People's Republic of China
| |
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
| |

Area controlled by the People's Republic of China shown in dark green; claimed but uncontrolled regions shown in light green.
| |
| Capital |
Beijing[a] 39°55′N 116°23′E |
| Largest city | Shanghai[1] |
| Official languages | Standard Chinese[2][b] |
| Official script | Simplified Chinese[c] |
| Recognised regional languages[3] | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion | See Religion in China |
| Demonym | Chinese |
| Government | Unitary one-party socialist republic[5] |
| Xi Jinping[e] | |
• Premier
| Li Keqiang |
| Li Zhanshu | |
| Wang Yang | |
• First Secretary of the Party Secretariat
| Wang Huning |
| Zhao Leji | |
• First Vice Premier
| Han Zheng |
| Wang Qishan[f] | |
| Legislature | National People's Congress |
| Formation | |
| 221 BCE | |
| 1 January 1912 | |
| 21 September 1949[7][8][9] | |
| 1 October 1949 | |
| 4 December 1982 | |
| 20 December 1999 | |
| Area | |
• Total
| 9,596,961 km2 (3,705,407 sq mi)[g] (3rd/4th) |
• Water (%)
| 2.8%[h] |
| Population | |
• 2016 estimate
|
1,403,500,365 |
• 2010 census
| 1,339,724,852[14] (1st) |
• Density
| 145[15]/km2 (375.5/sq mi) (83rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total
| $25.238 trillion[16] (1st) |
• Per capita
| $18,066[16] (79th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total
| $14.092 trillion[16] (2nd) |
• Per capita
| $10,087[16] (71st) |
| Gini (2015) |
46.2[17] high |
| HDI (2016) |
high · 90th |
| Currency | Renminbi (yuan; ¥)[i] (CNY) |
| Time zone | China Standard Time (UTC+8) |
| Date format | |
| Drives on the | right[j] |
| Calling code | +86 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN |
| Internet TLD | |
China emerged as one of the world's earliest civilizations, in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. For millennia, China's political system was based on hereditary monarchies, or dynasties, beginning with the semi-legendary Xia dynasty in 21st century BCE.[20] Since then, China has expanded, fractured, and re-unified numerous times. In the 3rd century BCE, the Qin unified core China and established the first Chinese dynasty. The succeeding Han dynasty, which ruled from 206 BC until 220 AD, saw some of the most advanced technology at that time, including papermaking and the compass,[21] along with agricultural and medical improvements. The invention of gunpowder and printing in the Tang dynasty (618–907) completed the Four Great Inventions. Tang culture spread widely in Asia, as the new maritime Silk Route brought traders to as far as Mesopotamia and Horn of Africa.[22] Dynastic rule ended in 1912 with the Xinhai Revolution, when a republic replaced the Qing dynasty. The Chinese Civil War resulted in a division of territory in 1949, when the Communist Party of China established the People’s Republic of China on Mainland China, while the Kuomintang-led government retreated to the island of Taiwan. The political status of Taiwan and the ROC remains disputed.
Since the introduction of economic reforms in 1978, China's economy has been one of the world's fastest-growing with annual growth rates consistently above 6 percent.[23] As of 2016, it is the world's second-largest economy by nominal GDP and largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).[24] China is also the world's largest exporter and second-largest importer of goods.[25] China is a recognized nuclear weapons state and has the world's largest standing army and second-largest defense budget.[26][27][28] The PRC is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council as it replaced the ROC in 1971, as well as an active global partner of ASEAN Plus mechanism. China is also a leading member of numerous formal and informal multilateral organizations, including the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), WTO, APEC, BRICS, the BCIM, and the G20. China is a great power and a major regional power within Asia, and has been characterized as a potential superpower.[29][30]
Names
| China | |||

"China" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters
| |||

"People's Republic of China" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters
| |||
| Chinese name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 中国 | ||
| Traditional Chinese | 中國 | ||
| Literal meaning | "Middle Kingdom"[31] or "Central State"[32] | ||
|
| |||
| |||
| People's Republic of China | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 中华人民共和国 | ||
| Traditional Chinese | 中華人民共和國 | ||
|
| |||
| |||
| Tibetan name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan |
ཀྲུང་ཧྭ་མི་དམངས་སྤྱི མཐུན་རྒྱལ་ཁབ | ||
|
| |||
| |||
| Zhuang name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhuang | Cunghvaz Yinzminz Gunghozgoz | ||
| Mongolian name | |||
| Mongolian |
 | ||
|
| |||
| |||
| Uyghur name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Uyghur |
جۇڭخۇا خەلق جۇمھۇرىيىتى
| ||
|
| |||
| |||
| Manchu name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manchu script |
ᡩᡠᠯᡳᠮᠪᠠᡳ ᠨᡳᠶᠠᠯᠮᠠᡳᡵᡤᡝᠨ ᡤᡠᠨᡥᡝ ᡤᡠᡵᡠᠨ (ᡩᡡᠯᡳᠮᠪᠠᡳ ᡤᡠᡵᡠᠨ) | ||
| Romanization | Dulimbai niyalmairgen gungheg' gurun(Dulimbai Gurun) | ||
The English word "China" is first attested in Richard Eden's 1555 translation[l] of the 1516 journal of the Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa.[m][37] The demonym, that is, the name for the people, and adjectival form "Chinese" developed later on the model of Portuguese chinês and French chinois.[38][n] Portuguese China is thought to derive from Persian Chīn (چین), and perhaps ultimately from Sanskrit Cīna (चीन).[40] Cīna was first used in early Hindu scripture, including the Mahābhārata (5th century BCE) and the Laws of Manu (2nd century BCE).[41] In 1655, Martino Martini suggested that the word China is derived from the name of the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC),[42] a proposal supported by many later scholars,[43][44][45] although there are also a number of alternative suggestions.[41][46]
The official name of the modern state is the "People's Republic of China" (Chinese: 中华人民共和国; pinyin: Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó). The shorter form is "China" Zhōngguó (中国), from zhōng ("central") and guó ("state"),[32][o] a term which developed under the Western Zhou dynasty in reference to its royal demesne.[p] It was then applied to the area around Luoyi (present-day Luoyang) during the Eastern Zhou and then to China's Central Plain before being used as an occasional synonym for the state under the Qing.[48] It was often used as a cultural concept to distinguish the Huaxia people from perceived "barbarians"[48] and was the source of the English name "Middle Kingdom".[50][51] A more literary or inclusive name, alluding to the "land of Chinese civilization", is Zhōnghuá (中华).[52] It developed during the Wei and Jin dynasties as a contraction of "the central state of the Huaxia".[48] Before the PRC's establishment, the proposed name of the country was the People's Democratic Republic of China (simplified Chinese: 中华人民民主共和国; traditional Chinese: 中華人民民主共和國; pinyin: Zhōnghuá Rénmín Mínzhǔ Gònghéguó) during the first CPPCC held on 15 June 1949.[53][54] During the 1950s and 1960s, after the defeat of the Kuomintang in the Chinese Civil War, it was also referred to as "Communist China" or "Red China", to be differentiated from "Nationalist China" or "Free China".[55]
History
Prehistory
Archaeological evidence suggests that early hominids inhabited China between 2.24 million and 250,000 years ago.[56] The hominid fossils of Peking Man, a Homo erectus who used fire,[57] were discovered in a cave at Zhoukoudian near Beijing; they have been dated to between 680,000 and 780,000 years ago.[58] The fossilized teeth of Homo sapiens (dated to 125,000–80,000 years ago) have been discovered in Fuyan Cave in Dao County, Hunan.[59] Chinese proto-writing existed in Jiahu around 7000 BCE,[60] Damaidi around 6000 BCE,[61] Dadiwan from 5800–5400 BCE, and Banpo dating from the 5th millennium BCE. Some scholars have suggested that the Jiahu symbols (7th millennium BCE) constituted the earliest Chinese writing system.[60]Early dynastic rule
According to Chinese tradition, the first dynasty was the Xia, which emerged around 2100 BCE.[62] The dynasty was considered mythical by historians until scientific excavations found early Bronze Age sites at Erlitou, Henan in 1959.[63] It remains unclear whether these sites are the remains of the Xia dynasty or of another culture from the same period.[64] The succeeding Shang dynasty is the earliest to be confirmed by contemporary records.[65] The Shang ruled the plain of the Yellow River in eastern China from the 17th to the 11th century BCE.[66] Their oracle bone script (from c. 1500 BCE)[67][68] represents the oldest form of Chinese writing yet found,[69] and is a direct ancestor of modern Chinese characters.[70]
The Shang were conquered by the Zhou, who ruled between the 11th and 5th centuries BCE, though centralized authority was slowly eroded by feudal warlords. Many independent states eventually emerged from the weakened Zhou state and continually waged war with each other in the 300-year Spring and Autumn period, only occasionally deferring to the Zhou king. By the time of the Warring States period of the 5th–3rd centuries BCE, there were seven powerful sovereign states in what is now China, each with its own king, ministry and army.
Imperial China
China's First Emperor, Qin Shi Huang, is famed for having united the Warring States' walls to form the Great Wall of China. Most of the present structure, however, dates to the Ming dynasty.
