| Denali National Park and Preserve | |
|---|---|
IUCN category V (protected landscape/seascape)
| |

Denali is the tallest peak in North America
| |
| Location | Denali Borough and Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska, United States |
| Nearest city | Healy |
| Coordinates | 63°20′N 150°30′WCoordinates: 63°20′N 150°30′W |
| Area | 4,740,911 acres (19,185.79 km2) (park) and 1,304,242 acres (5,278.08 km2) (preserve) |
| Established | February 26, 1917 |
| Visitors | 594,660 (in 2018) |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
| Website | Official website |
Denali National Park and Preserve is an American national park and preserve located in Interior Alaska, centered on Denali, the highest mountain in North America. The park and contiguous preserve encompass 6,045,153 acres (9,446 sq mi; 24,464 km2) which is larger than the state of New Hampshire. On December 2, 1980, 2,146,580-acre (3,354 sq mi; 8,687 km2) Denali Wilderness was established within the park. Denali's landscape is a mix of forest at the lowest elevations, including deciduous taiga, with tundra at middle elevations, and glaciers, snow, and bare rock at the highest elevations. The longest glacier is the Kahiltna Glacier. Wintertime activities include dog sledding, cross-country skiing, and snowmobiling. The park received 594,660 recreational visitors in 2018.
History
Prehistory and protohistory
Human
habitation in the Denali Region extends to more than 11,000 years
before the present, with documented sites just outside park boundaries
dated to more than 8,000 years before present. However, relatively few
archaeological sites have been documented within the park boundaries,
owing to the region's high elevation, with harsh winter conditions and
scarce resources compared to lower elevations in the area. The oldest
site within park boundaries is the Teklanika River site, dated to about
7130 BC. More than 84 archaeological sites have been documented within
the park. The sites are typically characterized as hunting camps rather
than settlements, and provide little cultural context. The presence of Athabaskan
peoples in the region is dated to 1,500 - 1,000 years before present on
linguistic and archaeological evidence, while researchers have proposed
that Athabaskans may have inhabited the area for thousands of years
before then. The principal groups in the park area in the last 500 years
include the Koyukon, Tanana and Dena'ina people.
Establishment of the park
Park map
In 1906, conservationist Charles Alexander Sheldon conceived the idea of preserving the Denali region as a national park. He presented the plan to his co-members of the Boone and Crockett Club.
They decided that the political climate at the time was unfavorable for
congressional action, and that the best hope of success rested on the
approval and support from the Alaskans themselves. Sheldon wrote, "The
first step was to secure the approval and cooperation of the delegate
who represented Alaska in Congress."
In October 1915, Sheldon took up the matter with Dr. E. W. Nelson of the Biological Survey at Washington, D.C. and with George Bird Grinnell,
with a purpose to introduce a suitable bill in the coming session of
Congress. The matter was then taken to the Game Committee of the Boone and Crockett Club and, after a full discussion, it received the committee's full endorsement.
On December 3, 1915, the plan was presented to Alaska's delegate, James Wickersham, who after some deliberation gave his approval. The plan then went to the Executive Committee of the Boone and Crockett Club and, on December 15, 1915, it was unanimously accepted. The plan was thereupon endorsed by the Club and presented to Stephen Mather, Assistant Secretary of the Interior in Washington, D.C., who immediately approved it.
The bill was introduced in April 1916, by Delegate Wickersham in the House and by Senator Key Pittman
of Nevada in the Senate. Much lobbying took place over the following
year, and on February 19, 1917, the bill passed. On February 26, 1917,
11 years from its conception, the bill was signed in legislation by the
President of the United States, Woodrow Wilson, thereby creating Mount McKinley National Park.
A portion of Denali, excluding the summit, was included the
original park boundary. On Thanksgiving Day in 1921, the Mount McKinley
Park Hotel opened. In July 1923, President Warren Harding stopped at the hotel, on a tour of the length of the Alaska Railroad, during which he drove a golden spike signaling its completion at Nenana.
The hotel was the first thing visitors saw stepping down from the
train. The flat-roofed, two-story log building featured exposed
balconies, glass windows, and electric lights. Inside were two dozen
guest rooms, a shop, lunch counter, kitchen, and storeroom. By the
1930s, there were reports of lice, dirty linen, drafty rooms, and
marginal food, which led to the hotel's eventually closing.
