions, etc.) or specify it (building codes, government, industry, etc.) have the responsibility to consider the available standards, specify the correct one, enforce compliance, and use the item correctly: validation and verification.
To avoid the proliferation of industry standards, also referred to as private standards, regulators in the United States are instructed by their government offices to adopt "voluntary consensus standards" before relying upon "industry standards" or developing "government standards".[24] Regulatory authorities can reference voluntary consensus standards to translate internationally accepted criteria into public policy.
Information exchange
In the context of information exchange, standardization refers to the process of developing standards for specific business processes using specific formal languages. These standards are usually developed in voluntary consensus standards bodies such as the United Nations Center for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business (UN/CEFACT), the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), and the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS).
There are many specifications that govern the operation and interaction of devices and software on the Internet, but they are rarely referred to as standards, so as to preserve that word as the domain of relatively disinterested bodies such as ISO. The W3C, for example, publishes "Recommendations", and the IETF publishes "Requests for Comments" (RFCs). However, these publications are sometimes referred to as standards.
Environmental protection
Standardized product certifications such as of organic food, buildings or possibly sustainable seafood as well as standardized product safety evaluation and dis/approval procedures (e.g. regulation of chemicals, cosmetics and food safety) can protect the environment. This effect may depend on associated modified consumer choices, strategic product support/obstruction, requirements and bans as well as their accordance with a scientific basis, the robustness and applicability of a scientific basis, whether adoption of the certifications is voluntary, and the socioeconomic context (systems of governance and the economy), with possibly most certifications being so far mostly largely ineffective.
Moreover, standardized scientific frameworks can enable evaluation of levels of environmental protection, such as of marine protected areas, and serve as, potentially evolving, guides for improving, planning and monitoring the protection-quality, -scopes and -extents.
Moreover, technical standards could decrease electronic waste and reduce resource-needs such as by thereby requiring (or enabling) products to be interoperable, compatible (with other products, infrastructures, environments, etc), durable, energy-efficient, modular, upgradeable/repairable and recyclable and conform to versatile, optimal standards and protocols.
Such standardization is not limited to the domain of electronic devices like smartphones and phone chargers but could also be applied to e.g. the energy infrastructure. Policy-makers could develop policies "fostering standard design and interfaces, and promoting the re-use of modules and components across plants to develop more sustainable energy infrastructure". Computers and the Internet are some of the tools that could be used to increase practicability and reduce suboptimal results, detrimental standards and bureaucracy, which is often associated with traditional processes and results of standardization. Taxes and subsidies, and funding of research and development could be used complementarily. Standardized measurement is used in monitoring, reporting and verification frameworks of environmental impacts, usually of companies, for example to prevent underreporting of greenhouse gas emissions by firms.
Product testing and analysis can also be done for, enable or aid environmental protection:
Product testing and analysis
In routine product testing and product analysis results can be reported using official or informal standards. It can be done to increase consumer protection, to ensure safety or healthiness or efficiency or performance or sustainability of products. It can be carried out by the manufacturer, an independent laboratory, a government agency, a magazine or others on a voluntary or commissioned/mandated basis.
Estimating the environmental impacts of food products in a standardized way – as has been done with a dataset of >57,000 food products in supermarkets – could e.g. be used to inform consumers or in policy. For example, such may be useful for approaches using personal carbon allowances (or similar quota) or for targeted alteration of (ultimate overall) costs.
Safety
Public information symbols
Public information symbols (e.g. hazard symbols), especially when related to safety, are often standardized, sometimes on the international level.
Biosafety
Standardization is also used to ensure safe design and operation of laboratories and similar potentially dangerous workplaces, e.g. to ensure biosafety levels. There is research into microbiology safety standards used in clinical and research laboratories.
Defense
In the context of defense, standardization has been defined by NATO as The development and implementation of concepts, doctrines, procedures and designs to achieve and maintain the required levels of compatibility, interchangeability or commonality in the operational, procedural, material, technical and administrative fields to attain interoperability.
Ergonomics, workplace and health
In some cases, standards are being used in the design and operation of workplaces and products that can impact consumers' health. Some of such standards seek to ensure occupational safety and health and ergonomics. For example, chairs (see e.g. active sitting and steps of research) could be potentially be designed and chosen using standards that may or may not be based on adequate scientific data. Standards could reduce the variety of products and lead to convergence on fewer broad designs – which can often be efficiently mass-produced via common shared automated procedures and instruments – or formulations deemed to be the most healthy, most efficient or best compromise between healthiness and other factors. Standardization is sometimes or could also be used to ensure or increase or enable consumer health protection beyond the workplace and ergonomics such as standards in food, food production, hygiene products, tab water, cosmetics, drugs/medicine, drink and dietary supplements, especially in cases where there is robust scientific data that suggests detrimental impacts on health (e.g. of ingredients) despite being substitutable and not necessarily of consumer interest.