The Terracotta Army (c. 210 BCE) discovered outside the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor, now Xi'an
The Warring States period ended in 221 BCE after the state of Qin conquered the other six kingdoms and established the first unified Chinese state. King Zheng of Qin proclaimed himself the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty. He enacted Qin's legalist reforms throughout China, notably the forced standardization of Chinese characters, measurements, road widths (i.e., cart axles' length), and currency. His dynasty also conquered the Yue tribes in Guangxi, Guangdong, and Vietnam.[71] The Qin dynasty lasted only fifteen years, falling soon after the First Emperor's death, as his harsh authoritarian policies led to widespread rebellion.[72][73]
Following a widespread civil war during which the imperial library at Xianyang was burned,[q] the Han dynasty emerged to rule China between 206 BCE and CE 220, creating a cultural identity among its populace still remembered in the ethnonym of the Han Chinese.[72][73] The Han expanded the empire's territory considerably, with military campaigns reaching Central Asia, Mongolia, South Korea, and Yunnan, and the recovery of Guangdong and northern Vietnam from Nanyue. Han involvement in Central Asia and Sogdia helped establish the land route of the Silk Road, replacing the earlier path over the Himalayas to India. Han China gradually became the largest economy of the ancient world.[75] Despite the Han's initial decentralization and the official abandonment of the Qin philosophy of Legalism in favor of Confucianism, Qin's legalist institutions and policies continued to be employed by the Han government and its successors.[76]
After the end of the Han dynasty, a period of strife known as Three Kingdoms followed,[77] whose central figures were later immortalized in one of the Four Classics of Chinese literature. At its end, Wei was swiftly overthrown by the Jin dynasty. The Jin fell to civil war upon the ascension of a developmentally-disabled emperor; the Five Barbarians then invaded and ruled northern China as the Sixteen States. The Xianbei unified them as the Northern Wei, whose Emperor Xiaowen reversed his predecessors' apartheid policies and enforced a drastic sinification on his subjects, largely integrating them into Chinese culture. In the south, the general Liu Yu secured the abdication of the Jin in favor of the Liu Song. The various successors of these states became known as the Northern and Southern dynasties, with the two areas finally reunited by the Sui in 581. The Sui restored the Han to power through China, reformed its agriculture and economy, constructed the Grand Canal, and patronized Buddhism. However, they fell quickly when their conscription for public works and a failed war with Korea provoked widespread unrest.[78][79]
A detail from Along the River During the Qingming Festival, a 12th-century painting showing everyday life in the Song dynasty's capital, Bianjing (present-day Kaifeng)
Under the succeeding Tang and Song dynasties, Chinese economy, technology, and culture entered a golden age.[80] The Tang Empire returned control of the Western Regions and the Silk Road,[81] and made the capital Chang'an a cosmopolitan urban center. However, it was devastated and weakened by the An Shi Rebellion in the 8th century.[82] In 907, the Tang disintegrated completely when the local military governors became ungovernable. The Song dynasty ended the separatist situation in 960, leading to a balance of power between the Song and Khitan Liao. The Song was the first government in world history to issue paper money and the first Chinese polity to establish a permanent standing navy which was supported by the developed shipbuilding industry along with the sea trade.[83] Between the 10th and 11th centuries, the population of China doubled in size to around 100 million people, mostly because of the expansion of rice cultivation in central and southern China, and the production of abundant food surpluses. The Song dynasty also saw a revival of Confucianism, in response to the growth of Buddhism during the Tang,[84] and a flourishing of philosophy and the arts, as landscape art and porcelain were brought to new levels of maturity and complexity.[85][86] However, the military weakness of the Song army was observed by the Jurchen Jin dynasty. In 1127, Emperor Huizong of Song and the capital Bianjing were captured during the Jin–Song Wars. The remnants of the Song retreated to southern China.[87]
The 13th century brought the Mongol conquest of China. In 1271, the Mongol leader Kublai Khan established the Yuan dynasty; the Yuan conquered the last remnant of the Song dynasty in 1279. Before the Mongol invasion, the population of Song China was 120 million citizens; this was reduced to 60 million by the time of the census in 1300.[88] A peasant named Zhu Yuanzhang overthrew the Yuan in 1368 and founded the Ming dynasty as the Hongwu Emperor. Under the Ming dynasty, China enjoyed another golden age, developing one of the strongest navies in the world and a rich and prosperous economy amid a flourishing of art and culture. It was during this period that Zheng He led the Ming treasure voyages throughout the world, reaching as far as Africa.[89]
In the early years of the Ming dynasty, China's capital was moved from Nanjing to Beijing. With the budding of capitalism, philosophers such as Wang Yangming further critiqued and expanded Neo-Confucianism with concepts of individualism and equality of four occupations.[90] The scholar-official stratum became a supporting force of industry and commerce in the tax boycott movements, which, together with the famines and defense against Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98) and Manchu invasions led to an exhausted treasury.[91]
In 1644, Beijing was captured by a coalition of peasant rebel forces led by Li Zicheng. The Chongzhen Emperor committed suicide when the city fell. The Manchu Qing dynasty, then allied with Ming dynasty general Wu Sangui, overthrew Li's short-lived Shun dynasty and subsequently seized control of Beijing, which became the new capital of the Qing dynasty.
End of dynastic rule
A 19th-century depiction of the Taiping Rebellion (1850–1864)
The Qing dynasty, which lasted from 1644 until 1912, was the last imperial dynasty of China. Its conquest of the Ming (1618–1683) cost 25 million lives and the economy of China shrank drastically.[92] After the Southern Ming ended, the further conquest of the Dzungar Khanate added Mongolia, Tibet and Xinjiang to the empire.[93] The centralized autocracy was strengthened to crack down on anti-Qing sentiment with the policy of valuing agriculture and restraining commerce, the Haijin ("sea ban"), and ideological control as represented by the literary inquisition, causing social and technological stagnation.[94][95] In the mid-19th century, the dynasty experienced Western imperialism in the Opium Wars with Britain and France. China was forced to pay compensation, open treaty ports, allow extraterritoriality for foreign nationals, and cede Hong Kong to the British[96] under the 1842 Treaty of Nanking, the first of the Unequal Treaties. The First Sino-Japanese War (1894–95) resulted in Qing China's loss of influence in the Korean Peninsula, as well as the cession of Taiwan to Japan.[97]
The Eight-Nation Alliance invaded China to defeat the anti-foreign Boxers and their Qing backers.
The Qing dynasty also began experiencing internal unrest in which tens of millions of people died, especially in the failed Taiping Rebellion that ravaged southern China in the 1850s and 1860s and the Dungan Revolt (1862–77) in the northwest. The initial success of the Self-Strengthening Movement of the 1860s was frustrated by a series of military defeats in the 1880s and 1890s.
In the 19th century, the great Chinese diaspora began. Losses due to emigration were added to by conflicts and catastrophes such as the Northern Chinese Famine of 1876–79, in which between 9 and 13 million people died.[98] The Guangxu Emperor drafted a reform plan in 1898 to establish a modern constitutional monarchy, but these plans were thwarted by the Empress Dowager Cixi. The ill-fated anti-foreign Boxer Rebellion of 1899–1901 further weakened the dynasty. Although Cixi sponsored a program of reforms, the Xinhai Revolution of 1911–12 brought an end to the Qing dynasty and established the Republic of China.
Republic of China (1912–1949)
Sun Yat-sen, the father of modern China (seated on right), and Chiang Kai-shek, later President of the Republic of China
Chiang Kai-shek and Mao Zedong toasting together in 1946 following the end of World War II
On 1 January 1912, the Republic of China was established, and Sun Yat-sen of the Kuomintang (the KMT or Nationalist Party) was proclaimed provisional president.[99] However, the presidency was later given to Yuan Shikai, a former Qing general who in 1915 proclaimed himself Emperor of China. In the face of popular condemnation and opposition from his own Beiyang Army, he was forced to abdicate and re-establish the republic.[100]
After Yuan Shikai's death in 1916, China was politically fragmented. Its Beijing-based government was internationally recognized but virtually powerless; regional warlords controlled most of its territory.[101][102] In the late 1920s, the Kuomintang, under Chiang Kai-shek, the then Principal of the Republic of China Military Academy, was able to reunify the country under its own control with a series of deft military and political maneuverings, known collectively as the Northern Expedition.[103][104] The Kuomintang moved the nation's capital to Nanjing and implemented "political tutelage", an intermediate stage of political development outlined in Sun Yat-sen's San-min program for transforming China into a modern democratic state.[105][106] The political division in China made it difficult for Chiang to battle the Communist, People's Liberation Army (PLA) against whom the Kuomintang had been warring since 1927 in the Chinese Civil War. This war continued successfully for the Kuomintang, especially after the PLA retreated in the Long March, until Japanese aggression and the 1936 Xi'an Incident forced Chiang to confront Imperial Japan.[107]
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945), a theater of World War II, forced an uneasy alliance between the Kuomintang and the PLA. Japanese forces committed numerous war atrocities against the civilian population; in all, as many as 20 million Chinese civilians died.[108] An estimated 200,000 Chinese were massacred in the city of Nanjing alone during the Japanese occupation.[109] During the war, China, along with the UK, the US and the Soviet Union, were referred to as "trusteeship of the powerful"[110] and were recognized as the Allied "Big Four" in the Declaration by United Nations.[111][112] Along with the other three great powers, China was one of the four major Allies of World War II, and was later considered one of the primary victors in the war.[113][114] After the surrender of Japan in 1945, Taiwan, including the Pescadores, was returned to Chinese control. China emerged victorious but war-ravaged and financially drained. The continued distrust between the Kuomintang and the Communists led to the resumption of civil war. Constitutional rule was established in 1947, but because of the ongoing unrest, many provisions of the ROC constitution were never implemented in mainland China.[115]
People's Republic of China (1949–present)
Mao Zedong proclaiming the establishment of the PRC in 1949
Major combat in the Chinese Civil War ended in 1949 with the Communist Party in control of most of mainland China, and the Kuomintang retreating offshore, reducing the ROC's territory to only Taiwan, Hainan, and their surrounding islands. On 21 September 1949, Communist Party Chairman Mao Zedong proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China.[7][8][9] This was followed by a mass celebration in Tiananmen Square on 1 October which became the new country's first National Day. In 1950, the People's Liberation Army succeeded in capturing Hainan from the ROC[116] and incorporating Tibet.[117] However, remaining Kuomintang forces continued to wage an insurgency in western China throughout the 1950s.[118] In modern US history studies, the founding of PRC China is often termed as "the loss of China" as reflected in US state policy documents of the time, which thinkers such as Noam Chomsky call the beginning of McCarthyism.[119]
The regime consolidated its popularity among the peasants through land reform, which saw between 1 and 2 million landlords executed.[120] Under its leadership, China developed an independent industrial system and its own nuclear weapons.[121] The Chinese population almost doubled from around 550 million to over 900 million.[122] However, the Great Leap Forward, a large-scale economic and social reform project, resulted in an estimated 45 million deaths between 1958 and 1961, mostly from starvation.[123] In 1966, Mao and his allies launched the Cultural Revolution, sparking a decade of political recrimination and social upheaval which lasted until Mao's death in 1976. In October 1971, the PRC replaced the Republic of China in the United Nations, and took its seat as a permanent member of the Security Council.[124]
After Mao's death, the Gang of Four was quickly arrested and held responsible for the excesses of the Cultural Revolution. Deng Xiaoping took power in 1978, and instituted significant economic reforms. The Communist Party loosened governmental control over citizens' personal lives, and the communes were gradually disbanded in favor of working contracted to households. This marked China's transition from a planned economy to a mixed economy with an increasingly open-market environment.[125] China adopted its current constitution on 4 December 1982. In 1989, the violent suppression of student protests in Tiananmen Square brought sanctions against the Chinese government from various countries.[126]
Jiang Zemin, Li Peng and Zhu Rongji led the nation in the 1990s. Under their administration, China's economic performance pulled an estimated 150 million peasants out of poverty and sustained an average annual gross domestic product growth rate of 11.2%.[127][128] The country formally joined the World Trade Organization in 2001, and maintained its high rate of economic growth under Hu Jintao and Wen Jiabao's leadership in the 2000s. However, rapid growth also severely impacted the country's resources and environment,[129][130] and caused major social displacement.[131][132] Living standards continued to improve rapidly despite the late-2000s recession, but centralized political control remained tight.[133]
Preparations for a decadal Communist Party leadership change in 2012 were marked by factional disputes and political scandals.[134] During China's 18th National Communist Party Congress in November 2012, Hu Jintao was replaced as General Secretary of the Communist Party by Xi Jinping.[135][136] Under Xi, the Chinese government began large-scale efforts to reform its economy,[137][138] which has suffered from structural instabilities and slowing growth.[139][140][141][142][143] The Xi–Li Administration also announced major reforms to the one-child policy and prison system.[144]
Geography

A composite satellite image showing the topography of China
Köppen climate types of China
China's landscape is vast and diverse, ranging from the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts in the arid north to subtropical forests in the wetter south. The Himalaya, Karakoram, Pamir and Tian Shan mountain ranges separate China from much of South and Central Asia. The Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, the third- and sixth-longest in the world, respectively, run from the Tibetan Plateau to the densely populated eastern seaboard. China's coastline along the Pacific Ocean is 14,500 kilometers (9,000 mi) long and is bounded by the Bohai, Yellow, East China and South China seas. China connects through the Kazakh border to the Eurasian Steppe which has been an artery of communication between East and West since the Neolithic through the Steppe route – the ancestor of the terrestrial Silk Road(s).