In 1947, the park boundaries expanded to include the area of the
hotel and railroad. After being abandoned for many years, the hotel was
destroyed in 1950 by a fire.
There was no road access to the park entrance until 1957. Now
with a highway connection to Anchorage and Fairbanks, park attendance
greatly expanded: there were 5,000 visitors in 1956 and 25,000 visitors
by 1958.
Graphic of Denali Park History - Denali Visitor Center
The park was designated an international biosphere reserve in 1976. A separate Denali National Monument was proclaimed by President Jimmy Carter on December 1, 1978.
Naming controversy
Aerial view of Denali's summit
The name of Mount McKinley National Park was subject to local
criticism from the beginning of the park. The word Denali means "the
high one" in the native Athabaskan language and refers to the mountain itself. The mountain was named after newly elected US president William McKinley
in 1897 by local prospector William A. Dickey. The United States
government formally adopted the name Mount McKinley after President
Wilson signed the bill creating Mount McKinley National Park into effect
in 1917. In 1980, Mount McKinley National Park was combined with Denali National Monument, and the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act
named the combined unit the Denali National Park and Preserve. At that
time the Alaska state Board of Geographic Names changed the name of the
mountain to Denali. However, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names
did not recognize the change and continued to denote the official name
as Mount McKinley. This situation lasted until Aug. 30, 2015, when
President Barack Obama directed Secretary of the Interior Sally Jewell
to rename the mountain to Denali, using statutory authority to act on
requests when the Board of Geographic Names does not do so in a
"reasonable" time period.
1990s
In 1992, Christopher McCandless ventured into the Alaskan wilderness and settled in an abandoned bus in the park, off the Stampede Trail, near Lake Wentitika. He carried little food or equipment, and hoped to live simply for a time in solitude. Almost four months later, McCandless' starved remains were found, weighing only 67 pounds (30 kg). His story has been widely publicized via articles, books, and films,
and the bus in which his remains were found has become a shrine of
sorts, attracting pilgrimages by people from around the world, many of
whom leave tributes in McCandless' memory.
2000s
On November 5, 2012, the United States Mint released the 15th of its America the Beautiful Quarters series, which honors Denali National Park. The coin's reverse side features a Dall sheep with Denali in the background.
In September 2013, President Barack Obama signed the Denali National Park Improvement Act into law. Hundreds, if not thousands of people had promoted the law and put it through Congress. The statute allows the United States Department of the Interior to "issue permits for microhydroelectric
projects in the Kantishna Hills area of the Denali National Park and
Preserve in Alaska"; it authorizes the Department of the Interior and a
company called Doyon Tourism, Inc. to exchange some land in the area; it
authorizes the National Park Service
(NPS) to "issue permits to construct a natural gas pipeline in the
Denali National Park"; and it renames the existing Talkeetna Ranger
Station the Walter Harper Talkeetna Ranger Station.
Geography
Denali National Park and Preserve includes the central, highest portion of the Alaska Range,
together with many of the glaciers and glacial valleys running
southwards out of the range. To the north the park and preserve
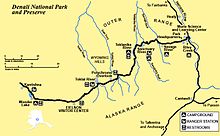
encompass the valleys of the McKinley, Toklat and Foraker Rivers, as well as the Kantishna and Wyoming Hills. The George Parks Highway runs along the eastern edge of the park, crossing the Alaska Range at the divide between the valleys of the Chultina River and the Nenana River. The entrance to the park is about 11 miles (18 km) south of Healy.
The Denali Visitor Center and the park headquarters are located just
inside the entrance. The park road parallels the Alaska Range for 92
miles (148 km), ending at Kantishna. Preserve lands are located on the
west side of the park, with one parcel encompassing areas of lakes in
the Highpower Creek and Muddy River areas, and the second preserve area
covering the southwest end of the high Alaska Range around Mount Dall.
In contrast to the park, where hunting is prohibited or restricted to
subsistence hunting by local residents, sport hunting is allowed in the
preserve lands.
Vehicle access
The single road within the park
The park is serviced by the 91-mile (146 km) long Denali Park Road, which begins at the George Parks Highway and continues to the west, ending at Kantishna.
