| Hepatitis B | |
|---|---|
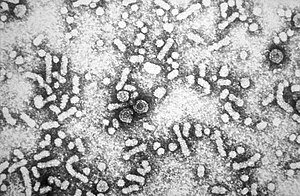 | |
| Electron micrograph of hepatitis B virus | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | None, yellowish skin, tiredness, dark urine, abdominal pain |
| Complications | Cirrhosis, liver cancer |
| Usual onset | Symptoms may take up to 6 months to appear |
| Duration | Short or long term |
| Causes | Hepatitis B virus spread by some body fluids |
| Risk factors | Intravenous drug use, sexual intercourse, dialysis, living with an infected person |
| Diagnostic method | Blood tests |
| Prevention | Hepatitis B vaccine |
| Treatment | Antiviral medication (tenofovir, interferon), liver transplantation |
| Frequency | 356 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 65,400 direct (2015), >750,000 (total) |
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, tiredness, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. Cirrhosis or liver cancer occur in about 25% of those with chronic disease.
The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection.[1] Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. The diagnosis is usually confirmed by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five main hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.
The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion, and that condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease, antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon may be useful; however, these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.
About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 343 million who have chronic infections. Another 129 million new infections occurred in 2013. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults are chronically infected. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as "serum hepatitis". Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.
Signs and symptoms
Acute infection with hepatitis B virus is associated with acute viral hepatitis,
an illness that begins with general ill-health, loss of appetite,
nausea, vomiting, body aches, mild fever, and dark urine, and then
progresses to development of jaundice. It has been noted that itchy skin
has been an indication as a possible symptom of all hepatitis virus
types. The illness lasts for a few weeks and then gradually improves in
most affected people. A few people may have a more severe form of liver
disease known as fulminant hepatic failure and may die as a result. The infection may be entirely asymptomatic and may go unrecognized.
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus either may be asymptomatic or may be associated with a chronic inflammation of the liver (chronic hepatitis), leading to cirrhosis over a period of several years. This type of infection dramatically increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC; liver cancer). Across Europe, hepatitis B and C cause approximately 50% of hepatocellular carcinomas. Chronic carriers are encouraged to avoid consuming alcohol as it increases their risk for cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis B virus has been linked to the development of membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN).
Symptoms outside of the liver are present in 1–10% of HBV-infected people and include serum-sickness–like syndrome, acute necrotizing vasculitis (polyarteritis nodosa), membranous glomerulonephritis, and papular acrodermatitis of childhood (Gianotti–Crosti syndrome). The serum-sickness–like syndrome occurs in the setting of acute hepatitis B, often preceding the onset of jaundice. The clinical features are fever, skin rash, and polyarteritis. The symptoms often subside shortly after the onset of jaundice but can persist throughout the duration of acute hepatitis B. About 30–50% of people with acute necrotizing vasculitis (polyarteritis nodosa) are HBV carriers. HBV-associated nephropathy has been described in adults but is more common in children. Membranous glomerulonephritis is the most common form. Other immune-mediated hematological disorders, such as essential mixed cryoglobulinemia and aplastic anemia
have been described as part of the extrahepatic manifestations of HBV
infection, but their association is not as well-defined; therefore, they
probably should not be considered etiologically linked to HBV.
Cause
Transmission
Transmission of hepatitis B virus results from exposure to infectious blood or body fluids containing blood. It is 50 to 100 times more infectious than human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Possible forms of transmission include sexual contact, blood transfusions and transfusion with other human blood products, re-use of contaminated needles and syringes, and vertical transmission
from mother to child (MTCT) during childbirth. Without intervention, a
mother who is positive for HBsAg has a 20% risk of passing the infection
to her offspring at the time of birth. This risk is as high as 90% if
the mother is also positive for HBeAg. HBV can be transmitted between
family members within households, possibly by contact of nonintact skin
or mucous membrane with secretions or saliva containing HBV. However, at least 30% of reported hepatitis B among adults cannot be associated with an identifiable risk factor. Breastfeeding after proper immunoprophylaxis does not appear to contribute to mother-to-child-transmission (MTCT) of HBV.
The virus may be detected within 30 to 60 days after infection and can
persist and develop into chronic hepatitis B. The incubation period of
the hepatitis B virus is 75 days on average but can vary from 30 to 180
days.
Virology
Structure
The structure of hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a member of the hepadnavirus family. The virus particle (virion) consists of an outer lipid envelope and an icosahedral nucleocapsid core composed of protein. These virions are 30–42 nm in diameter. The nucleocapsid encloses the viral DNA and a DNA polymerase that has reverse transcriptase activity.