Political geography
The People's Republic of China is the second-largest country in the world by land area[145] after Russia, and is either the third- or fourth-largest by total area, after Russia, Canada and, depending on the definition of total area, the United States.[r] China's total area is generally stated as being approximately 9,600,000 km2 (3,700,000 sq mi).[146] Specific area figures range from 9,572,900 km2 (3,696,100 sq mi) according to the Encyclopædia Britannica,[147] 9,596,961 km2 (3,705,407 sq mi) according to the UN Demographic Yearbook,[10] to 9,596,961 km2 (3,705,407 sq mi) according to the CIA World Factbook.[12]China has the longest combined land border in the world, measuring 22,117 km (13,743 mi) from the mouth of the Yalu River to the Gulf of Tonkin.[12] China borders 14 nations, more than any other country except Russia, which also borders 14.[148] China extends across much of East Asia, bordering Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar (Burma) in Southeast Asia; India, Bhutan, Nepal, Afghanistan, and Pakistan[s] in South Asia; Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan in Central Asia; and Russia, Mongolia, and North Korea in Inner Asia and Northeast Asia. Additionally, China shares maritime boundaries with South Korea, Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
Landscape and climate
The territory of China lies between latitudes 18° and 54° N, and longitudes 73° and 135° E. China's landscapes vary significantly across its vast width. In the east, along the shores of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea, there are extensive and densely populated alluvial plains, while on the edges of the Inner Mongolian plateau in the north, broad grasslands predominate. Southern China is dominated by hills and low mountain ranges, while the central-east hosts the deltas of China's two major rivers, the Yellow River and the Yangtze River. Other major rivers include the Xi, Mekong, Brahmaputra and Amur. To the west sit major mountain ranges, most notably the Himalayas. High plateaus feature among the more arid landscapes of the north, such as the Taklamakan and the Gobi Desert. The world's highest point, Mount Everest (8,848m), lies on the Sino-Nepalese border.[149] The country's lowest point, and the world's third-lowest, is the dried lake bed of Ayding Lake (−154m) in the Turpan Depression.[150]China's climate is mainly dominated by dry seasons and wet monsoons, which lead to pronounced temperature differences between winter and summer. In the winter, northern winds coming from high-latitude areas are cold and dry; in summer, southern winds from coastal areas at lower latitudes are warm and moist.[151] The climate in China differs from region to region because of the country's highly complex topography.
A major environmental issue in China is the continued expansion of its deserts, particularly the Gobi Desert.[152][153] Although barrier tree lines planted since the 1970s have reduced the frequency of sandstorms, prolonged drought and poor agricultural practices have resulted in dust storms plaguing northern China each spring, which then spread to other parts of east Asia, including Korea and Japan. China's environmental watchdog, SEPA, stated in 2007 that China is losing 4,000 km2 (1,500 sq mi) per year to desertification.[154] Water quality, erosion, and pollution control have become important issues in China's relations with other countries. Melting glaciers in the Himalayas could potentially lead to water shortages for hundreds of millions of people.[155]
Biodiversity
A giant panda, China's most famous endangered and endemic species, at the Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding in Sichuan
China is one of 17 megadiverse countries,[156] lying in two of the world's major ecozones: the Palearctic and the Indomalaya. By one measure, China has over 34,687 species of animals and vascular plants, making it the third-most biodiverse country in the world, after Brazil and Colombia.[157] The country signed the Rio de Janeiro Convention on Biological Diversity on 11 June 1992, and became a party to the convention on 5 January 1993.[158] It later produced a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, with one revision that was received by the convention on 21 September 2010.[159]
China is home to at least 551 species of mammals (the third-highest such number in the world),[160] 1,221 species of birds (eighth),[161] 424 species of reptiles (seventh)[162] and 333 species of amphibians (seventh).[163] Wildlife in China share habitat with and bear acute pressure from the world's largest population of homo sapiens. At least 840 animal species are threatened, vulnerable or in danger of local extinction in China, due mainly to human activity such as habitat destruction, pollution and poaching for food, fur and ingredients for traditional Chinese medicine.[164] Endangered wildlife is protected by law, and as of 2005, the country has over 2,349 nature reserves, covering a total area of 149.95 million hectares, 15 percent of China's total land area.[165] The Baiji has recently been confirmed extinct.
China has over 32,000 species of vascular plants,[166] and is home to a variety of forest types. Cold coniferous forests predominate in the north of the country, supporting animal species such as moose and Asian black bear, along with over 120 bird species.[167] The understorey of moist conifer forests may contain thickets of bamboo. In higher montane stands of juniper and yew, the bamboo is replaced by rhododendrons. Subtropical forests, which are predominate in central and southern China, support as many as 146,000 species of flora.[167] Tropical and seasonal rainforests, though confined to Yunnan and Hainan Island, contain a quarter of all the animal and plant species found in China.[167] China has over 10,000 recorded species of fungi,[168] and of them, nearly 6,000 are higher fungi.[169]
Environmental issues
The traffic in Beijing
In recent decades, China has suffered from severe environmental deterioration and pollution.[170][171] While regulations such as the 1979 Environmental Protection Law are fairly stringent, they are poorly enforced, as they are frequently disregarded by local communities and government officials in favor of rapid economic development.[172] Urban air pollution is a severe health issue in the country; the World Bank estimated in 2013 that 16 of the world's 20 most-polluted cities are located in China.[173] And China is the country with the highest death toll because of air pollution. There are 1.14 million deaths caused by exposure to ambient air pollution.[174] China is the world's largest carbon dioxide emitter.[175] The country also has significant water pollution problems: 40% of China's rivers had been polluted by industrial and agricultural waste by late 2011.[176] In 2014, the internal freshwater resources per capita of China reduced to 2,062m3, and it was below 500m3 in the North China Plain, while 5,920m3 in the world.[177][178][179]
In China, heavy metals also cause environmental pollution. Heavy metal pollution is an inorganic chemical hazard, which is mainly caused by lead (Pb), chromium (Cr), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni). Five metals among them, Pb, Cr, As, Cd, and Hg, are the key heavy metal pollutants in China. Heavy metal pollutants mainly come from mining, sewage irrigation, the manufacturing of metal-containing products, and other related production activities. High level of heavy metal exposure can also cause permanent intellectual and developmental disabilities, including reading and learning disabilities, behavioral problems, hearing loss, attention problems, and disruption in the development of visual and motor function. According to the data of a national census of pollution, China has more than 1.5 million sites of heavy metals exposure. The total volume of discharged heavy metals in the waste water, waste gas and solid wastes are around 900,000 tons each year from 2005–2011.[180]
However, China is the world's leading investor in renewable energy and its commercialization, with $52 billion invested in 2011 alone;[181][182][183] it is a major manufacturer of renewable energy technologies and invests heavily in local-scale renewable energy projects.[184][185][186] By 2015, over 24% of China's energy was derived from renewable sources, while most notably from hydroelectric power: a total installed capacity of 197 GW makes China the largest hydroelectric power producer in the world.[187][188] China also has the largest power capacity of installed solar photovoltaics system and wind power system in the world.[189][190] In 2011, the Chinese government announced plans to invest four trillion yuan (US$619 billion) in water infrastructure and desalination projects over a ten-year period, and to complete construction of a flood prevention and anti-drought system by 2020.[178][191] In 2013, China began a five-year, US$277 billion effort to reduce air pollution, particularly in the north of the country.[192]
Politics
Supreme Court Building, where the nation's highest court sits

|

|
| Xi Jinping General Secretary and President |
Li Keqiang Premier |
China's constitution states that The People's Republic of China "is a socialist state under the people's democratic dictatorship led by the working class and based on the alliance of workers and peasants," and that the state organs "apply the principle of democratic centralism."[193] The PRC is one of the world's few remaining socialist states openly endorsing communism (see Ideology of the Communist Party of China). The Chinese government has been variously described as communist and socialist, but also as authoritarian and corporatist,[194] with heavy restrictions in many areas, most notably against free access to the Internet, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, the right to have children, free formation of social organizations and freedom of religion.[195] Its current political, ideological and economic system has been termed by its leaders as the "people's democratic dictatorship", "socialism with Chinese characteristics" (which is Marxism adapted to Chinese circumstances) and the "socialist market economy" respectively.[196]
Communist Party
Sign in Tiananmen Square marking the 90th anniversary of the Communist Party of China