Located 1 mile (1.6 km) within the park, the Wilderness Access Center
(which houses a small gift shop, a coffee stand, and an information
desk) is the main location to arrange a bus trip into the park, or
reserve/check-in for a campground site. All shuttle buses depart from
here, as do some tours. The Denali Visitor Center is at mile marker 1.5
on the park road and is the main source of visitor information. Most
ranger-led programs begin at the Denali Visitor Center. Other features
include an exhibit hall. Within a short walking distance from the
Visitor Center are a restaurant, a bookstore, the Murie Science and
Learning Center, the Denali National Park railroad depot, and the McKinley National Park Airport.
The Denali Park Road runs north of and roughly parallel to the imposing Alaska Range. Only a small fraction of the road is paved because permafrost and the freeze-thaw cycle
would create a high cost for maintaining a paved road. The first 15
miles (24 km) of the road are available to private vehicles, allowing
easy access to the Riley Creek and Savage River campgrounds. Private
vehicle access is prohibited beyond the Savage River Bridge. There is a
turn around for motorists at this point, as well as a nearby parking
area for those who wish to hike the Savage River Loop Trail. Beyond this
point, visitors must access the interior of the park through
tour/shuttle buses.
The tours travel from the initial boreal forests through tundra to the Toklat River or Kantishna. Several portions of the road run alongside sheer cliffs that drop hundreds of feet at the edges. There are no guardrails. As a result of the danger involved, and because most of the gravel road is only one lane wide, drivers must be trained in procedures for navigating the sharp mountain curves, and yielding the right-of-way to opposing buses and park vehicles.
Road map with camping locations, visitor centers, and ranger stations
There are four camping areas located within the interior of the park (Sanctuary River, Teklanika River, Igloo Creek, and Wonder Lake).
Camper buses provide transportation to these campgrounds, but only
passengers camping in the park can use these particular buses. At mile
marker 53 on road is the Toklat River Contact Station. All shuttle and
tour buses make a stop at Toklat River. The contact station features
rest rooms, visitor information, and a small bookstore. Eielson Visitor
Center is located four hours into the park on the road (at mile marker
66). It features restrooms, daily ranger-led programs during the summer,
and on clear days, views of Denali and the Alaska Range. Wonder Lake
and Kantishna are a six-hour bus ride from the Visitors Center. During
the winter, only the portion of the Denali Park Road near the Visitors
Center remains open.
Kantishna features five lodges: the Denali Backcountry Lodge,
Kantishna Roadhouse, Skyline Lodge, Camp Denali and North Face Lodge.
Visitors can bypass the six hour bus ride and charter an air taxi flight
to the Kantishna Airport. The Kantishna resorts have no TVs, and there is no cell phone service in the area. Lodging with services can be found in McKinley Park,
one mile north of the park entrance on the George Parks Highway. Many
hotels, restaurants, gift shops, and a convenience store are located in
Denali Park.
While the main park road goes straight through the middle of the
Denali National Park Wilderness, the national preserve and portions of
the park not designated wilderness
are even more inaccessible. There are no roads extending out to the
preserve areas, which are on the far west end of the park. The far north
of the park, characterized by hills and rivers, is accessed by the Stampede Trail,
a dirt road which effectively stops at the park boundary near the "Into
the Wild" bus. The rugged south portion of the park, characterized by
large glacier-filled canyons,
is accessed by Petersville Road, a dirt road that stops about 5 miles
(8.0 km) outside the park. The mountains can be accessed most easily by
air taxis that land on the glaciers. Kantishna can also be reached by
air taxi via the Purkeypile Airport, which is just outside the park
boundary.
Visitors who want to climb Denali
need to obtain a climbing permit first, and go through an orientation
as well. These can be found at the Walter Harper Talkeetna Ranger
Station in Talkeetna, Alaska,
about 100 miles (160 km) south of the entrance to Denali National Park
and Preserve. This center serves as the center of mountaineering
operations. It is open year-round.
Wilderness
Camping in the Savage River drainage
The Denali Wilderness is a wilderness area within Denali National
Park and Preserve that protects the higher elevations of the central Alaska Range, including Denali. The wilderness comprises about one-third of the current national park and preserve—2,146,580 acres (3,354 sq mi; 8,687 km2) that correspond with the former park boundaries from 1917 to 1980.