The outer envelope contains embedded proteins that are involved in
viral binding of, and entry into, susceptible cells. The virus is one of
the smallest enveloped animal viruses. The 42 nm virions, which are
capable of infecting liver cells known as hepatocytes, are referred to as "Dane particles".
In addition to the Dane particles, filamentous and spherical bodies
lacking a core can be found in the serum of infected individuals.
These particles are not infectious and are composed of the lipid and
protein that forms part of the surface of the virion, which is called
the surface antigens (HBsAg), and is produced in excess during the life cycle of the virus.
Genome
The genome organisation of HBV. The genes overlap.
The genome of HBV is made of circular DNA, but it is unusual because the DNA is not fully double-stranded. One end of the full length strand is linked to the viral DNA polymerase. The genome is 3020–3320 nucleotides long (for the full-length strand) and 1700–2800 nucleotides long (for the short length-strand). The negative-sense (non-coding) is complementary to the viral mRNA. The viral DNA is found in the nucleus soon after infection of the cell. The partially double-stranded DNA is rendered fully double-stranded by completion of the (+) sense strand and removal of a protein molecule from the (−) sense strand and a short sequence of RNA
from the (+) sense strand. Non-coding bases are removed from the ends
of the (−) sense strand and the ends are rejoined. There are four known
genes encoded by the genome, called C, X, P, and S. The core protein is
coded for by gene C (HBcAg), and its start codon is preceded by an upstream in-frame AUG start codon from which the pre-core protein is produced. HBeAg is produced by proteolytic processing of the pre-core protein. In some rare strains of the virus known as Hepatitis B virus precore mutants, no HBeAg is present.
The DNA polymerase is encoded by gene P. Gene S is the gene that codes for the surface antigen
(HBsAg). The HBsAg gene is one long open reading frame but contains
three in frame "start" (ATG) codons that divide the gene into three
sections, pre-S1, pre-S2, and S. Because of the multiple start codons, polypeptides
of three different sizes called large (the order from surface to the
inside: pre-S1, pre-S2, and S ), middle (pre-S2, S), and small (S) are produced.
The function of the protein coded for by gene X is not fully understood
but it is associated with the development of liver cancer. It
stimulates genes that promote cell growth and inactivates growth
regulating molecules.
Pathogenesis
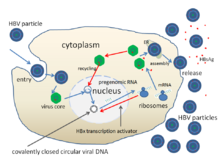
Hepatitis B virus replication
The life cycle of hepatitis B virus is complex. Hepatitis B is one of a few known pararetroviruses: non-retroviruses that still use reverse transcription in their replication process. The virus gains entry into the cell by binding to NTCP on the surface and being endocytosed.
Because the virus multiplies via RNA made by a host enzyme, the viral
genomic DNA has to be transferred to the cell nucleus by host proteins
called chaperones. The partially double-stranded viral DNA is then made
fully double stranded by a viral polymerase and transformed into
covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). This cccDNA serves as a
template for transcription of four viral mRNAs
by host RNA polymerase. The largest mRNA, (which is longer than the
viral genome), is used to make the new copies of the genome and to make
the capsid core protein and the viral DNA polymerase.
These four viral transcripts undergo additional processing and go on to
form progeny virions that are released from the cell or returned to the
nucleus and re-cycled to produce even more copies.
The long mRNA is then transported back to the cytoplasm where the
virion P protein (the DNA polymerase) synthesizes DNA via its reverse
transcriptase activity.
Serotypes and genotypes
The virus is divided into four major serotypes (adr, adw, ayr, ayw) based on antigenic epitopes
presented on its envelope proteins, and into eight major genotypes
(A–H). The genotypes have a distinct geographical distribution and are
used in tracing the evolution and transmission of the virus. Differences
between genotypes affect the disease severity, course and likelihood of
complications, and response to treatment and possibly vaccination. There are two other genotypes I and J but they are not universally accepted as of 2015.
Genotypes differ by at least 8% of their sequence and were first reported in 1988 when six were initially described (A–F). Two further types have since been described (G and H). Most genotypes are now divided into subgenotypes with distinct properties.
Mechanisms
Hepatitis B virus primarily interferes with the functions of the liver by replicating in hepatocytes. A functional receptor is NTCP. There is evidence that the receptor in the closely related duck hepatitis B virus is carboxypeptidase D.
The virions bind to the host cell via the preS domain of the viral
surface antigen and are subsequently internalized by endocytosis.