China's constitution declares that the country is ruled "under the leadership" of the Communist Party of China (CPC).[197] As China is a de facto one-party state, the General Secretary (party leader) holds ultimate power and authority over state and government serving as the paramount leader.[198] The electoral system is pyramidal. Local People's Congresses are directly elected, and higher levels of People's Congresses up to the National People's Congress (NPC) are indirectly elected by the People's Congress of the level immediately below.[199] The political system is decentralized, and provincial and sub-provincial leaders have a significant amount of autonomy.[200] Another eight political parties, have representatives in the NPC and the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC).[201] China supports the Leninist principle of "democratic centralism",[202] but critics describe the elected National People's Congress as a "rubber stamp" body.[203]
Government
Tiananmen with a portrait of Mao Zedong
The President is the titular head of state, elected by the National People's Congress. The Premier is the head of government, presiding over the State Council composed of four vice premiers and the heads of ministries and commissions. The incumbent president is Xi Jinping, who is also the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China and the Chairman of the Central Military Commission, making him China's paramount leader. The incumbent premier is Li Keqiang, who is also a senior member of the CPC Politburo Standing Committee, China's de facto top decision-making body.[204][135]
There have been some moves toward political liberalization, in that open contested elections are now held at the village and town levels.[205][206] However, the party retains effective control over government appointments: in the absence of meaningful opposition, the CPC wins by default most of the time. Political concerns in China include the growing gap between rich and poor and government corruption.[207][208] Nonetheless, the level of public support for the government and its management of the nation is high, with 80–95% of Chinese citizens expressing satisfaction with the central government, according to a 2011 survey.[209]
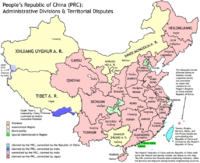
Administrative divisions
The People's Republic of China is divided into 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, each with a designated minority group; four municipalities; and two special administrative regions (SARs) which enjoy a degree of political autonomy. These 31 provincial-level divisions can be collectively referred to as "mainland China", a term which usually excludes two SARs of Hong Kong and Macau. Geographically, all 31 provincial divisions can be grouped into six regions, including North China, Northeast China, East China, South Central China, Southwest China and Northwest China.China considers Taiwan to be its 23rd province, although Taiwan is governed by the Republic of China, which rejects the PRC's claim.[210] None of the divisions are recognized by the ROC government, which claims the entirety of the PRC's territory.
Foreign relations
The PRC has diplomatic relations with 175 countries and maintains embassies in 162. Its legitimacy is disputed by the Republic of China and a few other countries; it is thus the largest and most populous state with limited recognition. In 1971, the PRC replaced the Republic of China as the sole representative of China in the United Nations and as one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.[211] China was also a former member and leader of the Non-Aligned Movement, and still considers itself an advocate for developing countries.[212] Along with Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa, China is a member of the BRICS group of emerging major economies and hosted the group's third official summit at Sanya, Hainan in April 2011.[213]Members Observers Dialogue partners Observer applicants Disputed territories
Under its interpretation of the One-China policy, Beijing has made it a precondition to establishing diplomatic relations that the other country acknowledges its claim to Taiwan and severs official ties with the government of the Republic of China. Chinese officials have protested on numerous occasions when foreign countries have made diplomatic overtures to Taiwan,[214] especially in the matter of armament sales.[215]
Diplomatic Relations of China
Much of current Chinese foreign policy is reportedly based on Premier Zhou Enlai's Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence, and is also driven by the concept of "harmony without uniformity", which encourages diplomatic relations between states despite ideological differences.[216] This policy may have led China to support states that are regarded as dangerous or repressive by Western nations, such as Zimbabwe, North Korea and Iran.[217] China has a close economic and military relationship with Russia,[218] and the two states often vote in unison in the UN Security Council.[219][220][221]
Trade relations
In recent decades, China has played an increasing role in calling for free trade areas and security pacts amongst its Asia-Pacific neighbours. China became a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) on 11 December 2001. In 2004, it proposed an entirely new East Asia Summit (EAS) framework as a forum for regional security issues.[222] The EAS, which includes ASEAN Plus Three, India, Australia and New Zealand, held its inaugural summit in 2005. China is also a founding member of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), along with Russia and the Central Asian republics.In 2000, the United States Congress approved "permanent normal trade relations" (PNTR) with China, allowing Chinese exports in at the same low tariffs as goods from most other countries.[223] China has a significant trade surplus with the United States, its most important export market.[224] In the early 2010s, US politicians argued that the Chinese yuan was significantly undervalued, giving China an unfair trade advantage.[225][226][227] In recent decades, China has followed a policy of engaging with African nations for trade and bilateral co-operation;[228][229][230] in 2012, Sino-African trade totalled over US$160 billion.[231] China has furthermore strengthened its ties with major South American economies, becoming the largest trading partner of Brazil and building strategic links with Argentina.[232][233]
Territorial disputes
Map depicting territorial disputes between the PRC and neighbouring states. For a larger map, see here.
Ever since its establishment after the second Chinese Civil War, the PRC has claimed the territories governed by the Republic of China (ROC), a separate political entity today commonly known as Taiwan, as a part of its territory. It regards the island of Taiwan as its Taiwan Province, Kinmen and Matsu as a part of Fujian Province and islands the ROC controls in the South China Sea as a part of Hainan Province and Guangdong Province. These claims are controversial because of the complicated Cross-Strait relations, with the PRC treating the One-China policy as one of its most important diplomatic principles.[234]
In addition to Taiwan, China is also involved in other international territorial disputes. Since the 1990s, China has been involved in negotiations to resolve its disputed land borders, including a disputed border with India and an undefined border with Bhutan. China is additionally involved in multilateral disputes over the ownership of several small islands in the East and South China Seas, such as the Senkaku Islands and the Scarborough Shoal.[235][236] On 21 May 2014 Xi Jinping, speaking at a conference in Shanghai, pledged to settle China's territorial disputes peacefully. "China stays committed to seeking peaceful settlement of disputes with other countries over territorial sovereignty and maritime rights and interests", he said.[237]
Emerging superpower status
China is regularly hailed as a potential new superpower, with certain commentators citing its rapid economic progress, growing military might, very large population, and increasing international influence as signs that it will play a prominent global role in the 21st century.[30][238] Others, however, warn that economic bubbles and demographic imbalances could slow or even halt China's growth as the century progresses.[239][240] Some authors also question the definition of "superpower", arguing that China's large economy alone would not qualify it as a superpower, and noting that it lacks the military power and cultural influence of the United States.[241]Sociopolitical issues, human rights and reform
March in memory of Chinese Nobel Peace Prize laureate Liu Xiaobo who died of organ failure while in government custody in 2017
The Chinese democracy movement, social activists, and some members of the Communist Party of China have all identified the need for social and political reform. While economic and social controls have been significantly relaxed in China since the 1970s, political freedom is still tightly restricted. The Constitution of the People's Republic of China states that the "fundamental rights" of citizens include freedom of speech, freedom of the press, the right to a fair trial, freedom of religion, universal suffrage, and property rights. However, in practice, these provisions do not afford significant protection against criminal prosecution by the state.[242][243] Although some criticisms of government policies and the ruling Communist Party are tolerated, censorship of political speech and information, most notably on the Internet,[244][245] are routinely used to prevent collective action.[246] In 2005, Reporters Without Borders ranked China 159th out of 167 states in its Annual World Press Freedom Index, indicating a very low level of press freedom.[247] In 2014, China ranked 175th out of 180 countries.[248]
Rural migrants to China's cities often find themselves treated as second-class citizens by the hukou household registration system, which controls access to state benefits.[249][250] Property rights are often poorly protected,[249] and taxation disproportionately affects poorer citizens.[250] However, a number of rural taxes have been reduced or abolished since the early 2000s, and additional social services provided to rural dwellers.[251][252]
A number of foreign governments, foreign press agencies and NGOs also routinely criticize China's human rights record, alleging widespread civil rights violations such as detention without trial, forced abortions,[253] forced confessions, torture, restrictions of fundamental rights,[195][254] and excessive use of the death penalty.[255][256] The government has suppressed popular protests and demonstrations that it considers a potential threat to "social stability", as was the case with the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989.