Geology
Geologic time scale and geologic map of terranes
Tectonic history
Denali from Ruth Glacier
Denali National Park and Preserve is located in the central area of
the Alaska Range, a mountain chain extending 600 miles (970 km) across
Alaska. Its best-known geologic feature is Denali,
formerly known as Mount McKinley. Its elevation of 20,310 feet
(6,190.5 m) makes it the highest mountain in North America. Its vertical
relief (distance from base to peak) of 18,000 feet (5,500 m) is the
highest of any mountain in the world. The mountain is still gaining
about 1 millimetre (0.039 in) in height each year due to the continued
convergence of the North American and Pacific Plates. The mountain is primarily made of granite, a hard rock that does not erode easily; this is why it has retained such a great height rather than being eroded.
The park area is characterized by collision tectonics: over the past millions of years, exotic terranes
in the Pacific Ocean have been moving toward the North American
landmass and accreting, or attaching, to the area that now makes up
Alaska. The oldest rocks in the park are part of the Yukon-Tanana
terrane. They originated from ocean sediments deposited between 400
million and 1 billion years ago. The original rocks have been affected
by the processes of regional metamorphism, folding, and faulting to form
rocks such as schist, quartzite, phyllite, slate, marble, and limestone. The next oldest group of rocks is the Farewell terrane. It is composed of rocks from the Paleozoic era
(250-500 million years old). The sediments that make up these rocks
were deposited in a variety of marine environments, ranging from deep
ocean basins to continental shelf areas. The abundant marine fossils are
evidence that around 380 million years ago, this area had a warm,
tropical climate. The Pingston, McKinley, and Chulitna terranes are the
next oldest; they were deposited in the Mesozoic era. The rock types include marble, chert, limestone, shale, and sandstone. There are intrusions of igneous rocks, such as gabbro, diabase, and diorite. Special features include pillow basalts,
which are formed when molten lava flows into water and a hard outer
crust forms, making a puffy, pillow shaped feature; as well as an
ophiolite sequence, which is a distinct sequence of rocks indicating
that a section of oceanic crust has been uplifted and thrust onto a
continental area.
Polychrome Mountain
Some of the youngest rocks in the park include the Kahlitna terrane,
which is a flysch sequence (a sedimentary rock sequence deposited in a
marine environment during the early stages of mountain building) formed
about 100 million years ago, during late Cretaceous time. Another rock sequence is the McKinley Intrusive Sequence, which includes Denali. The Cantwell Volcanics include basalt and rhyolite flows, as well as ash deposits. An example can be seen at Polychrome Pass in the park.
Mesozoic fossils include fossil trackways from therizinosaurids and hadrosaurids in the Cantwell Formation indicate the area was once an immigration point for dinosaurs
traveling between Asia and North America during the Late Cretaceous
period. Studies of fossil plants from the same formation indicate the
area was wet, with marshes and ponds throughout the region.
Denali National Park and Preserve is located in an area of
intense tectonic activity: the Pacific Plate is subducting under the
North American plate, creating the Denali fault system, which is a right-lateral strike-slip fault over 720 miles (1,160 km) long. This is a part of the larger fault system which includes the famous San Andreas Fault
of California. Over 600 earthquakes occur in the park each year,
helping seismologists to understand this fault system. Most of these
earthquakes are too small to be felt, although two large earthquakes did
occur in 2002. On October 23, 2002 a magnitude 6.7 earthquake occurred
in the park, and on November 3, 2002, a magnitude 7.9 earthquake
occurred. These earthquakes did not cause a significant loss of life or
property, since the area is very sparsely populated, but they did
trigger thousands of landslides.

Painting
of the heavily glaciated southern part of Denali, looking
north-northwest. Mount Foraker is at the left, and Denali, purposely
drawn on an exaggerated scale, is featured in the center. Mouse over the
painting, and click on an area of interest.