Clothing
Clinical assessment
In the context of assessment, standardization may define how a measuring instrument or procedure is similar to every subjects or patients. For example, educational psychologist may adopt structured interview to systematically interview the people in concern. By delivering the same procedures, all subjects is evaluated using same criteria and minimising any confounding variable that reduce the validity. Some other example includes mental status examination and personality test.
Social science
In the context of social criticism and social science, standardization often means the process of establishing standards of various kinds and improving efficiency to handle people, their interactions, cases, and so forth. Examples include formalization of judicial procedure in court, and establishing uniform criteria for diagnosing mental disease. Standardization in this sense is often discussed along with (or synonymously to) such large-scale social changes as modernization, bureaucratization, homogenization, and centralization of society.
Customer service
In the context of customer service, standardization refers to the process of developing an international standard that enables organizations to focus on customer service, while at the same time providing recognition of success through a third party organization, such as the British Standards Institution. An international standard has been developed by The International Customer Service Institute.
Supply and materials management
In the context of supply chain management and materials management, standardization covers the process of specification and use of any item the company must buy in or make, allowable substitutions, and build or buy decisions.
Process
The process of standardization can itself be standardized. There are at least four levels of standardization: compatibility, interchangeability, commonality and reference. These standardization processes create compatibility, similarity, measurement, and symbol standards.
There are typically four different techniques for standardization
- Simplification or variety control
- Codification
- Value engineering
- Statistical process control.
Types of standardization process:
- Emergence as de facto standard: tradition, market domination, etc.
- Written by a Standards organization:
- in a closed consensus process: Restricted membership and often having formal procedures for due-process among voting members
- in a full consensus process: usually open to all interested and qualified parties and with formal procedures for due-process considerations
- Written by a government or regulatory body
- Written by a corporation, union, trade association, etc.
- Agile standardization. A group of entities, themselves or through an association, creates and publishes a drafted version shared for public review based on actual examples of use.
Effects
Standardization has a variety of benefits and drawbacks for firms and consumers participating in the market, and on technology and innovation.
Effect on firms
The primary effect of standardization on firms is that the basis of competition is shifted from integrated systems to individual components within the system. Prior to standardization a company's product must span the entire system because individual components from different competitors are incompatible, but after standardization each company can focus on providing an individual component of the system. When the shift toward competition based on individual components takes place, firms selling tightly integrated systems must quickly shift to a modular approach, supplying other companies with subsystems or components.
Effect on consumers
Standardization has a variety of benefits for consumers, but one of the greatest benefits is enhanced network effects. Standards increase compatibility and interoperability between products, allowing information to be shared within a larger network and attracting more consumers to use the new technology, further enhancing network effects. Other benefits of standardization to consumers are reduced uncertainty, because consumers can be more certain that they are not choosing the wrong product, and reduced lock-in, because the standard makes it more likely that there will be competing products in the space. Consumers may also get the benefit of being able to mix and match components of a system to align with their specific preferences. Once these initial benefits of standardization are realized, further benefits that accrue to consumers as a result of using the standard are driven mostly by the quality of the technologies underlying that standard.
Probably the greatest downside of standardization for consumers is lack of variety. There is no guarantee that the chosen standard will meet all consumers' needs or even that the standard is the best available option. Another downside is that if a standard is agreed upon before products are available in the market, then consumers are deprived of the penetration pricing that often results when rivals are competing to rapidly increase market share in an attempt to increase the likelihood that their product will become the standard. It is also possible that a consumer will choose a product based upon a standard that fails to become dominant. In this case, the consumer will have spent resources on a product that is ultimately less useful to him or her as the result of the standardization process.
Effect on technology
Much like the effect on consumers, the effect of standardization on technology and innovation is mixed. Meanwhile, the various links between research and standardization have been identified, also as a platform of knowledge transfer and translated into policy measures (e.g. WIPANO).
Increased adoption of a new technology as a result of standardization is important because rival and incompatible approaches competing in the marketplace can slow or even kill the growth of the technology (a state known as market fragmentation). The shift to a modularized architecture as a result of standardization brings increased flexibility, rapid introduction of new products, and the ability to more closely meet individual customer's needs.
The negative effects of standardization on technology have to do with its tendency to restrict new technology and innovation. Standards shift competition from features to price because the features are defined by the standard. The degree to which this is true depends on the specificity of the standard. Standardization in an area also rules out alternative technologies as options while encouraging others.