Candlelight vigil on the 20th anniversary of the Tiananmen Square protests
Falun Gong was first taught publicly in 1992. In 1999, when there were 70 million practitioners,[257] the persecution of Falun Gong began, resulting in mass arrests, extralegal detention, and reports of torture and deaths in custody.[258][259] The Chinese state is regularly accused of large-scale repression and human rights abuses in Tibet and Xinjiang, including violent police crackdowns and religious suppression.[260][261] At least 120,000 members of China's Muslim Uyghur minority have been detained in mass detention camps, termed "reeducation camps", aimed at changing the political thinking of detainees, their identities and their religious beliefs.[262] The state has even sought to control offshore reporting of tensions in Xinjiang, intimidating foreign-based reporters by detaining their family members.[263]
The Chinese government has responded to foreign criticism by arguing that the right to subsistence and economic development is a prerequisite to other types of human rights, and that the notion of human rights should take into account a country's present level of economic development.[264] It emphasizes the rise in the Chinese standard of living, literacy rate and average life expectancy since the 1970s, as well as improvements in workplace safety and efforts to combat natural disasters such as the perennial Yangtze River floods.[264][265][266] Furthermore, some Chinese politicians have spoken out in support of democratization, although others remain more conservative.[267] Some major reform efforts have been conducted; for an instance in November 2013, the government announced plans to relax the one-child policy and abolish the much-criticized re-education through labour program,[144] though human rights groups note that reforms to the latter have been largely cosmetic.[258] During the 2000s and early 2010s, the Chinese government was increasingly tolerant of NGOs that offer practical, efficient solutions to social problems, but such "third sector" activity remained heavily regulated.[268][269]
State-sponsored slavery
According to the 2016 Global Slavery Index, an estimated 3,388,400 people are enslaved in modern-day China, or 0.25% of the population.[270] State-sponsored slavery is part of the Chinese penal system, and there are over a thousand slave labour prisons and camps known collectively as the Laogai. Prisoners are not paid at all, and need their families to send money to them. Prisoners who refuse to work are beaten, and some are beaten to death. Many of the prisoners are political or religious dissidents, and some are recognized internationally as prisoners of conscience. Laogai in Chinese means forced labour and reform. A Chinese president said that they want to see two products coming out of the prisons: the man who has been reformed, and the product made by the man. Harry Wu, himself a former prisoner of the Laogai, filmed undercover footage of the Laogai, and was charged with stealing state secrets. For this, Harry Wu was sentenced to 15 years in prison, but only served 66 days before being deported to the United States.[271][272][273]Military
With 2.3 million active troops, the People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the largest standing military force in the world, commanded by the Central Military Commission (CMC).[274] China has the second-biggest military reserve force, only behind North Korea. The PLA consists of the Ground Force (PLAGF), the Navy (PLAN), the Air Force (PLAAF), and the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF). According to the Chinese government, China's military budget for 2017 totalled US$151,5 billion, constituting the world's second-largest military budget, although the military expenditures-GDP ratio with 1,3% of GDP is below world average.[27] However, many authorities – including SIPRI and the U.S. Office of the Secretary of Defense – argue that China does not report its real level of military spending, which is allegedly much higher than the official budget.[27][275]
As a recognized nuclear weapons state, China is considered both a major regional military power and a potential military superpower.[276] According to a 2013 report by the US Department of Defense, China fields between 50 and 75 nuclear ICBMs, along with a number of SRBMs.[26] However, compared with the other four UN Security Council Permanent Members, China has relatively limited power projection capabilities.[277] To offset this, it has developed numerous power projection assets since the early 2000s – its first aircraft carrier entered service in 2012,[278][279][280] and it maintains a substantial fleet of submarines, including several nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines.[281] China has furthermore established a network of foreign military relationships along critical sea lanes.[282]
China has made significant progress in modernising its air force in recent decades, purchasing Russian fighter jets such as the Sukhoi Su-30, and also manufacturing its own modern fighters, most notably the Chengdu J-10, J-20 and the Shenyang J-11, J-15, J-16, and J-31.[278][283] China is furthermore engaged in developing an indigenous stealth aircraft and numerous combat drones.[284][285][286] Air and Sea denial weaponry advances have increased the regional threat from the perspective of Japan as well as Washington.[287][288] China has also updated its ground forces, replacing its ageing Soviet-derived tank inventory with numerous variants of the modern Type 99 tank, and upgrading its battlefield C3I and C4I systems to enhance its network-centric warfare capabilities.[289] In addition, China has developed or acquired numerous advanced missile systems,[290][291] including anti-satellite missiles,[292] cruise missiles[293] and submarine-launched nuclear ICBMs.[294] According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute's data, China became the world's third largest exporter of major arms in 2010–14, an increase of 143 per cent from the period 2005–09.[295] Chinese officials stated that spending on the military will rise to U.S. $173B in 2018. fox
In August 2018, China tested its first hypersonic flight. The China Academy of Aerospace Aerodynamics (CAAA) claims to have successfully conducted the test with the aircraft Starry Sky-2 that touched a speed of Mach 6 - which is six times the speed of sound.[296]
Economy
China and other major developing economies by GDP per capita at purchasing-power parity, 1990–2013. The rapid economic growth of China (blue) is readily apparent.[297]
The Shanghai Stock Exchange building in Shanghai's Lujiazui financial district. Shanghai has the 25th-largest city GDP in the world, totalling US$304 billion in 2011[298]
China had the largest economy in the world for most of the past two thousand years, during which it has seen cycles of prosperity and decline.[299][300] As of 2014, China has the world's second-largest economy in terms of nominal GDP, totalling approximately US$10.380 trillion according to the International Monetary Fund.[citation needed] In terms of purchasing power parity (PPP) GDP, China's economy is the largest in the world, with a 2014 PPP GDP of US$17.632 trillion.[301] In 2013, its PPP GDP per capita was US$12,880, while its nominal GDP per capita was US$7,589. Both cases put China behind around eighty countries (out of 183 countries on the IMF list) in global GDP per capita rankings.[301]
Economic history and growth
From its founding in 1949 until late 1978, the People's Republic of China was a Soviet-style centrally planned economy. Following Mao's death in 1976 and the consequent end of the Cultural Revolution, Deng Xiaoping and the new Chinese leadership began to reform the economy and move towards a more market-oriented mixed economy under one-party rule. Agricultural collectivization was dismantled and farmlands privatized, while foreign trade became a major new focus, leading to the creation of Special Economic Zones (SEZs). Inefficient state-owned enterprises (SOEs) were restructured and unprofitable ones were closed outright, resulting in massive job losses. Modern-day China is mainly characterized as having a market economy based on private property ownership,[302] and is one of the leading examples of state capitalism.[303][304] The state still dominates in strategic "pillar" sectors such as energy production and heavy industries, but private enterprise has expanded enormously, with around 30 million private businesses recorded in 2008.[305][306][307][308]
Headquarters of Alibaba Group in Hangzhou
Since economic liberalization began in 1978, China has been among the world's fastest-growing economies,[309] relying largely on investment- and export-led growth.[310][311][312] According to the IMF, China's annual average GDP growth between 2001 and 2010 was 10.5%. Between 2007 and 2011, China's economic growth rate was equivalent to all of the G7 countries' growth combined.[313] According to the Global Growth Generators index announced by Citigroup in February 2011, China has a very high 3G growth rating.[314] Its high productivity, low labor costs and relatively good infrastructure have made it a global leader in manufacturing. However, the Chinese economy is highly energy-intensive and inefficient;[315] China became the world's largest energy consumer in 2010,[316] relies on coal to supply over 70% of its energy needs, and surpassed the US to become the world's largest oil importer in September 2013.[317][318] In the early 2010s, China's economic growth rate began to slow amid domestic credit troubles, weakening international demand for Chinese exports and fragility in the global economy.[319][320][321]
In recent years, government claimed growth numbers have come under increased scrutiny, with both non-Chinese financial and economic observes as well as Chinese government officials claiming the government has been inflating its economic output. Examples include, the provincial government in Liaoning publicly admitted that the government has been cooking the books when publishing it's economic data from 2011 to 2014, making an overclaim of over 20%. Tianjin's trillion yuan GDP claim for 2016, was in fact a third lower, at 665 billion yuan ($103 billion).[322][323][324] Regarding the credibility of official data, china's premier has been quoted as saying the GDP numbers are "man-made" and unreliable and should be used "for reference only".[325] A Wall Street Journal survey of 64 select economists found that 96% of respondents think China's GDP estimates don't "accurately reflect the state of the Chinese economy.",[326] while some analysts claim the Chinese growth rate is overstated by 2-3%.[327]
In the online realm, China's e-commerce industry has grown more slowly than the EU and the US, with a significant period of development occurring from around 2009 onwards. According to Credit Suisse, the total value of online transactions in China grew from an insignificant size in 2008 to around RMB 4 trillion (US$660 billion) in 2012. The Chinese online payment market is dominated by major firms such as Alipay, Tenpay and China UnionPay.[328]
China in the global economy
China is a member of the WTO and is the world's largest trading power, with a total international trade value of US$3.87 trillion in 2012.[25] Its foreign exchange reserves reached US$2.85 trillion by the end of 2010, an increase of 18.7% over the previous year, making its reserves by far the world's largest.[329][330] In 2012, China was the world's largest recipient of inward foreign direct investment (FDI), attracting $253 billion.[331] In 2014, China's foreign exchange remittances were $US64 billion making it the second largest recipient of remittances in the world.[332] China also invests abroad, with a total outward FDI of $62.4 billion in 2012,[331] and a number of major takeovers of foreign firms by Chinese companies.[333] In 2009, China owned an estimated $1.6 trillion of US securities,[334] and was also the largest foreign holder of US public debt, owning over $1.16 trillion in US Treasury bonds.[335][336] China's undervalued exchange rate has caused friction with other major economies,[226][337][338] and it has also been widely criticized for manufacturing large quantities of counterfeit goods.[339][340] According to consulting firm McKinsey, total outstanding debt in China increased from $7.4 trillion in 2007 to $28.2 trillion in 2014, which reflects 228% of China's GDP.[341] In 2017 the Institute of International Finance reported that China's debt had reached 304% of its GDP.[342]China ranked 29th in the Global Competitiveness Index in 2009,[344] although it is only ranked 136th among the 179 countries measured in the 2011 Index of Economic Freedom.[345] In 2014, Fortune's Global 500 list of the world's largest corporations included 95 Chinese companies, with combined revenues of US$5.8 trillion.[346] The same year, Forbes reported that five of the world's ten largest public companies were Chinese, including the world's largest bank by total assets, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China.[347]