Glaciers
The Kichatna Mountains in the southwestern portion of the preserve
Glaciers cover about 16% of the 6 million acres of Denali National
Park and Preserve. There are more extensive glaciers on the southeastern
side of the range because more snow is dropped on this side from the
moisture-bearing winds from the Gulf of Alaska. The 5 largest south-facing glaciers are Yentna (20 miles (32 km) long), Kahiltna (30 miles (48 km)), Tokositna (23 miles (37 km)), Ruth (31 miles (50 km)), and Eldrige (30 miles (48 km)). The Ruth glacier is 3,800 feet (1,200 m) thick.[18] However, the largest glacier, Muldrow Glacier
(32 miles (51 km) long), is located on the north side. Nonetheless, the
northern side has smaller and shorter glaciers overall. Muldrow glacier
has "surged"
twice in the last hundred years. Surging means that it has moved
forward for a short time at a greatly increased rate of speed, due to a
build-up of water between the bottom of the glacier and the bedrock
channel floating on the ice (due to hydrostatic pressure).
At the upper ends of Denali's glaciers are steep-walled semicircular basins called cirques.
Cirques form from freeze-thaw cycles of meltwater in the rocks above
the glacier, and by glacial erosion and mass wasting occurring under the
glacier. As cirques on the opposite sides of a ridge are cut deeper
into the divide, they form a narrow, sharp, serrated ridge called an arête. As the arête wears away from glacial ice breaking it down, the low point between cirques is called a col
(or if it is large, a pass). Cols are saddle-shaped depressions in the
ridge between cirques. A spire-like sharp peak, called a horn, is formed when cirques cut back into a mountaintop from three or four sides.
Glaciers deposit rock fragments, but the most notable of the
depositions are the erratics, which are large rock fragments carried
some distance from the source, found on glacial terraces and ridge tops
in many places throughout Denali. Headquarter erratics are made of
granite and can be the size of a house. Some erratics (like those from
the Yanert Valley) are located 30 miles (48 km) away from their original
location.
Ruth Glacier and medial moraine - the dark stripe of debris down the middle
Large amounts of rock debris are carried on, in, and beneath the ice
as the glaciers move downslope. Lateral moraines are created as debris
accumulates as low ridges of till that ride along the edge of the moving
glaciers. When lateral moraines adjacent to each other join, they create medial moraines, which are also carried down on the surface of the moving ice.
Braided meltwater streams heavily loaded with rock debris
continually shift and intertwine their channels over valley floors.
Valley trains are built up as streams drop quantities of poorly sorted
sediment. Valley trains are long, narrow accumulation of glacial
outwash, confined by valley walls.
Kettles
are formed when glacial retreat and melting is rapid, and blocks of ice
are still buried under till. When the ice under the till melts, the
till slumps in and forms depressions called kettles. When kettles fill
with water, they are known as kettle lakes. Kettle lakes are visible near the Polychrome Overlook, the Teklanika rest stop and near Wonder Lake.
Permafrost
During the very cold Pleistocene
climates, all of Denali was solidly frozen. In the northern areas of
the range, it is very much still frozen due to continued cold
temperatures. Permanently frozen ground is known as permafrost.
In Denali, the permafrost is discontinuous, meaning due to difference
in vegetation, temperatures, snow cover, hydrology, etc., not all of the
ground is solidly frozen. The active layer (the layer that freezes and
thaws seasonally) can be from 1 inch (25 mm) to 10 feet (3.0 m) thick.
The permafrost layer below the active layer has been measured to be
between 30 and 100 feet (9.1 and 30.5 m) deep depending on the location
of measurement in the park. A stand of white spruce growing on a lower
slope of Denali is called the Drunken Forest
because of the oddly leaning trees which seem to look "drunk." This
appearance is due to the sliding soil beneath them, due to the
permafrost difference and freeze-thaw oscillations that occur due to
differences in temperature, vegetation, and hydrology.
Shallow ponds in Denali are known as thaw lakes and cave-in
lakes. They form where sunwarmed water has melted basins in the
underlying permafrost. They deepen gradually in the summer months
depending on the temperature variance. If the temperature is high
enough, the thaw lakes and cave-in lakes will enlarge as their rims
collapse.
Ice has 10 percent greater volume than water, so it continues to
exert pressure on the ground. Thermal expansion and contraction can
cause cracks to develop in the permafrost. During the thaw season in the
freeze-thaw cycle, water gets into the cracks and forms veins of ice
called ice wedges. Ice wedges enlarge with successive seasons of
freezing and thawing. Some ice wedges that have been buried for
centuries are revealed during excavations or landslides.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Denali National Park has a Subarctic with Cool Summers and Year Around Rainfall Climate (‘’Dfc’’). The plant hardiness zone at Denali Visitor Center is 3a with an average annual extreme minimum temperature of -38.9 °F (-39.4 °C).