HBV-preS-specific receptors are expressed primarily on hepatocytes;
however, viral DNA and proteins have also been detected in extrahepatic
sites, suggesting that cellular receptors for HBV may also exist on
extrahepatic cells.
During HBV infection, the host immune response
causes both hepatocellular damage and viral clearance. Although the
innate immune response does not play a significant role in these
processes, the adaptive immune response, in particular virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes(CTLs),
contributes to most of the liver injury associated with HBV infection.
CTLs eliminate HBV infection by killing infected cells and producing
antiviral cytokines, which are then used to purge HBV from viable hepatocytes. Although liver damage is initiated and mediated by the CTLs, antigen-nonspecific inflammatory cells can worsen CTL-induced immunopathology, and platelets activated at the site of infection may facilitate the accumulation of CTLs in the liver.
Diagnosis
The tests, called assays, for detection of hepatitis B virus infection involve serum or blood tests that detect either viral antigens (proteins produced by the virus) or antibodies produced by the host. Interpretation of these assays is complex.
The hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)
is most frequently used to screen for the presence of this infection.
It is the first detectable viral antigen to appear during infection.
However, early in an infection, this antigen may not be present and it
may be undetectable later in the infection as it is being cleared by the
host. The infectious virion contains an inner "core particle" enclosing
viral genome. The icosahedral core particle is made of 180 or 240
copies of the core protein, alternatively known as hepatitis B core antigen, or HBcAg. During this 'window' in which the host remains infected but is successfully clearing the virus, IgM antibodies specific to the hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc IgM) may be the only serological evidence of disease. Therefore, most hepatitis B diagnostic panels contain HBsAg and total anti-HBc (both IgM and IgG).
Shortly after the appearance of the HBsAg, another antigen called hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)
will appear. Traditionally, the presence of HBeAg in a host's serum is
associated with much higher rates of viral replication and enhanced
infectivity; however, variants of the hepatitis B virus do not produce the 'e' antigen, so this rule does not always hold true. During the natural course of an infection, the HBeAg may be cleared, and antibodies to the 'e' antigen (anti-HBe) will arise immediately afterwards. This conversion is usually associated with a dramatic decline in viral replication.
Ground glass hepatocytes as seen in a chronic hepatitis B liver biopsy. H&E stain
If the host is able to clear the infection, eventually the HBsAg will become undetectable and will be followed by IgG antibodies to the hepatitis B surface antigen and core antigen (anti-HBs and anti HBc IgG). The time between the removal of the HBsAg and the appearance of anti-HBs is called the window period. A person negative for HBsAg but positive for anti-HBs either has cleared an infection or has been vaccinated previously.
Individuals who remain HBsAg positive for at least six months are considered to be hepatitis B carriers. Carriers of the virus may have chronic hepatitis B, which would be reflected by elevated serum alanine aminotransferase
(ALT) levels and inflammation of the liver, if they are in the immune
clearance phase of chronic infection. Carriers who have seroconverted to
HBeAg negative status, in particular those who acquired the infection
as adults, have very little viral multiplication and hence may be at
little risk of long-term complications or of transmitting infection to
others. However, it is possible for individuals to enter an "immune escape" with HBeAg-negative hepatitis.
The five phases of chronic hepatitis B infection as defined by European Association for the Study of the Liver
PCR tests have been developed to detect and measure the amount of HBV DNA, called the viral load, in clinical specimens. These tests are used to assess a person's infection status and to monitor treatment. Individuals with high viral loads, characteristically have ground glass hepatocytes on biopsy.
Prevention
Vaccine
Vaccines for the prevention of hepatitis B have been routinely recommended for babies since 1991 in the United States. The first dose is generally recommended within a day of birth.
Most vaccines are given in three doses over a course of months. A
protective response to the vaccine is defined as an anti-HBs antibody
concentration of at least 10 mIU/ml in the recipient's serum. The
vaccine is more effective in children and 95 percent of those vaccinated
have protective levels of antibody. This drops to around 90% at
40 years of age and to around 75 percent in those over 60 years. The
protection afforded by vaccination is long lasting even after antibody
levels fall below 10 mIU/ml. For newborns of HBsAg-positive mothers:
hepatitis B vaccine alone, hepatitis B immunoglobulin alone, or the
combination of vaccine plus hepatitis B immunoglobulin, all prevent
hepatitis B occurrence. Furthermore, the combination of vaccine plus hepatitis B immunoglobulin is superior to vaccine alone. This combination prevents HBV transmission around the time of birth in 86% to 99% of cases.
Tenofovir
given in the second or third trimester can reduce the risk of mother to
child transmission by 77% when combined with hepatitis B immunoglobulin
and the hepatitis B vaccine, especially for pregnant women with high
hepatitis B virus DNA levels.