Class and income inequality
China's middle-class population (if defined as those with annual income of between US$10,000 and US$60,000) had reached more than 300 million by 2012.[348] More than 75 percent of China’s urban consumers are expected to earn between 60.000 to 229.000 RMB per year by 2022.[349] According to the Hurun Report, the number of US dollar billionaires in China increased from 130 in 2009 to 251 in 2012, giving China the world's second-highest number of billionaires.[350][351] China's domestic retail market was worth over 20 trillion yuan (US$3.2 trillion) in 2012[352] and is growing at over 12% annually as of 2013,[353] while the country's luxury goods market has expanded immensely, with 27.5% of the global share.[354] However, in recent years, China's rapid economic growth has contributed to severe consumer inflation,[355][356] leading to increased government regulation.[357] China has a high level of economic inequality,[358] which has increased in the past few decades.[359] In 2012, China's official Gini coefficient was 0.474.[360][361] A study conducted by Southwestern University of Finance and Economics showed that China’s Gini coefficient actually had reached 0.61 in 2012, and top 1% Chinese held more than 25% of China’s wealth.[362]Internationalization of the renminbi
Following the 2008 global financial crisis, China realized the dependency on the US Dollar and the weakness of the international monetary system.[363] The RMB Internationalization accelerated in 2009 when China established dim sum bond market and expanded the Cross-Border Trade RMB Settlement Pilot Project, which helps establish pools of offshore RMB liquidity.[364][365] In November 2010, Russia began using the Chinese renminbi in its bilateral trade with China.[366] This was soon followed by Japan,[367] Australia,[368] Singapore,[369] the United Kingdom,[370] and Canada.[371] As a result of the rapid internationalization of the renminbi, it became the eighth-most-traded currency in the world in 2013.[372]Science and technology
Historical
China was once a world leader in science and technology up until the Ming dynasty. Ancient Chinese discoveries and inventions, such as papermaking, printing, the compass, and gunpowder (the Four Great Inventions), became widespread across East Asia, the Middle East and later to Europe. Chinese mathematicians were the first to use negative numbers.[373][374] By the 17th century, Europe and the Western world surpassed China in scientific and technological advancement.[375] The causes of this early modern Great Divergence continue to be debated by scholars to this day.[376]After repeated military defeats by the European colonial powers and Japan in the 19th century, Chinese reformers began promoting modern science and technology as part of the Self-Strengthening Movement. After the Communists came to power in 1949, efforts were made to organize science and technology based on the model of the Soviet Union, in which scientific research was part of central planning.[377] After Mao's death in 1976, science and technology was established as one of the Four Modernizations,[378] and the Soviet-inspired academic system was gradually reformed.[379]
Modern era
Since the end of the Cultural Revolution, China has made significant investments in scientific research,[380] with $163 billion spent on scientific research and development in 2012.[381] Science and technology are seen as vital for achieving China's economic and political goals, and are held as a source of national pride to a degree sometimes described as "techno-nationalism".[382] Nonetheless, China's investment in basic and applied scientific research remains behind that of leading technological powers such as the United States and Japan.[380][381] Chinese-born scientists have won the Nobel Prize in Physics four times, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry and Physiology or Medicine once respectively, though most of these scientists conducted their Nobel-winning research in western nations.[t]China is developing its education system with an emphasis on science, mathematics and engineering; in 2009, China graduated over 10,000 Ph.D. engineers, and as many as 500,000 BSc graduates, more than any other country.[388] China is also the world's second-largest publisher of scientific papers, producing 121,500 in 2010 alone, including 5,200 in leading international scientific journals.[389] Chinese technology companies such as Huawei and Lenovo have become world leaders in telecommunications and personal computing,[390][391][392] and Chinese supercomputers are consistently ranked among the world's most powerful.[393][394] China is also expanding its use of industrial robots; from 2008 to 2011, the installation of multi-role robots in Chinese factories rose by 136 percent.[395]
The Chinese space program is one of the world's most active, and is a major source of national pride.[396][397] In 1970, China launched its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong I, becoming the fifth country to do so independently.[398] In 2003, China became the third country to independently send humans into space, with Yang Liwei's spaceflight aboard Shenzhou 5; as of 2015, ten Chinese nationals have journeyed into space, including two women. In 2011, China's first space station module, Tiangong-1, was launched, marking the first step in a project to assemble a large manned station by the early 2020s.[399] In 2013, China successfully landed the Chang'e 3 lander and Yutu rover onto the lunar surface; China plans to collect lunar soil samples by 2017.[400] In 2016, China's 2nd space station module, Tiangong-2, was launched from Jiuquan aboard a Long March 2F rocket on 15 September 2016. Then Shenzhou 11 successfully docked with Tiangong-2 on 19 October 2016.
Infrastructure
Telecommunications
Beidou satellites are mainly launched using Long March 3 rocket family.
China currently has the largest number of active cellphones of any country in the world, with over 1 billion users by February 2012.[401] It also has the world's largest number of internet and broadband users,[402] with over 688 million internet users as of 2016, equivalent to around half of its population.[403] The national average broadband connection speed is 9.46 Mbit/s, ranking China 91st in the world in terms of internet speed.[403] As of July 2013, China accounts for 24% of the world's internet-connected devices.[404] Since 2011 China is the nation with the most installed telecommunication bandwidth in the world. By 2014, China hosts more than twice as much national bandwidth potential than the U.S., the historical leader in terms of installed telecommunication bandwidth (China: 29% versus US:13% of the global total).[405]
China Telecom and China Unicom, the world's two largest broadband providers, accounted for 20% of global broadband subscribers. China Telecom alone serves more than 50 million broadband subscribers, while China Unicom serves more than 40 million.[406] Several Chinese telecommunications companies, most notably Huawei and ZTE, have been accused of spying for the Chinese military.[407]
China is developing its own satellite navigation system, dubbed Beidou, which began offering commercial navigation services across Asia in 2012,[408] and is planned to offer global coverage by 2020.[409]
Transport
The Baling River Bridge is one of the highest bridges in the world.
Since the late 1990s, China's national road network has been significantly expanded through the creation of a network of national highways and expressways. In 2011 China's highways had reached a total length of 85,000 km (53,000 mi), making it the longest highway system in the world.[410] In 1991, there were only six bridges across the main stretch of the Yangtze River, which bisects the country into northern and southern halves. By October 2014, there were 81 such bridges and tunnels.
China has the world's largest market for automobiles, having surpassed the United States in both auto sales and production. Auto sales in 2009 exceeded 13.6 million[411] and may reach 40 million by 2020.[412] A side-effect of the rapid growth of China's road network has been a significant rise in traffic accidents,[413] with poorly enforced traffic laws cited as a possible cause—in 2011 alone, around 62,000 Chinese died in road accidents.[414] In urban areas, bicycles remain a common mode of transport, despite the increasing prevalence of automobiles – as of 2012, there are approximately 470 million bicycles in China.[415]
Terminal 3 of Beijing Capital International Airport is the 2nd-largest airport terminal in the world
China's railways, which are state-owned, are among the busiest in the world, handling a quarter of the world's rail traffic volume on only 6 percent of the world's tracks in 2006.[416][417] As of 2013, the country had 103,144 km (64,091 mi) of railways, the third longest network in the world.[418] All provinces and regions are connected to the rail network except Macau. The railways strain to meet enormous demand particularly during the Chinese New Year holiday, when the world's largest annual human migration takes place.[417] In 2013, Chinese railways delivered 2.106 billion passenger trips, generating 1,059.56 billion passenger-kilometers and carried 3.967 billion tons of freight, generating 2,917.4 billion cargo tons-kilometers.[418]
China's high-speed rail (HSR) system started construction in the early 2000s. Today it has over 19,000 kilometers (11,806 miles) of dedicated lines alone, a length that exceeds rest of the world's high-speed rail tracks combined,[419] making it the longest HSR network in the world.[420] With an annual ridership of over 1.1 billion passengers in 2015 it is the world's busiest.[421] The network includes the Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen High-Speed Railway, the single longest HSR line in the world, and the Beijing–Shanghai High-Speed Railway, which has three of longest railroad bridges in the world.[422] The HSR track network is set to reach approximately 16,000 km (9,900 mi) by 2020.[423] The Shanghai Maglev Train, which reaches 431 km/h (268 mph), is the fastest commercial train service in the world.[424]
Since 2000, the growth of rapid transit systems in Chinese cities has accelerated. As of January 2016, 26 Chinese cities have urban mass transit systems in operation and 39 more have metro systems approved[425] with a dozen more to join them by 2020.[426] The Shanghai Metro, Beijing Subway, Guangzhou Metro, Hong Kong MTR and Shenzhen Metro are among the longest and busiest in the world.
The China Standardized EMU, also known as Fuxing Hao, is an indigenous Chinese bullet train whose maximum operating speed reaches 350 km/h (217 mph)
There were approximately 200 airports in 2015 with around 240 planned by 2020. More than two-thirds of the airports under construction worldwide in 2013 were in China,[427] and Boeing expects that China's fleet of active commercial aircraft in China will grow from 1,910 in 2011 to 5,980 in 2031.[427] With rapid expansion in civil aviation, the largest airports in China have also joined the ranks of the busiest in the world. In 2013, Beijing's Capital Airport ranked second in the world by passenger traffic (it was 26th in 2002). Since 2010, the Hong Kong International Airport and Shanghai Pudong International Airport have ranked first and third in air cargo tonnage.