Long winters are followed by short growing seasons. Eighty
percent of the bird population returns after cold months, raising their
young. Most mammals and other wildlife in the park spend the brief
summer months preparing for winter and raising their young.
Summers are usually cool and damp, but temperatures in the 70s
are not rare. The weather is so unpredictable that there have even been
instances of snow in August.
The north and south side of the Alaskan Range have a completely different climate. The Gulf of Alaska
carries moisture to the south side, but the mountains block water to
the north side. This brings a drier climate and huge temperature
fluctuations to the north. The south has transitional maritime
continental climates, with moister, cooler summers and warmer winters.
Ecology
Alpine forest and lakes in Denali
The Alaska Range
is a mountainous expanse running through the entire park, strongly
influencing the park's ecosystems. Vegetation in the park depends on the
altitude. The treeline is at 2,500 feet (760 m), causing most of the park to be a vast expanse of tundra. In the lowland areas of the park, such as the western sections surrounding Wonder Lake, spruces and willows
dominate the forest. Most trees and shrubs do not reach full size, due
to unfavorable climate and thin soils. There are three types of forest
in the park: from lowest to highest, they are low brush bog, bottomland spruce-poplar forest, upland spruce-hardwood forest. The forest grows in a mosaic, due to periodic fires.
In the tundra of the park, layers of topsoil collect on rotten fragmented rock moved by thousands of years of glacial activity. Mosses, ferns, grasses, and fungi grow on the topsoil. In areas of muskeg, tussocks form and may collect algae. The term 'muskeg' includes spongy waterlogged tussocks as well as deep pools of water covered by solid-looking moss. Wild blueberries and soap berries thrive in the tundra and provide the bears of Denali with the main part of their diet.
Over 450 species of flowering plants fill the park and can be viewed in bloom throughout summer. Images of goldenrod, fireweed, lupine, bluebell, and gentian filling the valleys of Denali are often used on postcards and in artwork.
Adult brown bear (Ursus arctos) and cub on the park road
Denali is home to a variety of North American birds and mammals, including an estimated 300-350 grizzly bears on the north side of the Alaska Range (70 bears per 1000 square miles) and an estimated 2,700 black bears (334 per 1,000 square miles). As of 2014, park biologists were monitoring about 51 wolves in 13 packs (7.4 wolves per 1,000 square miles), while surveys estimated 2,230 caribou in 2013, and 1,477 moose in 2011. Dall sheep are often seen on mountainsides. Smaller animals such as coyotes, hoary marmots, shrews, Arctic ground squirrels, beavers, pikas, and snowshoe hares are seen in abundance. Red foxes, martens, lynxes, wolverines also inhabit the park, but are more rarely seen due to their elusive natures.
Many migratory bird species reside in the park during late spring and summer. There are waxwings, Arctic warblers, pine grosbeaks, and wheatears, as well as ptarmigan and the tundra swan. Raptors include a variety of hawks, owls, and gyrfalcons, as well as the abundant but striking golden eagles.
A caribou and tour bus on the park road
Ten species of fish, including trout, salmon, and Arctic grayling,
share the waters of the park. Because many of the rivers and lakes of
Denali are fed by glaciers, glacial silt and cold temperatures slow the
metabolism of the fish, preventing them from reaching normal sizes. A single amphibious species, the wood frog, also lives among the lakes of the park.
Denali park rangers maintain a constant effort to keep the
wildlife wild by limiting the interaction between humans and park
animals. Feeding any animal is strictly forbidden, as it may cause
adverse effects on the feeding habits of the creature. Visitors are
encouraged to view animals from safe distances. In August 2012 the park
experienced its first known fatal bear attack when a lone hiker
apparently startled a large male grizzly while photographing it.
Analysis of the scene and the hiker's camera strongly suggest he
violated park regulations regarding backcountry bear encounters, which
all permit holders are made aware of.
Certain areas of the park are often closed due to uncommon wildlife
activity, such as denning areas of wolves and bears or recent kill
sites.
Panoramic view of the Polychrome Mountains