However, there is no sufficient evidence that the administration of
hepatitis B immunoglobulin alone during pregnancy, might reduce
transmission rates to the newborn infant.
No randomized control trial has been conducted to assess the effects
of hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy for preventing infant infection.
All those with a risk of exposure to body fluids such as blood should be vaccinated, if not already.
Testing to verify effective immunization is recommended and further
doses of vaccine are given to those who are not sufficiently immunized.
In 10- to 22-year follow-up studies there were no cases of
hepatitis B among those with a normal immune system who were vaccinated.
Only rare chronic infections have been documented.
Vaccination is particularly recommended for high risk groups including:
health workers, people with chronic renal failure, and men who have sex
with men.
Both types of the hepatitis B vaccine, the plasma-derived vaccine
(PDV) and recombinant vaccine (RV) are of similar effectiveness in
preventing the infection in both healthcare workers and chronic renal
failure groups.
With one difference noticed among health worker group, that the RV
intramuscular route is significantly more effective compared with RV
intradermal route of administration.
Other
In assisted reproductive technology, sperm washing
is not necessary for males with hepatitis B to prevent transmission,
unless the female partner has not been effectively vaccinated.
In females with hepatitis B, the risk of transmission from mother to
child with IVF is no different from the risk in spontaneous conception.
Those at high risk of infection should be tested as there is effective treatment for those who have the disease.
Groups that screening is recommended for include those who have not
been vaccinated and one of the following: people from areas of the world
where hepatitis B occurs in more than 2%, those with HIV, intravenous
drug users, men who have sex with men, and those who live with someone
with hepatitis B.
Treatment
Acute hepatitis B infection does not usually require treatment and most adults clear the infection spontaneously.
Early antiviral treatment may be required in fewer than 1% of people,
whose infection takes a very aggressive course (fulminant hepatitis) or
who are immunocompromised. On the other hand, treatment of chronic infection may be necessary to reduce the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Chronically infected individuals with persistently elevated serum alanine aminotransferase, a marker of liver damage, and HBV DNA levels are candidates for therapy. Treatment lasts from six months to a year, depending on medication and genotype. Treatment duration when medication is taken by mouth, however, is more variable and usually longer than one year.
Although none of the available medications can clear the
infection, they can stop the virus from replicating, thus minimizing
liver damage. As of 2018, there are eight medications licensed for the
treatment of hepatitis B infection in the United States. These include antiviral medications lamivudine, adefovir, tenofovir disoproxil, tenofovir alafenamide, telbivudine, and entecavir, and the two immune system modulators interferon alpha-2a and PEGylated interferon alpha-2a. In 2015 the World Health Organization recommended tenofovir or entecavir as first-line agents. Those with current cirrhosis are in most need of treatment.
The use of interferon, which requires injections daily or thrice weekly, has been supplanted by long-acting PEGylated interferon, which is injected only once weekly. However, some individuals are much more likely to respond than others, and this might be because of the genotype of the infecting virus or the person's heredity. The treatment reduces viral replication in the liver, thereby reducing the viral load (the amount of virus particles as measured in the blood). Response to treatment differs between the genotypes. Interferon
treatment may produce an e antigen seroconversion rate of 37% in
genotype A but only a 6% seroconversion in type D. Genotype B has
similar seroconversion rates to type A while type C seroconverts only in
15% of cases. Sustained e antigen loss after treatment is ~45% in types
A and B but only 25–30% in types C and D.
Prognosis
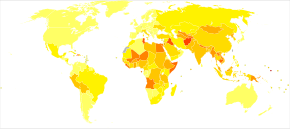
Estimate of disability-adjusted life year for hepatitis B per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2004
|
no data
<10 span="">
10–20
20–40
40–60
60–80
80–100
|
100–125
125–150
150–200
200–250
250–500
>500
|
Hepatitis B virus infection may be either
acute (self-limiting) or chronic (long-standing). Persons with
self-limiting infection clear the infection spontaneously within weeks
to months.
Children are less likely than adults to clear the infection. More
than 95% of people who become infected as adults or older children will
stage a full recovery and develop protective immunity to the virus.
However, this drops to 30% for younger children, and only 5% of newborns
that acquire the infection from their mother at birth will clear the
infection. This population has a 40% lifetime risk of death from cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. Of those infected between the age of one to six, 70% will clear the infection.
Hepatitis D (HDV) can occur only with a concomitant hepatitis B infection, because HDV uses the HBV surface antigen to form a capsid. Co-infection with hepatitis D increases the risk of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Polyarteritis nodosa is more common in people with hepatitis B infection.