Some 80% of China's airspace remains restricted for military use, and Chinese airlines made up eight of the 10 worst-performing Asian airlines in terms of delays.[428] China has over 2,000 river and seaports, about 130 of which are open to foreign shipping. In 2012, the Ports of Shanghai, Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Guangzhou, Qingdao, Tianjin, Dalian ranked in the top in the world in container traffic and cargo tonnage.[429]
Water supply and sanitation
Water supply and sanitation infrastructure in China is facing challenges such as rapid urbanization, as well as water scarcity, contamination, and pollution.[430] According to data presented by the Joint Monitoring Program for Water Supply and Sanitation of WHO and UNICEF in 2015, about 36% of the rural population in China still did not have access to improved sanitation.[431] In June 2010, there were 1,519 sewage treatment plants in China and 18 plants were added each week.[432] The ongoing South–North Water Transfer Project intends to abate water shortage in the north.[433]Demographics
A
2009 population density map of the People's Republic of China and
Taiwan. The eastern coastal provinces are much more densely populated
than the western interior
The national census of 2010 recorded the population of the People's Republic of China as approximately 1,370,536,875. About 16.60% of the population were 14 years old or younger, 70.14% were between 15 and 59 years old, and 13.26% were over 60 years old.[434] The population growth rate for 2013 is estimated to be 0.46%.[435]
Although a middle-income country by Western standards, China's rapid growth has pulled hundreds of millions of its people out of poverty since 1978. Today, about 10% of the Chinese population lives below the poverty line of US$1 per day, down from 64% in 1978. In 2014, the urban unemployment rate of China was about 4.1%.[436][437]
In 1979 the government was concerned with population growth and implemented a strict family planning policy, known as the "one-child policy" from 1979 to 2013, this policy had little effect on population growth[438] or the size of the total population.[439] Before 2013, this policy sought to restrict families to one child each, with exceptions for ethnic minorities and a degree of flexibility in rural areas. A major loosening of the policy was enacted in December 2013, allowing families to have two children if one parent is an only child.[440] In 2016, the one-child policy was replaced in favor of a two-child policy.[441] Data from the 2010 census implies that the total fertility rate may be around 1.4.[442]
Population of China from 1949 to 2008[needs update]
The policy, along with traditional preference for boys, may be contributing to an imbalance in the sex ratio at birth.[443][444] According to the 2010 census, the sex ratio at birth was 118.06 boys for every 100 girls,[445] which is beyond the normal range of around 105 boys for every 100 girls.[446] The 2010 census found that males accounted for 51.27 percent of the total population.[445] However, China's sex ratio is more balanced than it was in 1953, when males accounted for 51.82 percent of the total population.[445]
Ethnic groups
A trilingual sign in Sibsongbanna, with Tai Lü language on the top
China officially recognizes 56 distinct ethnic groups, the largest of which are the Han Chinese, who constitute about 91.51% of the total population.[14] The Han Chinese – the world's largest single ethnic group[447] – outnumber other ethnic groups in every provincial-level division except Tibet and Xinjiang.[448] Ethnic minorities account for about 8.49% of the population of China, according to the 2010 census.[14] Compared with the 2000 population census, the Han population increased by 66,537,177 persons, or 5.74%, while the population of the 55 national minorities combined increased by 7,362,627 persons, or 6.92%.[14] The 2010 census recorded a total of 593,832 foreign citizens living in China. The largest such groups were from South Korea (120,750), the United States (71,493) and Japan (66,159).[449]
Languages
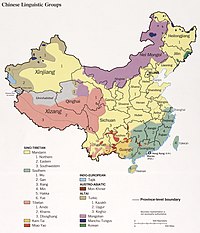
1990 map of Chinese ethnolinguistic groups
There are as many as 292 living languages in China.[450] The languages most commonly spoken belong to the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family, which contains Mandarin (spoken by 70% of the population),[451] and other varieties of Chinese language: Yue (including Cantonese and Taishanese), Wu (including Shanghainese and Suzhounese), Min (including Fuzhounese, Hokkien and Teochew), Xiang, Gan and Hakka. Languages of the Tibeto-Burman branch, including Tibetan, Qiang, Naxi and Yi, are spoken across the Tibetan and Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. Other ethnic minority languages in southwest China include Zhuang, Thai, Dong and Sui of the Tai-Kadai family, Miao and Yao of the Hmong–Mien family, and Wa of the Austroasiatic family. Across northeastern and northwestern China, local ethnic groups speak Altaic languages including Manchu, Mongolian and several Turkic languages: Uyghur, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Salar and Western Yugur. Korean is spoken natively along the border with North Korea. Sarikoli, the language of Tajiks in western Xinjiang, is an Indo-European language. Taiwanese aborigines, including a small population on the mainland, speak Austronesian languages.[452]
Standard Mandarin, a variety of Mandarin based on the Beijing dialect, is the official national language of China and is used as a lingua franca in the country between people of different linguistic backgrounds.[453]
Chinese characters have been used as the written script for the Sinitic languages for thousands of years. They allow speakers of mutually unintelligible Chinese varieties to communicate with each other through writing. In 1956, the government introduced simplified characters, which have supplanted the older traditional characters in mainland China. Chinese characters are romanized using the Pinyin system. Tibetan uses an alphabet based on an Indic script. Uyghur is most commonly written in Persian alphabet based Uyghur Arabic alphabet. The Mongolian script used in China and the Manchu script are both derived from the Old Uyghur alphabet. Zhuang uses both an official Latin alphabet script and a traditional Chinese character script.
Urbanization
Map of the ten largest cities in China (2010)
China has urbanized significantly in recent decades. The percent of the country's population living in urban areas increased from 20% in 1980 to over 55% in 2016.[454][455][456][457] It is estimated that China's urban population will reach one billion by 2030, potentially equivalent to one-eighth of the world population.[455][456] As of 2012, there are more than 262 million migrant workers in China, mostly rural migrants seeking work in cities.[458]
China has over 160 cities with a population of over one million,[459] including the seven megacities (cities with a population of over 10 million) of Chongqing, Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Shenzhen, and Wuhan.[460][461][462] By 2025, it is estimated that the country will be home to 221 cities with over a million inhabitants.[455] The figures in the table below are from the 2010 census,[4] and are only estimates of the urban populations within administrative city limits; a different ranking exists when considering the total municipal populations (which includes suburban and rural populations). The large "floating populations" of migrant workers make conducting censuses in urban areas difficult;[463] the figures below include only long-term residents.
Education
Since 1986, compulsory education in China comprises primary and junior secondary school, which together last for nine years.[465] In 2010, about 82.5 percent of students continued their education at a three-year senior secondary school.[466] The Gaokao, China's national university entrance exam, is a prerequisite for entrance into most higher education institutions. In 2010, 27 percent of secondary school graduates are enrolled in higher education.[467] This number increased significantly over the last years, reaching a tertiary school enrollment of 48.4 percent in 2016.[468] Vocational education is available to students at the secondary and tertiary level.[469]
In February 2006, the government pledged to provide completely free nine-year education, including textbooks and fees.[470] Annual education investment went from less than US$50 billion in 2003 to more than US$250 billion in 2011.[471] However, there remains an inequality in education spending. In 2010, the annual education expenditure per secondary school student in Beijing totalled ¥20,023, while in Guizhou, one of the poorest provinces in China, only totalled ¥3,204.[472] Free compulsory education in China consists of primary school and junior secondary school between the ages of 6 and 15. In 2011, around 81.4% of Chinese have received secondary education.[473] By 2007, there were 396,567 primary schools, 94,116 secondary schools, and 2,236 higher education institutions in China.[474]
As of 2010, 94% of the population over age 15 are literate.[475] In 1949, only 20% of the population could read, compared to 65.5% thirty years later.[476] In 2009, Chinese students from Shanghai achieved the world's best results in mathematics, science and literacy, as tested by the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), a worldwide evaluation of 15-year-old school pupils' scholastic performance.[477] Despite the high results, Chinese education has also faced both native and international criticism for its emphasis on rote memorization and its gap in quality from rural to urban areas.[citation needed]
Health
Chart showing the rise of China's Human Development Index from 1970 to 2010
The National Health and Family Planning Commission, together with its counterparts in the local commissions, oversees the health needs of the Chinese population.[478] An emphasis on public health and preventive medicine has characterized Chinese health policy since the early 1950s. At that time, the Communist Party started the Patriotic Health Campaign, which was aimed at improving sanitation and hygiene, as well as treating and preventing several diseases. Diseases such as cholera, typhoid and scarlet fever, which were previously rife in China, were nearly eradicated by the campaign. After Deng Xiaoping began instituting economic reforms in 1978, the health of the Chinese public improved rapidly because of better nutrition, although many of the free public health services provided in the countryside disappeared along with the People's Communes. Healthcare in China became mostly privatized, and experienced a significant rise in quality. In 2009, the government began a 3-year large-scale healthcare provision initiative worth US$124 billion.[479] By 2011, the campaign resulted in 95% of China's population having basic health insurance coverage.[480] In 2011, China was estimated to be the world's third-largest supplier of pharmaceuticals, but its population has suffered from the development and distribution of counterfeit medications.[481]
As of 2012, the average life expectancy at birth in China is 75 years,[482] and the infant mortality rate is 12 per thousand.[483] Both have improved significantly since the 1950s.[u] Rates of stunting, a condition caused by malnutrition, have declined from 33.1% in 1990 to 9.9% in 2010.[486] Despite significant improvements in health and the construction of advanced medical facilities, China has several emerging public health problems, such as respiratory illnesses caused by widespread air pollution,[487] hundreds of millions of cigarette smokers,[488] and an increase in obesity among urban youths.[489][490] China's large population and densely populated cities have led to serious disease outbreaks in recent years, such as the 2003 outbreak of SARS, although this has since been largely contained.[491] In 2010, air pollution caused 1.2 million premature deaths in China.[492]
Religion
Freedom of religion is guaranteed by China's constitution, although religious organizations that lack official approval can be subject to state persecution.[254][493] The government of the People's Republic of China is officially atheist. Religious affairs and issues in the country are overseen by the State Administration for Religious Affairs.[494]Over the millennia, Chinese civilization has been influenced by various religious movements. The "three teachings", including Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism (Chinese Buddhism), historically have a significant role in shaping Chinese culture,[495][496] enriching a theological and spiritual framework which harkens back to the early Shang and Zhou dynasty. Chinese popular or folk religion, which is framed by the three teachings and other traditions,[497] consists in allegiance to the shen (神), a character that signifies the "energies of generation", who can be deities of the environment or ancestral principles of human groups, concepts of civility, culture heroes, many of whom feature in Chinese mythology and history.[498] Among the most popular cults are those of Mazu (goddess of the seas),[499] Huangdi (one of the two divine patriarchs of the Chinese race),[499][500] Guandi (god of war and business), Caishen (god of prosperity and richness), Pangu and many others. China is home to many of the world's tallest religious statues, including the tallest of all, the Spring Temple Buddha in Henan.
Clear data on religious affiliation in China is difficult to gather due to varying definitions on "religion" and the unorganized, diffusive nature of Chinese religious traditions. Scholars note that in China there is no clear boundary between three teachings religions, Buddhism, Taoism and local folk religious practice.[495] A 2015 poll conducted by Gallup International found that 61% of Chinese people self-identified as "convinced atheist",[501] though it is worthwhile to note that Chinese religions or some of their strands are definable as non-theistic and humanistic religions, since they do not believe that divine creativity is completely transcendent, but it is inherent in the world and in particular in the human being.[502] According to a 2014 study, approximately 74% are either non-religious or practise Chinese folk belief, 16% are Buddhists, 2% are Christians, 1% are Muslims, and 8% adhere to other religions including Taoists and folk salvationism.[503][504] In addition to Han people's local religious practices, there are also various ethnic minority groups in China who maintain their traditional autochthone religions. The various folk salvationisms today comprise 2–3% of the population, while Confucianism as a religious self-identification is common within the intellectual class. Significant faiths specifically connected to certain ethnic groups include Tibetan Buddhism and the Islamic religion of the Hui people, also of Uyghur, Kazakh, Kyrgyz and other peoples in the Northwest China.
- Temple of the White Sulde of Genghis Khan in the town of Uxin in Inner Mongolia, in the Mu Us Desert. Religion in Inner Mongolia blends Chinese and Mongolian folk religious traditions.
- Xuanyuan Temple in Huangling, Yan'an, Shaanxi, dedicated to the worship of the Yellow Emperor (said to be the ancestor of all Chinese) at the ideal sacred centre of China.[v]
- Temple of Guandi in Chaoyang, Liaoning. Religion in Northeast China is characterised by the interaction of folk religions of Chinese and Manchus (Manchu folk religion). Confucian religious movements like Shanrendao are widespread.
- Taoist priests of the Zhengyi order bowing during a rite at the White Cloud Temple of Shanghai. Taoism is a set of orders of philosophy and rite that operate as frameworks of Chinese religion, alongside vernacular ritual traditions.
- Larung Gar Academy of Tibetan Buddhism in Sêrtar, Garzê, Sichuan. Founded in the 1980s, it is now the largest monastic institution in the world, with about 40,000 members of which 1/10 Han Chinese.
- The City of the Eight Symbols in Qi County, Hebi, is the headquarters of the Weixinist Church in Henan. Weixinism is a 21st-century renewal movement of Chinese religion and philosophy.
- Temple of the City God of Sheng County, Zhejiang. City Gods are tutelary deities of administrative units whose worship became common by the late Tang dynasty. Generally, they are deified historical persons from that given locality who distinguished themselves through extraordinary attainments.
- Temple of the Culture Deity (Confucius) in Liuzhou, Guangxi. Confucius is widely worshipped as the Culture Deity in popular religion. Confucianism as a religion is practised by Confucian churches, for instance the Holy Confucian Church established in 2009 in Shenzhen.
Culture
The Temple of Heaven, a center of heaven worship and an UNESCO World Heritage site, symbolizes the Interactions Between Heaven and Mankind.[506]
Since ancient times, Chinese culture has been heavily influenced by Confucianism and conservative philosophies. For much of the country's dynastic era, opportunities for social advancement could be provided by high performance in the prestigious imperial examinations, which have their origins in the Han dynasty.[507] The literary emphasis of the exams affected the general perception of cultural refinement in China, such as the belief that calligraphy, poetry and painting were higher forms of art than dancing or drama. Chinese culture has long emphasized a sense of deep history and a largely inward-looking national perspective.[30] Examinations and a culture of merit remain greatly valued in China today.[508]
The first leaders of the People's Republic of China were born into the traditional imperial order, but were influenced by the May Fourth Movement and reformist ideals. They sought to change some traditional aspects of Chinese culture, such as rural land tenure, sexism, and the Confucian system of education, while preserving others, such as the family structure and culture of obedience to the state. Some observers see the period following the establishment of the PRC in 1949 as a continuation of traditional Chinese dynastic history, while others claim that the Communist Party's rule has damaged the foundations of Chinese culture, especially through political movements such as the Cultural Revolution of the 1960s, where many aspects of traditional culture were destroyed, having been denounced as "regressive and harmful" or "vestiges of feudalism". Many important aspects of traditional Chinese morals and culture, such as Confucianism, art, literature, and performing arts like Peking opera,[509] were altered to conform to government policies and propaganda at the time. Access to foreign media remains heavily restricted.[510]
Today, the Chinese government has accepted numerous elements of traditional Chinese culture as being integral to Chinese society. With the rise of Chinese nationalism and the end of the Cultural Revolution, various forms of traditional Chinese art, literature, music, film, fashion and architecture have seen a vigorous revival,[511][512] and folk and variety art in particular have sparked interest nationally and even worldwide.[513] China is now the third-most-visited country in the world,[514] with 55.7 million inbound international visitors in 2010.[515] It also experiences an enormous volume of domestic tourism; an estimated 740 million Chinese holidaymakers travelled within the country in October 2012 alone.[516]
Literature
The stories in Journey to the West are common themes in Peking opera
Chinese literature is based on the literature of the Zhou dynasty.[517] Concepts covered within the Chinese classic texts present a wide range of thoughts and subjects including calendar, military, astrology, herbology, geography and many others.[518] Some of the most important early texts include the I Ching and the Shujing within the Four Books and Five Classics which served as the Confucian authoritative books for the state-sponsored curriculum in dynastic era.[519] Inherited from the Classic of Poetry, classical Chinese poetry developed to its floruit during the Tang dynasty. Li Bai and Du Fu opened the forking ways for the poetic circles through romanticism and realism respectively.[520] Chinese historiography began with the Shiji, the overall scope of the historiographical tradition in China is termed the Twenty-Four Histories, which set a vast stage for Chinese fictions along with Chinese mythology and folklore.[521] Pushed by a burgeoning citizen class in the Ming dynasty, Chinese classical fiction rose to a boom of the historical, town and gods and demons fictions as represented by the Four Great Classical Novels which include Water Margin, Romance of the Three Kingdoms, Journey to the West and Dream of the Red Chamber.[522] Along with the wuxia fictions of Jin Yong and Liang Yusheng,[523] it remains an enduring source of popular culture in the East Asian cultural sphere.[524]
Bian Lian(Face-Changing) Performer
In the wake of the New Culture Movement after the end of the Qing dynasty, Chinese literature embarked on a new era with written vernacular Chinese for ordinary citizens. Hu Shih and Lu Xun were pioneers in modern literature.[525] Various literary genres, such as misty poetry, scar literature, young adult fiction and the xungen literature, which is influenced by magic realism,[526] emerged following the Cultural Revolution. Mo Yan, a xungen literature author, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2012.[527]
Cuisine
Chinese foods originated from different regional cuisines: laziji from Sichuan in the west, xiaolongbao from Jiangsu in the east, rice noodle roll from Cantonese in the south and Peking duck from Shandong in the north.[528]
Chinese cuisine is highly diverse, drawing on several millennia of culinary history and geographical variety, in which the most influential are known as the "Eight Major Cuisines", including Sichuan, Cantonese, Jiangsu, Shandong, Fujian, Hunan, Anhui, and Zhejiang cuisines.[529] All of them are featured by the precise skills of shaping, heating, colorway and flavoring.[530] Chinese cuisine is also known for its width of cooking methods and ingredients,[531] as well as food therapy that is emphasized by traditional Chinese medicine.[532] Generally, China's staple food is rice in the south, wheat based breads and noodles in the north. The diet of the common people in pre-modern times was largely grain and simple vegetables, with meat reserved for special occasions. And the bean products, such as tofu and soy milk, remain as a popular source of protein.[533] Pork is now the most popular meat in China, accounting for about three-fourths of the country's total meat consumption.[534] While pork dominates the meat market, there is also pork-free Buddhist cuisine and Chinese Islamic cuisine. Southern cuisine, due to the area's proximity to the ocean and milder climate, has a wide variety of seafood and vegetables; it differs in many respects from the wheat-based diets across dry northern China. Numerous offshoots of Chinese food, such as Hong Kong cuisine and American Chinese food, have emerged in the nations that play host to the Chinese diaspora.
Sports
Dragon boat racing, a popular traditional Chinese sport
China has become a prime sports destination worldwide. The country gained the hosting rights for several major global sports tournaments including the 2008 Summer Olympics, the 2015 World Championships in Athletics, the upcoming 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup and the upcoming 2022 Winter Olympics.
China has one of the oldest sporting cultures in the world. There is evidence that archery (shèjiàn) was practiced during the Western Zhou dynasty. Swordplay (jiànshù) and cuju, a sport loosely related to association football[535] date back to China's early dynasties as well.[536]
Physical fitness is widely emphasized in Chinese culture, with morning exercises such as qigong and t'ai chi ch'uan widely practiced,[537] and commercial gyms and private fitness clubs are gaining popularity across the country.[538] Basketball is currently the most popular spectator sport in China.[539] The Chinese Basketball Association and the American National Basketball Association have a huge following among the people, with native or ethnic Chinese players such as Yao Ming and Yi Jianlian held in high esteem.[540] China's professional football league, now known as Chinese Super League, was established in 1994, it is the largest football market in Asia.[541] Other popular sports in the country include martial arts, table tennis, badminton, swimming and snooker. Board games such as go (known as wéiqí in Chinese), xiangqi, mahjong, and more recently chess, are also played at a professional level.[542] In addition, China is home to a huge number of cyclists, with an estimated 470 million bicycles as of 2012.[415] Many more traditional sports, such as dragon boat racing, Mongolian-style wrestling and horse racing are also popular.[543]
China has participated in the Olympic Games since 1932, although it has only participated as the PRC since 1952. China hosted the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, where its athletes received 51 gold medals – the highest number of gold medals of any participating nation that year.[544] China also won the most medals of any nation at the 2012 Summer Paralympics, with 231 overall, including 95 gold medals.[545][546] In 2011, Shenzhen in Guangdong, China hosted the 2011 Summer Universiade. China hosted the 2013 East Asian Games in Tianjin and the 2014 Summer Youth Olympics in Nanjing. Beijing and its nearby city Zhangjiakou of Hebei province will also collaboratively host the 2022 Olympic Winter Games, which will make Beijing the first city in the world to hold both the Summer Olympics and the Winter Olympics.