Cirrhosis
A number of different tests are available to determine the degree of cirrhosis present. Transient elastography (FibroScan) is the test of choice, but it is expensive. Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index may be used when cost is an issue.
Reactivation
Hepatitis B virus DNA persists in the body after infection, and in some people the disease recurs. Although rare, reactivation is seen most often following alcohol or drug use, or in people with impaired immunity.
HBV goes through cycles of replication and non-replication.
Approximately 50% of overt carriers experience acute reactivation. Males
with baseline ALT of 200 UL/L are three times more likely to develop a
reactivation than people with lower levels. Although reactivation can
occur spontaneously, people who undergo chemotherapy have a higher risk. Immunosuppressive drugs favor increased HBV replication while inhibiting cytotoxic T cell function in the liver.
The risk of reactivation varies depending on the serological profile;
those with detectable HBsAg in their blood are at the greatest risk, but
those with only antibodies to the core antigen are also at risk. The
presence of antibodies to the surface antigen, which are considered to
be a marker of immunity, does not preclude reactivation. Treatment with prophylactic antiviral drugs can prevent the serious morbidity associated with HBV disease reactivation.
Epidemiology
Prevalence of hepatitis B virus as of 2005
In 2004, an estimated 350 million individuals were infected
worldwide. National and regional prevalences range from over 10% in Asia
to under 0.5% in the United States and Northern Europe.
Routes of infection include vertical transmission (such as
through childbirth), early life horizontal transmission (bites, lesions,
and sanitary habits), and adult horizontal transmission (sexual
contact, intravenous drug use).
The primary method of transmission reflects the prevalence of
chronic HBV infection in a given area. In low prevalence areas such as
the continental United States and Western Europe, injection drug abuse
and unprotected sex are the primary methods, although other factors may
also be important.
In moderate prevalence areas, which include Eastern Europe, Russia, and
Japan, where 2–7% of the population is chronically infected, the
disease is predominantly spread among children. In high-prevalence areas
such as China
and South East Asia, transmission during childbirth is most common,
although in other areas of high endemicity such as Africa, transmission
during childhood is a significant factor. The prevalence of chronic HBV infection in areas of high endemicity is at least 8% with 10–15% prevalence in Africa/Far East.
As of 2010, China has 120 million infected people, followed by India
and Indonesia with 40 million and 12 million, respectively. According to
World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 600,000 people die every year related to the infection.
In the United States about 19,000 new cases occurred in 2011 down nearly 90% from 1990.
History
The hepatitis B virus has infected humans since at least the Bronze Age. The evidence was obtained from 4,500-year-old human remains. According to the 2018 study, the viral genomes obtained by shotgun sequencing became the oldest ever recovered from vertebrate samples. It was also found that some ancient hepatitis viral strains still infect humans, while other became extinct. This disproved the belief that hepatitis B originated in the New World and spread to Europe around 16th century. Another 2018 study of the remains of a mummified child found in the Basilica of San Domenico Maggiore
in Naples concluded that the child, who had lived in the 16th century,
had a form of HBV, and that the virus was closely related to modern
variants.
The earliest record of an epidemic caused by hepatitis B virus was made by Lurman in 1885. An outbreak of smallpox occurred in Bremen in 1883 and 1,289 shipyard employees were vaccinated with lymph from other people. After several weeks, and up to eight months later, 191 of the vaccinated workers became ill with jaundice
and were diagnosed as suffering from serum hepatitis. Other employees
who had been inoculated with different batches of lymph remained
healthy. Lurman's paper, now regarded as a classical example of an epidemiological
study, proved that contaminated lymph was the source of the outbreak.
Later, numerous similar outbreaks were reported following the
introduction, in 1909, of hypodermic needles that were used, and, more importantly, reused, for administering Salvarsan for the treatment of syphilis. The virus was not discovered until 1966 when Baruch Blumberg, then working at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), discovered the Australia antigen (later known to be hepatitis B surface antigen, or HBsAg) in the blood of Aboriginal Australian people. Although a virus had been suspected since the research published by Frederick MacCallum in 1947, David Dane and others discovered the virus particle in 1970 by electron microscopy. By the early 1980s the genome of the virus had been sequenced, and the first vaccines were being tested.
Society and culture
World Hepatitis Day, observed July 28, aims to raise global awareness of hepatitis B and hepatitis C
and encourage prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. It has been led by
the World Hepatitis Alliance since 2007 and in May 2010, it received
global endorsement from the World Health Organization.